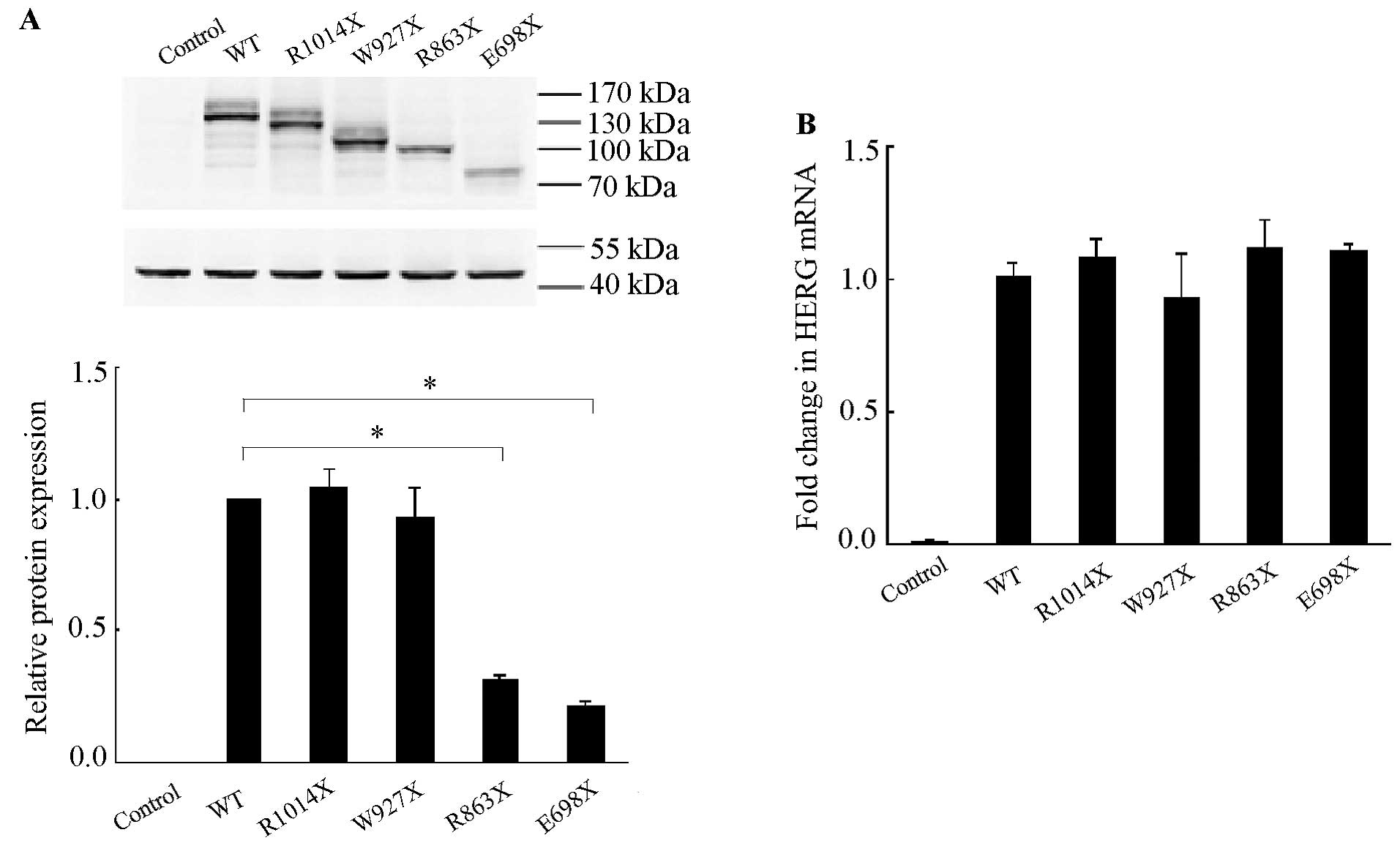
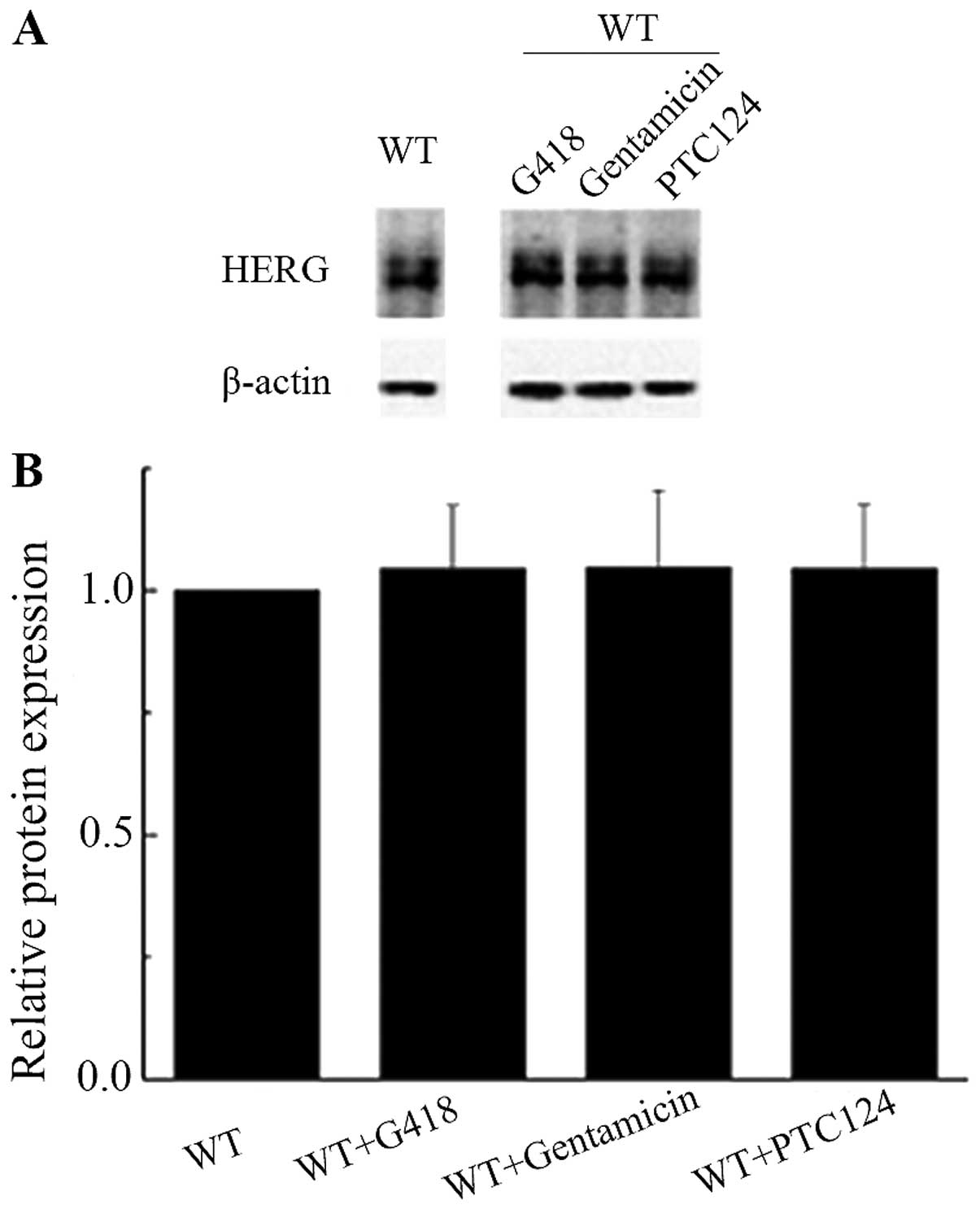
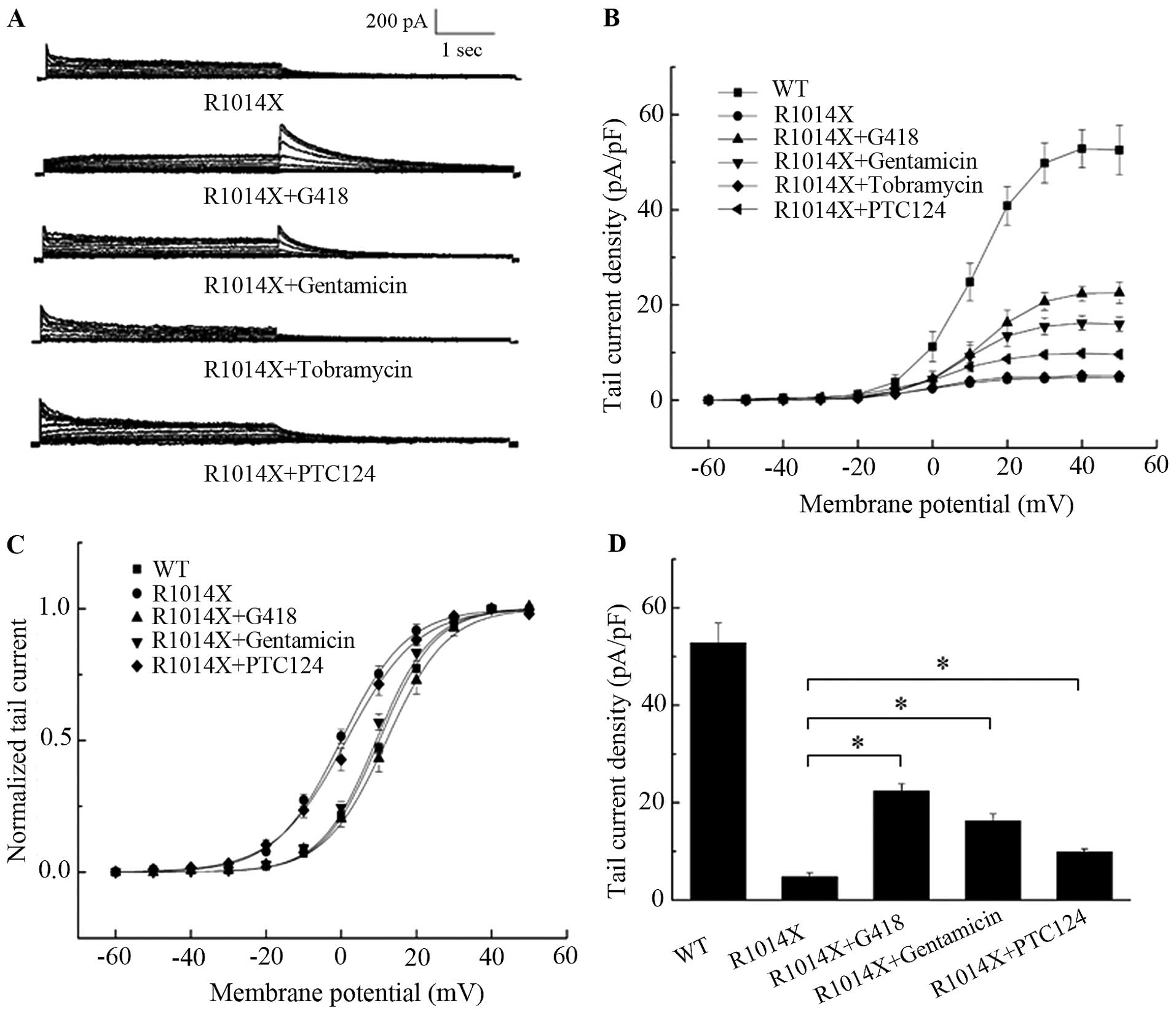
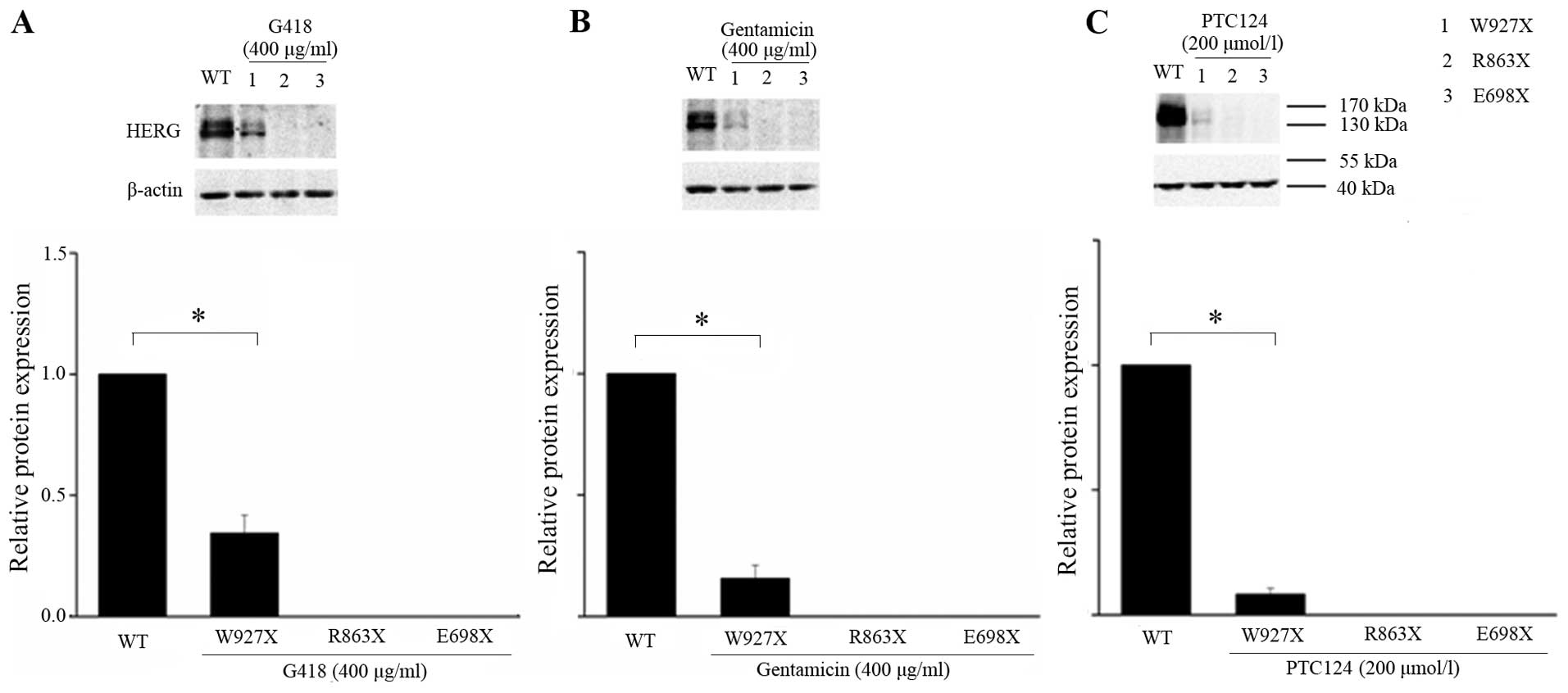
|
1
|
Splawski I, Shen J, Timothy KW, et al:
Spectrum of mutations in long-QT syndrome genes. KVLQT1, HERG,
SCN5A, KCNE1, and KCNE2. Circulation. 102:1178–1185. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anderson CL, Delisle BP, Anson BD, et al:
Most LQT2 mutations reduce Kv11.1 (hERG) current by a class 2
(trafficking-deficient) mechanism. Circulation. 113:365–373. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee HL and Dougherty JP: Pharmaceutical
therapies to recode nonsense mutations in inherited diseases.
Pharmacol Ther. 136:227–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zilberberg A, Lahav L and Rosin-Arbesfeld
R: Restoration of APC gene function in colorectal cancer cells by
aminoglycoside- and macrolide-induced read-through of premature
termination codons. Gut. 59:496–507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malik V, Rodino-Klapac LR, Viollet L, et
al: Gentamicin-induced readthrough of stop codons in Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 67:771–780. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howard M, Frizzell RA and Bedwell DM:
Aminoglycoside antibiotics restore CFTR function by overcoming
premature stop mutations. Nat Med. 2:467–469. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yao Y, Teng S, Li N, Zhang Y, Boyden PA
and Pu J: Aminoglycoside antibiotics restore functional expression
of truncated HERG channels produced by nonsense mutations. Heart
Rhythm. 6:553–560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wilschanski M, Miller LL, Shoseyov D, et
al: Chronic ataluren (PTC124) treatment of nonsense mutation cystic
fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 38:59–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldmann T, Overlack N, Wolfrum U and
Nagel-Wolfrum K: PTC124-mediated translational readthrough of a
nonsense mutation causing Usher syndrome type 1C. Hum Gene Ther.
22:537–547. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan L, Narayan SB, Chen J, Meyers GD and
Bennett MJ: PTC124 improves readthrough and increases enzymatic
activity of the CPT1A R160X nonsense mutation. J Inherit Metab Dis.
34:443–447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Welch EM, Barton ER, Zhuo J, et al: PTC124
targets genetic disorders caused by nonsense mutations. Nature.
447:87–91. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Crotti L, Celano G, Dagradi F and Schwartz
PJ: Congenital long QT syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 3:182008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent
GM, Green ED and Keating MT: A molecular basis for cardiac
arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell.
80:795–803. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alders M and Mannens M: Romano-Ward
Syndrome. Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, et al: GeneReviews™
(internet). University of Washington; Seattle, WA: 2003, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1129/.
Last update: May 31, 2012.
|
|
15
|
Schweingruber C, Rufener SC, Zünd D,
Yamashita A and Mühlemann O: Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay -
mechanisms of substrate mRNA recognition and degradation in
mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1829:612–623. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akhavan A, Atanasiu R, Noguchi T, Han W,
Holder N and Shrier A: Identification of the
cyclic-nucleotide-binding domain as a conserved determinant of
ion-channel cell-surface localization. J Cell Sci. 118:2803–2812.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akhavan A, Atanasiu R and Shrier A:
Identification of a COOH-terminal segment involved in maturation
and stability of human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium
channels. J Biol Chem. 278:40105–40112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moazed D and Noller HF: Interaction of
antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature.
327:389–394. 1987. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kondo J, Urzhumtsev A and Westhof E: Two
conformational states in the crystal structure of the Homo sapiens
cytoplasmic ribosomal decoding A site. Nucleic Acids Res.
34:676–685. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kondo J, Francois B, Urzhumtsev A and
Westhof E: Crystal structure of the Homo sapiens cytoplasmic
ribosomal decoding site complexed with apramycin. Angew Chem Int Ed
Engl. 45:3310–3314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hermann T, Tereshko V, Skripkin E and
Patel DJ: Apramycin recognition by the human ribosomal decoding
site. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 38:193–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Amrani N, Ganesan R, Kervestin S, Mangus
DA, Ghosh S and Jacobson A: A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant
termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature.
432:112–118. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Floquet C, Deforges J, Rousset JP and
Bidou L: Rescue of non-sense mutated p53 tumor suppressor gene by
aminoglycosides. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3350–3362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Luca A, Nico B, Rolland JF, et al:
Gentamicin treatment in exercised mdx mice: identification of
dystrophin-sensitive pathways and evaluation of efficacy in
work-loaded dystrophic muscle. Neurobiol Dis. 32:243–253.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Manuvakhova M, Keeling K and Bedwell DM:
Aminoglycoside antibiotics mediate context-dependent suppression of
termination codons in a mammalian translation system. RNA.
6:1044–1055. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Du M, Liu X, Welch EM, Hirawat S, Peltz SW
and Bedwell DM: PTC124 is an orally bioavailable compound that
promotes suppression of the human CFTR-G542X nonsense allele in a
CF mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2064–2069. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kerem E, Hirawat S, Armoni S, et al:
Effectiveness of PTC124 treatment of cystic fibrosis caused by
nonsense mutations: a prospective phase II trial. Lancet.
372:719–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ho G, Reichardt J and Christodoulou J: In
vitro read-through of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) nonsense
mutations using aminoglycosides: a potential therapy for
phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis. Mar 27–2013.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
29
|
Brumm H, Mühlhaus J, Bolze F, et al:
Rescue of melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) nonsense mutations by
aminoglycoside-mediated read-through. Obesity (Silver Spring).
20:1074–1081. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dranchak PK, Di Pietro E, Snowden A, et
al: Nonsense suppressor therapies rescue peroxisome lipid
metabolism and assembly in cells from patients with specific PEX
gene mutations. J Cell Biochem. 112:1250–1258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bartolomeo R, Polishchuk EV, Volpi N,
Polishchuk RS and Auricchio A: Pharmacological read-through of
nonsense ARSB mutations as a potential therapeutic approach for
mucopolysaccharidosis VI. J Inherit Metab Dis. 36:363–371. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Engelberg-Kulka H: UGA suppression by
normal tRNA Trp in Escherichia coli: codon context effects.
Nucleic Acids Res. 9:983–991. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nilsson M and Ryden-Aulin M: Glutamine is
incorporated at the nonsense codons UAG and UAA in a
suppressor-free Escherichia coli strain. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1627:1–6. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brendel C, Belakhov V, Werner H, et al:
Readthrough of nonsense mutations in Rett syndrome: evaluation of
novel aminoglycosides and generation of a new mouse model. J Mol
Med (Berl). 89:389–398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|