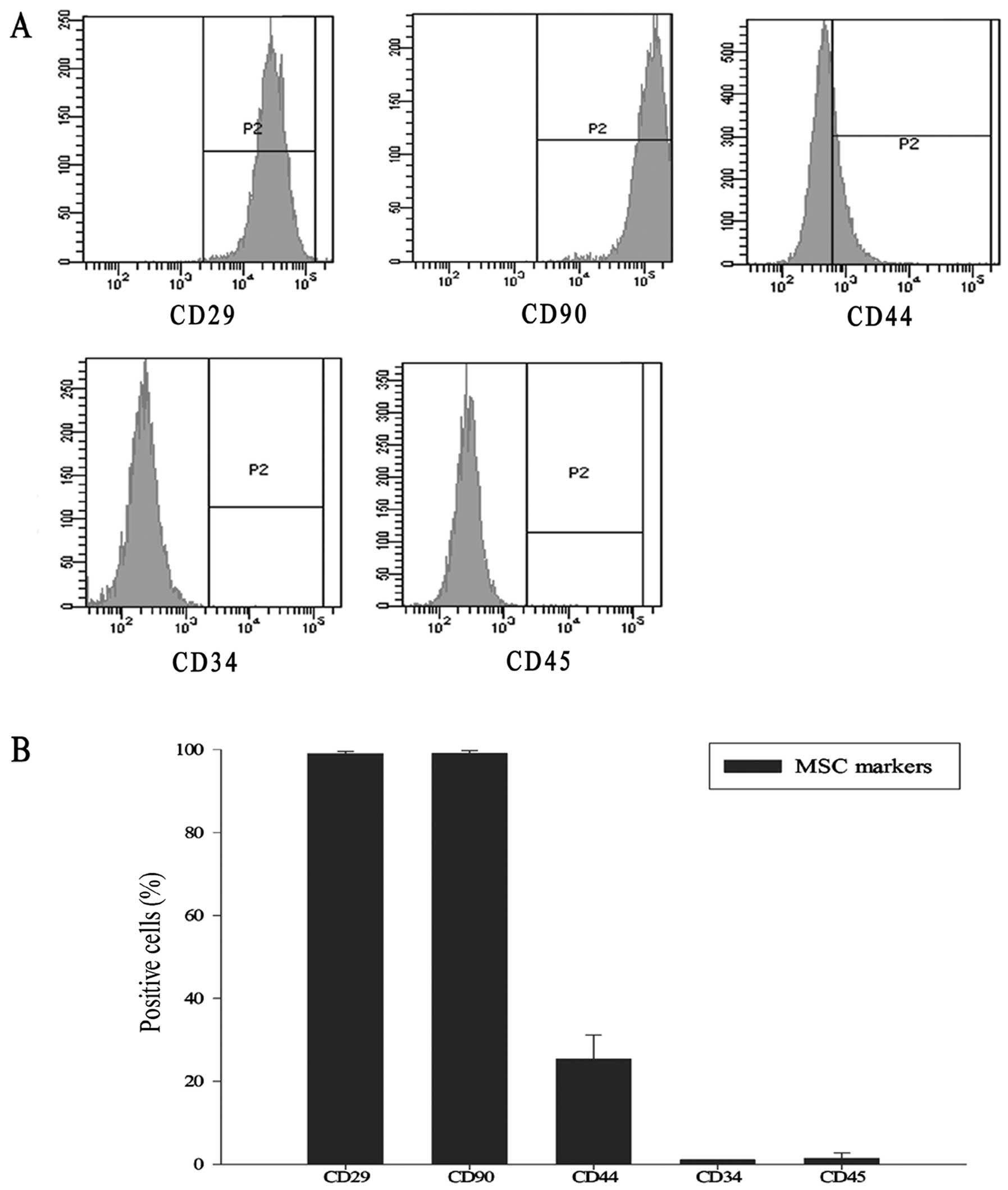
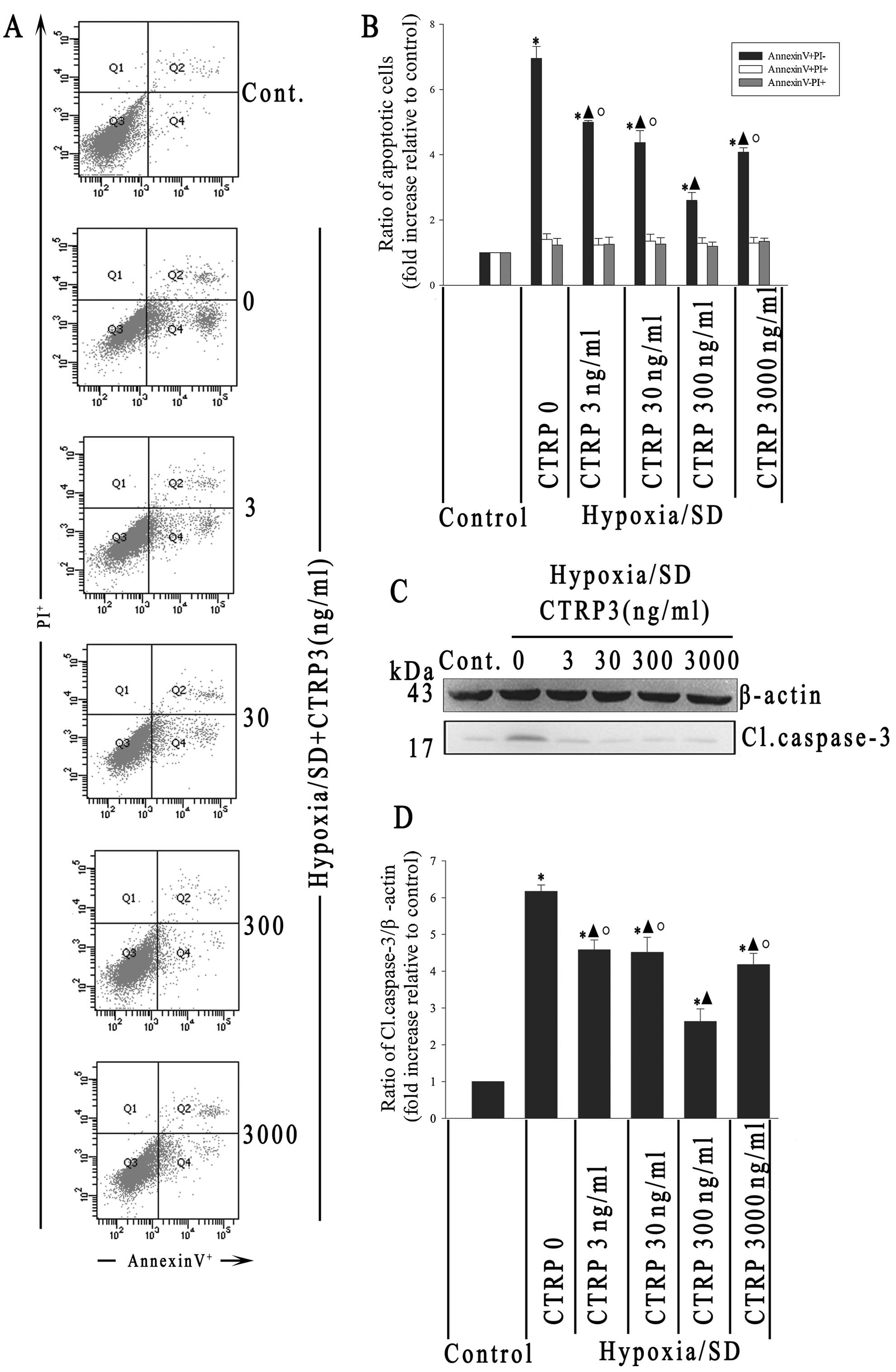
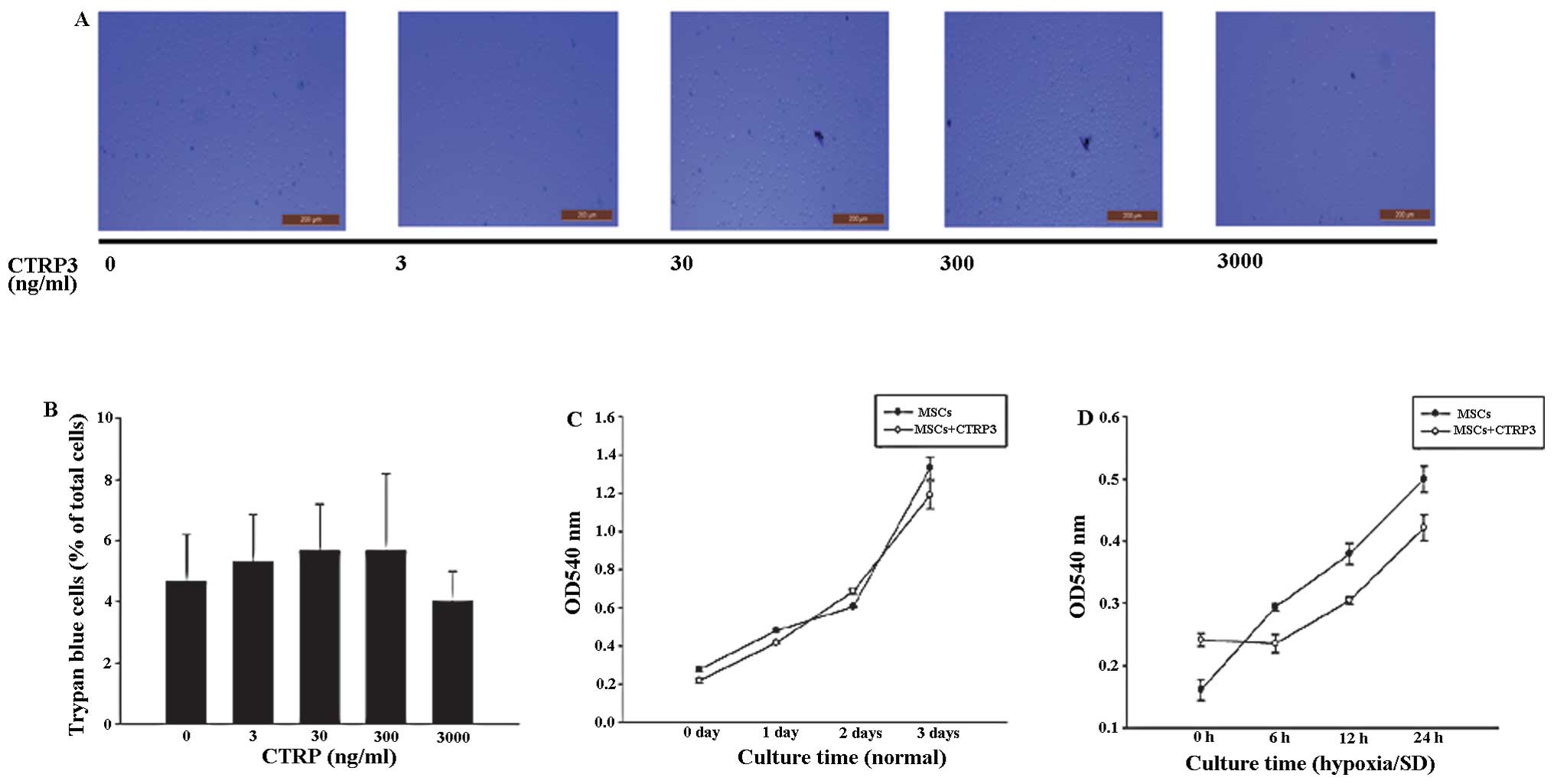
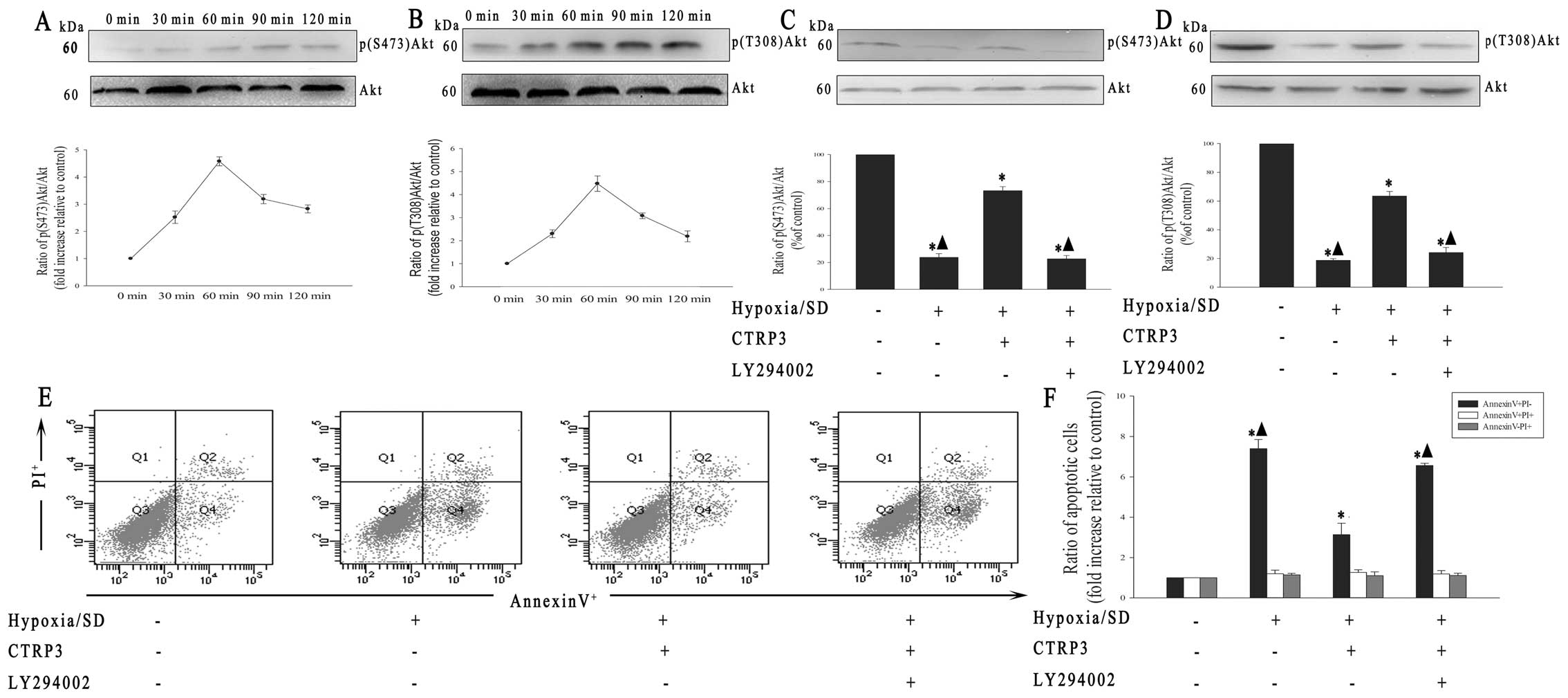
|
1
|
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT
and Murray CJ: Global and regional burden of disease and risk
factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data.
Lancet. 367:1747–1757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al:
Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature.
410:701–705. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stamm C, Westphal B, Kleine HD, et al:
Autologous bone-marrow stem-cell transplantation for myocardial
regeneration. Lancet. 361:45–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wollert KC, Meyer GP, Lotz J, et al:
Intracoronary autologous bone-marrow cell transfer after myocardial
infarction: the BOOST randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet.
364:141–148. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang M, Methot D, Poppa V, Fujio Y, Walsh
K and Murry CE: Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair: graft
cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:907–921. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geng YJ: Molecular mechanisms for
cardiovascular stem cell apoptosis and growth in the hearts with
atherosclerotic coronary disease and ischemic heart failure. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1010:687–697. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chao W, Shen Y, Li L and Rosenzweig A:
Importance of FADD signaling in serum deprivation- and
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
277:31639–31645. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bonavita F, Stefanelli C, Giordano E, et
al: H9c2 cardiac myoblasts undergo apoptosis in a model of ischemia
consisting of serum deprivation and hypoxia: inhibition by PMA.
FEBS Lett. 536:85–91. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kishore U, Gaboriaud C, Waters P, et al:
C1q and tumor necrosis factor superfamily: modularity and
versatility. Trends Immunol. 25:551–561. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wong GW, Wang J, Hug C, Tsao TS and Lodish
HF: A family of Acrp30/adiponectin structural and functional
paralogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10302–10307. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schaffler A, Ehling A, Neumann E, et al:
Genomic organization, promoter, amino acid sequence, chromosomal
localization, and expression of the human gene for CORS-26
(collagenous repeat-containing sequence of 26-kDa protein). Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1630:123–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Weigert J, Neumeier M, Schaffler A, et al:
The adiponectin paralog CORS-26 has anti-inflammatory properties
and is produced by human monocytic cells. FEBS Lett. 579:5565–5570.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Compton SA and Cheatham B: CTRP-3:
blocking a toll booth to obesity-related inflammation.
Endocrinology. 151:5095–5097. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kopp A, Bala M, Buechler C, et al:
C1q/TNF-related protein-3 represents a novel and endogenous
lipopolysaccharide antagonist of the adipose tissue. Endocrinology.
151:5267–5278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kopp A, Bala M, Weigert J, et al: Effects
of the new adiponectin paralogous protein CTRP-3 and of LPS on
cytokine release from monocytes of patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Cytokine. 49:51–57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hofmann C, Chen N, Obermeier F, et al:
C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) is secreted by visceral adipose
tissue and exerts antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effects in
primary human colonic fibroblasts. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:2462–2471.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yi W, Sun Y, Yuan Y, et al: C1q/tumor
necrosis factor-related protein-3, a newly identified adipokine, is
a novel antiapoptotic, proangiogenic, and cardioprotective molecule
in the ischemic mouse heart. Circulation. 125:3159–3169. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al:
Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.
Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu W, Chen J, Cong X, Hu S and Chen X:
Hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 24:416–425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Baydoun AR, Xu R, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid protects mesenchymal stem cells against
hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Stem Cells.
26:135–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and
restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 9:1195–1201.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hahn JY, Cho HJ, Kang HJ, et al:
Pre-treatment of mesenchymal stem cells with a combination of
growth factors enhances gap junction formation, cytoprotective
effect on cardiomyocytes, and therapeutic efficacy for myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 51:933–943. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu G, Haider HK, Jiang S and Ashraf M:
Sca-1+ stem cell survival and engraftment in the
infarcted heart: dual role for preconditioning-induced connexin-43.
Circulation. 119:2587–2596. 2009.
|
|
24
|
Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al:
Mobilized bone marrow cells repair the infarcted heart, improving
function and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:10344–10349.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Q, Wang L, Tan W, et al: Identification
of C1qTNF-related protein 4 as a potential cytokine that stimulates
the STAT3 and NF-κB pathways and promotes cell survival in human
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 308:203–214. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu P, Tan MJ, Huang RL, et al:
Angiopoietin-like 4 protein elevates the prosurvival intracellular
O2(−):H2O2 ratio and confers
anoikis resistance to tumors. Cancer Cell. 19:401–415. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Albrecht-Schgoer K, Schgoer W, Holfeld J,
et al: The angiogenic factor secretoneurin induces coronary
angiogenesis in a model of myocardial infarction by stimulation of
vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells.
Circulation. 126:2491–2501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kanwar JR, Kamalapuram SK and Kanwar RK:
Survivin signaling in clinical oncology: a multifaceted dragon. Med
Res Rev. 33:765–789. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shortt J, Martin BP, Newbold A, et al:
Combined inhibition of PI3K-related DNA damage response kinases and
mTORC1 induces apoptosis in MYC-driven B-cell lymphomas. Blood.
121:2964–2974. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu R, Chen J, Cong X, Hu S and Chen X:
Lovastatin protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and
serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by activation of PI3K/Akt and
ERK1/2. J Cell Biochem. 103:256–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|