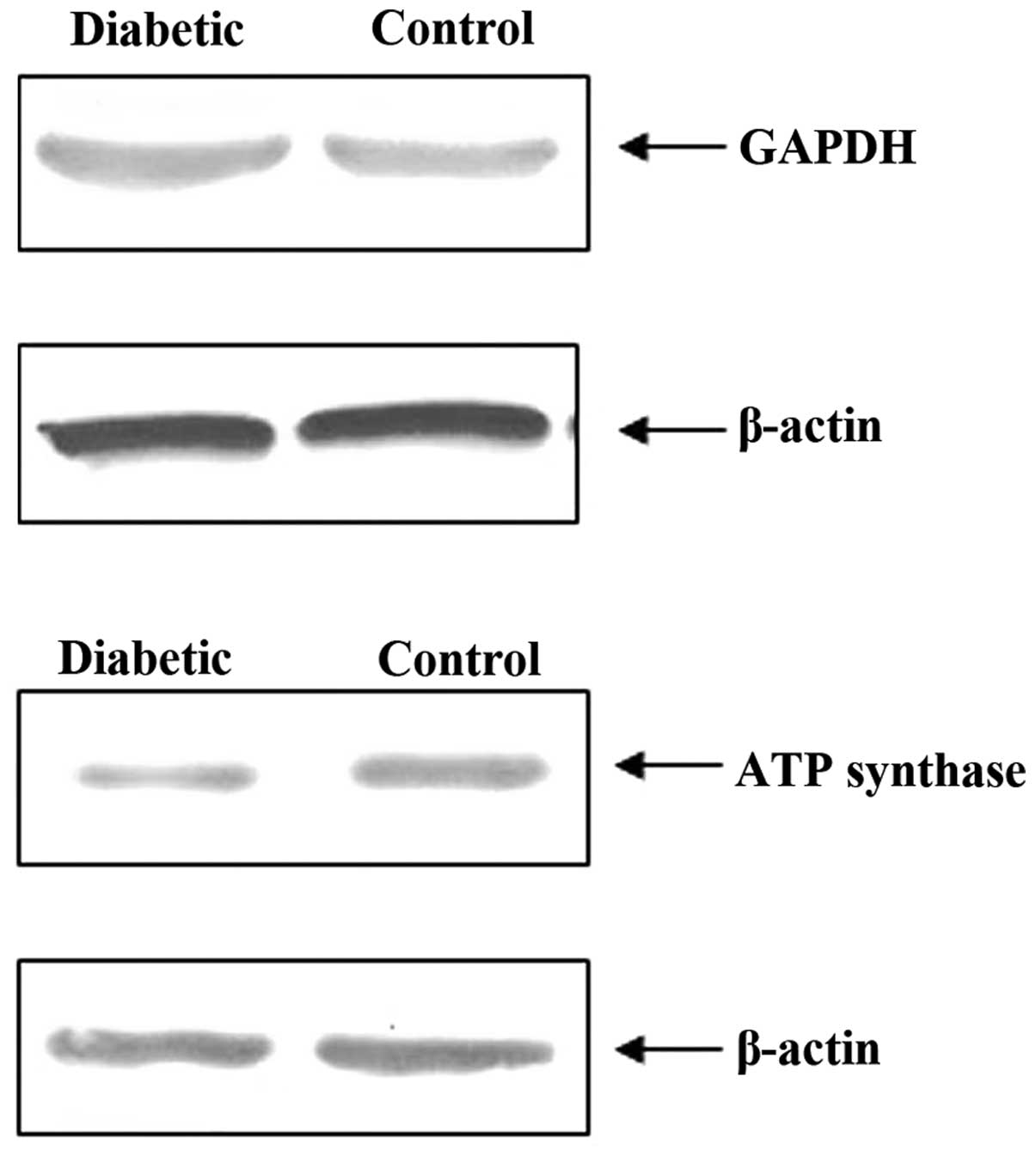
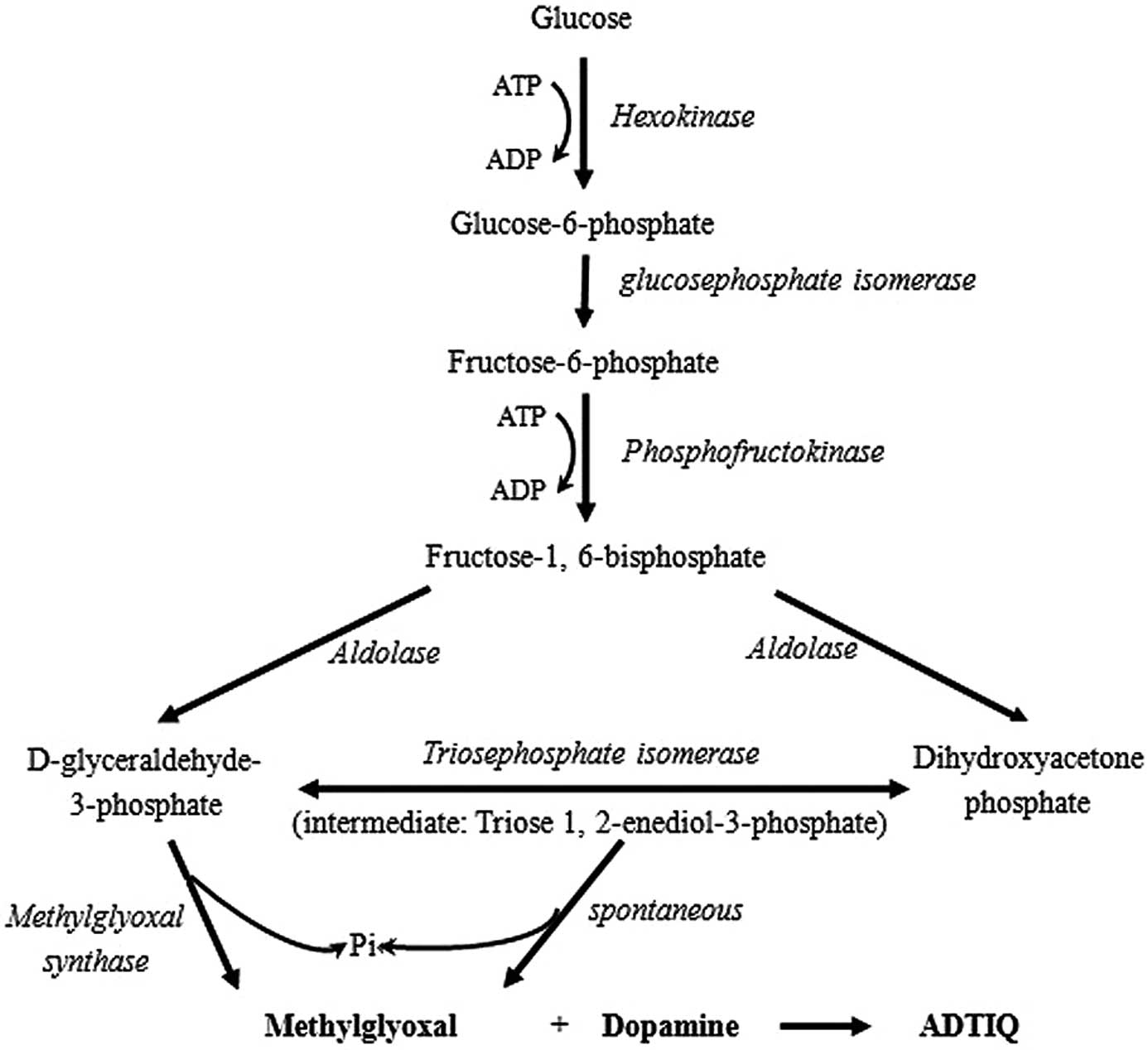
|
1
|
Xu Q, Park Y, Huang X, Hollenbeck A, Blair
A, Schatzkin A and Chen H: Diabetes and Risk of Parkinson’s
Disease. Diabetes Care. 34:910–915. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Schernhammer E, Hansen J, Rugbjerg K,
Wermuth L and Ritz B: Diabetes and the risk of developing
Parkinson’s disease in Denmark. Diabetes Care. 34:1102–1108.
2011.
|
|
3
|
Arvanitakis Z, Wilson RS, Schneider JA,
Bienias JL, Evans DA and Bennett DA: Diabetes mellitus and
progression of rigidity and gait disturbance in older persons.
Neurology. 63:996–1001. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng YL, Zhang YQ, Li YJ, Xiao SY, Song
DW, Qing H, Li Q and Rajput AH: Occurrence and distribution of
salsolinol-like compound,
1-acetyl-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (ADTIQ) in
parkinsonian brains. J Neural Transm. 119:435–441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ristow M: Neurodegenerative disorders
associated with diabetes mellitus. J Mol Med (Berl). 82:510–529.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deng YL and Rajput AM: 126th Annual
Meeting, American Neurological Association: Abstracts: Plenary
Session: Epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 50(Suppl 1): S19–S22. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Haik GM Jr, Lo TW and Thornalley PJ:
Methylglyoxal concentration and glyoxalase activities in the human
lens. Exp Eye Res. 59:497–500. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu W, Wang D, Zheng J, An Y, Wang Q,
Zhang W, Jin L, Gao H and Lin L: Effect of (R)-salsolinol and
N-methyl-(R)-salsolinol on the balance impairment between dopamine
and acetylcholine in rat brain: involvement in pathogenesis of
Parkinson disease. Clin Chem. 54:705–712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Xiao S, Wang L, Wang H, Zhu Y, Li
Y and Deng Y: Absolute quantification of semicarbazide-sensitive
amine oxidase in human umbilical artery by single-reaction
monitoring with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal
Chem. 397:709–715. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang R, Qing H, Liu XQ, Zheng XL and Deng
YL: Iron contributes to the formation of catechol isoquinolines and
oxidative toxicity induced by overdose dopamine in dopaminergic
SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Bull. 24:125–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song DW, Du HQ, Wang L, Hu GF and Deng YL:
Analysis of catechol quinoline substance in corpus striatum and
hippocampus from brains of diabetic rat models by HPLC-MS.
Chemistry. 11:1049–1052. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Song DW, Hu GF, Zhou Y, Wang HB, Wang L,
Zhu Y and Deng YL: Proteomic analysis of proteins related to
Parkinson’s disease in the corpus striatum and hippocampus of
diabetes rat model. Chemistry. 6:430–434. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Kuhla B, Loske C, Garcia De Arriba S,
Schinzel R, Huber J and Münch G: Differential effects of ‘Advanced
glycation endproducts’ and beta-amyloid peptide on glucose
utilization and ATP levels in the neuronal cell line SH-SY5Y. J
Neural Transm. 11:427–439. 2004.
|
|
14
|
Emdadul Haque M, Asanuma M, Higashi Y,
Miyazaki I, Tanaka K and Ogawa N: Apoptosis-inducing neurotoxicity
of dopamine and its metabolites via reactive quinone generation in
neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1619:39–52.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Collins MO, Yu L, Coba MP, Husi H,
Campuzano I, Blackstock WP, Choudhary JS and Grant SGN: Proteomic
analysis of in vivo phosphorylated synaptic proteins. J Biol Chem.
280:5972–5982. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song DW, Li Q, Luan YJ, Niu LY, Qing H and
Deng YL: Comparative proteomic analysis of neural stem cells
between differentiating and undifferentiating to dopaminergic
neuron. Complex Medical Engineering (CME). In: IEEE/ICME
International Conference, 1817–1823; 2007
|
|
17
|
Diez L, Livertoux MH, Stark AA,
Wellman-Rousseau M and Leroy P: High-performance liquid
chromatographic assay of hydroxyl free radical using salicylic acid
hydroxylation during in vitro experiments involving thiols. J
Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 763:185–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ferger B, Spratt C, Earl CD, Teismann P,
Oertel WH and Kuschinsky K: Effects of nicotine on hydroxyl free
radical formation in vitro and on MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in
vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 358:351–359. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Copeland RL Jr, Das JR, Kanaan YM, Taylor
RE and Tizabi Y: Antiapoptotic effects of nicotine in its
protection against salsolinol-induced cytotoxicity. Neurotox Res.
12:61–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yi H, Maruyama W, Akao Y, Takahashi T,
Iwasa K, Youdim MB and Naoi M: N-Propargylamine protects SH-SY5Y
cells from apoptosis induced by an endogenous neurotoxin,
N-methyl(R)salsolinol, through stabilization of mitochondrial
membrane and induction of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2. J Neural Transm.
113:21–32. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Youdim MB, Davis BA
and Naoi M: Transfection-enforced Bcl-2 overexpression and an
anti-Parkinson drug, rasagiline, prevent nuclear accumulation of
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induced by an endogenous
dopaminergic neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol. J Neurochem.
78:727–735. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wanpen S, Kooncumchoo P, Shavali S,
Govitrapong P and Ebadi M: Salsolinol, an endogenous neurotoxin,
activates JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways in human
neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem Res. 32:443–450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kheradpezhouh M, Shavali S and Ebadi M:
Salsolinol causing parkinsonism activates endoplasmic
reticulum-stress signaling pathways in human dopaminergic SK-N-SH
cells. Neurosignals. 12:315–324. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Thornalley PJ, Jahan I and Ng R:
Suppression of the accumulation of triosephosphates and increased
formation of methylglyoxal in human red blood cells during
hyperglycaemia by thiamine in vitro. J Biochem. 129:543–549. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dmitriev LF and Dugin SF: Aldehydes and
disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism: some consequences and
possible approaches to its normalization. Arch Physiol Biochem.
113:87–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sheu KF, Ho HT, Nolan LD, Markovitz P,
Richard JP, Utter MF and Frey PA: Stereochemical course of
thiophosphoryl group transfer catalyzed by mitochondrial
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Biochemistry. 23:1779–1783.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Richard JP: Mechanism for the formation of
methylglyoxal from triosephosphates. Biochem Soc Trans. 21:549–553.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han YC, Randell E, Vasdev S, Gill V, Gadag
V, Newhook LA, Grant M and Hagerty D: Plasma methylglyoxal and
glyoxal are elevated and related to early membrane alteration in
young, complication-free patients with Type 1 diabetes. Mol Cell
Biochem. 305:123–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
MacDonald MJ, Chaplen FWR, Triplett CK,
Gong Q and Drought H: Stimulation of insulin release by
glyceraldehyde may not be similar to glucose. Arch Biochem Biophys.
447:118–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Caccese D, Pratico D, Ghiselli A, Natoli
S, Pignatelli P, Sanguigni V, Luliano L and Violi F: Superoxide
anion and hydroxyl radical release by collagen-induced platelet
aggregation - role of arachidonic acid metabolism. Thromb Haemost.
83:485–490. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi HL and Liu KJ: Effects of glucose
concentration on redox status in rat primary cortical neurons under
hypoxia. Neurosci Lett. 410:57–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Adam W, Kurz A and Saha-Möller CR:
Peroxidase-catalyzed oxidative damage of DNA and 2′-deoxyguanosine
by model compounds of lipid hydroperoxides: involvement of peroxyl
radicals. Chem Res Toxicol. 13:1199–1207. 2000.
|
|
33
|
Hong JH, Kim MJ, Park MR, Kwag OG, Lee IS,
Byun BH, Lee SC, Lee KB and Rhee SJ: Effects of vitamin E on
oxidative stress and membrane fluidity in brain of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Clin Chim Acta. 340:107–115.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sima AAF and Li ZG: The effect of
C-peptide on cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal apoptosis in
type 1 diabetic rats. Diabetes. 54:1497–1505. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stevens MJ, Zhang W, Li F and Sima AA:
C-peptide corrects endoneurial blood flow but not oxidative stress
in type 1 BB/Wor rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
287:E497–E505. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|