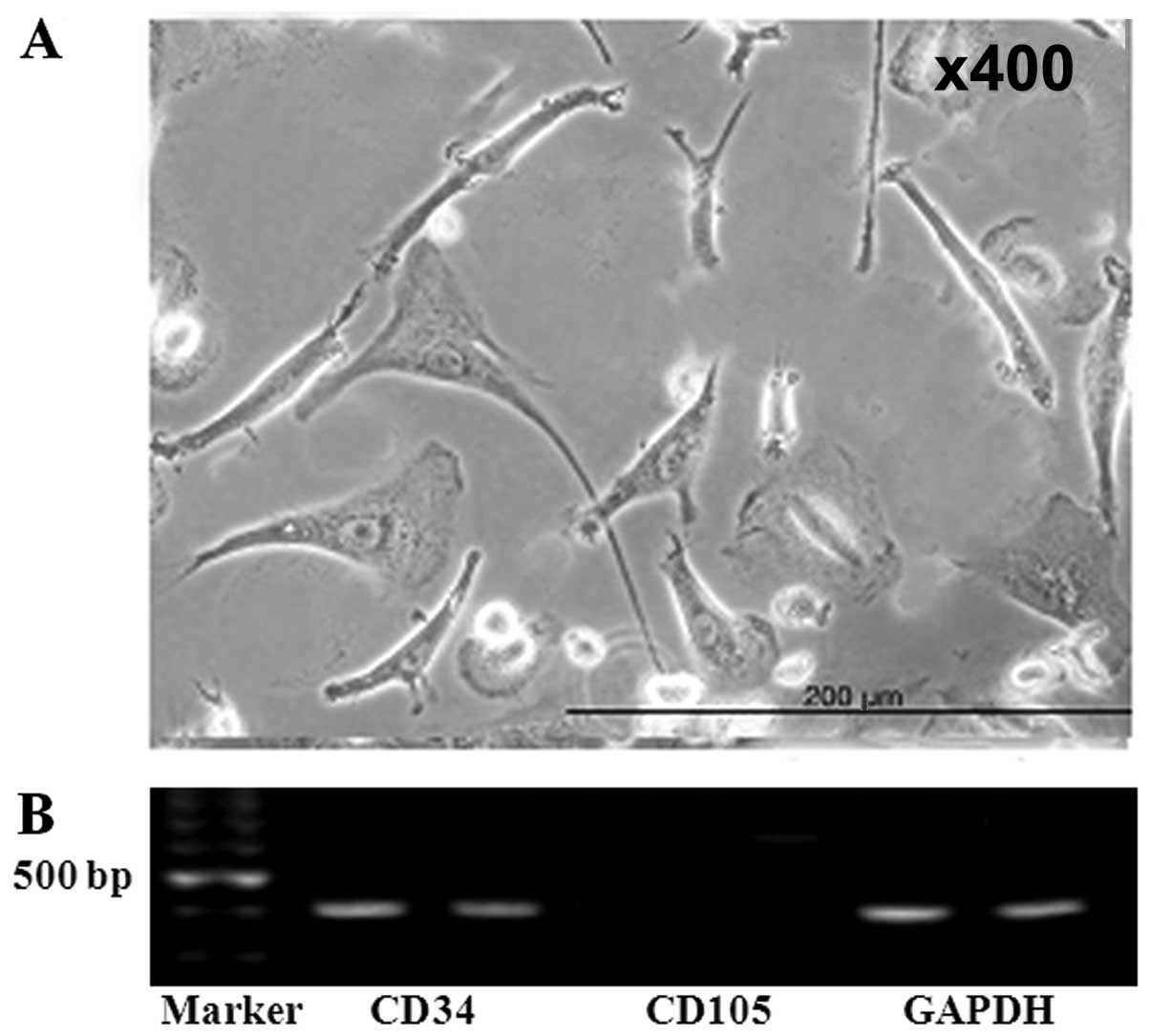
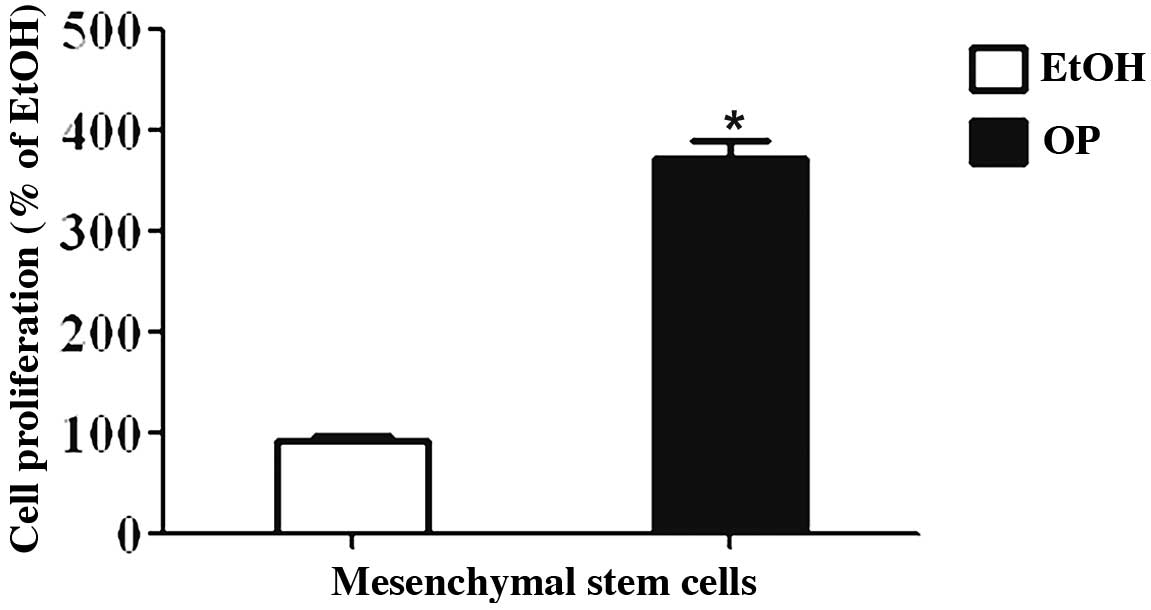
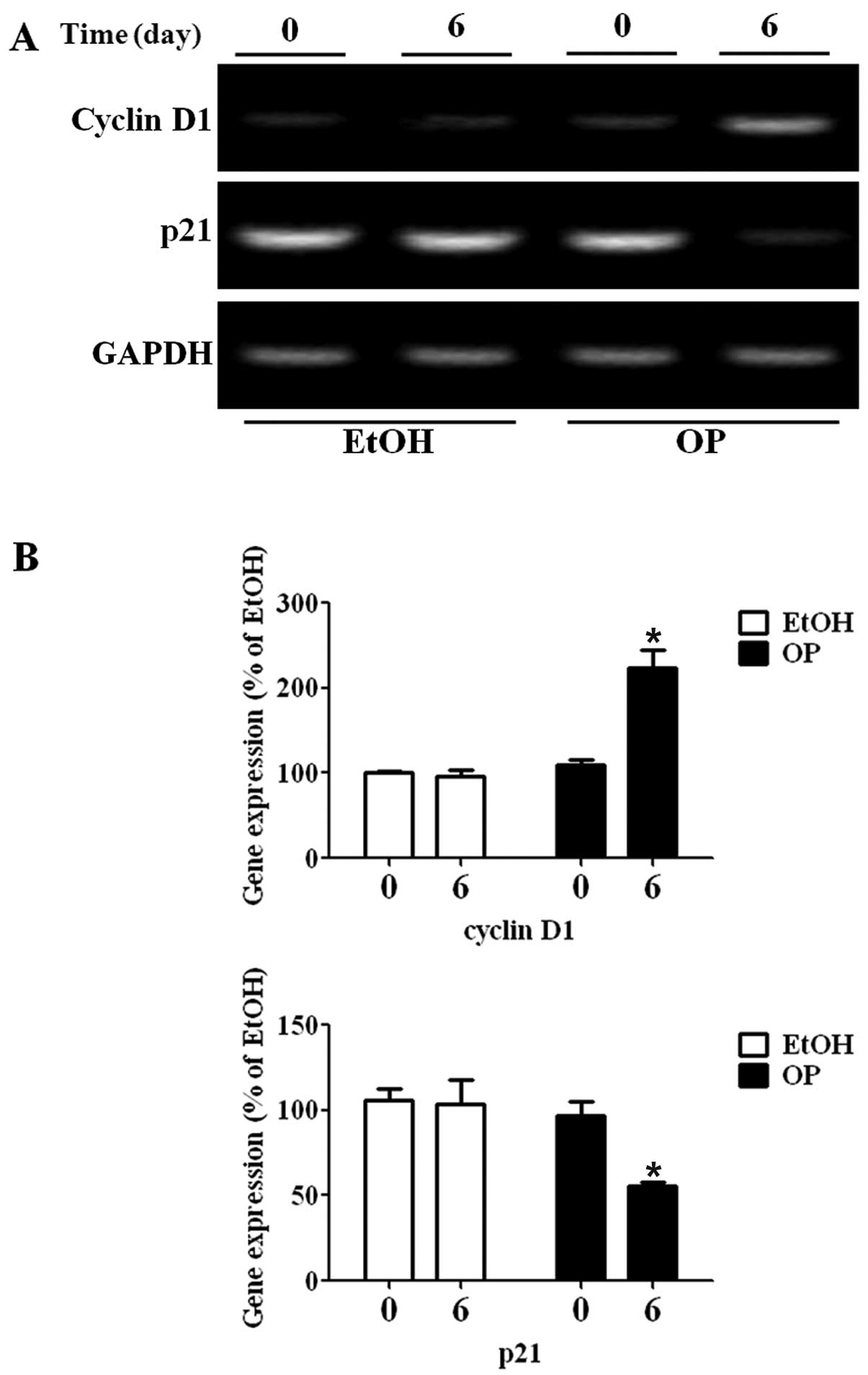
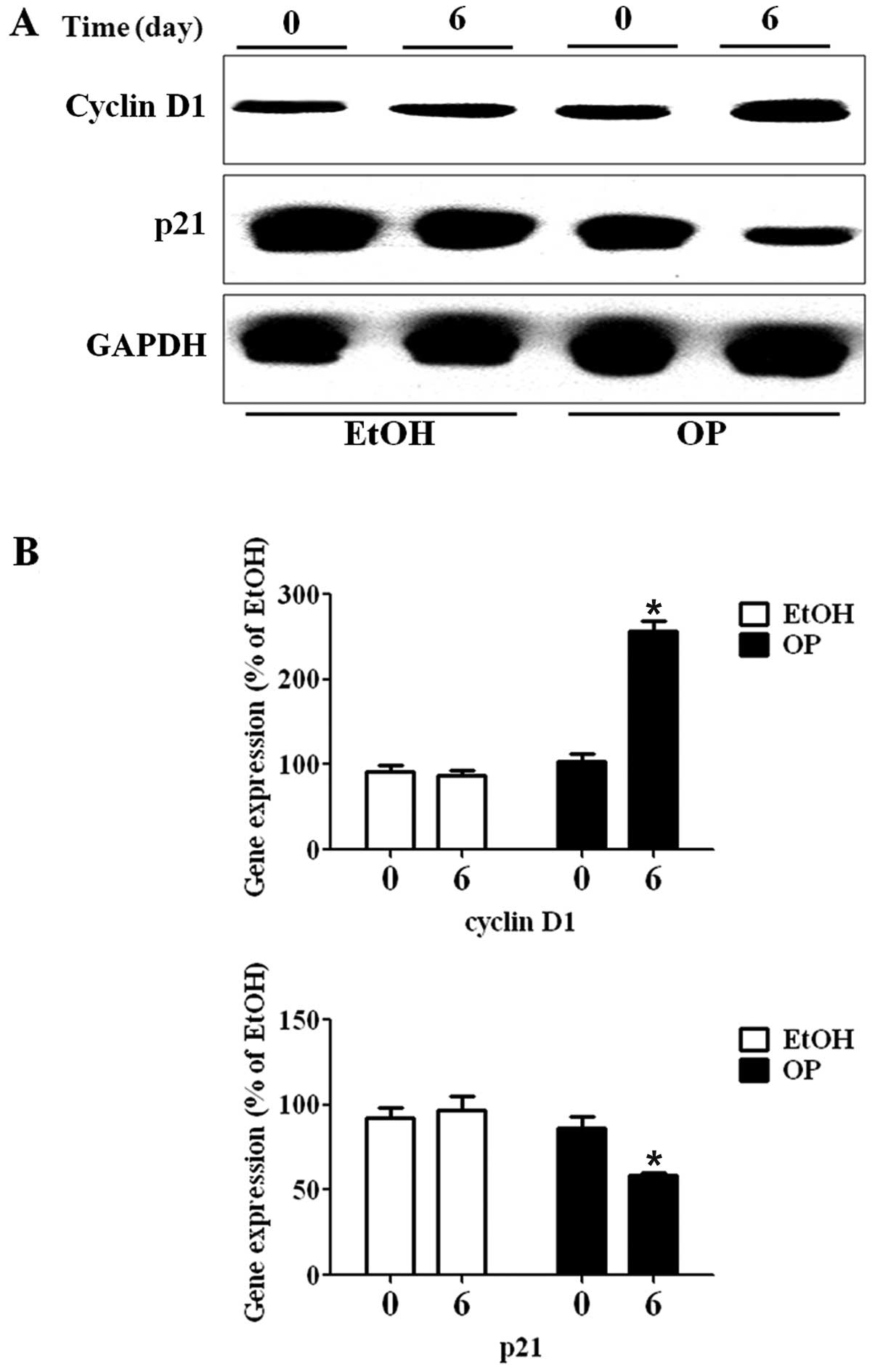
|
1
|
Wong CJ, Casper RF and Rogers IM:
Epigenetic changes to human umbilical cord blood cells cultured
with three proteins indicate partial reprogramming to a pluripotent
state. Exp Cell Res. 316:927–939. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kermani AJ, Fathi F and Mowla SJ:
Characterization and genetic manipulation of human umbilical cord
vein mesenchymal stem cells: potential application in cell-based
gene therapy. Rejuvenation Res. 11:379–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reddi AS, Kuppasani K and Ende N: Human
umbilical cord blood as an emerging stem cell therapy for diabetes
mellitus. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:356–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Han YF, Tao R, Sun TJ, Chai JK, Xu G and
Liu J: Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell
isolation and culture methods. Cytotechnology. 65:819–827. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fonseka M, Ramasamy R, Tan BC and Seow HF:
Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells
(hUCB-MSC) inhibit the proliferation of K562 (human
erythromyeloblastoid leukaemic cell line). Cell Biol Int.
36:793–801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jung S, Sen A, Rosenberg L and Behie LA:
Human mesenchymal stem cell culture: rapid and efficient isolation
and expansion in a defined serum-free medium. J Tissue Eng Regen
Med. 6:391–403. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Asari T, Furukawa K, Tanaka S, Kudo H,
Mizukami H, Ono A, Numasawa T, Kumagai G, Motomura S, Yagihashi S
and Toh S: Mesenchymal stem cell isolation and characterization
from human spinal ligaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
417:1193–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lechner V, Hocht B, Ulrichs K, Thiede A
and Meyer T: Obtaining of mesenchymal progenitor cells from the
human umbilical cord. Zentralbl Chir. 132:358–364. 2007.(In
German).
|
|
9
|
Xu Y, Huang S, Ma K, Fu X, Han W and Sheng
Z: Promising new potential for mesenchymal stem cells derived from
human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly: sweat gland cell-like
differentiative capacity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 6:645–654.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamolz LP, Kolbus A, Wick N, Mazal PR,
Eisenbock B, Burjak S and Meissl G: Cultured human epithelium:
human umbilical cord blood stem cells differentiate into
keratinocytes under in vitro conditions. Burns. 32:16–19. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hussain I, Magd SA, Eremin O and El-Sheemy
M: New approach to isolate mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) from human
umbilical cord blood. Cell Biol Int. 36:595–600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee HR, Hwang KA, Park MA, Yi BR, Jeung EB
and Choi KC: Treatment with bisphenol A and methoxychlor results in
the growth of human breast cancer cells and alteration of the
expression of cell cycle-related genes, cyclin D1 and p21, via an
estrogen receptor-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
29:883–890. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Lee HR and Choi KC: 4-tert-Octylphenol
stimulates the expression of cathepsins in human breast cancer
cells and xenografted breast tumors of a mouse model via an
estrogen receptor-mediated signaling pathway. Toxicology.
304:13–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dang VH, Choi KC and Jeung EB: Estrogen
receptors are involved in xenoestrogen induction of growth hormone
in the rat pituitary gland. J Reprod Dev. 55:206–213. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Li Q, Li G, Wang Z and Yan C:
Levels of estrogenic compounds in Xiamen Bay sediment, China. Mar
Pollut Bull. 58:1210–1216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hamelin G, Charest-Tardif G, Krishnan K,
Cyr D, Charbonneau M, Devine PJ, Haddad S, Cooke GM, Schrader T and
Tardif R: Toxicokinetics of p-tert-octylphenol in male and female
Sprague-Dawley rats after intravenous, oral, or subcutaneous
exposures. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 72:541–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Kim TH, Hyun SH, Jeung
EB and Choi KC: Induced growth of BG-1 ovarian cancer cells by
17β-estradiol or various endocrine disrupting chemicals was
reversed by resveratrol via downregulation of cell cycle
progression. Mol Med Rep. 6:151–156. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Sharma VK, Anquandah GA, Yngard RA, Kim H,
Fekete J, Bouzek K, Ray AK and Golovko D: Nonylphenol, octylphenol,
and bisphenol-A in the aquatic environment: a review on occurrence,
fate, and treatment. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst
Environ Eng. 44:423–442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang KA, Park SH, Yi BR and Choi KC: Gene
alterations of ovarian cancer cells expressing estrogen receptors
by estrogen and bisphenol a using microarray analysis. Lab Anim
Res. 27:99–107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park MA, Hwang KA, Lee HR, Yi BR, Jeung EB
and Choi KC: Cell growth of BG-1 ovarian cancer cells is promoted
by di-n-butyl phthalate and hexabromocyclododecane via upregulation
of the cyclin D and cyclin-dependent kinase-4 genes. Mol Med Rep.
5:761–766. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung EM, An BS, Yang H, Choi KC and Jeung
EB: Biomarker genes for detecting estrogenic activity of endocrine
disruptors via estrogen receptors. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
9:698–711. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park SH, Kim KY, An BS, Choi JH, Jeung EB,
Leung PC and Choi KC: Cell growth of ovarian cancer cells is
stimulated by xenoestrogens through an estrogen-dependent pathway,
but their stimulation of cell growth appears not to be involved in
the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK-1 and
p38. J Reprod Dev. 55:23–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fernandez-Sanjuan M, Rigol A, Sahuquillo
A, Rodriguez-Cruz S and Lacorte S: Determination of alkylphenols
and alkylphenol ethoxylates in sewage sludge: effect of sample
pre-treatment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 394:1525–1533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rhee JS, Lee YM, Raisuddin S and Lee JS:
Expression of R-ras oncogenes in the hermaphroditic fish
Kryptolebias marmoratus, exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicals.
Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 149:433–439. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ajj H, Chesnel A, Pinel S, Plenat F,
Flament S and Dumond H: An alkylphenol mix promotes seminoma
derived cell proliferation through an ERalpha36-mediated mechanism.
PLoS One. 8:e617582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu QL, Chow YY, Sun SJ, Zeng QX, Li HB,
Shi JB, Sun YQ, Wen W, Tse HF, Lian Q and Xu G: Mesenchymal stem
cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells modulate
T-cell phenotypes in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 67:1215–1222.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fossett E and Khan WS: Optimising human
mesenchymal stem cell numbers for clinical application: a
literature review. Stem Cells Int. 2012:4652592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim ES, Ahn SY, Im GH, Sung DK, Park YR,
Choi SH, Choi SJ, Chang YS, Oh W, Lee JH and Park WS: Human
umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
attenuates severe brain injury by permanent middle cerebral artery
occlusion in newborn rats. Pediatr Res. 72:277–284. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fickert S, Schroter-Bobsin U, Gross AF,
Hempel U, Wojciechowski C, Rentsch C, Corbeil D and Günther KP:
Human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation during long-term ex vivo cultivation is not age
dependent. J Bone Miner Metab. 29:224–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galindo LT, Filippo TR, Semedo P, Ariza
CB, Moreira CM, Camara NO and Porcionatto MA: Mesenchymal stem cell
therapy modulates the inflammatory response in experimental
traumatic brain injury. Neurol Res Int. 2011:5640892011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hafizi M, Atashi A, Bakhshandeh B, Kabiri
M, Nadri S, Hosseini RH and Soleimani M: MicroRNAs as markers for
neurally committed CD133+/CD34+ stem cells
derived from human umbilical cord blood. Biochem Genet. 51:175–188.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oodi A, Noruzinia M, Habibi Roudkenar M,
Nikougoftar M, Soltanpour MS, Khorshidfar M and Amirizadeh N:
Expression of P16 cell cycle inhibitor in human cord blood
CD34+ expanded cells following co-culture with bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Hematology. 17:334–340.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|