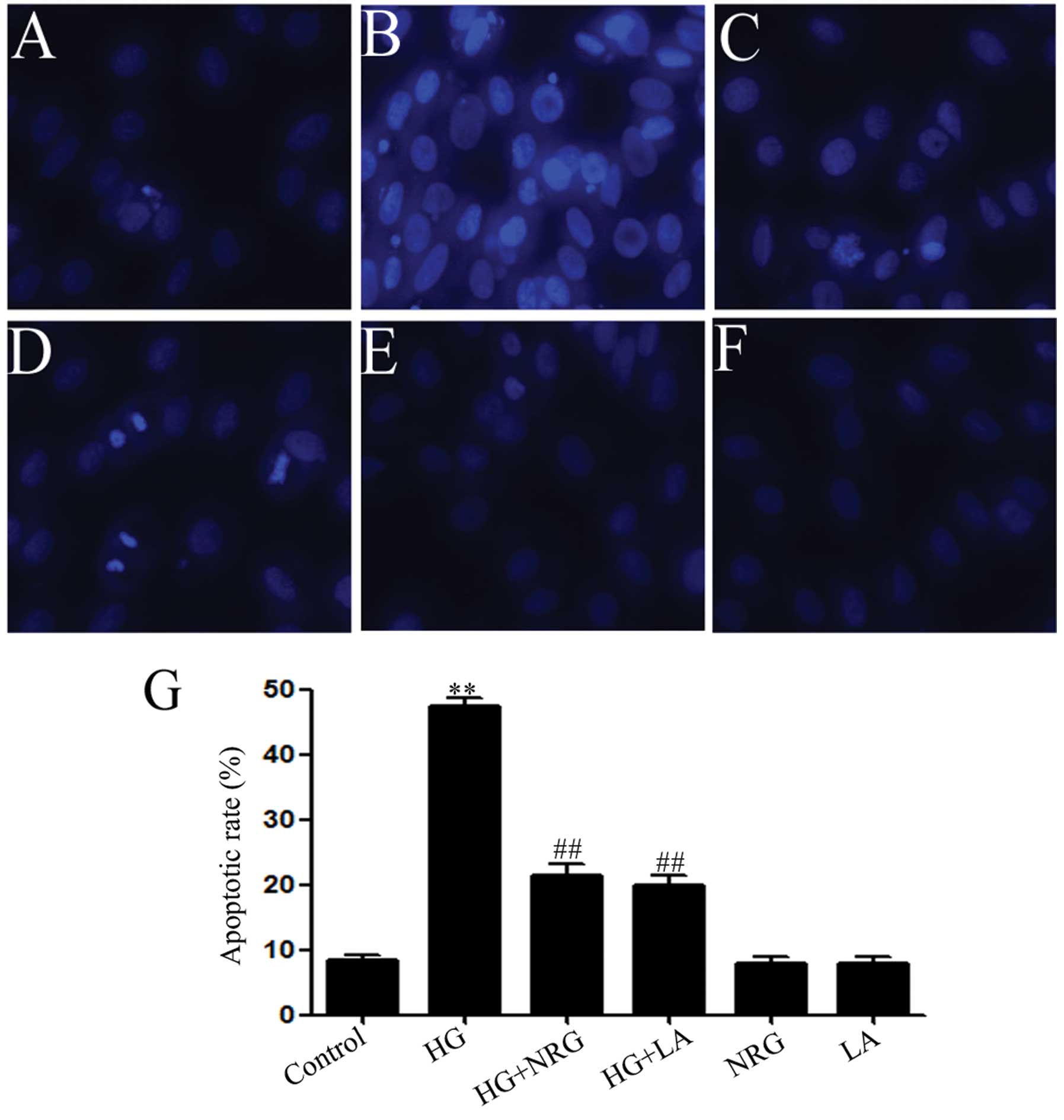
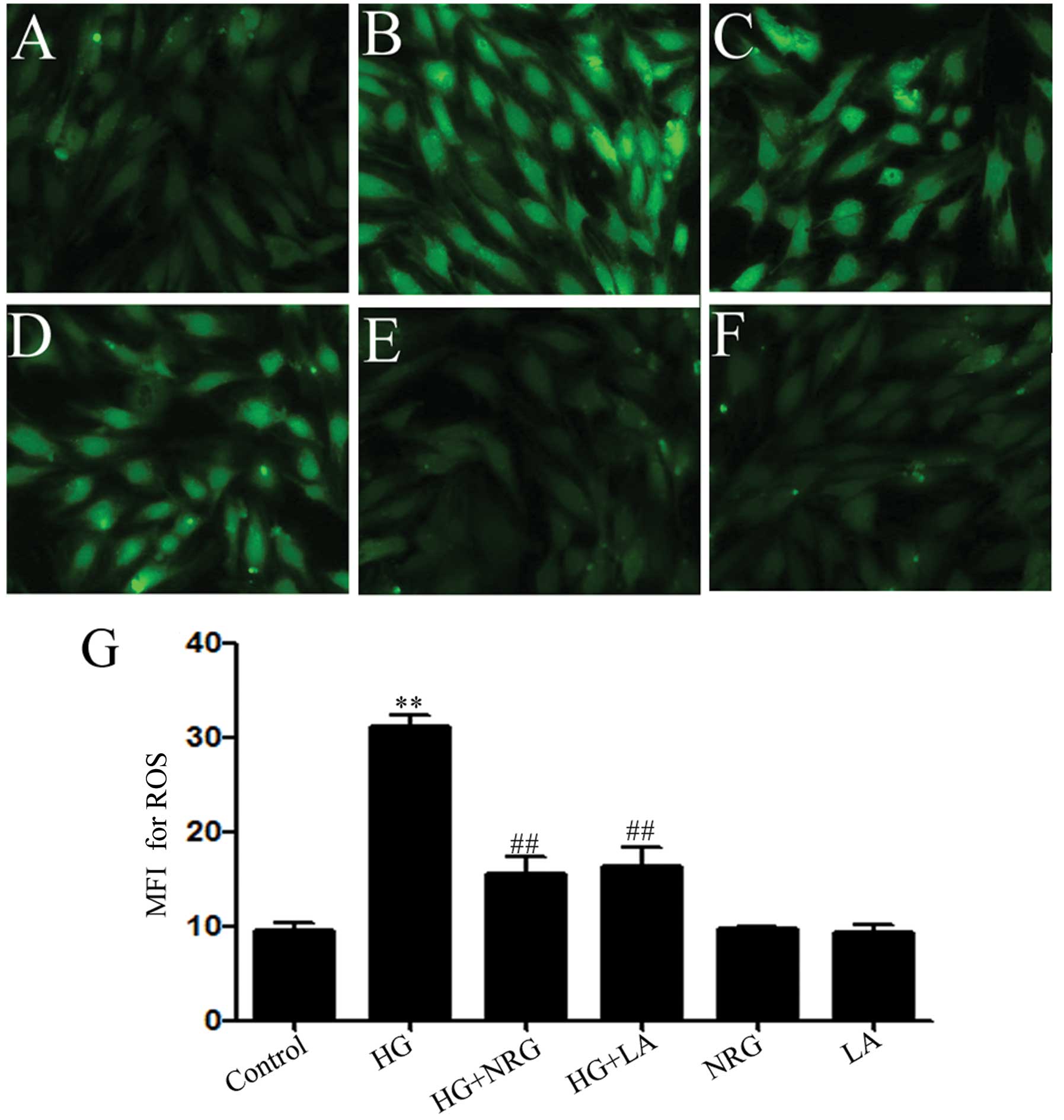
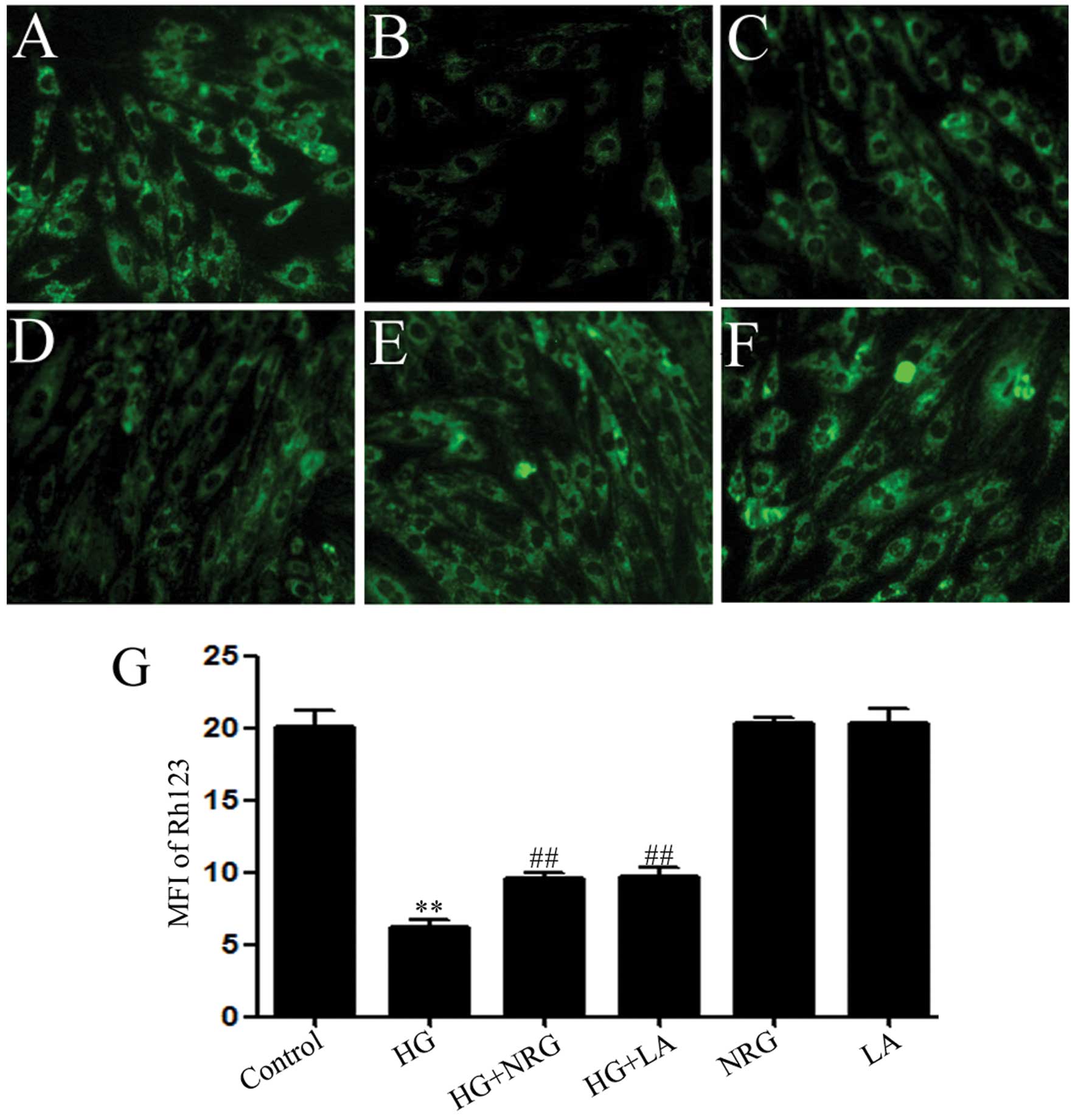
|
1
|
Mahmoud AM, Ashour MB, Abdel-Moneim A and
Ahmed OM: Hesperidin and naringin attenuate hyperglycemia-mediated
oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokine production in high
fat fed/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Diabetes
Complications. 26:483–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Preventive
effect of naringin on isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in
Wistar rats: an in vivo and in vitro study. Toxicology.
232:216–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeon SM, Park YB and Choi MS:
Antihypercholesterolemic property of naringin alters plasma and
tissue lipids, cholesterol-regulating enzymes, fecal sterol and
tissue morphology in rabbits. Clin Nutr. 23:1025–1034. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jain M and Parmar HS: Evaluation of
antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential of hesperidin and
naringin on the rat air pouch model of inflammation. Inflamm Res.
60:483–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bodas R, Prieto N, López-Campos O,
Giráldez FJ and Andrés S: Naringin and vitamin E influence the
oxidative stability and lipid profile of plasma in lambs fed fish
oil. Res Vet Sci. 91:98–102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jung UJ, Kim HJ, Lee JS, et al: Naringin
supplementation lowers plasma lipids and enhances erythrocyte
antioxidant enzyme activities in hypercholesterolemic subjects.
Clin Nutr. 22:561–568. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim HJ, Oh GT, Park YB, Lee MK, Seo HJ and
Choi MS: Naringin alters the cholesterol biosynthesis and
antioxidant enzyme activities in LDL receptor-knockout mice under
cholesterol fed condition. Life Sci. 74:1621–1634. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nie YC, Wu H, Li PB, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of naringin in chronic pulmonary
neutrophilic inflammation in cigarette smoke-exposed rats. J Med
Food. 15:894–900. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jagetia GC, Venkatesha VA and Reddy TK:
Naringin, a citrus flavonone, protects against radiation-induced
chromosome damage in mouse bone marrow. Mutagenesis. 18:337–343.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanno S, Shouji A, Asou K and Ishikawa M:
Effects of naringin on hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity and
apoptosis in P388 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 92:166–170. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kanno S, Shouji A, Hirata R, Asou K and
Ishikawa M: Effects of naringin on cytosine arabinoside
(Ara-C)-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in P388 cells. Life Sci.
75:353–365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang H and Wu K, You Q, Huang R, Li S and
Wu K: Naringin inhibits high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte
apoptosis by attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and modulating
the activation of the p38 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
32:396–402. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Adel AM, Mohamed BA, Ayman MM and Osama
MA: Insulin sensitizing effects of hesperidin and naringin in
experimental kmodel of induced type 2 diabetes in rats: focus on
tumor necrosis factor-alpha and resistin. Nat Sci. 7:134–141.
2011.
|
|
14
|
Osama MA, Ayman MM, Adel AM and Mohamed
BA: Antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic effects of hesperidin
and naringin in high fat diet/streptozotocin type 2 diabetic rats.
Life Sci J. 8:91–101. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Preventive
effect of naringin on cardiac mitochondrial enzymes during
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: a transmission
electron microscopic study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 21:354–361.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Naringin
ameliorates mitochondrial lipid peroxides, antioxidants and lipids
in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats.
Phytother Res. 23:358–362. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tartaglia LA: The leptin receptor. J Biol
Chem. 272:6093–6096. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murad A, Nath AK, Cha ST, Demir E,
Flores-Riveros J and Sierra-Honigmann MR: Leptin is an
autocrine/paracrine regulator of wound healing. FASEB J.
17:1895–1897. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
La Cava A, Alviggi C and Matarese G:
Unraveling the multiple roles of leptin in inflammation and
autoimmunity. J Mol Med (Berl). 82:4–11. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren J: Leptin and hyperleptinemia - from
friend to foe for cardiovascular function. J Endocrinol. 181:1–10.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Figenschau Y, Knutsen G, Shahazeydi S,
Johansen O and Sveinbjörnsson B: Human articular chondrocytes
express functional leptin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
287:190–197. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Majumdar P, Chen S, George B, Sen S,
Karmazyn M and Chakrabarti S: Leptin and endothelin-1 mediated
increased extracellular matrix protein production and cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy in diabetic heart disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
25:452–463. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wallace AM, McMahon AD, Packard CJ, et al:
Plasma leptin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the west of
Scotland coronary prevention study (WOSCOPS). Circulation.
104:3052–3056. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoggard N, Mercer JG, Rayner DV, Moar K,
Trayhurn P and Williams LM: Localization of leptin receptor mRNA
splice variants in murine peripheral tissues by RT-PCR and in situ
hybridization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 232:383–387. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kieffer TJ, Heller RS and Habener JF:
Leptin receptors expressed on pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 224:522–537. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin J, Barb CR, Matteri RL, Kraeling RR,
Chen X, Meinersmann RJ and Rampacek GB: Long form leptin receptor
mRNA expression in the brain, pituitary, and other tissues in the
pig. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 19:53–61. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bjørbaek C, Uotani S, da Silva B and Flier
JS: Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms
of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem. 272:32686–32695.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bjørbaek C, Buchholz RM, Davis SM, et al:
Divergent roles of SHP-2 in ERK activation by leptin receptors. J
Biol Chem. 276:4747–4755. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bouloumie A, Marumo T, Lafontan M and
Busse R: Leptin induces oxidative stress in human endothelial
cells. FASEB J. 13:1231–1238. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van den Brink GR, O’Toole T, Hardwick JC,
van den Boogaardt DE, Versteeg HH, van Deventer SJ and
Peppelenbosch MP: Leptin signaling in human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells, activation of p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated
protein (MAP) kinase and p70 S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun.
4:144–150. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shin HJ, Oh J, Kang SM, et al: Leptin
induces hypertrophy via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in rat
vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
329:18–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rajapurohitam V, Gan XT, Kirshenbaum LA
and Karmazyn M: The obesity-associated peptide leptin induces
hypertrophy in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Circ Res.
93:277–279. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeidan A, Javadov S, Chakrabarti S and
Karmazyn M: Leptin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy involves
selective caveolae and RhoA/ROCK-dependent p38 MAPK translocation
to nuclei. Cardiovasc Res. 77:64–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han DC, Isono M, Chen S, Casaretto A, Hong
SW, Wolf G and Ziyadeh FN: Leptin stimulates type I collagen
production in db/db mesangial cells: glucose uptake and TGF-beta
type II receptor expression. Kidney Int. 59:1315–1323. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peake BF, Nicholson CK, Lambert JP, Hood
RL, Amin H, Amin S and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide preconditions
the db/db diabetic mouse heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury
by activating Nrf2 signaling in an Erk-dependent manner. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1215–H1224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ganesan K, Gani SB and Arunachalam GM:
Effect of Helicteres isora bark extracts on heart
antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin
diabetic rats. J Appl Biomed. 6:89–95. 2008.
|
|
37
|
Boudina S, Sena S, Theobald H, et al:
Mitochondrial energetics in the heart in obesity-related diabetes:
direct evidence for increased uncoupled respiration and activation
of uncoupling proteins. Diabetes. 56:2457–2466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ceriello A: Cardiovascular effects of
acute hyperglycaemia: pathophysiological underpinnings. Diab Vasc
Dis Res. 5:260–268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ren J and Davidoff AJ: Diabetes rapidly
induces contractile dysfunctions in isolated ventricular myocytes.
Am J Physiol. 272:H148–H158. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Sukumaran V, et al:
Curcumin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats: possible involvement of PKC-MAPK signaling pathway.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 47:604–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu W, Wu W, Chen J, Guo R, Lin J, Liao X
and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury by inhibiting the activities of
the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Mol Med. 32:917–925.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yan J, Young ME, Cui L, Lopaschuk GD, Liao
R and Tian R: Increased glucose uptake and oxidation in mouse
hearts prevent high fatty acid oxidation but cause cardiac
dysfunction in diet-induced obesity. Circulation. 119:2818–2828.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu AL, Wang XW, Liu AH, Su XW, Jiang WJ,
Qiu PX and Yan GM: JNK and p38 were involved in hypoxia and
reoxygenation-induced apoptosis of cultured rat cerebellar granule
neurons. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 61:137–143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lan A, Liao X, Mo L, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by
inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in
PC12 cells. PLoS One. 6:e259212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guo R, Lin J, Xu W, Shen N, Mo L, Zhang C
and Feng J: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity by inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway in H9c2 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 31:644–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo RM, Xu WM, Lin JC, et al: Activation
of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway contributes to doxorubicin-induced
inflammation and cytotoxicity in H9c2 cardiac cells. Mol Med Rep.
8:603–608. 2013.
|
|
48
|
Chen L, Liu L, Yin J, Luo Y and Huang S:
Hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal apoptosis is associated with
inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A and 5, leading to activation
of MAPK pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1284–1295. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tajmir P, Ceddia RB, Li RK, Coe IR and
Sweeney G: Leptin increases cardiomyocyte hyperplasia via
extracellular signal-regulated kinase- and phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-dependent signaling pathways. Endocrinology.
145:1550–1555. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|