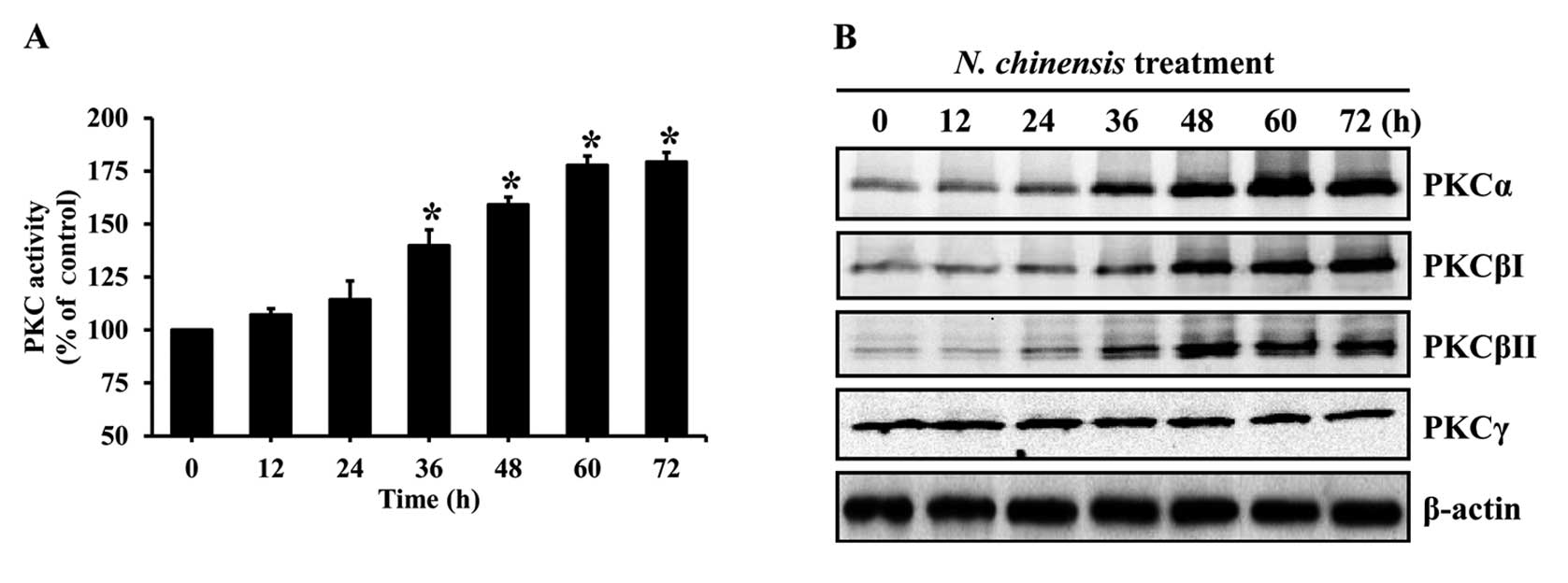
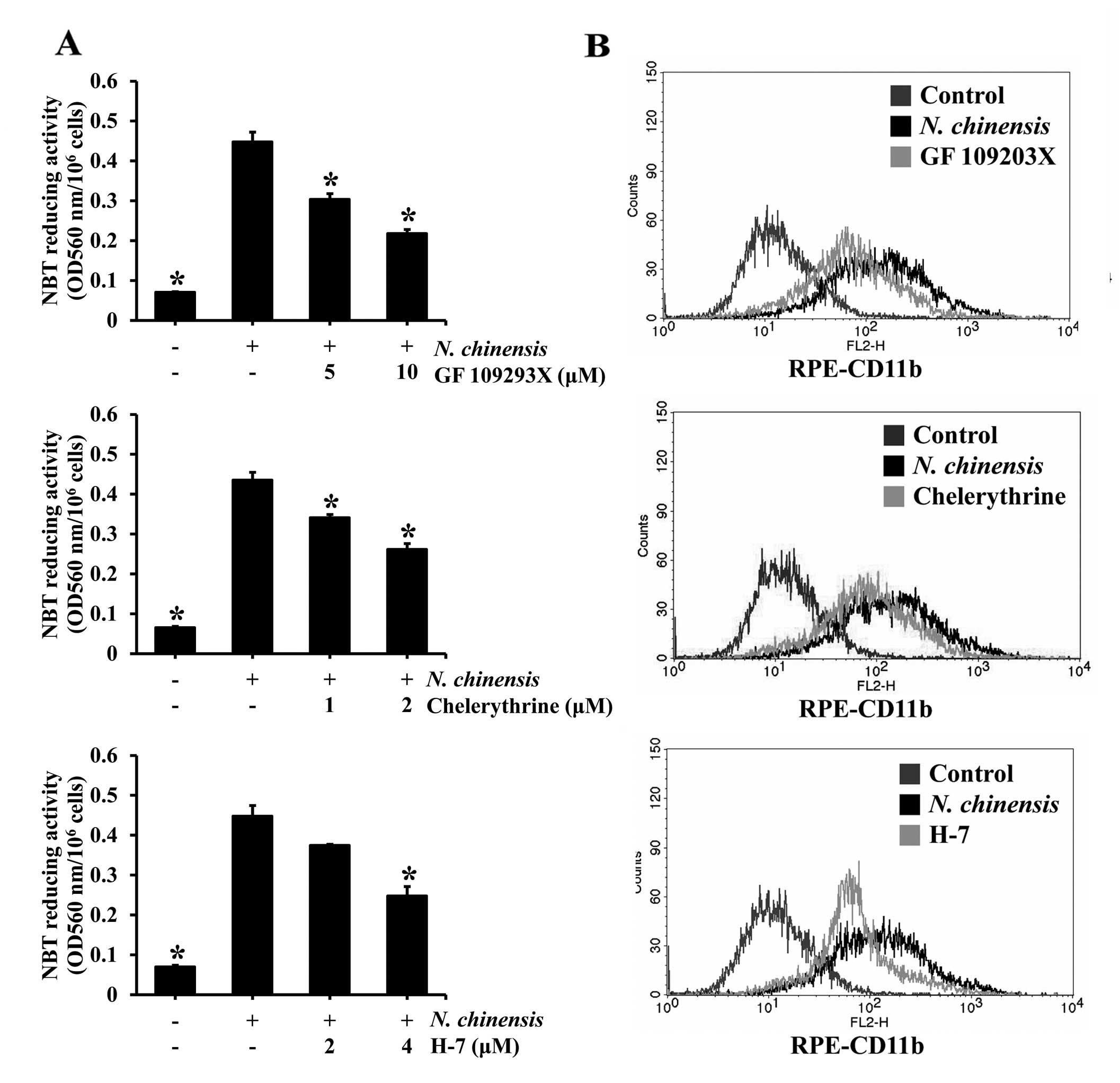
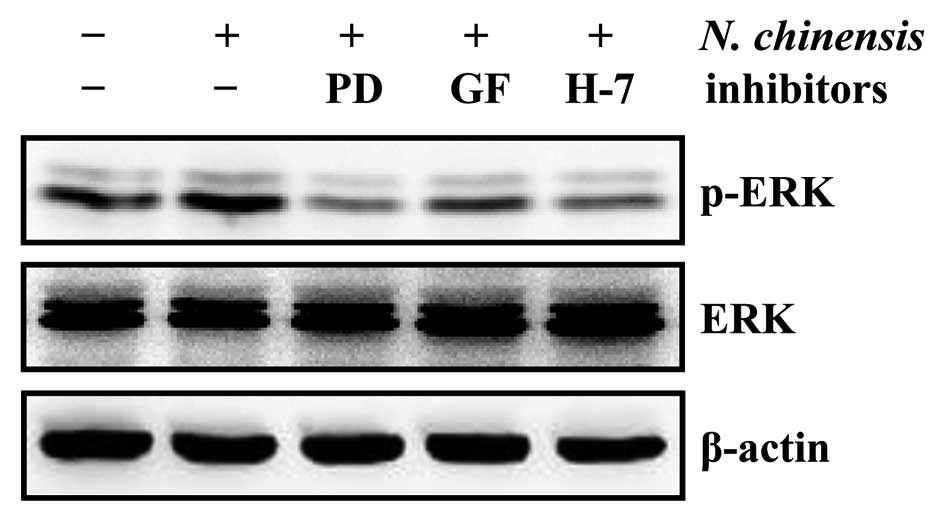
|
1
|
Seo BI, Lee JH, Choi HY, Kwon DY and Boo
YM: Korean Medicine Herbology. Younglim Press; Seoul: pp. 496–497.
2008
|
|
2
|
Xiao PG, Li DP and Yang SL: Modern Chinese
Materia Medica. Chemical Industry Press; Beijing: pp. 2522002
|
|
3
|
Takaya Y, Takeuji Y, Akasaka M, et al:
Novel guaiane endoperoxides, nardoguaianone A–D, from
Nardostachys chinensis roots and their antinociceptive and
antimalarial activities. Tetrahedron. 56:7683–7678. 2000.
|
|
4
|
Itokawa H, Masuyama K, Morita H and Takeya
K: Cytotoxic sesquiterpenes from Nardostachys chinensis.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 41:1183–1184. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li P, Matsunaga K, Yamamoto K, Yoshikawa
R, Kawashima K and Ohizumi Y: Nardosinone, a novel enhancer of
nerve growth factor in neurite outgrowth from PC12D cells. Neurosci
Lett. 273:53–56. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwang JS, Lee SA, Hong SS, et al:
Inhibitory constituents of Nardostachys chinensis on nitric
oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
22:706–708. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Huberman E and Callaham MF: Induction of
terminal differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by
tumor-promoting agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:1293–1297. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rovera G, Santoli D and Damsky C: Human
promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into
macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:2779–2783. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Collins SJ, Ruscetti FW, Gallagher RE and
Gallo RC: Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia
cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 75:2458–2462. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pan Q, Granger J, O’Connell TD, Somerman
MJ and Simpson RU: Promotion of HL-60 cell differentiation by
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulation of protein kinase C levels and
activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 54:909–915. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kharbanda S, Saleem A, Emoto Y, Stone R,
Rapp U and Kufe D: Activation of Raf-1 and mitogen-activated
protein kinases during monocytic differentiation of human myeloid
leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 269:872–878. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim SH, Oh SM and Kim TS: Induction of
human leukemia HL-60 cell differentiation via a PKC/ERK pathway by
helenalin, a pseudoguainolide sesquiterpene lactone. Eur J
Pharmacol. 511:89–97. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SH, Kim HJ and Kim TS: Differential
involvement of protein kinase C in human promyelocytic leukemia
cell differentiation enhanced by artemisinin. Eur J Pharmacol.
482:67–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV,
Deacon E, Salmon M and Lord JM: Serine/threonine protein kinases
and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 256:34–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cobb MH: MAP kinase pathways. Prog Biophys
Mol Biol. 71:479–500. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yen A, Roberson MS, Varvayanis S and Lee
AT: Retinoic acid induced mitogen-activated protein
(MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase-dependent
MAP kinase activation needed to elicit HL-60 cell differentiation
and growth arrest. Cancer Res. 58:3163–3172. 1998.
|
|
20
|
Yen A, Roberson MS and Varvayanis S:
Retinoic acid selectively activates the ERK2 but not JNK/SAPK or
p38 MAP kinases when inducing myeloid differentiation. In Vitro
Cell Dev Biol Anim. 35:527–532. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X and Studzinski GP: Activation of
extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) defines the first
phase of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation of HL60
cells. J Cell Biochem. 80:471–482. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Rao J and Studzinski GP:
Inhibition of p38 MAP kinase activity up-regulates multiple MAP
kinase pathways and potentiates 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)-induced
differentiation of human leukemia HL60 cells. Exp Cell Res.
258:425–437. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X and Studzinski GP: Inhibition of
p38MAP kinase potentiates the JNK/SAPK pathway and AP-1 activity in
monocytic but not in macrophage or granulocytic differentiation of
HL60 cells. J Cell Biochem. 82:68–77. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caponigro F, French RC and Kaye SB:
Protein kinase C: a worthwhile target for anticancer drugs?
Anticancer Drugs. 8:26–33. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishikawa M and Shirakawa S: The
expression and possible roles of protein kinase C in haematopoietic
cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 8:201–211. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Quest AF: Regulation of protein kinase C:
a tale of lipids and proteins. Enzyme Protein. 49:231–261.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Komada F, Nishikawa M, Uemura Y, Morita K,
Hidaka H and Shirakawa S: Expression of three major protein kinase
C isozymes in various types of human leukemic cells. Cancer Res.
51:4271–4278. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sakashita A, Nakamaki T, Tsuruoka N, Honma
Y and Hozumi M: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, not
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, co-operates with
retinoic acid on the induction of functional
N-formyl-methionyl-phenylalanine receptors in HL-60 cells.
Leukemia. 5:26–31. 1991.
|
|
29
|
Marcinkowska E, Wiedlocha A and
Radzikowski C: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induced activation and
subsequent nuclear translocation of MAPK is upstream regulated by
PKC in HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 241:419–426. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Breitman TR, Selonick SE and Collins SJ:
Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia
cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
77:2936–2940. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tanaka H, Abe E, Miyaura C, Shiina Y and
Suda T: 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces differentiation of
human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) into
monocyte-macrophages, but not into granulocytes. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 117:86–92. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang SN, Lee MH, Kim KM, Cho D and Kim TS:
Induction of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell
differentiation into monocytes by silibinin: involvement of protein
kinase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 61:1487–1495. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|