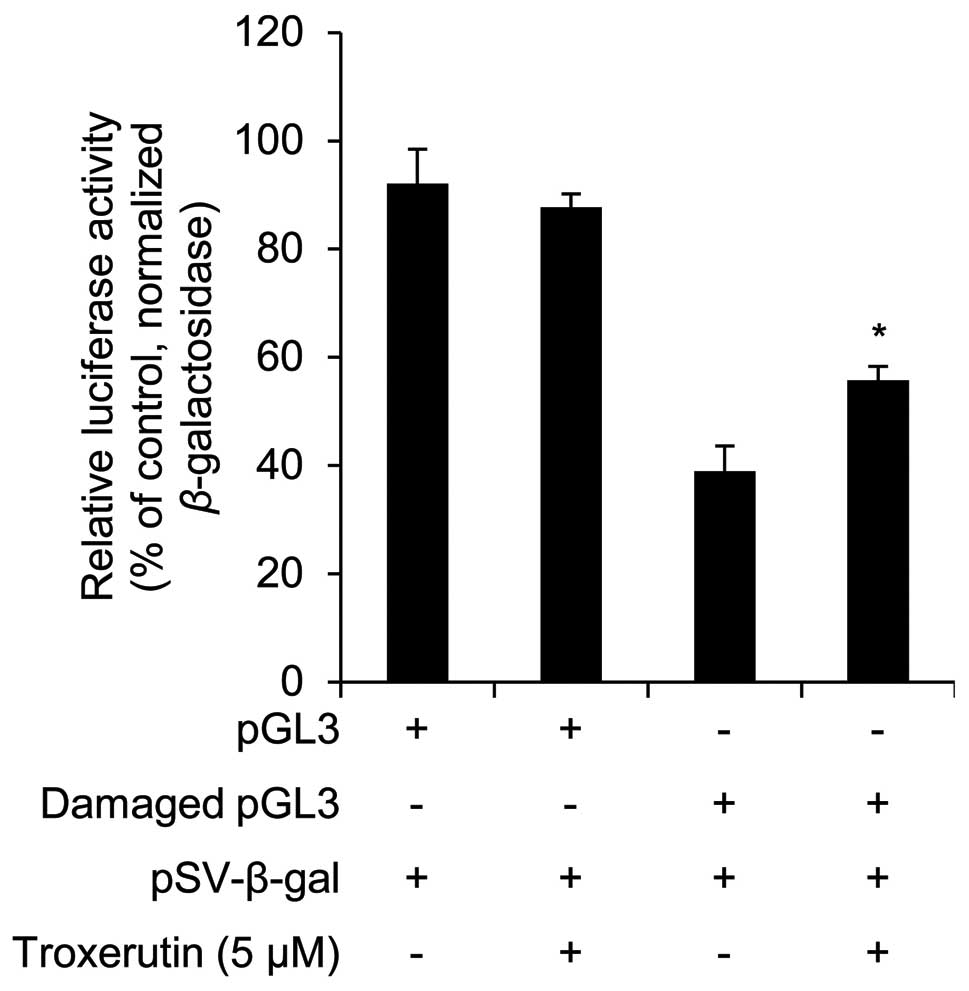
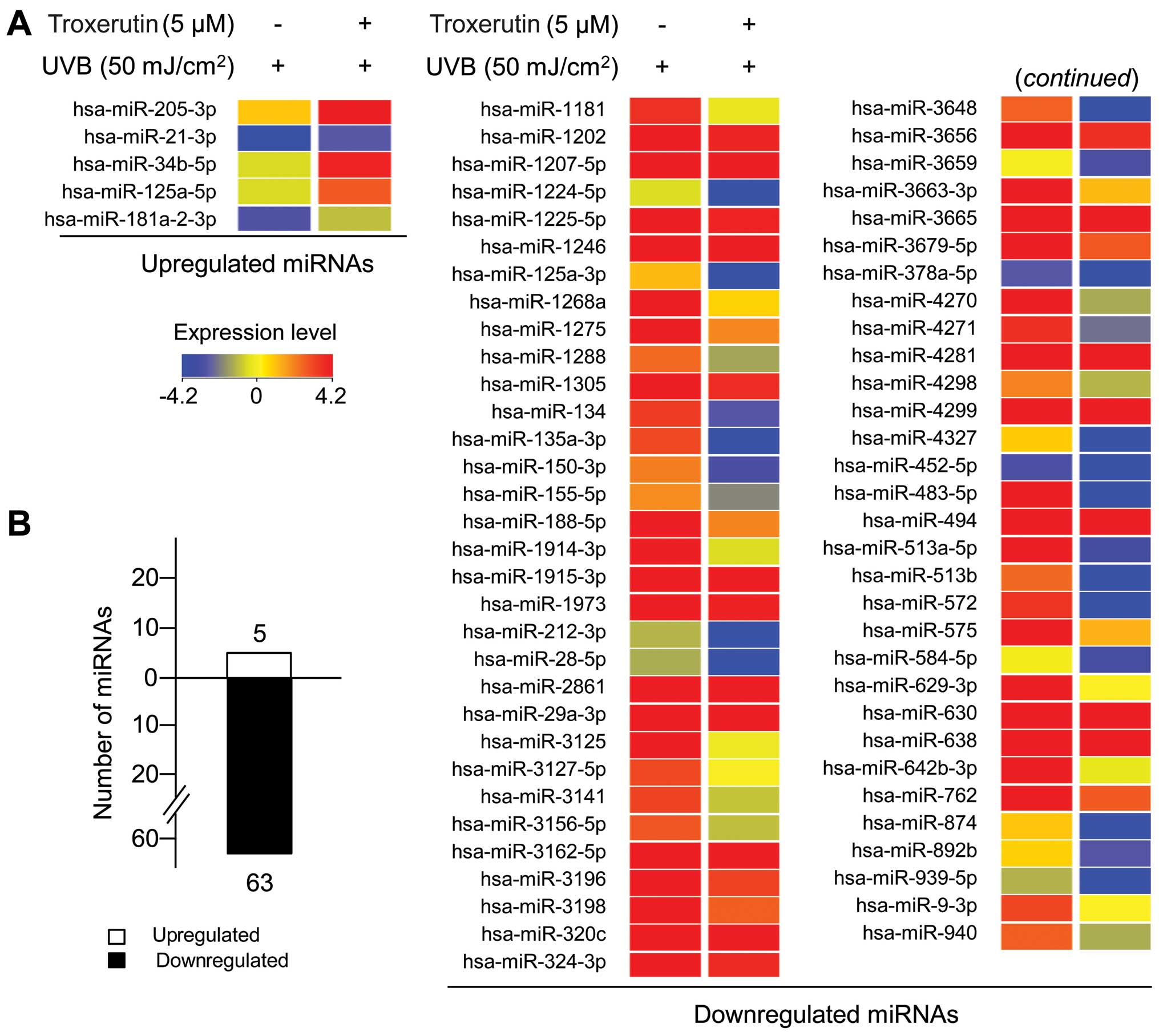
|
1
|
Oresajo C, Pillai S, Manco M, Yatskayer M
and McDaniel D: Antioxidants and the skin: understanding
formulation and efficacy. Dermatol Ther. 25:252–259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Campbell C, Quinn AG, Angus B, Farr PM and
Rees JL: Wavelength specific patterns of p53 induction in human
skin following exposure to UV radiation. Cancer Res. 53:2697–2699.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Gruijl FR and Van der Leun JC: Estimate
of the wavelength dependency of ultraviolet carcinogenesis in
humans and its relevance to the risk assessment of a stratospheric
ozone depletion. Health Phys. 67:319–325. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chainiaux F, Magalhaes JP, Eliaers F,
Remacle J and Toussaint O: UVB-induced premature senescence of
human diploid skin fibroblasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
34:1331–1339. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsumura Y and Ananthaswamy HN: Toxic
effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 195:298–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka M, Koyama Y and Nomura Y: Effects
of collagen peptide ingestion on UV-B-induced skin damage. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 73:930–932. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Everett MA, Yeargers E, Sayre RM and Olson
RL: Penetration of epidermis by ultraviolet rays. Photochem
Photobiol. 5:533–542. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suter MM, Schulze K, Bergman W, Welle M,
Roosje P and Müller EJ: The keratinocyte in epidermal renewal and
defense. Vet Dermatol. 20:515–532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kulms D, Zeise E, Pöppelmann B and Schwarz
T: DNA damage, death receptor activation and reactive oxygen
species contribute to ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis in an
essential and independent way. Oncogene. 21:5844–5851. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bode AM and Dong Z: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase activation in UV-induced signal transduction. Sci
STKE. 2003.RE22003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Assefa Z, Van Laethem A, Garmyn M and
Agostinis P: Ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis in
keratinocytes: on the role of cytosolic factors. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1755:90–106. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rezvani HR, Mazurier F, Cario-André M, et
al: Protective effects of catalase overexpression on UVB-induced
apoptosis in normal human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem.
281:17999–18007. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Henseleit U, Zhang J, Wanner R, Haase I,
Kolde G and Rosenbach T: Role of p53 in UVB-induced apoptosis in
human HaCaT keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 109:722–727. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Enk CD, Jacob-Hirsch J, Gal H, et al: The
UVB-induced gene expression profile of human epidermis in vivo is
different from that of cultured keratinocytes. Oncogene.
25:2601–2614. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y, Permatasari F, et al:
Characterization of the miRNA profile in UVB-irradiated normal
human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 21:317–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou BR, Xu Y and Luo D: Effect of UVB
irradiation on microRNA expression in mouse epidermis. Oncol Lett.
3:560–564. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Z, Zhou B, Liu W, et al: MiR-23a
regulates DNA damage repair and apoptosis in UVB-irradiated HaCaT
cells. J Dermatol Sci. 69:68–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li W, Di W, Hua L, Zhou B, Guo Z and Luo
D: UVB suppresses PTEN expression by upregulating miR-141 in HaCaT
cells. J Biomed Res. 25:135–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pothof J, Verkaik NS, van IJcken W, et al:
MicroRNA-mediated gene silencing modulates the UV-induced
DNA-damage response. EMBO J. 28:2090–2099. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan SH, Zhang ZF, Zheng YL, et al:
Troxerutin protects the mouse kidney from D-galactose-caused injury
through anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:91–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang ZF, Fan SH, Zheng YL, et al:
Troxerutin protects the mouse liver against oxidative
stress-mediated injury induced by D-galactose. J Agric Food Chem.
57:7731–7736. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, et al: Chronic
administration of troxerutin protects mouse brain against
D-galactose-induced impairment of cholinergic system. Neurobiol
Learn Mem. 93:157–164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF and
Wang YJ: NGF-dependent activation of TrkA pathway: a mechanism for
the neuroprotective effect of troxerutin in D-galactose-treated
mice. Brain Pathol. 20:952–965. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu J, Wu DM and Zhang ZF, Zheng YL, Hu B
and Zhang ZF: troxerutin protects against high cholesterol-induced
cognitive deficits in mice. Brain. 134:783–797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Budzianowski J, Korzeniowska K, Chmara E
and Mrozikiewicz A: Microvascular protective activity of flavonoid
glucuronides fraction from Tulipa gesneriana. Phytother Res.
13:166–168. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boisseau MR, Taccoen A, Garreau C, Vergnes
C, Roudaut MF and Garreau-Gomez B: Fibrinolysis and hemorheology in
chronic venous insufficiency: A double blind study of troxerutin
efficiency. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 36:369–374. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ping X, Junqing J, Junfeng J and Enjin J:
Radioprotective effects of troxerutin against gamma irradiation in
V79 cells and mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2593–2596.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maurya DK, Balakrishnan S, Salvi VP and
Nair CK: Protection of cellular DNA from gamma-radiation-induced
damages and enhancement in DNA repair by troxerutin. Mol Cell
Biochem. 280:57–68. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raj D, Brash DE and Grossman D:
Keratinocyte apoptosis in epidermal development and disease. J
Invest Dermatol. 126:243–257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Maurya DK, Salvi VP and Krishnan Nair CK:
Radioprotection of normal tissues in tumor-bearing mice by
troxerutin. J Radiat Res. 45:221–228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taylor MA, Sossey-Alaoui K, Thompson CL,
Danielpour D and Schiemann WP: TGF-β upregulates miR-181a
expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest.
123:150–163. 2013.
|
|
33
|
Li S, Niu X, Cui A, He Y and Wu W: The
effects of miR-181a on proliferation, migration and invasion
abilities of esophageal carcinoma cell line TE11. Tumor.
31:613–618. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Shin S, Moon KC, Park KU and Ha E:
MicroRNA-513a-5p mediates TNF-α and LPS induced apoptosis via
downregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptotic protein in
endothelial cells. Biochimie. 94:1431–1436. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T, et al:
Tumour-suppressive microRNA-874 contributes to cell proliferation
through targeting of histone deacetylase 1 in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1648–1658. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang B, Li Z, Zhang W, et al: miR-874
Inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion through
targeting aquaporin-3 in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. June
26–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Liao JM, Zeng SX and Lu H: p53
downregulates Down syndrome-associated DYRK1A through miR-1246.
EMBO Rep. 12:811–817. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Romano G, Acunzo M, Garofalo M, et al:
MiR-494 is regulated by ERK1/2 and modulates TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer through BIM
down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:16570–16575. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Zhang X, Ren XP, et al:
MicroRNA-494 targeting both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins
protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury.
Circulation. 122:1308–1318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|