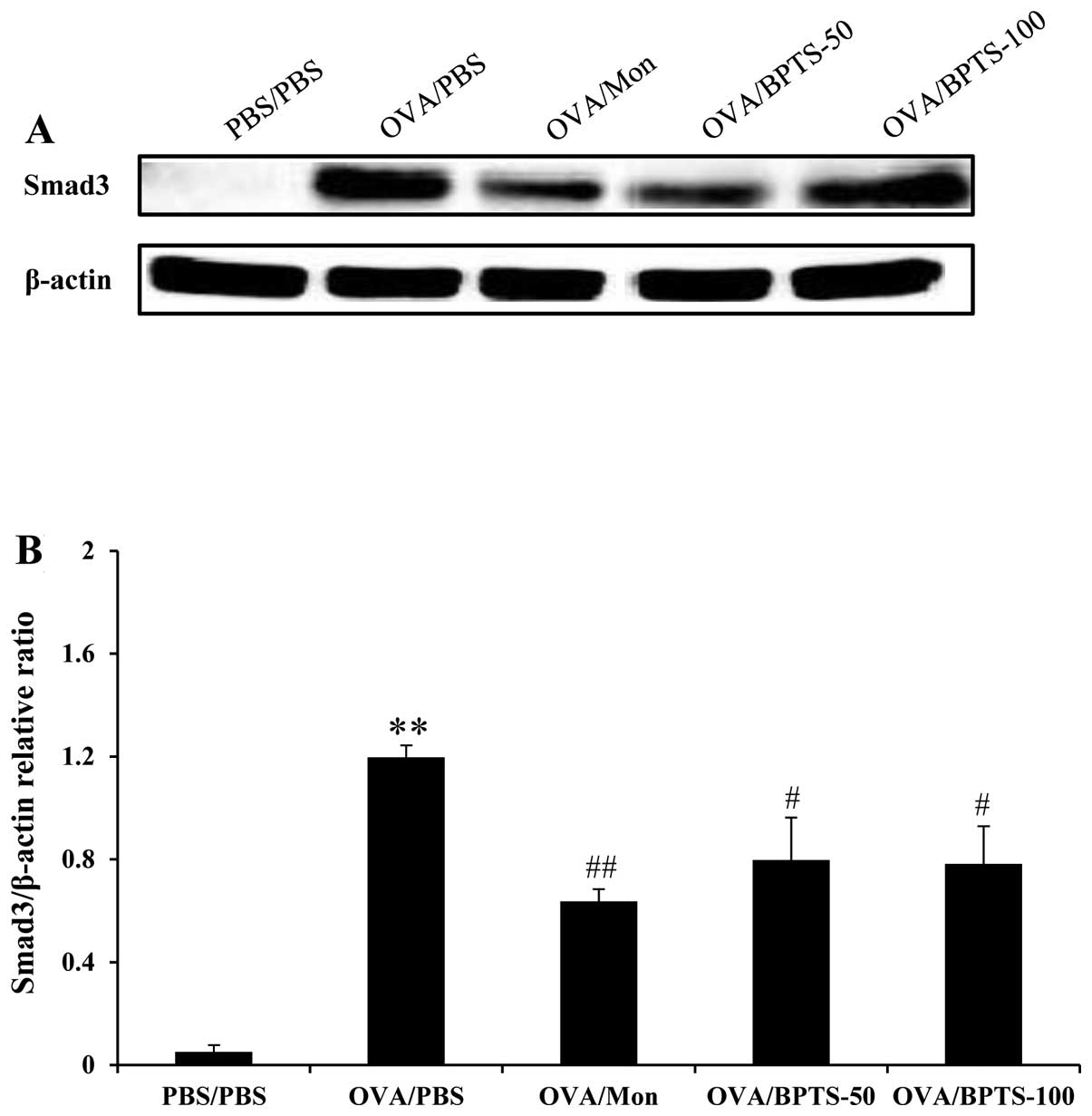
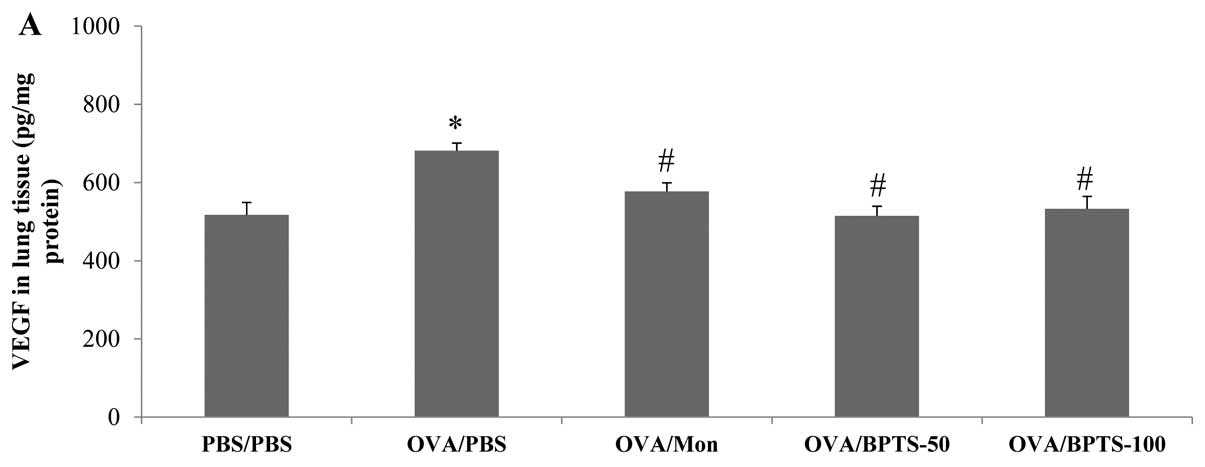
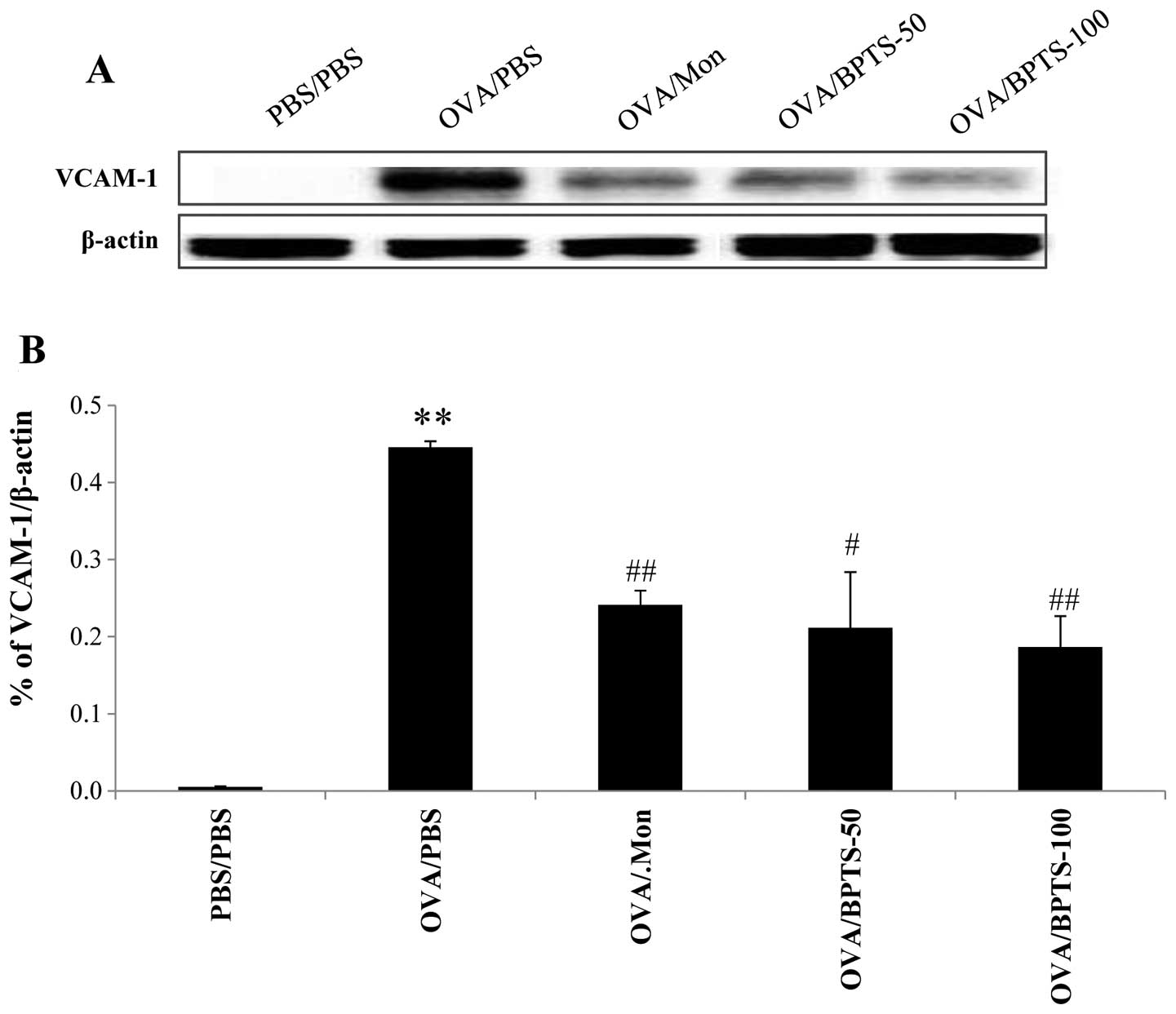
|
1
|
Busse WW and Lemanske RF Jr: Asthma. N
Engl J Med. 344:350–362. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rincon M and Irvin CG: Role of IL-6 in
asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int J Biol Sci.
8:1281–1290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Finkelman FD, Holmes J, Urban JF Jr, Paul
WE and Katona IM: T help requirements for the generation of an in
vivo IgE response: a late acting form of T cell help other than
IL-4 is required for IgE but not for IgG1 production. J Immunol.
142:403–408. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adachi T, Motojima S, Hirata A, Fukuda T
and Makino S: Eosinophil viability-enhancing activity in sputum
from patients with bronchial asthma, Contributions of interleukin-5
and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 151:618–623. 1995.
|
|
5
|
Sur S, Kita H, Gleich GJ, Chenier TC and
Hunt LW: Eosinophil recruitment is associated with IL-5, but not
with RANTES, twenty-four hours after allergen challenge. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 97:1272–1278. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oettgen HC and Geha RS: IgE in asthma and
atopy: cellular and molecular connections. J Clin Invest.
104:829–835. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ
and Paul WE: The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic
functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 17:701–738. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zurita-Salinas CS, Palacios-Boix A, Yáñez
A, González F and Alcocer-Varela J: Contamination with Mycoplasma
spp. induces interleukin-13 expression by human skin fibroblasts in
culture. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 15:123–128. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Botero JE, Contreras A and Parra B:
Profiling of inflammatory cytokines produced by gingival
fibroblasts after human cytomegalovirus infection. Oral Microbiol
Immunol. 23:291–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilson MS and Wynn TA: Pulmonary fibrosis:
pathogenesis, etiology and regulation. Mucosal Immunol. 2:103–121.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mauviel A: Transforming growth factor
beta: a key mediator of fibrosis. Meth Mol Med. 117:69–80.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Minshall EM, Leung DY, Martin RJ, Song YL,
Cameron L, Ernst P and Hamid Q: Eosinophil-associated TGF-beta1
mRNA expression and airways fibrosis in bronchial asthma. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 17:326–333. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vasquez-Pinto LM, Nantel F, Sirois P and
Jancar S: Bradykinin B(1) receptor antagonist R954 inhibits
eosinophil activation/proliferation/migration and increases
TGF-beta and VEGF in a murine model of asthma. Neuropeptides.
44:107–113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee KS, Park SJ, Kim SR, Min KH, Lee KY,
Choe YH, Hong SH, Lee YR, Kim JS, Hong SJ and Lee YC: Inhibition of
VEGF blocks TGF-β1 production through a PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Eur Respir J. 31:523–531. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Foster CA: VCAM-1/α 4-integrin adhesion
pathway: therapeutic target for allergic inflammatory disorders. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 98:S270–S277. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Zhu X, Subbaraman R, Sano H, Jacobs B,
Sano A, Boetticher E, Muñoz NM and Leff AR: A surrogate method for
assessment of β2-integrin-dependent adhesion of human eosinophils
to ICAM-1. J Immunol Methods. 240:157–164. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Shimada T, Kudo T, Akase T and Aburada M:
Preventive effects of Bofutsushosan on obesity and various
metabolic disorders. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1362–1367. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohno K, Chung HJ, Maruyama I and Tani T:
Bofutsushosan, a traditional Chinese formulation, prevents intimal
thickening and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by
balloon endothelial denudation in rats. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:2162–2165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Morimoto Y, Sakata M, Ohno A, Maegawa T
and Tajima S: Effects of Byakko-ka-ninjin-to, Bofu-tsusho-san and
Gorei-san on blood glucose level, water intake and urine volume in
KKAy mice. Yakugaku Zasshi. 122:163–168. 2002.(In Japanese).
|
|
20
|
Kim HJ, Yoon KM, Im EY, Byun JS, Kim DJ
and Kwak MA: Three case report of Bangpungtongsung-san effect on
improvement of hypertension patients. KJOPP. 23:740–743. 2009.
|
|
21
|
Kim HJ, Park OS, Kim KS, Cha JH and Kim
YB: The effect of Bangpungtongsung-San on model of allergic
rhinitis. JKOOD. 19:21–30. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Lee MY, Shin IS, Lim HS, Seo CS, Ha H and
Shin HK: Kochia scoparia fruit attenuates allergic airway
inflammation in ovalbumin (OVA)-induced murine asthma model. Inhal
Toxicol. 23:938–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuk JE, Lee MY, Kwon OK, Cai XF, Jang HY,
Oh SR, Lee HK and Ahn KS: Effects of astilbic acid on airway
hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a mouse model of allergic
asthma. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:266–273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee G, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval
S, Bhandari V, Kang MJ, Cohn L, Kim YK, McDonald DM and Elias JA:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and
enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung.
Nat Med. 10:1095–1103. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chaudhary NI, Roth GJ, Hilberg F,
Müller-Quernheim J, Prasse A, Zissel G, Schnapp A and Park JE:
Inhibition of PDGF, VEGF and FGF signaling attenuates fibrosis. Eur
Respir J. 29:976–985. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Richter A, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL,
Bucchieri F, Wilson SJ, Djukanovic R, Dent G, Holgate ST and Davies
DE: The contribution of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 to the
epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 25:385–391. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sumi Y and Hamid Q: Airway remodeling in
asthma. Allergol Int. 56:341–348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Westergren-Thorsson G, Larsen K, Nihlberg
K, Andersson-Sjöland A, Hallgren O, Marko-Varga G and Bjermer L:
Pathological airway remodelling in inflammation. Clin Respir J.
4:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Howell JE and McAnulty RJ: TGF-β: its role
in asthma and therapeutic potential. Current Drug Targets.
7:547–565. 2006.
|
|
30
|
Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H and
Hamid Q: Role of transforming growth factor-β in airway remodeling
in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:127–133. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Salib RJ and Howarth PH: Transforming
growth factor-β in allergic inflammatory disease of the upper
airways: friend or foe? Clin Exp Allergy. 39:1128–1135. 2009.
|
|
32
|
Baek KJ, Cho JY, Rosenthal P, Alexander
LE, Nizet V and Broide DH: Hypoxia potentiates allergen induction
of HIF-1α, chemokines, airway inflammation, TGF-β1, and airway
remodeling in a mouse model. Clin Immunol. 147:27–37.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamaguchi M, Niimi A, Matsumoto H, Ueda T,
Takemura M, Matsuoka H, Jinnai M, Otsukda K, Oguma T, Takeda T, Ito
I, Chin K and Mishima M: Sputum levels of transforming growth
factor-β1 in asthma: relation to clinical and computed tomography
findings. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 18:202–206. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Hoshino M, Takahashi M and Aoike N:
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast
growth factor, and angiogenin immunoreactivity in asthmatic airways
and its relationship to angiogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
107:295–301. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chavakis E and Dimmeler S: Regulation of
endothelial cell survival and apoptosis during angiogenesis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:887–893. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and Le Couter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|