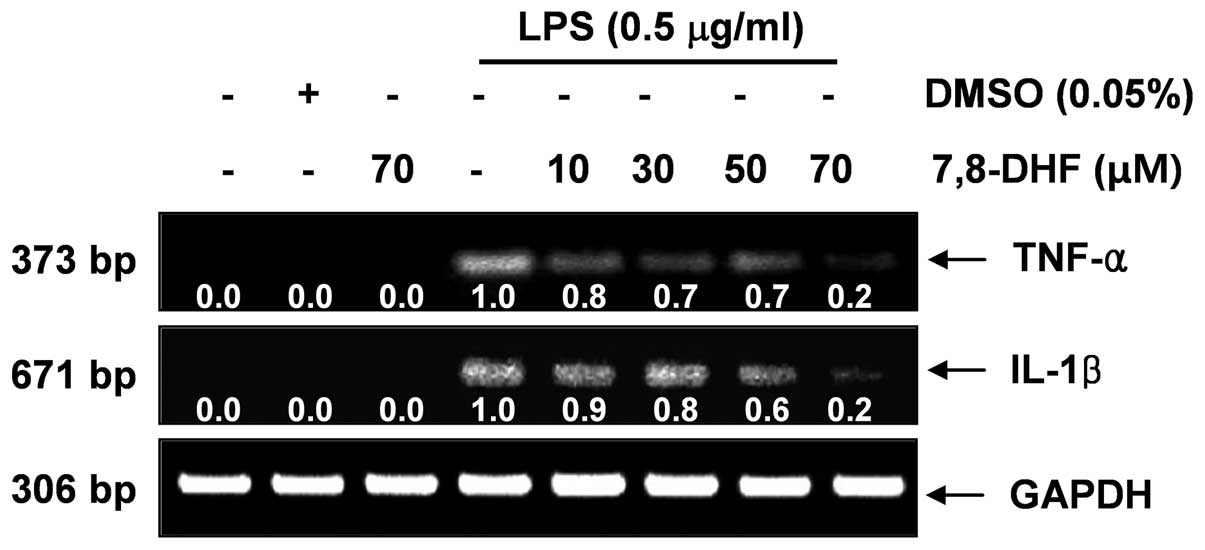
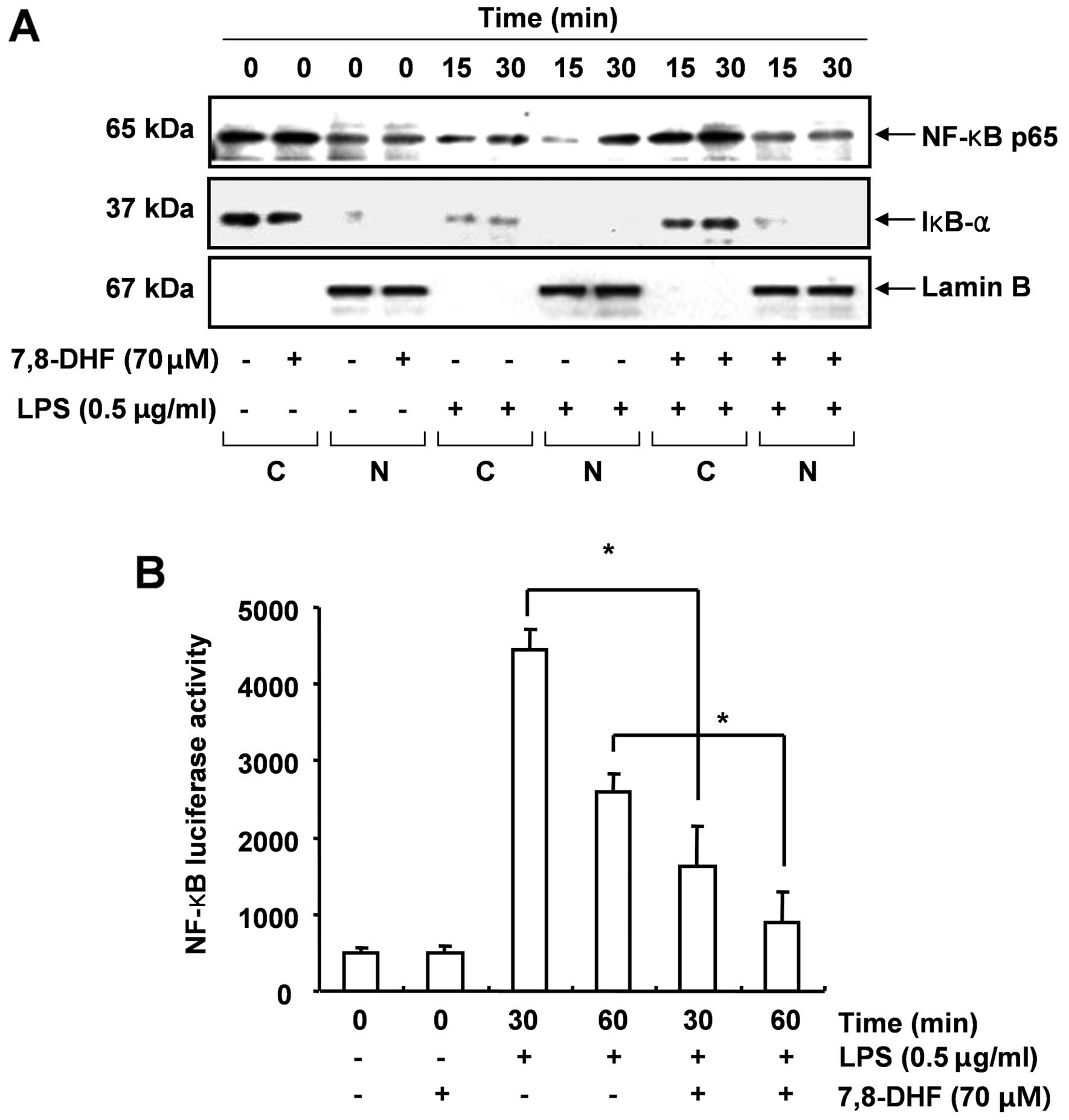
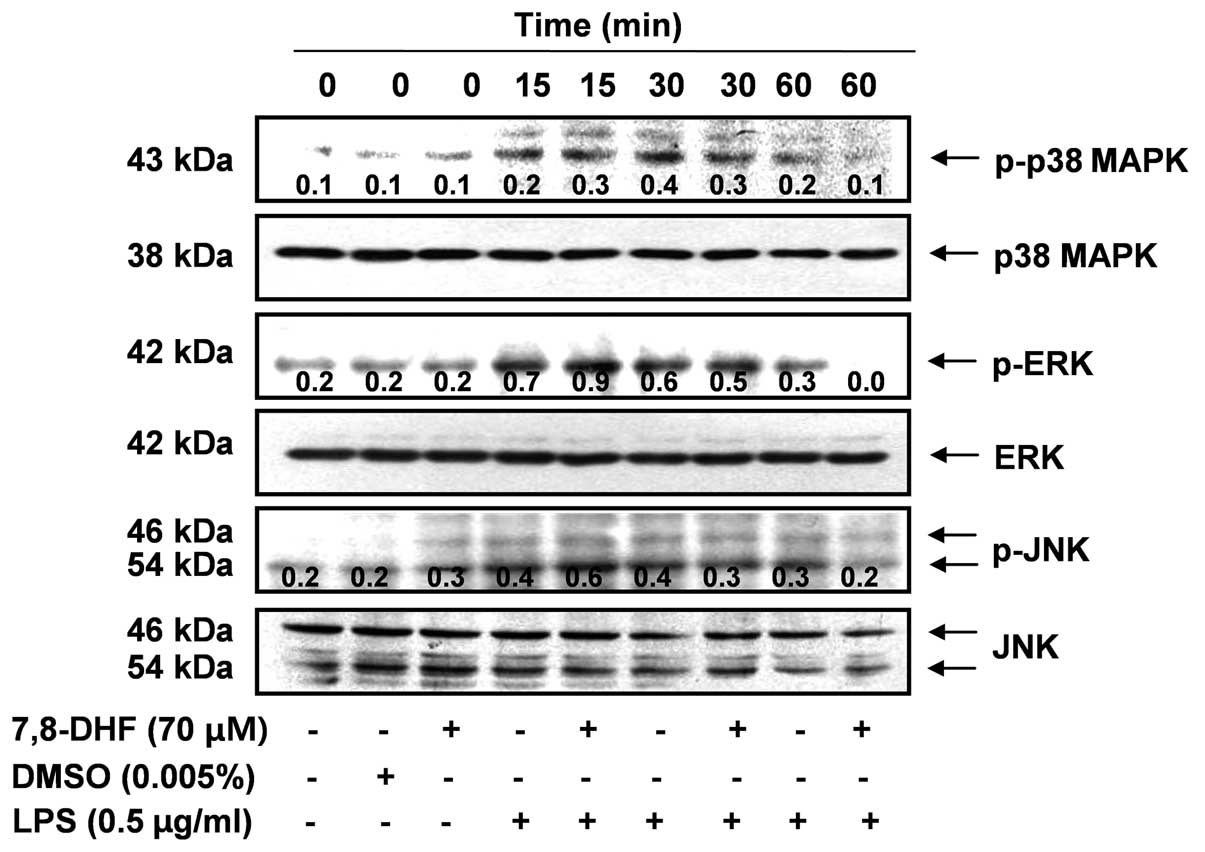
|
1
|
Napoli I and Neumann H: Microglial
clearance function in health and disease. Neuroscience.
158:1030–1038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loane DJ and Byrnes KR: Role of microglia
in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics. 7:366–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meda L, Cassatella MA, Szendrei GI, Otvos
L Jr, Baron P, Villalba M, Ferrari D and Rossi F: Activation of
microglial cells by β-amyloid protein and interferon-γ. Nature.
373:647–650. 1995.
|
|
4
|
Eikelenboom P and van Gool WA:
Neuroinflammatory perspectives on the two faces of Alzheimer’s
disease. J Neural Transm. 111:281–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W and Hong JS: Novel
anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:395–401. 2003.
|
|
6
|
Liu B and Hong JS: Role of microglia in
inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and
strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
304:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rock RB and Peterson PK: Microglia as a
pharmacological target in infectious and inflammatory diseases of
the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:117–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaur C and Ling EA: Antioxidants and
neuroprotection in the adult and developing central nervous system.
Curr Med Chem. 15:3068–3080. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng YY, Lu J, Ling EA and Kaur C: Role of
microglia in the process of inflammation in the hypoxic developing
brain. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 3:884–900. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ramos S: Cancer chemoprevention and
chemotherapy: dietary polyphenols and signalling pathways. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 52:507–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo W, Kong E and Meydani M: Dietary
polyphenols, inflammation, and cancer. Nut Cancer. 61:807–810.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen S: Natural products triggering
biological targets-a review of the anti-inflammatory phytochemicals
targeting the arachidonic acid pathway in allergy asthma and
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 12:288–301. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
García-Lafuente A, Guillamón E, Villares
A, Rostagno MA and Martínez JA: Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory
agents: implications in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Inflamm
Res. 58:537–552. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
González-Gallego J, García-Mediavilla MV,
Sánchez-Campos S and Tuñón MJ: Fruit polyphenols, immunity and
inflammation. Br J Nut. 104(Suppl 3): S15–S27. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Magrone T and Jirillo E: Potential
application of dietary polyphenols from red wine to attaining
healthy ageing. Curr Top Med Chem. 11:1780–1796. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Juurlink BH and Paterson PG: Review of
oxidative stress in brain and spinal cord injury: suggestions for
pharmacological and nutritional management strategies. J Spinal
Cord Med. 21:309–334. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramassamy C: Emerging role of polyphenolic
compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review
of their intracellular targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 545:51–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
del Campos-Esparza MR and Torres-Ramos MA:
Neuroprotection by natural polyphenols: molecular mechanisms. Cent
Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 10:269–277. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jang SW, Liu X, Yepes M, Shepherd KR,
Miller GW, Liu Y, Wilson WD, Xiao G, Blanchi B, Sun YE and Ye K: A
selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by
7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:2687–2692. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andero R, Heldt SA, Ye K, Liu X, Armario A
and Ressler KJ: Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule
TrkB agonist, on emotional learning. Am J Psychiatry. 168:163–172.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Chua KW, Chua CC, Yu H, Pei A,
Chua BH, Hamdy RC, Xu X and Liu CF: Antioxidant activity of
7,8-dihydroxyflavone provides neuroprotection against
glutamate-induced toxicity. Neurosci Lett. 499:181–185. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang R, Kang KA, Piao MJ, Ko DO, Wang ZH,
Chang WY, You HJ, Lee IK, Kim BJ, Kang SS and Hyun JW: Preventive
effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone against oxidative stress induced
genotoxicity. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:166–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kozics K, Valovicova Z and Slamenova D:
Structure of flavonoids influences the degree inhibition of
Benzo(a)pyrene-induced DNA damage and micronuclei in HepG2 cells.
Neoplasma. 58:516–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park HY, Kim GY, Hyun JW, Hwang HJ, Kim
ND, Kim BW and Choi YH: 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone exhibits
anti-inflammatory properties by downregulating the NF-κB and MAPK
signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW264.7 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 29:1146–1152. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kyung J, Kim D, Park D, Yang YH, Choi EK,
Lee SP, Kim TS, Lee YB and Kim YB: Synergistic anti-inflammatory
effects of Laminaria japonica fucoidan and Cistanche
tubulosa extract. Lab Anim Res. 28:91–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee SH, Kim DW, Eom SA, Jun SY, Park M,
Kim DS, Kwon HJ, Kwon HY, Han KH, Park J, Hwang HS, Eum WS and Choi
SY: Suppression of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
(TPA)-induced skin inflammation in mice by transduced Tat-Annexin
protein. BMB Rep. 45:354–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McGeer PL, Yasojima K and McGeer EG:
Inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol. 86:83–89.
2001.
|
|
28
|
Leone S, Ottani A and Bertolini A: Dual
acting anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr Topics Med Chem. 7:265–275.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mariani MM and Kielian T: Microglia in
infectious diseases of the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune
Pharmacol. 4:448–461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saha RN and Pahan K: Regulation of
inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in glial cells. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 8:929–947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brown GC and Neher JJ: Inflammatory
neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons.
Mol Neurobiol. 41:242–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hawkey CJ: COX-2 inhibitors. Lancet.
353:307–314. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vane JR, Mitchell JA, Appleton I,
Tomlinson A, Bishop-Bailey D, Croxtall J and Willoughby DA:
Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:2046–2050. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giovannini MG, Scali C, Prosperi C,
Bellucci A, Pepeu G and Casamenti G: Experimental brain
inflammation and neurodegeneration as model of Alzheimer’s disease:
protective effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 16(Suppl 2): S31–S40. 2003.
|
|
35
|
Minghetti L and Pocchiari M:
Cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2, and microglial
activation in prion diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol. 82:265–275. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Choi SH, Aid S and Bosetti F: The distinct
roles of cyclooxygenase-1 and −2 in neuroinflammation: implications
for translational research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:174–181.
2009.
|
|
37
|
Boka G, Anglade P, Wallach D, Javoy-Agid
F, Agid Y and Hirsch EC: Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor
necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosc
Lett. 172:151–154. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hunot S, Dugas N, Faucheux B, Hartmann A,
Tardieu M, Debre P, Agid Y, Dugas B and Hirsch EC:
FcepsilonRII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson’s disease and induces,
in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha in glial cells. J Neurosci. 19:3440–3447.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De Nardin E: The role of inflammatory and
immunological mediators in periodontitis and cardiovascular
disease. Ann Periodontol. 6:30–40. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sawada M, Kondo N, Suzumura A and
Marunouchi T: Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by
microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 491:394–397. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Botchkina GI, Meistrell ME III, Botchkina
IL and Tracey KJ: Expression of TNF and TNF receptors (p55 and p75)
in the rat brain after focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med. 3:765–781.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Akassoglou K, Bauer J, Kassiotis G,
Pasparakis M, Lassmann H, Kollias G and Probert L: Oligodendrocyte
apoptosis and primary demyelination induced by local TNF/p55TNF
receptor signaling in the central nervous system of transgenic
mice: models for multiple sclerosis with primary
oligodendrogliopathy. Am J Pathol. 153:801–813. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller
DB, Luster MI and O’Callaghan JP: Mice deficient in TNF receptors
are protected against dopaminergic neurotoxicity: implications for
Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 16:1474–1476. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gougeon PY, Lourenssen S, Han TY, Nair DG,
Ropeleski MJ and Blennerhassett MG: The pro-inflammatory cytokines
IL-1β and TNFα are neurotrophic for enteric neurons. J Neurosci.
33:3339–3351. 2013.
|
|
45
|
Rothwell N, Allan S and Toulmond S: The
role of interleukin 1 in acute neurodegeneration and stroke:
pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. J Clin Invest.
100:2648–2652. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Haddad JJ: The role of inflammatory
cytokines and NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathways in the evolution of
familial Mediterranean fever: current clinical perspectives and
potential therapeutic approaches. Cell Immunol. 260:6–13. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hamilton T, Novotny M, Pavicic PJ Jr,
Herjan T, Hartupee J, Sun D, Zhao C and Datta S: Diversity in
post-transcriptional control of neutrophil chemoattractant cytokine
gene expression. Cytokine. 52:116–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Ann Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moon DO, Choi YH, Kim ND, Park YM and Kim
GY: Anti-inflammatory effects of beta-lapachone in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:506–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sarkar FH and Li Y: NF-kappaB: a potential
target for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Front Biosci.
13:2950–2959. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wertz IE and Dixit VM: Signaling to
NF-kappaB: regulation by ubiquitination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 2:a0033502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mattson MP and Camandola S: NF-kappaB in
neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Invest.
107:247–254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nakajima K and Kohsaka S: Characterization
of brain microglia and the biological significance in the central
nervous system. Adv Neurol. 60:734–743. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim YJ, Hwang SY, Oh ES, Oh S and Han IO:
IL-1beta, an immediate early protein secreted by activated
microglia, induces iNOS/NO in C6 astrocytoma cells through p38 MAPK
and NF-kappaB pathways. J Neurosci Res. 84:1037–1046. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|