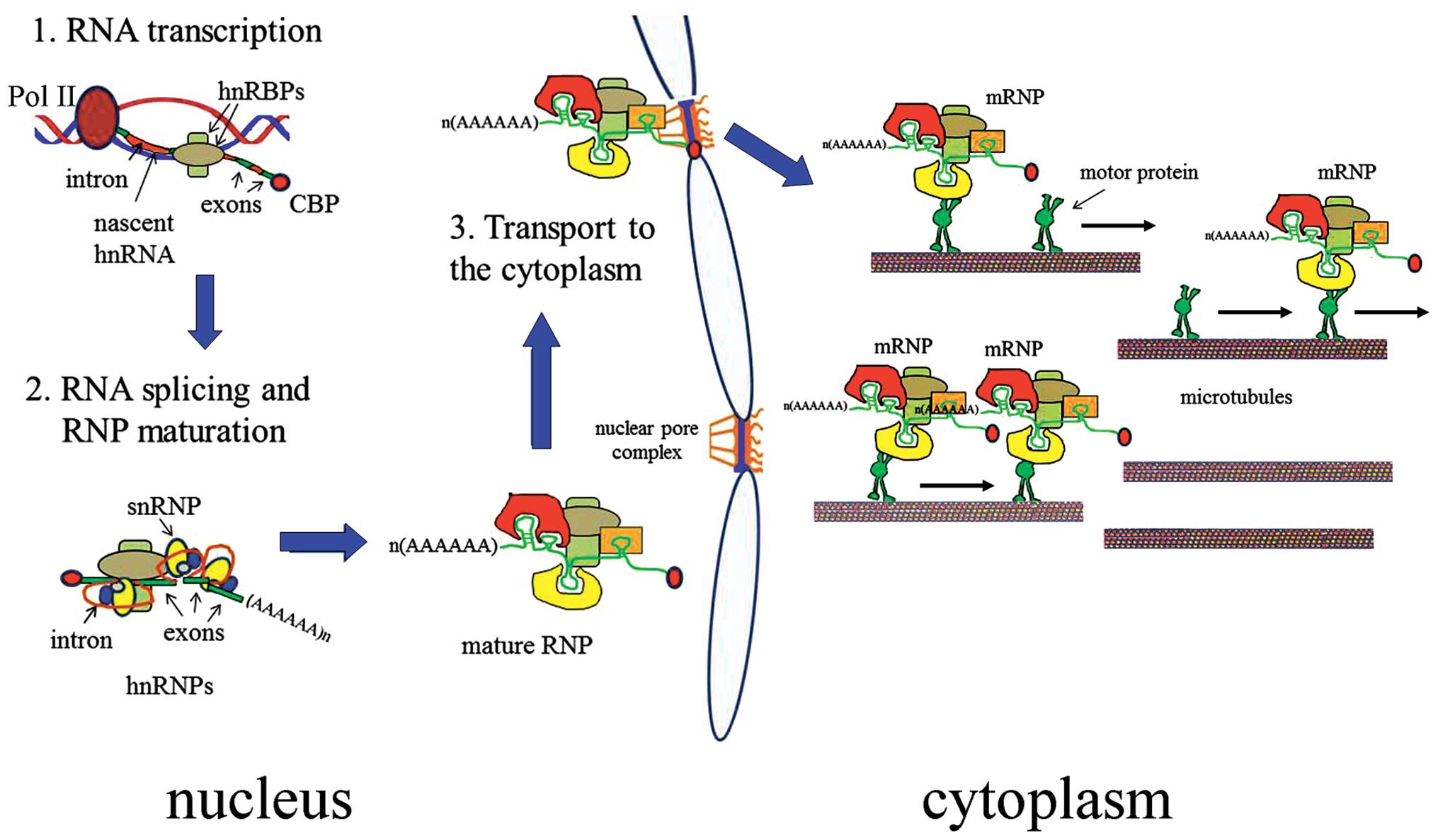
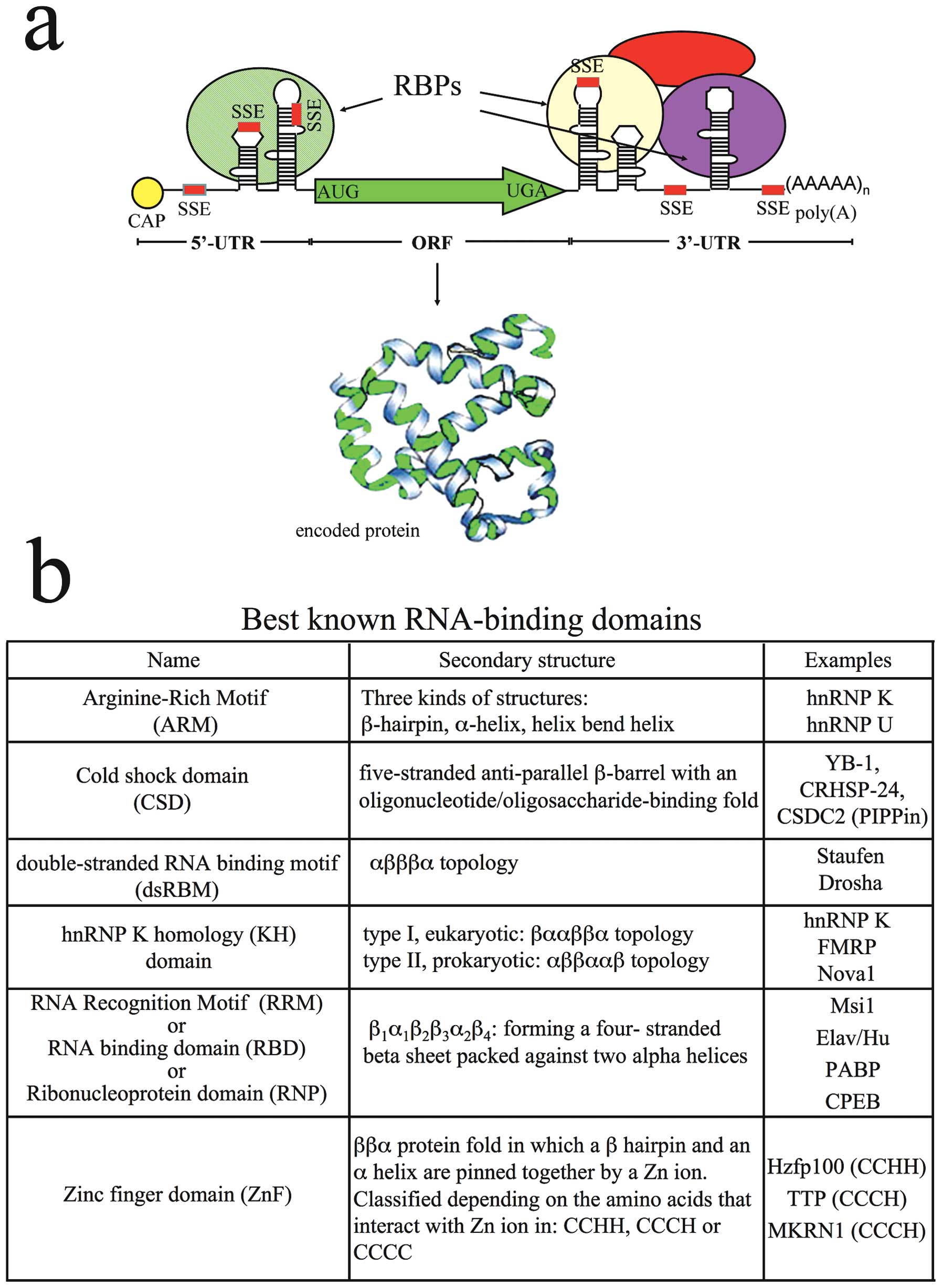
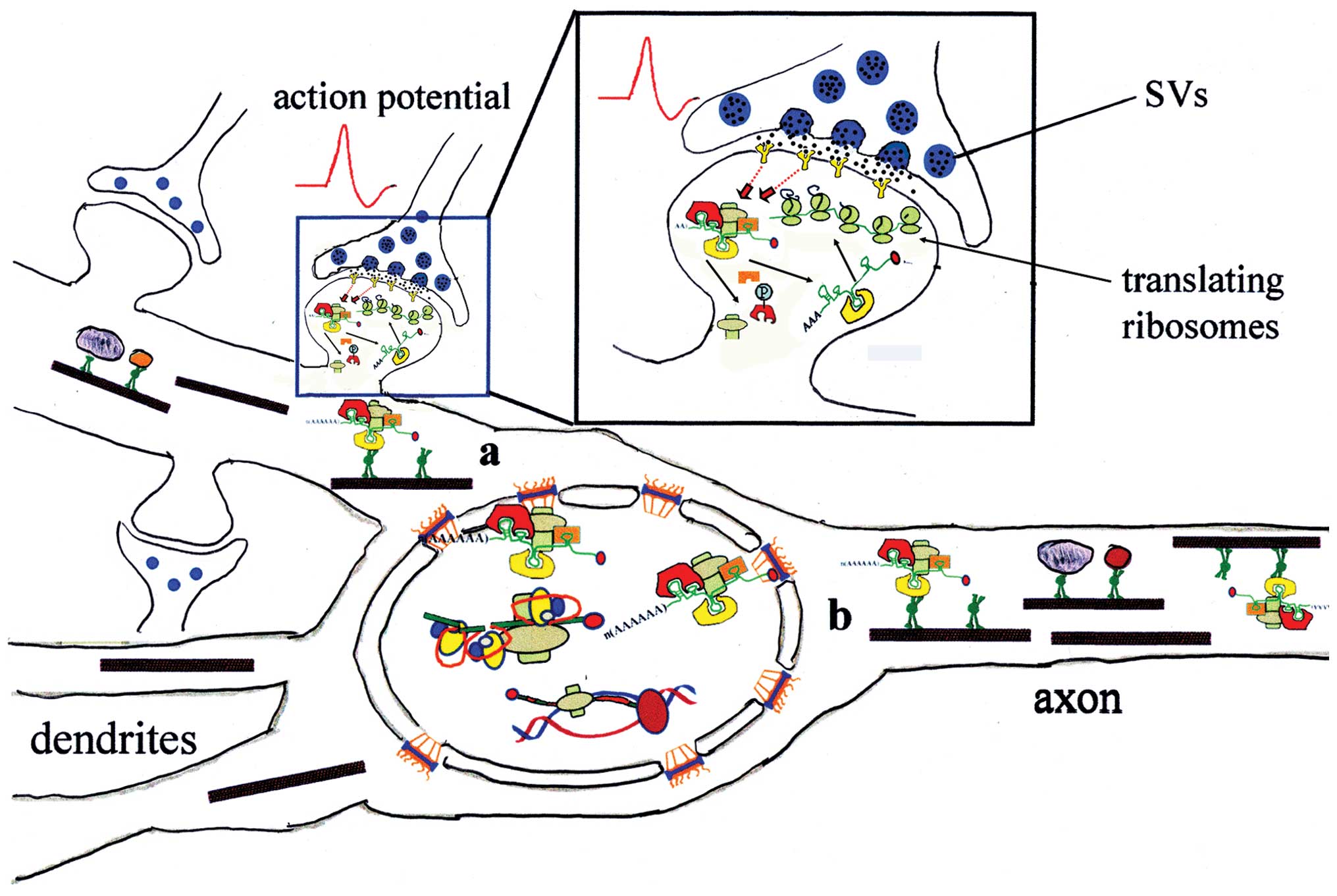
|
1
|
Mauger DM, Siegfried NA and Weeks KM: The
genetic code as expressed through relationships between mRNA
structure and protein function. FEBS Lett. 587:1180–1188. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thapar R and Denmon AP: Signaling pathways
that control mRNA turnover. Cell Signal. 25:1699–1710. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Will CL and Lührmann R: Spliceosome
structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:pii:
a003707. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Chiou NT, Shankarling G and Lynch KW:
hnRNP L and hnRNP A1 induce extended U1 snRNA interactions with an
exon to repress spliceosome assembly. Mol Cell. 49:972–982. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suzuki H, Kameyama T, Ohe K, Tsukahara T
and Mayeda A: Nested introns in an intron: evidence of multi-step
splicing in a large intron of the human dystrophin pre-mRNA. FEBS
Lett. 587:555–561. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sasaki-Haraguchi N, Shimada MK, Taniguchi
I, Ohno M and Mayeda A: Mechanistic insights into human pre-mRNA
splicing of human ultra-short introns: potential unusual mechanism
identifies G-rich introns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:289–294.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsumoto K, Wassarman KM and Wolffe AP:
Nuclear history of a pre-mRNA determines the translational activity
of cytoplasmic mRNA. EMBO J. 17:2107–2121. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stewart M: Nuclear export of mRNA. Trends
Biochem Sci. 35:609–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ramos A, Gubser CC and Varani G: Recent
solution structures of RNA and its complexes with drugs, peptides
and proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 7:317–323. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Linder P and Tuite MF: The versatility of
RNA structure and function. In: Jacques Monod Conference: New
insights into the mechanism of mRNA translation: the significance
of RNA structure; Aussois, France. 22–26 March 1999; Trends Genet.
15. pp. 302–303. 1999, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Caprara MG and Nilsen TW: RNA: versatility
in form and function. Nat Struct Biol. 7:831–833. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Derrigo M, Cestelli A, Savettieri G and Di
Liegro I: RNA-protein interactions in the control of stability and
localization of messenger RNA (Review). Int J Mol Med. 5:111–123.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Butcher SE and Pyle AM: The molecular
interactions that stabilize RNA tertiary structure: RNA motifs,
patterns, and networks. Acc Chem Res. 44:1302–1311. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hajdin CE, Bellaousov S, Huggins W,
Leonard CW, Mathews DH and Weeks KM: Accurate SHAPE-directed RNA
secondary structure modeling, including pseudoknots. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:5498–5503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Doetsch M, Schroeder R and Fürtig B:
Transient RNA-protein interactions in RNA folding. FEBS J.
278:1634–1642. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weeks KM: Protein-facilitated RNA folding.
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 7:336–342. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu L and Chen SJ: Coarse-grained
prediction of RNA loop structures. PLoS One. 7:e484602012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fuller-Pace FV: RNA helicases: modulators
of RNA structure. Trends Cell Biol. 4:271–274. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De la Cruz J, Kressler D and Linder P:
Unwinding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DEAD-box,
proteins and related families. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:192–198.
1999.
|
|
20
|
Linder P: mRNA export: RNP remodeling by
DEAD-box proteins. Curr Biol. 18:R297–R299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Herschlag D: RNA chaperones and the RNA
folding problem. J Biol Chem. 270:20871–20874. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clodi E, Semrad K and Schroeder R:
Assaying RNA chaperone activity in vivo using a novel folding trap.
EMBO J. 18:3776–3782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grohman JK, Gorelick RJ, Lickwar CR, Lieb
JD, Bower BD, Znosko BM and Weeks KM: A guanosine-centric mechanism
for RNA chaperone function. Science. 340:190–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kislauskis EH and Singer RH: Determinants
of mRNA localization. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 4:975–978. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jambhekar A and Derisi JL: Cis-acting
determinants of asymmetric, cytoplasmic RNA transport. RNA.
13:625–642. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lunde BM, Moore C and Varani G:
RNA-binding proteins: modular design for efficient function. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:479–490. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Doyle M and Kiebler MA: A zipcode
unzipped. Genes Dev. 26:110–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dienstbier M, Boehl F, Li X and Bullock
SL: Egalitarian is a selective RNA-binding protein linking mRNA
localization signals to the dynein motor. Genes Dev. 23:1546–1558.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patel VL, Mitra S, Harris R, Buxbaum AR,
Lionnet T, Benowitz M, Girvin M, Levy M, Almo SC, Singer RH and
Chao JA: Spatial arrangement of an RNA zipcode identifies mRNAs
under post-transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 26:43–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chao JA, Patskovsky Y, Patel V, Levy M,
Almo SC and Singer RH: ZBP1 recognition of β-actin zipcode induces
RNA looping. Genes Dev. 24:148–158. 2010.
|
|
31
|
Burd CG and Dreyfuss G: Conserved
structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins.
Science. 265:615–621. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siomi H, Matunis MJ, Michael WM and
Dreyfuss G: The pre-mRNA binding K protein contains a novel
evolutionary conserved motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:1193–1198.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
St Johnston D, Benchle D and
Nusslein-Volhard C: Staufen, a gene required to localize maternal
RNAs in the Drosophila egg. Cell. 66:51–63. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dubnau J, Chiang AS, Grady L, Barditch J,
Gossweiler S, McNeil J, Smith P, Buldoc F, Scott R, Certa U, Broger
C and Tully T: The staufen/pumilio pathway is involved in
Drosophila long-term memory. Curr Biol. 13:286–296. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Hu JY, Wu F, Schwartz JH and
Schacher S: Two mRNA-binding proteins regulate the distribution of
syntaxin mRNA in Aplysia sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 26:5204–5214.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Furic L, Maher-Laporte M and
DesGroseillers L: A genome-wide approach identifies distinct but
overlapping subsets of cellular mRNAs associated with Staufen1- and
Staufen2-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes. RNA. 14:324–335.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lebeau G, DesGroseillers L, Sossin W and
Lacaille JC: mRNA binding protein staufen 1-dependent regulation of
pyramidal cell spine morphology via NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic
plasticity. Mol Brain. 4:222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu Z, Fan D, Gui B, Shi L, Xuan C, Shan L,
Wang Q, Shang Y and Wang Y: Neurodegeneration-associated TDP-43
interacts with fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP)/Staufen
(STAU1) and regulates SIRT1 expression in neuronal cells. J Biol
Chem. 287:22560–22572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ravasi T, Huber T, Zavolan M, Forrest A,
Gaasterland T, Grimmond S and Hume DA; RIKEN GER Group. GSL
Members: Systematic characterization of the zinc-finger-containing
proteins in the mouse transcriptome. Genome Res. 13:1430–1442.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brown RS: Zinc finger proteins: getting a
grip on RNA. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 15:94–98. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu B and Koenig RJ: An RNA-binding domain
in the thyroid hormone receptor enhances transcriptional
activation. J Biol Chem. 279:33051–33056. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dominski Z, Erkmann JA, Yang X, Sanchez R
and Marzluff WF: A novel zinc finger protein is associated with U7
snRNP and interacts with the stem-loop binding protein in the
histone pre-mRNP to stimulate 3′-end processing. Genes Dev.
16:58–71. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brewer BY, Malicka J, Blackshear PJ and
Wilson GM: RNA sequence elements required for high affinity binding
by the zinc finger domain of tristetraprolin: conformational
changes coupled to the bipartite nature of AU-rich
mRNA-destabilizing motifs. J Biol Chem. 279:27870–27877. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sanduja S, Blanco FF and Dixon DA: The
roles of TTP and BRF proteins in regulated mRNA decay. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2:42–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Carballo E, Lai WS and Blackshear PJ:
Feedback inhibition of macrophage tumor necrosis factor-α
production by tristetraprolin. Science. 281:1001–1005. 1998.
|
|
46
|
Miroci H, Schob C, Kindler S,
Ölschläger-Schütt J, Fehr S, Jungenitz T, Schwarzacher SW, Bagni C
and Mohr E: Makorin ring zinc finger protein 1 (MKRN1), a novel
poly(A)-binding protein-interacting protein, stimulates translation
in nerve cells. J Biol Chem. 287:1322–1334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Grauman PL and Marahiel MA: A superfamily
of proteins that contain the cold-shock domain. Trends Biochem Sci.
23:286–290. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Matsumoto K, Meric F and Wolffe AP:
Translational repression dependent on the interaction of the
Xenopus Y-box Protein FRGY2 with mRNA. Role of the cold shock
domain, tail domain, and selective RNA sequence recognition. J Biol
Chem. 271:22706–22712. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nastasi T, Scaturro M, Bellafiore M,
Raimondi L, Beccari S, Cestelli A and Di Liegro I: PIPPin is a
brain-specific protein that contains a cold-shock domain and binds
specifically to H1 degrees and H3.3 mRNAs. J Biol Chem.
274:24087–24093. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Di Liegro CM, Schiera G, Proia P, Saladino
P and Di Liegro I: Identification in the rat brain of a set of
nuclear proteins interacting with H1° mRNA. Neuroscience.
229:71–76. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chu E and Allegra CJ: The role of
thymidylate synthase as an RNA binding protein. Bioessays.
18:191–198. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Preiss T, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM and
Lightowlers RN: Glutamate dehydrogenase: an organelle-specific
mRNA-binding protein. Trends Biochem Sci. 22:2901997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou Y, Yi X, Stoffer JB, Bonafe N,
Gilmore-Hebert M, McAlpine J and Chambers SK: The multifunctional
protein glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is both regulated
and controls colony-stimulating factor-1 messenger RNA stability in
ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1375–1384. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Saladino P, Di Liegro CM, Proia P, Sala A,
Schiera G, Lo Cicero A and Di Liegro I: RNA-binding activity of the
rat calmodulin-binding PEP-19 protein and of the long PEP-19
isoform. Int J Mol Med. 29:141–145. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bartel B: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fabian MR and Sonenberg N: The mechanics
of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: a look under the hood of miRISC.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:586–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mendell JT: MicroRNAs: critical regulators
of development, cellular physiology and malignancy. Cell Cycle.
4:1179–1184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ciafrè S and Galardi S: MicroRNAs and
RNA-binding proteins: a complex network of interactions and
reciprocal regulations in cancer. RNA Biol. 10:935–942.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kosik KS and Krichevsky AM: The elegance
of the microRNAs: a neuronal perspective. Neuron. 47:779–782. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG,
Sabatini ME, Kiebler M and Greenberg ME: A brain-specific microRNA
regulates dendritic spine development. Nature. 439:283–289. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Im HI and Kenny PJ: MicroRNAs in neuronal
function and disfunction. Trends Neurosci. 35:325–334. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lee SR and Lykke-Andersen J: Emerging
roles for ribonucleoprotein modification and remodelling in
controlling RNA fate. Trends Cell Biol. 23:504–510. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Paquin N and Chartrand P: Local regulation
of mRNA translation: new insights from the bud. Trends Cell Biol.
18:105–111. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Struhl K and Segal E: Determinants of
nucleosome positioning. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:267–273. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Paul S and Knott JG: Epigenetic control of
cell fate in mouse blastocysts: the role of covalent histone
modifications and chromatin remodeling. Mol Reprod Dev. Jul
24–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
71
|
Szenker E, Ray-Gallet D and Almouzni G:
The double face of the histone variant H3.3. Cell Res. 21:421–434.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Castiglia D, Cestelli A, Scaturro M,
Nastasi T and Di Liegro I: H1(0) and H3.3B mRNA levels in
developing rat brain. Neurochem Res. 19:1531–1537. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Scaturro M, Cestelli A, Castiglia D,
Nastasi T and Di Liegro I: Posttranscriptional regulation of H1
zero and H3.3B histone genes in differentiating rat cortical
neurons. Neurochem Res. 20:969–976. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Scaturro M, Nastasi T, Raimondi L,
Bellafiore M, Cestelli A and Di Liegro I: H1(0) RNA-binding
proteins specifically expressed in the rat brain. J Biol Chem.
273:22788–22791. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Castiglia D, Scaturro M, Nastasi T,
Cestelli A and Di Liegro I: PIPPin, a putative RNA-binding protein
specifically expressed in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 218:390–394. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sala A, Scaturro M, Proia P, Schiera G,
Balistreri E, Aflalo-Rattenbach R, Créau N and Di Liegro I: Cloning
of a rat-specific long PCP4/PEP19 isoform. Int J Mol Med.
19:501–509. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ziai R, Pan YC, Hulmes JD, Sangameswaran L
and Morgan JI: Isolation, sequence, and developmental profile of a
brain-specific polypeptide, PEP-19. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
83:8420–8423. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Slemmon JR, Morgan JI, Fullerton SM, Danho
W, Hilbush BS and Wengenack TM: Camstatins are peptide antagonists
of calmodulin based upon a conserved structural motif in PEP-19,
neurogranin, and neuromodulin. J Biol Chem. 271:15911–15917. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Auld GC, Campbell DG, Morrice N and Cohen
P: Identification of calcium-regulated heat-stable protein of 24
kDa (CRHSP24) as a physiological substrate for PKB and RSK using
KESTREL. Biochem J. 389:775–783. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
St Johnston D: Moving messages: the
intracellular localization of mRNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
6:363–375. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Palacios IM: How does an mRNA find its
way? Intracellular localisation of transcripts. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 18:163–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gonsalvez GB and Long RM: Spatial
regulation of translation through RNA localization. F1000 Biol Rep.
4:162012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
St Johnston D: The intracellular
localization of messenger RNAs. Cell. 81:161–170. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Doyle M and Kiebler MA: Mechanisms of
dendritic mRNA transport and its role in synaptic tagging. EMBO J.
30:3540–3552. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Andreassi C and Riccio A: To localize or
not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3′UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol.
19:465–474. 2009.
|
|
86
|
Jung H, Yoon BC and Holt CE: Axonal mRNA
localization and local protein synthesis in nervous system
assembly, maintenance and repair. Nat Rev Neurosci. 13:308–324.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Holt CE and Bullock SL: Subcellular mRNA
localization in animal cells and why it matters. Science.
326:1212–1216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Donnelly CJ, Fainzilber M and Twiss JL:
Subcellular communication through RNA transport and localized
protein synthesis. Traffic. 11:1498–1505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Eberwine J, Miyashiro K, Kacharmina JE and
Job C: Local translation of classes of mRNAs that are targeted to
neuronal dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:7080–7085. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Grooms SY, Noh KM, Regis R, Bassell GJ,
Bryan MK, Carroll RC and Zukin RS: Activity bidirectionally
regulates AMPA receptor mRNA abundance in dendrites of hippocampal
neurons. J Neurosci. 26:8339–8351. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Rook MS, Lu M and Kosik KS: CaMKIIalpha 3′
untranslated region-directed mRNA translocation in living neurons:
visualization by GFP linkage. J Neurosci. 20:6385–6393. 2000.
|
|
92
|
Tiruchinapalli DM, Oleynikov Y, Kelic S,
Shenoy SM, Hartley A, Stanton PK, Singer RH and Bassell GJ:
Activity-dependent trafficking and dynamic localization of zipcode
binding protein 1 and beta-actin mRNA in dendrites and spines of
hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 23:3251–3261. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Muslimov IA, Santi E, Homel P, Perini S,
Higgins D and Tiedge H: RNA transport in dendrites: a cis-acting
targeting element is contained within neuronal BC1 RNA. J Neurosci.
17:4722–4733. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Rozhdestvensky TS, Kopylov AM, Brosius J
and Hüttenhofer A: Neuronal BC1 RNA structure: evolutionary
conversion of a tRNA(Ala) domain into an extended stem-loop
structure. RNA. 7:722–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Cristofanilli M, Iacoangeli A, Muslimov IA
and Tiedge H: Neuronal BC1 RNA: microtubule-dependent dendritic
delivery. J Mol Biol. 356:1118–1123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Blichenberg A, Schwanke B, Rehbein M,
Garner CC, Richter D and Kindler S: Identification of a cis-acting
dendritic targeting element in MAP2 mRNAs. J Neurosci.
19:8818–8829. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ainger K, Avossa D, Diana AS, Barry C,
Barbarese E and Carson JH: Transport and localization elements in
myelin basic protein mRNA. J Cell Biol. 138:1077–1087. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hoek KS, Kidd GJ, Carson JH and Smith R:
hnRNP A2 selectively binds the cytoplasmic transport sequence of
myelin basic protein mRNA. Biochemistry. 37:7021–7029. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Munro TP, Magee RJ, Kidd GJ, Carson JH,
Barbarese E, Smith LM and Smith R: Mutational analysis of a
heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2 response element for RNA
trafficking. J Biol Chem. 274:34389–34395. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Gao Y, Tatavarty V, Korza G, Levin MK and
Carson JH: Multiplexed dendritic targeting of alpha calcium
calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, neurogranin, and
activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein RNAs by the A2
pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 19:2311–2327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Mikl M, Vendra G and Kiebler MA:
Independent localization of MAP2, CaMKIIα and β-actin RNAs in low
copy numbers. EMBO Rep. 12:1077–1084. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Tübing F, Vendra G, Mikl M, Macchi P,
Thomas S and Kiebler MA: Dendritically localized transcripts are
sorted into distinct ribonucleoprotein particles that display fast
directional motility along dendrites of hippocampal neurons. J
Neurosci. 30:4160–4170. 2010.
|
|
103
|
Mayford M, Baranes D, Podsypanina K and
Kandel ER: The 3′-untranslated region of CaMKII alpha is a
cis-acting signal for the localization and translation of mRNA in
dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:13250–13255. 1996.
|
|
104
|
Blichenberg A, Rehbein M, Muller R, Garner
CC, Richter D and Kindler S: Identification of a cis-acting
dendritic targeting element in the mRNA encoding the alpha subunit
of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Eur J
Neurosci. 13:1881–1888. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Huang YS, Carson JH, Barbarese E and
Richter JD: Facilitation of dendritic mRNA transport by CPEB. Genes
Dev. 17:638–653. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Mori Y, Imaizumi K, Katayama T, Yoneda T
and Tohyama M: Two cis-acting elements in the 3′ untranslated
region of alpha-CaMKII regulate its dendritic targeting. Nat
Neurosci. 3:1079–1084. 2000.
|
|
107
|
Zeitelhofer M, Macchi P and Dahm R:
Perplexing bodies: the putative roles of P-bodies in neurons. RNA
Biol. 5:244–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Miller LC, Blandford V, McAdam R,
Sanchez-Carbente MR, Badeaux F, DesGroseillers L and Sossin WS:
Combinations of DEAD box proteins distinguish distinct types of
RNA: protein complexes in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 40:485–495.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ma B, Savas JN, Yu MS, Culver BP, Chao MV
and Tanese N: Huntingtin mediates dendritic transport of β-actin
mRNA in rat neurons. Sci Rep. 1:1402011.
|
|
110
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Cytotopic
localization by long noncoding RNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
25:195–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Lloyd RE: Regulation of stress granules
and P-bodies during RNA virus infection. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
4:317–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Oh JY, Kwon A, Jo A, Kim H, Goo YS, Lee JA
and Kim HK: Activity-dependent synaptic localization of processing
bodies and their role in dendritic structural plasticity. J Cell
Sci. 126:2114–2123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Keene JD and Tenenbaum SA: Eukaryotic
mRNPs may represent posttranscriptional operons. Mol Cell.
9:1161–1167. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li C, Bassell GJ and Sasaki Y: Fragile X
mental retardation protein is involved in protein
synthesis-dependent collapse of growth cones induced by
semaphorin-3A. Front Neural Circuits. 3:112009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
An JJ, Gharami K, Liao GY, Woo NH, Lau AG,
Vanevski F, Torre ER, Jones KR, Feng Y, Lu B and Xu B: Distinct
role of long 3′ UTR BDNF mRNA in spine morphology and synaptic
plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Cell. 134:175–187. 2008.
|
|
116
|
Lau AG, Irier HA, Gu J, Tian D, Ku L, Liu
G, Xia M, Fritsch B, Zheng JQ, Dingledine R, Xu B, Lu B and Feng Y:
Distinct 3′UTRs differentially regulate activity-dependent
translation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:15945–15950. 2010.
|
|
117
|
Allen M, Bird C, Feng W, Liu G, Li W and
Perrone-Bizzozero NI: HuD promotes BDNF expression in brain neurons
via selective stabilization of the BDNF long 3′UTR mRNA. PLoS One.
8:e557182013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ratti A, Fallini C, Cova L, Fantozzi R,
Calzarossa C, Zennaro E, Pascale A, Quattrone A and Silani V: A
role for the ELAV RNA-binding proteins in neural stem cells:
stabilization of Msi1 mRNA. J Cell Sci. 119:1442–1452. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Martin KC and Ephrussi A: mRNA
localization: gene expression in the spatial dimension. Cell.
136:719–730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Eom T, Antar LN, Singer RH and Bassell GJ:
Localization of a beta-actin messenger ribonucleoprotein complex
with zipcode-binding protein modulates the density of dendritic
filopodia and filopodial synapses. J Neurosci. 23:10433–10444.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Perycz M, Urbanska AS, Krawczyk PS,
Parobczak K and Jaworski J: Zipcode binding protein 1 regulates the
development of dendritic arbors in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci.
31:5271–5285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Klein ME, Younts TJ, Castillo PE and
Jordan BA: RNA-binding protein Sam68 controls synapse number and
local β-actin mRNA metabolism in dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:3125–3130. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Cooper MW and Smith SJ: A real time
analysis of growth cone target cell interactions during the
formation of stable contacts between hippocampal neurons in
culture. J Neurobiol. 23:814–828. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Ziv NE and Smith SJ: Evidence for a role
of dendritic filopodia in synaptogenesis and spine formation.
Neuron. 17:91–102. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Fiala JC, Feinberg M, Popov V and Harris
KM: Synaptogenesis via dendritic filopodia in developing
hippocampal area CA1. J Neurosci. 18:8900–8911. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hüttelmaier S, Zenklusen D, Lederer M,
Dictenberg J, Lorenz M, Meng X, Bassell GJ, Condeelis J and Singer
RH: Spatial regulation of beta-actin translation by Src-dependent
phosphorylation of ZBP1. Nature. 438:512–515. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Giorgi C and Moore MJ: The nuclear nurture
and cytoplasmic nature of localized mRNPs. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
18:186–193. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Sasaki Y, Welshhans K, Wen Z, Yao J, Xu M,
Goshima Y, Zheng JQ and Bassell GJ: Phosphorylation of zipcode
binding protein 1 is required for brain-derived neurotrophic factor
signaling of local beta-actin synthesis and growth cone turning. J
Neurosci. 30:9349–9358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Brouwer JR, Willemsen R and Oostra BA: The
FMR1 gene and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Am J Med
Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 150B:782–798. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Sellier C, Rau F, Liu Y, Tassone F, Hukema
RK, Gattoni R, Schneider A, Richard S, Willemsen R, Elliott DJ,
Hagerman PJ and Charlet-Berguerand N: Sam68 sequestration and
partial loss of function are associated with splicing alterations
in FXTAS patients. EMBO J. 29:1248–1261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gu W, Pan F, Zhang H, Bassell GJ and
Singer RH: A predominantly nuclear protein affecting cytoplasmic
localization of beta-actin mRNA in fibroblasts and neurons. J Cell
Biol. 156:41–51. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Min H, Turck CW, Nikolic JM and Black DL:
A new regulatory protein, KSRP, mediates exon inclusion through an
intronic splicing enhancer. Genes Dev. 11:1023–1036. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Rehbein M, Kindler S, Horke S and Richter
D: Two trans-acting rat-brain proteins, MARTA1 and MARTA2, interact
specifically with the dendritic targeting element in MAP2 mRNAs.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 79:192–201. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Rehbein M, Wege K, Buck F, Schweizer M,
Richter D and Kindler S: Molecular characterization of MARTA1, a
protein interacting with the dendritic targeting element of MAP2
mRNAs. J Neurochem. 82:1039–1046. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Pan F, Huttelmaier S, Singer RH and Gu W:
ZBP2 facilitates binding of ZBP1 to beta-actin mRNA during
transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 27:8340–8351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
White R, Gonsior C, Bauer NM,
Krämer-Albers EM, Luhmann HJ and Trotter J: Heterogeneous nuclear
ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) F is a novel component of
oligodendroglial RNA transport granules contributing to regulation
of myelin basic protein (MBP) synthesis. J Biol Chem.
287:1742–1754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Kiebler MA and Bassell GJ: Neuronal RNA
granules: movers and makers. Neuron. 51:685–690. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Kelly RB and Grote E: Protein targeting in
the neuron. Annu Rev Neurosci. 16:95–127. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Alvarez J, Giuditta A and Koenig E:
Protein synthesis in axons and terminals: significance for
maintenance, plasticity and regulation of phenotype. With a
critique of slow transport theory. Prog Neurobiol. 62:1–62. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Satkauskas S and Bagnard D: Local protein
synthesis in axonal growth cones: what is next? Cell Adh Migr.
1:179–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Giuditta A, Chun JT, Eyman M, Cefaliello
C, Bruno AP and Crispino M: Local gene expression in axons and
nerve endings: the glia-neuron unit. Physiol Rev. 88:515–555. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Twiss JL and Fainzilber M: Ribosomes in
axons - scrounging from the neighbors? Trends Cell Biol.
19:236–243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Perry RB and Fainzilber M: Local
translation in neuronal processes-in vivo tests of a ‘heretical
hypothesis’. Dev Neurobiol. Aug 8–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
144
|
Gumy LF, Katrukha EA, Kapitein LC and
Hoogenraad CC: New insights into mRNA trafficking in axons. Dev
Neurobiol. Aug 19–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
145
|
Willis DE, Xu M, Donnelly CJ, Tep C,
Kendall M, Erenstheyn M, English AW, Schanen NC, Kirn-Safran CB,
Yoon SO, Bassell GJ and Twiss JL: Axonal localization of transgene
mRNA in mature PNS and CNS neurons. J Neurosci. 31:14481–14487.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Donnelly CJ, Willis DE, Xu M, Tep C, Jiang
C, Yoo S, Schanen NC, Kirn-Safran CB, van Minnen J, English A, Yoon
SO, Bassell GJ and Twiss JL: Limited availability of ZBP1 restricts
axonal mRNA localization and nerve regeneration capacity. EMBO J.
30:4665–4677. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Donnelly CJ, Park M, Spillane M, Yoo S,
Pacheco A, Gomes C, Vuppalanchi D, McDonald M, Kim HH, Merianda TT,
Gallo G and Twiss JL: Axonally synthesized beta-actin and GAP-43
proteins support distinct modes of axonal growth. J Neurosci.
33:3311–3322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Welshhans K and Bassell GJ:
Netrin-1-induced local beta-actin synthesis and growth cone
guidance requires zipcode binding protein 1. J Neurosci.
31:9800–9813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Jirikowski GF, Sanna PP and Bloom FE: mRNA
coding for oxytocin is present in axons of the
hypothalamo-neurohypophysial tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
87:7400–7404. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Trembleau A, Morales M and Bloom FE:
Differential compartmentalization of vasopressin messenger RNA and
neuropeptide within the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial axonal
tracts: light and electron microscopic evidence. Neuroscience.
70:113–125. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Eng H, Lund K and Campenot RB: Synthesis
of beta-tubulin, actin, and other proteins in axons of sympathetic
neurons in compartmented cultures. J Neurosci. 19:1–9.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lee SK and Hollenbeck PJ: Organization and
translation of mRNA in sympathetic axons. J Cell Sci.
116:4467–4478. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Antar LN, Li C, Zhang H, Carroll RC and
Bassell GJ: Local functions for FMRP in axon growth cone motility
and activity-dependent regulation of filopodia and spine synapses.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 32:37–48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Litman P, Barg J, Rindzoonski L and
Ginzburg I: Subcellular localization of tau mRNA in differentiating
neuronal cell culture: implications for neuronal polarity. Neuron.
10:627–638. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Wu KY, Hengst U, Cox LJ, Macosko EZ,
Jeromin A, Urquhart ER and Jaffrey SR: Local translation of RhoA
regulates growth cone collapse. Nature. 436:1020–1024. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Bi J, Tsai NP, Lin YP, Loh HH and Wei LN:
Axonal mRNA transport and localized translational regulation of
kappa-opioid receptor in primary neurons of dorsal root ganglia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:19919–19924. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Willis D, Li KW, Zheng JQ, Chang JH, Smit
A, Kelly T, Merianda TT, Sylvester J, van Minnen J and Twiss JL:
Differential transport and local translation of cytoskeletal,
injury-response, and neurodegeneration protein mRNAs in axons. J
Neurosci. 25:778–791. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Cox LJ, Hengst U, Gurskaya NG, Lukyanov KA
and Jaffrey SR: Intra-axonal translation and retrograde trafficking
of CREB promotes neuronal survival. Nat Cell Biol. 10:149–159.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Willis DE, van Niekerk EA, Sasaki Y,
Mesngon M, Merianda TT, Williams GG, Kendall M, Smith DS, Bassell
GJ and Twiss JL: Extracellular stimuli specifically regulate
localized levels of individual neuronal mRNAs. J Cell Biol.
178:965–980. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Yoon BC, Zivraj KH and Holt CE: Local
translation and mRNA trafficking in axon pathfinding. Results Probl
Cell Differ. 48:269–288. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Gumy LF, Yeo GS, Tung YC, Zivraj KH,
Willis D, Coppola G, Lam BY, Twiss JL, Holt CE and Fawcett JW:
Transcriptome analysis of embryonic and adult sensory axons reveals
changes in mRNA repertoire localization. RNA. 17:85–98. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Koenig E: Organized ribosome-containing
structural domains in axons. Results Probl Cell Differ. 48:173–191.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Tcherkezian J, Brittis PA, Thomas F, Roux
PP and Flanagan JG: Transmembrane receptor DCC associates with
protein synthesis machinery and regulates translation. Cell.
141:632–644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Court FA, Hendriks WT, Macgillavry HD,
Alvarez J and van Minnen J: Schwann cell to axon transfer of
ribosomes: toward a novel understanding of the role of glia in the
nervous system. J Neurosci. 28:11024–11029. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Sotelo JR, Canclini L, Kun A,
Sotelo-Silveira JR, Xu L, Wallrabe H, Calliari A, Rosso G, Cal K
and Mercer JA: Myosin-Va-dependent cell-to-cell transfer of RNA
from Schwann cells to axons. PLoS One. 8:e619052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Kapitein LC and Hoogenraad CC: Which way
to go? Cytoskeletal organization and polarized transport in
neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 46:9–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Franco SJ and Müller U: Shaping our minds:
stem and progenitor cell diversity in the mammalian neocortex.
Neuron. 77:19–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Douen AG, Dong L, Vanance S, Munger R,
Hogan MJ, Thompson CS and Hakim AM: Regulation of nestin expression
after cortical ablation in adult rat brain. Brain Res.
1008:139–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Brus M, Keller M and Lévy F: Temporal
features of adult neurogenesis: differences and similarities across
mammalian species. Front Neurosci. 7:1352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B and
Kronenberg G: Milestones of neuronal development in the adult
hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 27:447–452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Pan YW, Storm DR and Xia Z: Role of adult
neurogenesis in hippocampus-dependent memory, contextual fear
extinction and remote contextual memory: new insights from ERK5 MAP
kinase. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 105:81–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Ming GL, Wong ST, Henley J, Yuan XB, Song
HJ, Spitzer NC and Poo MM: Adaptation in the chemotactic guidance
of nerve growth cones. Nature. 417:411–418. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Piper M, Salih S, Weinl C, Holt CE and
Harris WA: Endocytosis-dependent desensitization and protein
synthesis-dependent resensitization in retinal growth cone
adaptation. Nat Neurosci. 8:179–186. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Hörnberg H and Holt C: RNA-binding
proteins and translational regulation in axons and growth cones.
Front Neurosci. 7:812013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Charlesworth A, Meijer HA and de Moor CH:
Specificity factors in cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 4:437–461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Richter JD: CPEB: a life in translation.
Trends Biochem Sci. 32:279–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Kundel M, Jones KJ, Shin CY and Wells DG:
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein regulates
neurotrophin-3-dependent beta-catenin mRNA translation in
developing hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 29:13630–13639. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Michlewski G, Guil S, Semple CA and
Cáceres JF: Posttranscriptional regulation of miRNAs harboring
conserved terminal loops. Mol Cell. 32:383–393. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Edbauer D, Neilson JR, Foster KA, Wang CF,
Seeburg DP, Batterton MN, Tada T, Dolan BM, Sharp PA and Sheng M:
Regulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated
microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132. Neuron. 65:373–384. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Xu XL, Zong R, Li Z, Biswas MH, Fang Z,
Nelson DL and Gao FB: FXR1P but not FMRP regulates the levels of
mammalian brain-specific microRNA-9 and microRNA-124. J Neurosci.
31:13705–13709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Hengst U, Cox LJ, Macosko EZ and Jaffrey
SR: Functional and selective RNA interference in developing axons
and growth cones. J Neurosci. 26:5727–5732. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Aschrafi A, Schwechter AD, Mameza MG,
Natera-Naranjo O, Gioio AE and Kaplan BB: microRNA-338 regulates
local cytochrome c oxidase IV mRNA levels and oxidative
phosphorylation in the axons of sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci.
28:12581–12590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
McKee AE, Minet E, Stern C, Riahi S,
Stiles CD and Silver PA: A genome-wide in situ hybridization map of
RNA-binding proteins reveals anatomically restricted expression in
the developing mouse brain. BMC Dev Biol. 5:14–22. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Gehman LT, Stoilov P, Maguire J, Damianov
A, Lin CH, Shiue L, Ares M Jr, Mody I and Black DL: The splicing
regulator Rbfox1 (A2BP1) controls neuronal excitation in the
mammalian brain. Nat Genet. 43:706–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Hamada N, Ito H, Iwamoto I, Mizuno M,
Morishita R, Inaguma Y, Kawamoto S, Tabata H and Nagata KI:
Biochemical and morphological characterization of A2BP1 in neuronal
tissue. J Neurosci Res. 91:1303–1311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Kusek G, Campbell M, Doyle F, Tenenbaum
SA, Kiebler M and Temple S: Asymmetric segregation of the
double-stranded RNA binding protein Staufen2 during mammalian
neural stem cell divisions promotes lineage progression. Cell Stem
Cell. 11:505–516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Vessey JP, Amadei G, Burns SE, Kiebler MA,
Kaplan DR and Miller FD: An asymmetrically localized
Staufen2-dependent RNA complex regulates maintenance of mammalian
neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 11:517–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Nakamura M, Okano H, Blendy JA and Montell
C: Musashi, a neural RNA-binding protein required for
Drosophila adult external sensory organ development. Neuron.
13:67–81. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Kaneko Y, Sakakibara S, Imai T, Suzuki A,
Nakamura Y, Sawamoto K, Ogawa Y, Toyama Y, Miyata T and Okano H:
Musashi1: an evolutionally conserved marker for CNS progenitor
cells including neural stem cells. Dev Neurosci. 22:139–153. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Maslov AY, Barone TA, Plunkett RJ and
Pruitt SC: Neural stem cell detection, characterization, and
age-related changes in the subventricular zone of mice. J Neurosci.
24:1726–1733. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Okano H, Kawahara H, Toriya M, Nakao K,
Shibata S and Imai T: Function of RNA-binding protein Musashi-1 in
stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 306:349–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Okamoto K, Nakatsukasa M, Alié A, Masuda
Y, Agata K and Funayama N: The active stem cell specific expression
of sponge Musashi homolog EflMsiA suggests its involvement in
maintaining the stem cell state. Mech Dev. 129:24–37. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Sutherland JM, McLaughlin EA, Hime GR and
Siddall NA: The musashi family of RNA binding proteins: master
regulators of multiple stem cell populations. Adv Exp Med Biol.
786:233–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Imai T, Tokunaga A, Yoshida T, Hashimoto
M, Mikoshiba K, Weinmaster G, Nakafuku M and Okano H: The neural
RNA-binding protein Musashi1 translationally regulates mammalian
numb gene expression by interacting with its mRNA. Mol Cell Biol.
21:3888–3900. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Perez-Asensio FJ, Perpiñá U, Planas AM and
Pozas E: Interleukin-10 regulates progenitor differentiation and
modulates neurogenesis in adult brain. J Cell Sci. 126:4208–4219.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Battelli C, Nikopoulos GN, Mitchell JG and
Verdi JM: The RNA binding protein Musashi-1 regulates neural
development through the translational repression of p21(WAF-1). Mol
Cell Neurosci. 31:85–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T,
Nakamura S, Sakakibara S, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB and Okano
H: Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC
promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral
nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:9885–9890. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Akamatsu W, Fujihara H, Mitsuhashi T, Yano
M, Shibata S, Hayakawa Y, Okano HJ, Sakakibara S, Takano H, Takano
T, Takahashi T, Noda T and Okano H: The RNA binding protein HuD
regulates neuronal cell identity and maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:4625–4630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Kasashima K, Terashima K, Yamamoto K,
Sakashita E and Sakamoto H: Cytoplasmic localization is required
for the mammalian ELAV-like protein HuD to induce neuronal
differentiation. Genes Cells. 4:667–683. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Okano HJ and Darnell RB: A hierarchy of Hu
RNA binding proteins in developing and adult neurons. J Neurosci.
17:3024–3037. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Szabo A, Dalmau J, Manley G, Rosenfeld M,
Wong E, Henson J, Posner JB and Furneaux HM: HuD, a paraneoplastic
encephalomyelitis antigen, contains RNA binding domains and is
homologous to Elav and Sex-lethal. Cell. 67:325–333. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Darnell RB: RNA protein interaction in
neurons. Annu Rev Neurosci. 36:243–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Bolognani F, Merhege MA, Twiss J and
Perrone-Bizzozero NI: Dendritic localization of the RNA-binding
protein HuD in hippocampal neurons: association with polysomes and
upregulation during contextual learning. Neurosci Lett.
371:152–157. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Pascale A, Gusev PA, Amadio M, Dottorini
T, Govoni S, Alkon DL and Quattrone A: Increase of the RNA-binding
protein HuD and post-transcriptional upregulation of the GAP-43
gene during spatial memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1217–1222.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Clayton GH, Perez GM, Smith RL and Owens
GC: Expression of mRNA for the elav-like neural-specific RNA
binding protein, HuD, during nervous system development. Brain Res
Dev Brain Res. 109:271–280. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Pascale A, Amadio M and Quattrone A:
Defining a neuron: neuronal ELAV proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:128–140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Ratti A, Fallini C, Colombrita C, Pascale
A, Laforenza U, Quattrone A and Silani V: Post-transcriptional
regulation of neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 by the neuronal
RNA-binding proteins ELAV. J Biol Chem. 283:7531–7541. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Ule J, Ule A, Spencer J, Williams A, Hu
JS, Cline M, Wang H, Clark T, Fraser C, Ruggiu M, Zeeberg BR, Kane
D, Weinstein JN, Blume J and Darnell RB: Nova regulates
brain-specific splicing to shape the synapse. Nat Genet.
37:844–852. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Ule J and Darnell RB: RNA binding proteins
and the regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin
Neurobiol. 16:102–110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Wakamatsu Y and Weston JA: Sequential
expression and role of Hu RNA-binding proteins during neurogenesis.
Development. 124:3449–3460. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Quattrone A, Pascale A, Nogues X, Zhao W,
Gusev P, Pacini A and Alkon DL: Posttranscriptional regulation of
gene expression in learning by the neuronal ELAV-like
mRNA-stabilizing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11668–11673.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Bolognani F, Qiu S, Tanner DC, Paik J,
Perrone-Bizzozero NI and Weeber EJ: Associative and spatial
learning and memory deficits in transgenic mice overexpressing the
RNA-binding protein HuD. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 87:635–643. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Smith CL, Afroz R, Bassell GJ, Furneaux
HM, Perrone-Bizzozero NI and Burry RW: GAP-43 mRNA in growth cones
is associated with HuD and ribosomes. J Neurobiol. 61:222–235.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Lim CS and Alkon DL: Protein kinase C
stimulates HuD-mediated mRNA stability and protein expression of
neurotrophic factors and enhances dendritic maturation of
hippocampal neurons in culture. Hippocampus. 22:2303–2319. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Iijima T, Imai T, Kimura Y, Bernstein A,
Okano HJ, Yuzaki M and Okano H: Hzf protein regulates dendritic
localization and BDNF-induced translation of type 1 inositol 1,4,5
trisphosphate receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:17190–17195. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Iijima T, Ogura H, Takatsuki K, Kawahara
S, Wakabayashi K, Nakayama D, Fujioka M, Kimura Y, Bernstein A,
Okano HJ, Kirino Y and Okano H: Impaired motor functions in mice
lacking the RNA-binding protein Hzf. Neurosci Res. 58:183–189.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Miller S, Yasuda M, Coats JK, Jones Y,
Martone ME and Mayford M: Disruption of dendritic translation of
CaMKIIalpha impairs stabilization of synaptic plasticity and memory
consolidation. Neuron. 36:507–519. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Bassell GJ and Warren ST: Fragile X
syndrome: loss of local mRNA regulation alters synaptic development
and function. Neuron. 60:201–214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Pfeiffer BE and Huber KM: The state of
synapses in fragile X syndrome. Neuroscientist. 15:549–567. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Sidorov MS, Auerbach BD and Bear MF:
Fragile X mental retardation protein and synaptic plasticity. Mol
Brain. 6:152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Westmark CJ and Malter JS: FMRP mediates
mGluR5-dependent translation of amyloid precursor protein. PLoS
Biol. 5:e522007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Ascano M Jr, Mukherjee N, Bandaru P,
Miller JB, Nusbaum JD, Corcoran DL, Langlois C, Munschauer M,
Dewell S, Hafner M, Williams Z, Ohler U and Tuschl T: FMRP targets
distinct mRNA sequence elements to regulate protein expression.
Nature. 492:382–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Dictenberg JB, Swanger SA, Antar LN,
Singer RH and Bassell GJ: A direct role for FMRP in
activity-dependent dendritic mRNA transport links filopodial-spine
morphogenesis to fragile X syndrome. Dev Cell. 14:926–939. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Zhao MG, Toyoda H, Ko SW, Ding HK, Wu LJ
and Zhuo M: Deficits in trace fear memory and long-term
potentiation in a mouse model for fragile X syndrome. J Neurosci.
25:7385–7392. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Dölen G, Osterweil E, Rao BS, Smith GB,
Auerbach BD, Chattarji S and Bear MF: Correction of fragile X
syndrome in mice. Neuron. 56:955–962. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Iacoangeli A and Tiedge H: Translational
control at the synapse: role of RNA regulators. Trends Biochem Sci.
38:47–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Luo Y, Shan G, Guo W, Smrt RD, Johnson EB,
Li X, Pfeiffer RL, Szulwach KE, Duan R, Barkho BZ, Li W, Liu C, Jin
P and Zhao X: Fragile x mental retardation protein regulates
proliferation and differentiation of adult neural stem/progenitor
cells. PLoS Genet. 6:e10008982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Guo W, Allan AM, Zong R, Zhang L, Johnson
EB, Schaller EG, Murthy AC, Goggin SL, Eisch AJ, Oostra BA, Nelson
DL, Jin P and Zhao X: Ablation of Fmrp in adult neural stem cells
disrupts hippocampus-dependent learning. Nat Med. 17:559–565. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Krueger DD, Osterweil EK, Chen SP, Tye LD
and Bear MF: Cognitive dysfunction and prefrontal synaptic
abnormalities in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:2587–2592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Stein JM, Bergman W, Fang Y, Davison L,
Brensinger C, Robinson MB, Hecht NB and Abel T: Behavioral and
neurochemical alterations in mice lacking the RNA-binding protein
translin. J Neurosci. 26:2184–2196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee VM and Trojanowski
JQ: TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat
Rev Neurol. 6:211–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Kwong LK, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ and Lee
VM: TDP-43 proteinopathies: neurodegenerative protein misfolding
diseases without amyloidosis. Neurosignals. 16:41–51. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Aparicio-Erriu IM and Prehn JH: Molecular
mechanisms in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the role of
angiogenin, a secreted RNase. Front Neurosci. 6:1672012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Ivanov P, Emara MM, Villen J, Gygi SP and
Anderson P: Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation
initiation. Mol Cell. 43:613–623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Tadesse H, Deschênes-Furry J, Boisvenue S
and Côté J: KH-type splicing regulatory protein interacts with
survival motor neuron protein and is misregulated in spinal
muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 17:506–524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Glinka M, Herrmann T, Funk N, Havlicek S,
Rossoll W, Winkler C and Sendtner M: The heterogeneous nuclear
ribonucleoprotein-R is necessary for axonal beta-actin mRNA
translocation in spinal motor neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 19:1951–1966.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|