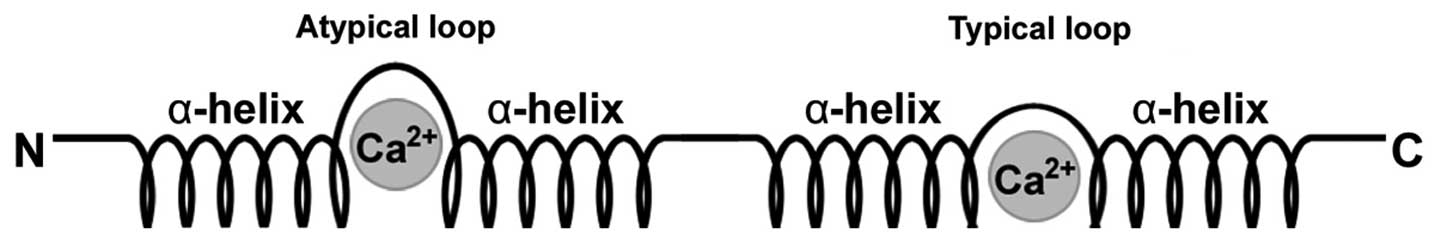
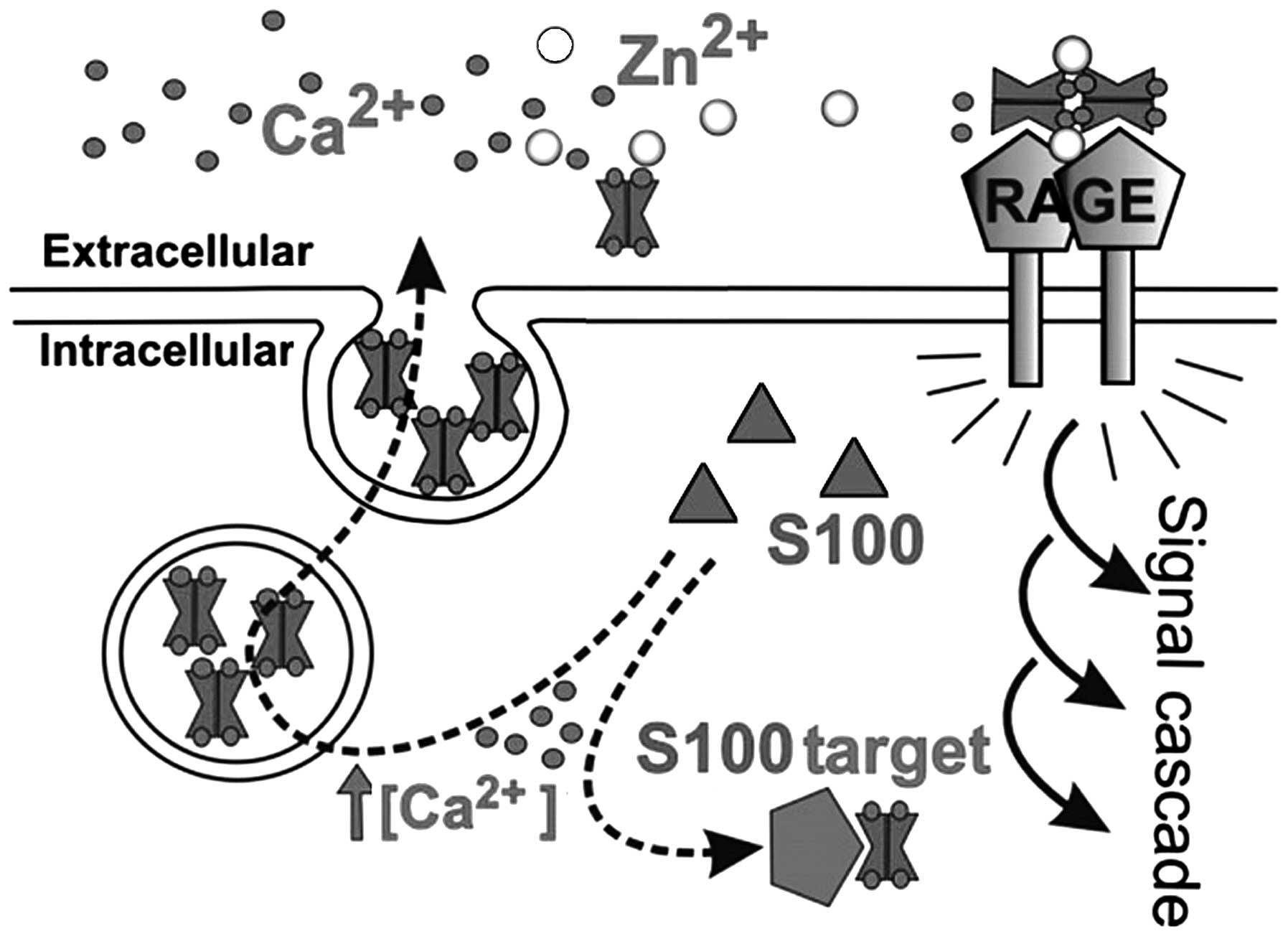
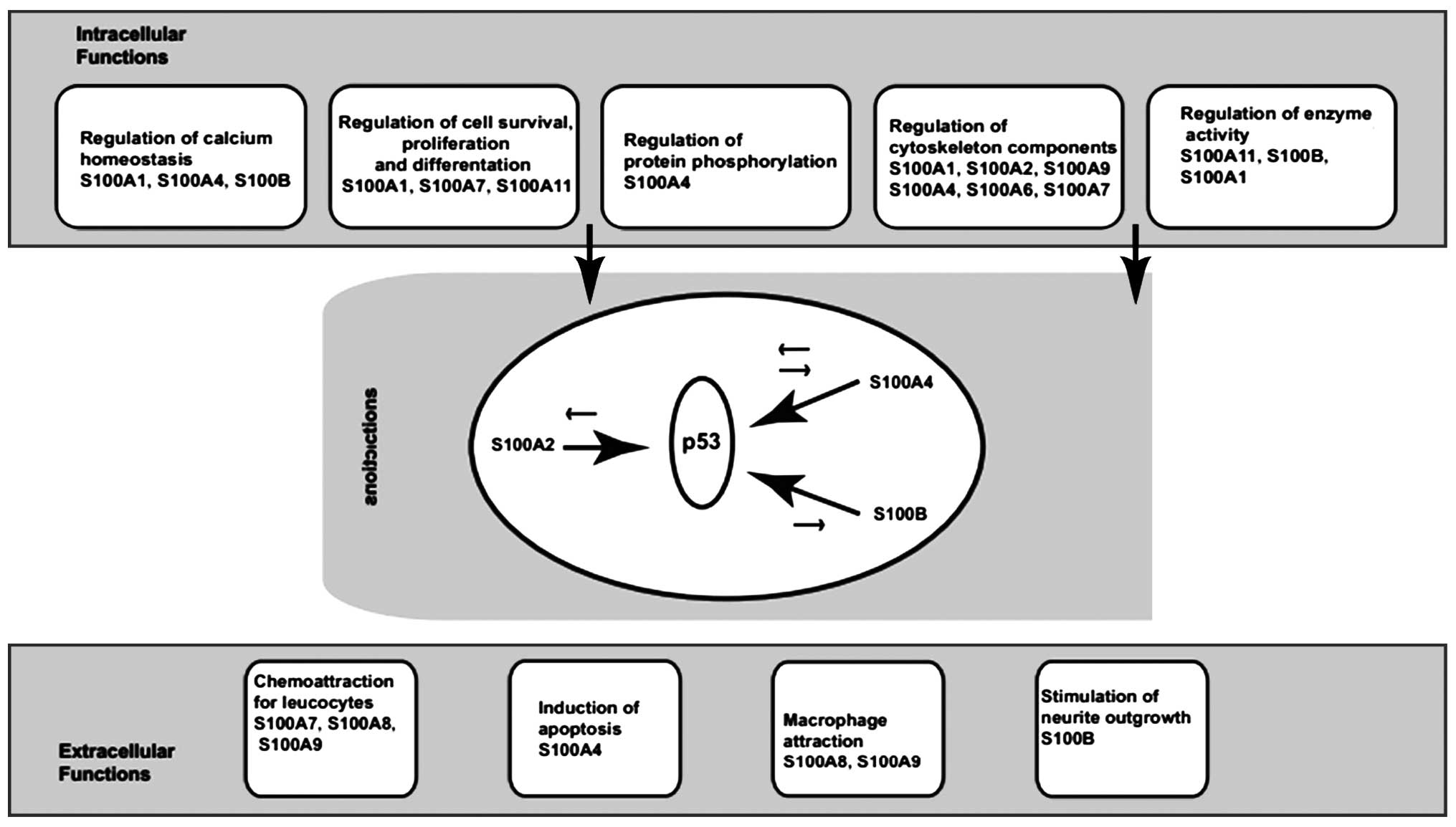
|
1
|
Li N, Song MM, Chen XH, Liu LH and Li FS:
S100A4 siRNA inhibits human pancreatic cancer cell invasion in
vitro. Biomed Environ Sci. 25:465–470. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arumugam T and Logsdon CD: S100P: a novel
therapeutic target for cancer. Amino acids. 41:893–899. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xie L, Ni WK, Chen XD, Xiao MB, Chen BY,
He S, Lu CH, Li XY, Jiang F and Ni RZ: The expressions and clinical
significances of tissue and serum galectin-3 in pancreatic
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1035–1043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Danovi SA, Wong HH and Lemoine NR:
Targeted therapies for pancreatic cancer. Br Med Bull. 87:97–130.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rezvanpour A and Shaw GS: Unique S100
target protein interactions. Gen Physiol Biophys. 28:F39–F46.
2009.
|
|
6
|
Yao R, Lopez-Beltran A, Maclennan GT,
Montironi R, Eble JN and Cheng L: Expression of S100 protein family
members in the pathogenesis of bladder tumors. Anticancer Res.
27:3051–3058. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salama I, Malone PS, Mihaimeed F and Jones
JL: A review of the S100 proteins in cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol.
34:357–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Donato R: S100: a multigenic family of
calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular
and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
33:637–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marenholz I, Heizmann CW and Fritz G: S100
proteins in mouse and man: from evolution to function and pathology
(including an update of the nomenclature). Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 322:1111–1122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moore BW: A soluble protein characteristic
of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 19:739–744.
1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A and Song
W: The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression.
Brain Res Bull. 37:417–429. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Berge G and Mælandsmo GM: Evaluation of
potential interactions between the metastasis-associated protein
S100A4 and the tumor suppressor protein p53. Amino Acids.
41:863–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Komatsu K, Kobune-Fujiwara Y, Andoh A, et
al: Increased expression of S100A6 at the invading fronts of the
primary lesion and liver metastasis in patients with colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 83:769–774. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Melle C, Ernst G, Schimmel B, Bleul A and
Eggeling FV: Colon-derived liver metastasis, colorectal carcinoma,
and hepatocellular carcinoma can be discriminated by the
Ca(2+)-binding proteins S100A6 and S100A11. PloS One.
3:e37672008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schäfer BW and Heizmann CW: The S100
family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and
pathology. Trends Biochem Sci. 21:134–140. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mishra SK, Siddique HR and Saleem M:
S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression
and metastasis: preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 31:163–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heizmann CW, Ackermann GE and Galichet A:
Pathologies involving the S100 proteins and RAGE. Subcell Biochem.
45:93–138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saleem M, Kweon MH, Johnson JJ, et al:
S100A4 accelerates tumorigenesis and invasion of human prostate
cancer through the transcriptional regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14825–14830. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gross SR, Sin CG, Barraclough R and
Rudland PS: Joining S100 proteins and migration: for better or for
worse, in sickness and in health. Cell Mol Life Sci. 30:June
30–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
20
|
Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Giambanco I and Donato
R: RAGE in tissue homeostasis, repair and regeneration. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1833:101–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xie J, Méndez JD, Méndez-Valenzuela and
Aguilar-Hernández MM: Cellular signalling of the receptor for
advanced glycation end products (RAGE). Cell Signal. 25:2185–2197.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maletzki C, Bodammer P, Breitrück A and
Kerkhoff C: S100 proteins as diagnostic and prognostic markers in
colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon.
12:e72402012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Volz HC, Laohachewin D, Seidel C, et al:
S100A8/A9 aggravates post-ischemic heart failure through activation
of RAGE-dependent NF-κB signaling. Basic Res Cardiol.
107:2502012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hung KW, Chang YM and Yu C: Resonance
assignments of Ca2+-bound human S100A11. Biomol NMR
Assign. 7:211–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Gomez SB,
Schmidt AM and Logsdon CD: S100P-derived RAGE antagonistic peptide
reduces tumor growth and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4356–4364.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Sun D, et al:
Designing and developing S100P inhibitor 5-methyl cromolyn for
pancreatic cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:654–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Miyasaka Y, et al:
Over-expression of S100A2 in pancreatic cancer correlates with
progression and poor prognosis. J Pathol. 213:275–282. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leclerc E, Fritz G, Weibel M, Heizmann CW
and Calichet A: S100B and S100A6 differentially modulate cell
survival by interacting with distinct RAGE (receptor for advanced
glycation end products) immunoglobulin domains. J Biol Chem.
282:31317–31331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leclerc E and Heizmann CW: The importance
of Ca2+/Zn2+ signaling S100 proteins and RAGE
in translational medicine. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 3:1232–1262.
2011.
|
|
30
|
Filipek A, Michowski W and Kuznicki J:
Involvement of S100A6 (calcyclin) and its binding partners in
intracellular signaling pathways. Adv Enzyme Regul. 48:225–239.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Sorci G,
Agneletti AL, Donato R and Rauuala H: Coregulation of neurite
outgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) activation. J
Biol Chem. 275:40096–40105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taguchi A, Blood DC, del Toro G, et al:
Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and
metastases. Nature. 405:354–360. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lukanidin E and Sleeman JP: Building the
niche: the role of the S100 proteins in metastatic growth. Semin
Cancer Biol. 22:216–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen H, Fernig DG, Rudland PS, Sparks A,
Wilkinson MC and Barraclough R: Binding to intracellular targets of
the metastasis-inducing protein, S100A4 (p9Ka). Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 286:1212–1217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kriajevska MV, Cardenas MN, Grigorian MS,
Ambartsumian NS, Georgiev GP and Lukanidin EM: Non-muscle myosin
heavy chain as a possible target for protein encoded by
metastasis-related mts-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 269:19679–19682.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zimmer DB and Van Eldik LJ: Analysis of
the calcium-modulated proteins, S100 and calmodulin, and their
target proteins during C6 glioma cell differentiation. J Cell Biol.
108:141–151. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao XQ, Naka M, Muneyuki M and Tanaka T:
Ca(2+)-dependent inhibition of actin-activated myosin ATPase
activity by S100C (S100A11), a novel member of the S100 protein
family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 267:77–79. 2000.
|
|
38
|
Broome AM and Eckert RL:
Microtubule-dependent redistribution of a cytoplasmic cornified
envelope precursor. J Invest Dermatol. 122:29–38. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hayes MJ, Shao D, Bailly M and Moss SE:
Regulation of actin dynamics by annexin 2. EMBO J. 25:1816–1826.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
de Graauw M, Tijdens I, Smeets MB, et al:
Annexin A2 phosphorylation mediates cell scattering and branching
morphogenesis via cofilin activation. Mol Cell Biol. 28:1029–1040.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rust RR, Baldisseri DM and Weber DJ:
Structure of the negative regulatory domain of p53 bound to S100B
(betabeta). Nat Struct Biol. 7:570–574. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kato K, Kamada H, Fujimori T, Aritomo Y,
Ono M and Masaki T: Molecular biologic approach to the diagnosis of
pancreatic carcinoma using specimens obtained by EUS-guided fine
needle aspiration. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012:2435242012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sablina AA, Budanov AV, Ilyinskaya GV,
Agapova LS, Kravchenko JE and Chumakov PM: The antioxidant function
of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nat Med. 11:1306–1313. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Green ML, Pisano MM, Prough RA and Knudsen
TB: Release of targeted p53 from the mitochondrion as an early
signal during mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Signal. 25:2383–2390.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Leśniak W, Słomnicki LP and Filipek A:
S100A6-new facts and features. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
390:1087–1092. 2009.
|
|
46
|
Van Dieck J, Lum JK and Fersht AR: S100
proteins interact with the N-terminal domain of MDM2. FEBS Letts.
584:3269–3274. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wolf S, Haase-Kohn C and Pietzsch J:
S100A2 in cancerogenesis: a friend or a foe? Amino Acids.
41:849–861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nishioku T, Furusho K, Tomita A, et al:
Potential role for S100A4 in the disruption of the blood-brain
barrier in collagen-induced arthritic mice, an animal model of
rheumatoid arthritis. Neuroscience. 189:286–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sapkota D, Costea DE, Blø M, Bruland O,
Lorens JB, Vasstrand EN and Ibrahim SO: S100A14 inhibits
proliferation of oral carcinoma derived cells through G1-arrest.
Oral Oncol. 48:219–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Grigorian M, Andresen S, Tulchinsky E, et
al: Tumor suppressor p53 protein is a new target for the
metastasis-associated Mts1/S100A4 protein: functional consequences
of their interaction. J Biol Chem. 276:22699–22708. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shimamoto S, Kubota Y, Yamaguchi F,
Tokumitsu H and Kobayashi R: Ca2+/S100 proteins act as
upstream regulators of the chaperone-associated ubiquitin ligase
CHIP (C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein). J Biol Chem.
288:7158–7168. 2013.
|
|
52
|
Romanov VS, Pospelov VA and Pospelova TV:
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Waf1): contemporary view on
its role in senescence and oncogenesis. Biochemistry (Mosc).
77:575–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sakaguchi M, Miyazaki M, Takaishi M, et
al: S100C/A11 is a key mediator of Ca(2+)-induced growth
inhibition of human epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell Biol.
163:825–835. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li B, Wan X, Zhu Q, et al: Net expression
inhibits the growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell PL45
in vitro and in vivo. PloS One. 8:e578182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sakaguchi M and Huh NH: S100A11, a dual
growth regulator of epidermal keratinocytes. Amino Acids.
41:797–807. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
He H, Li J, Weng S, LI M and Yu Y:
S100A11: diverse function and pathology corresponding to different
target proteins. Cell Biochem Biophys. 55:117–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Ohhashi S, et al:
S100A11, a putative tumor suppressor gene, is overexpressed in
pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5417–5422. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mann K and Hainaut P: Aminothiol WR1065
induces differential gene expression in the presence of wild-type
p53. Oncogene. 24:3964–3975. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Brain JG, Robertson H, Thompson E, et al:
Biliary epithelial senescence and plasticity in acute cellular
rejection. Am J Transplant. 13:1688–1702. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang SY, Miah A, Pabari A and Winslet M:
Growth Factors and their receptors in cancer metastases. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:531–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jia W, Gao XJ, Yang ZX and Zhang ZD:
S100A4 silencing suppresses proliferation, angiogenesis and
invasion of thyroid cancer cells through downregulation of MMP-9
and VEGF. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:1495–1508. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen H, Yuan Y, Zhang C, et al:
Involvement of S100A14 protein in cell invasion by affecting
expression and function of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 via
p53-dependent transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem.
287:17109–17119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gebhardt C, Németh J, Angel P and Hess J:
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1622–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hsu TC, Young MR, Cmarik J and Colburn NH:
Activator 1 (AP-1)- and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent
transcriptional events in carcinogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med.
28:1338–48. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bachet JB, Maréchal R, Demetter P, et al:
S100A2 is a predictive biomarker of adjuvant therapy benefit in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 49:2643–53. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jamieson NB, Carter CR, McKay CJ and Oien
KA: Tissue biomarkers for prognosis in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:3316–3331. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Biankin AV, Kench JG, Colvin EK, et al:
Expression of S100A2 calcium-binding protein predicts response to
pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology.
137:558–568. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Russo SM, Ove R and Saif MW:
Identification of prognostic and predictive markers in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. In: Highlights from the ‘2011 ASCO Gastrointestinal
Cancers Sympsoium’; San Francisco, CA, USA. January 20–22, 2011;
JOP. 12. pp. 92–95. 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sekine H, Chen N, Sato K, et al: S100A4,
frequently overexpressed in various human cancers, accelerates cell
motility in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
429:214–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ilg EC, Schäfer BW and Heizmann CW:
Expression pattern of S100 calcium-binding proteins in human
tumors. Int J Cancer. 68:325–332. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tsukamoto N, Egawa S, Akada M, et al: The
expression of S100A4 in human pancreatic cancer is associated with
invasion. Pancreas. 42:1027–1033. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chang D, Colvin E, Scarlett C, et al: A
molecular prognostic nomogram for resectable pancreatic cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 29(Suppl 4): abs. 154. 2011.
|
|
73
|
Ikenaga N, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, et al:
S100A4 mRNA is a diagnostic and prognostic marker in pancreatic
carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 13:1852–1858. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Schneider G and Filipek A: S100A6 binding
protein and Siah-1 interacting protein (CacyBP/SIP): spotlight on
properties and cellular function. Amino Acids. 41:773–780. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Ishikawa N, et al:
The role of S100A6 in pancreatic cancer development and its
clinical implication as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:7785–7793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J, et al:
S100A6 is increased in a stepwise manner during pancreatic
carcinogenesis: clinical value of expression analysis in 98
pancreatic juice samples. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:649–654. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Vimalachandran D, Greenhalf W, Thompson C,
et al: High nuclear S100A6 (Calcyclin) is significantly associated
with poor survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Cancer Res.
65:3218–3225. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Dowen SE, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T,
Gangeswaran R, et al: Expression of S100P and its novel binding
partner S100PBPR in early pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol.
166:81–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Han H, Bearss DJ, Browne LW, Calaluce R,
Nagle RB and Von Hoff DD: Identification of differentially
expressed genes in pancreatic cancer cells using cDNA microarray.
Cancer Res. 62:2890–2896. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Egami T, et al:
S100P is an early developmental marker of pancreatic
carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5411–5416. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Nakata K, Nagai E, Ohuchida K, et al:
S100P is a novel marker to identify intraductal papillary mucinous
neoplasms. Hum Pathol. 41:824–831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Missiaglia E,
Blaveri E, et al: Molecular alterations in pancreatic carcinoma:
expression profiling shows that dysregulated expression of S100
genes is highly prevalent. J Pathol. 201:63–74. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Barry S, Chelala C, Lines K, et al: S100P
is a metastasis-associated gene that facilitates transendothelial
migration of pancreatic cancer cell. Clin Exp Metastasis.
30:251–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Inada H, Naka M, Tanaka T, Davey GE and
Heizmann CW: Human S100A11 exhibits differential steady-state RNA
levels in various tissues and a distinct subcellular localization.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 263:135–138. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen JH, Ni RZ, Xiao MB, Guo JG and Zhou
JW: Comparative proteomic analysis of differentially expressed
proteins in human pancreatic cancer tissue. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 8:193–200. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Memon AA, Sorensen BS, Meldgaard P, Fokdal
L, Thykjaer T and Nexo E: Down-regulation of S100C is associated
with bladder cancer progression and poor survival. Clin Cancer Res.
11:606–611. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nakashima T, Wang XF, Masuda M, Inokuchi A
and Komiyama S: Overexpression of p53 nuclear protein in
premalignant and malignant laryngeal lesions. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 256:S56–S59. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shin DM, Kim J, Ro JY, Hittelman J, Roth
JA, Hong WK and Hittelman WN: Activation of p53 gene expression in
premalignant lesions during head and neck tumorigenesis. Cancer
Res. 54:321–326. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xiao MB, Jiang F, Ni WK, Chen BY, Lu CH,
Li XY and Ni RZ: High expression of S100A11 in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma is an unfavorable prognostic marker. Med Oncol.
29:1886–1891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Arumugam T, Simeone DM, Van Golen K and
Logsdon CD: S100P promotes pancreatic cancer growth, survival, and
invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5356–5364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|