|
1
|
Davis MS, Malayer JR, Vandeventer L, Royer
CM, McKenzie EC and Williamson KK: Cold weather exercise and airway
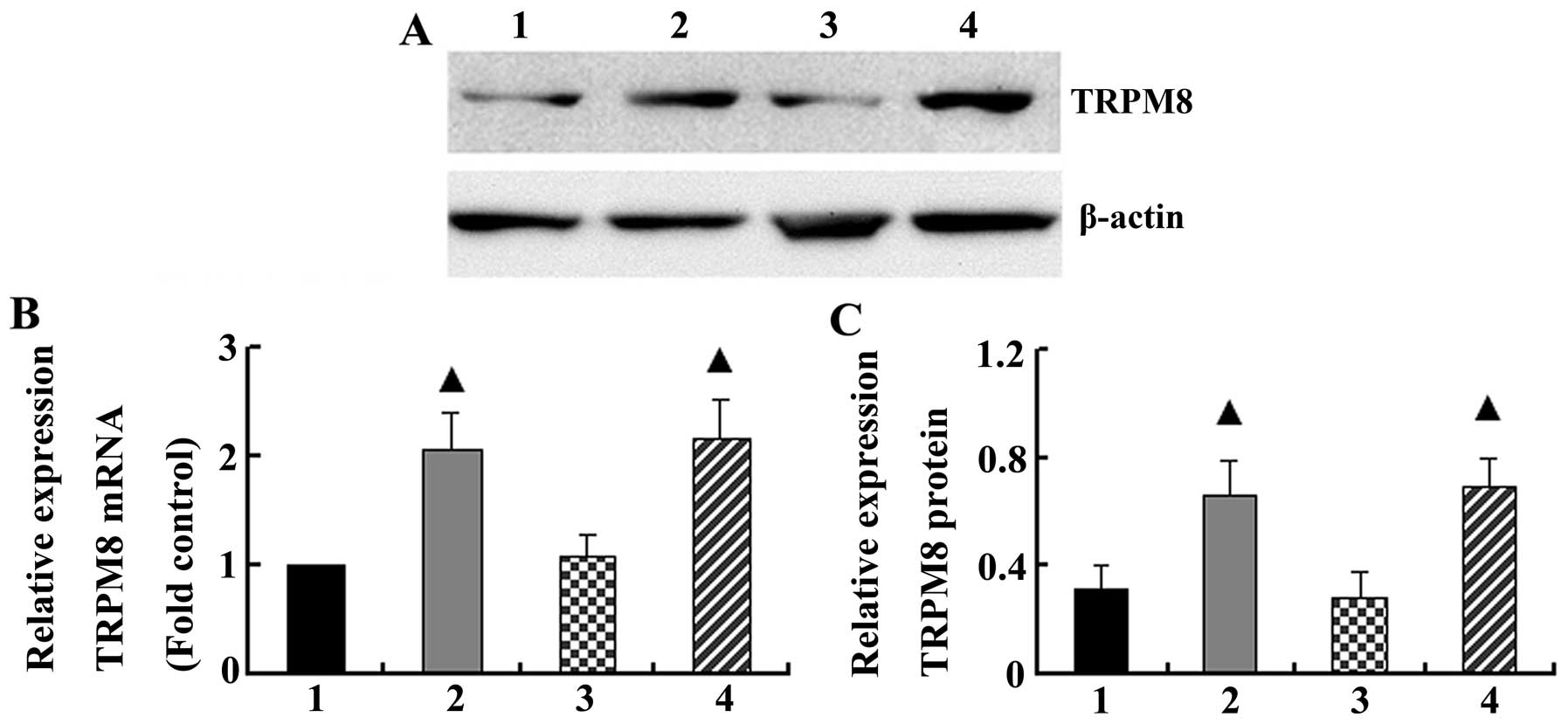
cytokine expression. J Appl Physiol. 98:2132–2136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koskela HO: Cold air-provoked respiratory
symptoms: the mechanisms and management. Int J Circumpolar Health.
66:91–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Larsson K, Tornling G, Gavhed D,
Muller-Suur C and Palmberg L: Inhalation of cold air increases the
number of inflammatory cells in the lungs in healthy subjects. Eur
Respir J. 12:825–830. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
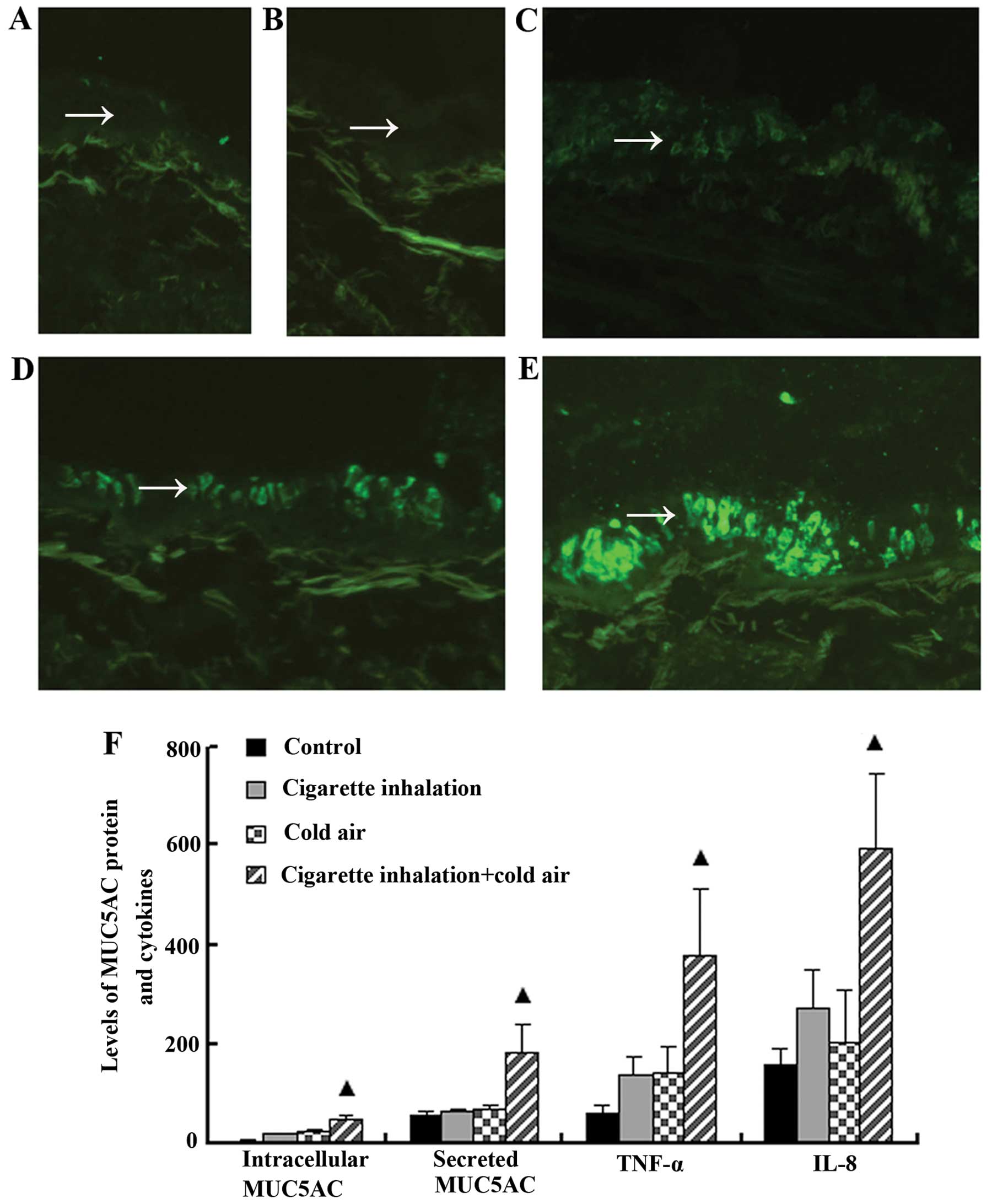
4
|
Giesbrecht GG: The respiratory system in a
cold environment. Aviat Space Environ Med. 66:890–902.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
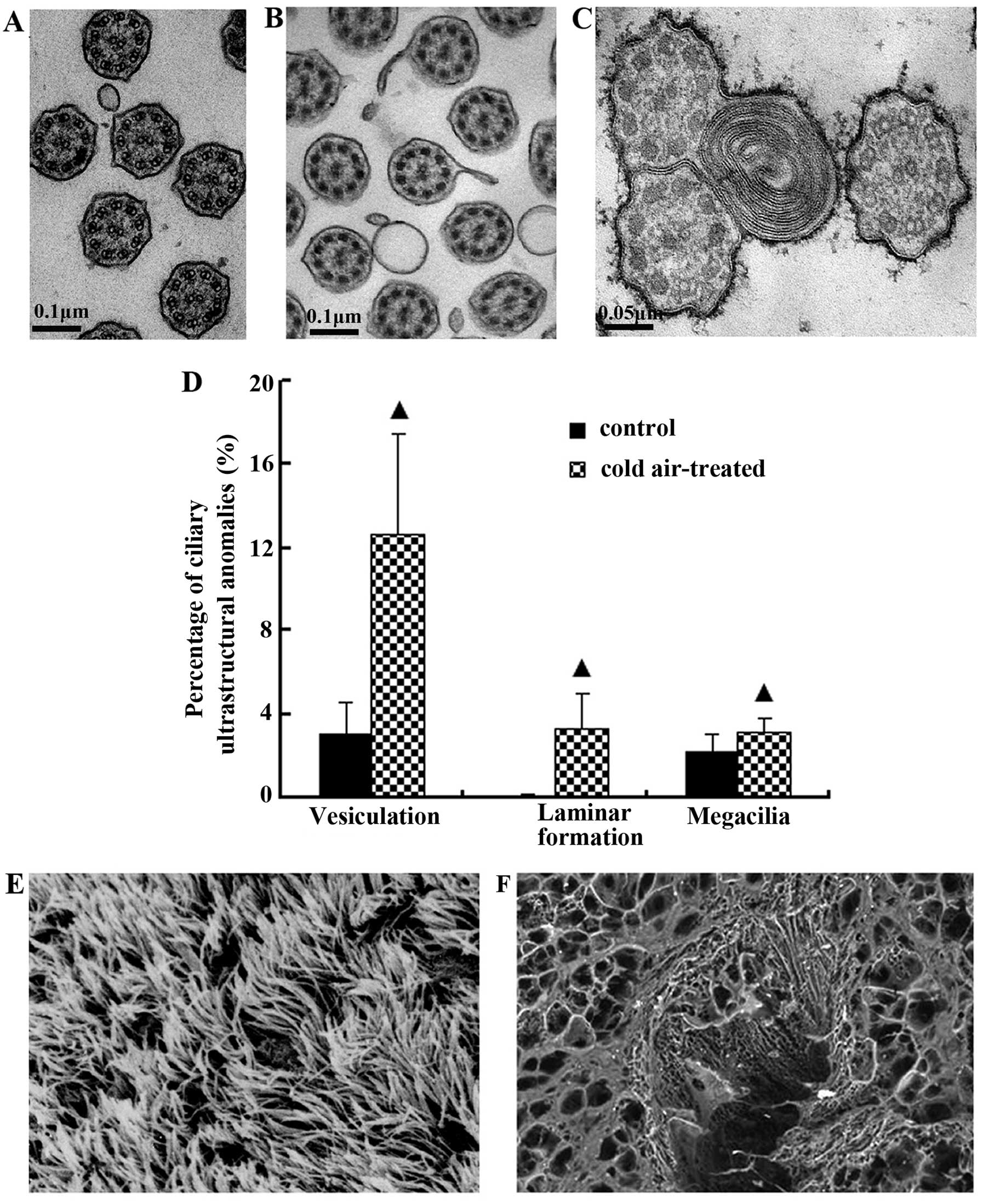
|
5
|
Donaldson GC, Seemungal T, Jeffries DJ and
Wedzicha JA: Effect of temperature on lung function and symptoms in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 13:844–849.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sabnis AS, Shadid M, Yost GS and Reilly
CA: Human lung epithelial cells express a functional cold-sensing
TRPM8 variant. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 39:466–474. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Montell C: The TRP superfamily of cation
channels. Sci STKE. 2005:re32005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song MY and Yuan JX: Introduction to TRP
channels: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol.
661:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peier AM, Moqrich A, Hergarden AC, et al:
A TRP channel that senses cold stimuli and menthol. Cell.
108:705–715. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwan KY, Allchorne AJ, Vollrath MA,
Christensen AP, Zhang DS, Woolf CJ and Corey DP: TRPA1 contributes
to cold, mechanical, and chemical nociception but is not essential
for hair-cell transduction. Neuron. 50:277–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karashima Y, Talavera K, Everaerts W, et
al: TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:1273–1278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colburn RW, Lubin ML, Stone DJ Jr, et al:
Attenuated cold sensitivity in TRPM8 null mice. Neuron. 54:379–386.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang J, Zhang X and McNaughton PA:
Modulation of temperature-sensitive TRP channels. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 17:638–645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nealen ML, Gold MS, Thut PD and Caterina
MJ: TRPM8 mRNA is expressed in a subset of cold-responsive
trigeminal neurons from rat. J Neurophysiol. 90:515–520. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Haute C, De Ridder D and Nilius B: TRP
channels in human prostate. Scientific World Journal. 10:1597–1611.
2010.
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Wang X, Yang Z, Wang B and Li S:
Menthol induces cell death via the TRPM8 channel in the human
bladder cancer cell line T24. Oncology. 77:335–341. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang XR, Lin MJ, McIntosh LS and Sham JS:
Functional expression of transient receptor potential melastatin-
(TRPM) and vanilloid-related (TRPV) channels in pulmonary arterial
and aortic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
290:L1267–L1276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Voets T, Owsianik G and Nilius B: TRPM8.
Handb Exp Pharmacol. 179:329–344. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mälkiä A, Madrid R, Meseguer V, de la Peña
E, Valero M, Belmonte C and Viana F: Bidirectional shifts of TRPM8
channel gating by temperature and chemical agents modulate the cold
sensitivity of mammalian thermoreceptors. J Physiol. 581:155–174.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li M, Li Q, Yang G, Kolosov VP, Perelman
JM and Zhou XD: Cold temperature induces mucin hypersecretion from
normal human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro through a
transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8)-mediated
mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:626–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Laniado-Laborín R: Smoking and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Parallel epidemics of the 21
century. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 6:209–224.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taylor JD: COPD and the response of the
lung to tobacco smoke exposure. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 23:376–383.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Voynow JA, Gendler SJ and Rose MC:
Regulation of mucin genes in chronic inflammatory airway diseases.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 34:661–665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rogers DF: Physiology of airway mucus
secretion and pathophysiology of hypersecretion. Respir Care.
52:1134–1146. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang IJ, Wu CY and Hu FR: Effect of
proinflammatory cytokines on the human MUC5AC promoter activity in
vitro and in vivo. Clin Ophthalmol. 1:71–77. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bautista MV, Chen Y, Ivanova VS, Rahimi
MK, Watson AM and Rose MC: IL-8 regulates mucin gene expression at
the posttranscriptional level in lung epithelial cells. J Immunol.
183:2159–2166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Davis MS, Lockard AJ, Marlin DJ and Freed
AN: Airway cooling and mucosal injury during cold weather exercise.
Equine Vet J Suppl. 34:413–416. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Houtmeyers E, Gosselink R, Gayan-Ramirez G
and Decramer M: Regulation of mucociliary clearance in health and
disease. Eur Respir J. 13:1177–1188. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Armengot M, Milara J, Mata M, Carda C and
Cortijo J: Cilia motility and structure in primary and secondary
ciliary dyskinesia. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 24:175–180. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith CM, Hirst RA, Bankart MJ, Jones DW,
Easton AJ, Andrew PW and O’Callaghan C: Cooling of cilia allows
functional analysis of the beat pattern for diagnostic testing.
Chest. 140:186–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Calderón-Garcidueñas L, Valencia-Salazar
G, Rodríguez-Alcaraz A, et al: Ultrastructural nasal pathology in
children chronically and sequentially exposed to air pollutants. Am
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 24:132–138. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abe J, Hosokawa H, Sawada Y, Matsumura K
and Kobayashi S: Ca2+-dependent PKC activation mediates
menthol-induced desensitization of transient receptor potential M8.
Neurosci Lett. 397:140–144. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Daniels RL, Takashima Y and McKemy DD:
Activity of the neuronal cold sensor TRPM8 is regulated by
phospholipase C via the phospholipid phosphoinositol
4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 284:1570–1582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baroody FM: Mucociliary transport in
chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Allergy Immunol. 20:103–119. 2007.
|
|
35
|
Kim YM, Lee CH, Won TB, Kim SW, Kim JW,
Rhee CS and Min YG: Functional recovery of rabbit maxillary sinus
mucosa in two different experimental injury models. Laryngoscope.
118:541–545. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sabnis AS, Reilly CA, Veranth JM and Yost
GS: Increased transcription of cytokine genes in human lung
epithelial cells through activation of a TRPM8 variant by cold
temperatures. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 295:L194–L200.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arnson Y, Shoenfeld Y and Amital H:
Effects of tobacco smoke on immunity, inflammation and
autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 34:J258–J265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adcock IM, Caramori G and Barnes PJ:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer: new
molecular insights. Respiration. 81:265–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mulligan RM, Atkinson C, Vertegel AA,
Reukov V and Schlosser RJ: Cigarette smoke extract stimulates
interleukin-8 production in human airway epithelium and is
attenuated by superoxide dismutase in vitro. Am J Rhinol Allergy.
23:e1–e4. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li YT, He B and Wang YZ: Exposure to
cigarette smoke upregulates AP-1 activity and induces TNF-alpha
overexpression in mouse lungs. Inhal Toxicol. 21:641–647. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takeyama K, Jung B, Shim JJ, et al:
Activation of epidermal growth factor receptors is responsible for
mucin synthesis induced by cigarette smoke. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 280:L165–L172. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Baginski TK, Dabbagh K, Satjawatcharaphong
C and Swinney DC: Cigarette smoke synergistically enhances
respiratory mucin induction by proinflammatory stimuli. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 35:165–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Innes AL, Woodruff PG, Ferrando RE,
Donnelly S, Dolganov GM, Lazarus SC and Fahy JV: Epithelial mucin
stores are increased in the large airways of smokers with airflow
obstruction. Chest. 130:1102–1108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haswell LE, Hewitt K, Thorne D, Richter A
and Gaça MD: Cigarette smoke total particulate matter increases
mucous secreting cell numbers in vitro: a potential model of goblet
cell hyperplasia. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:981–987. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|