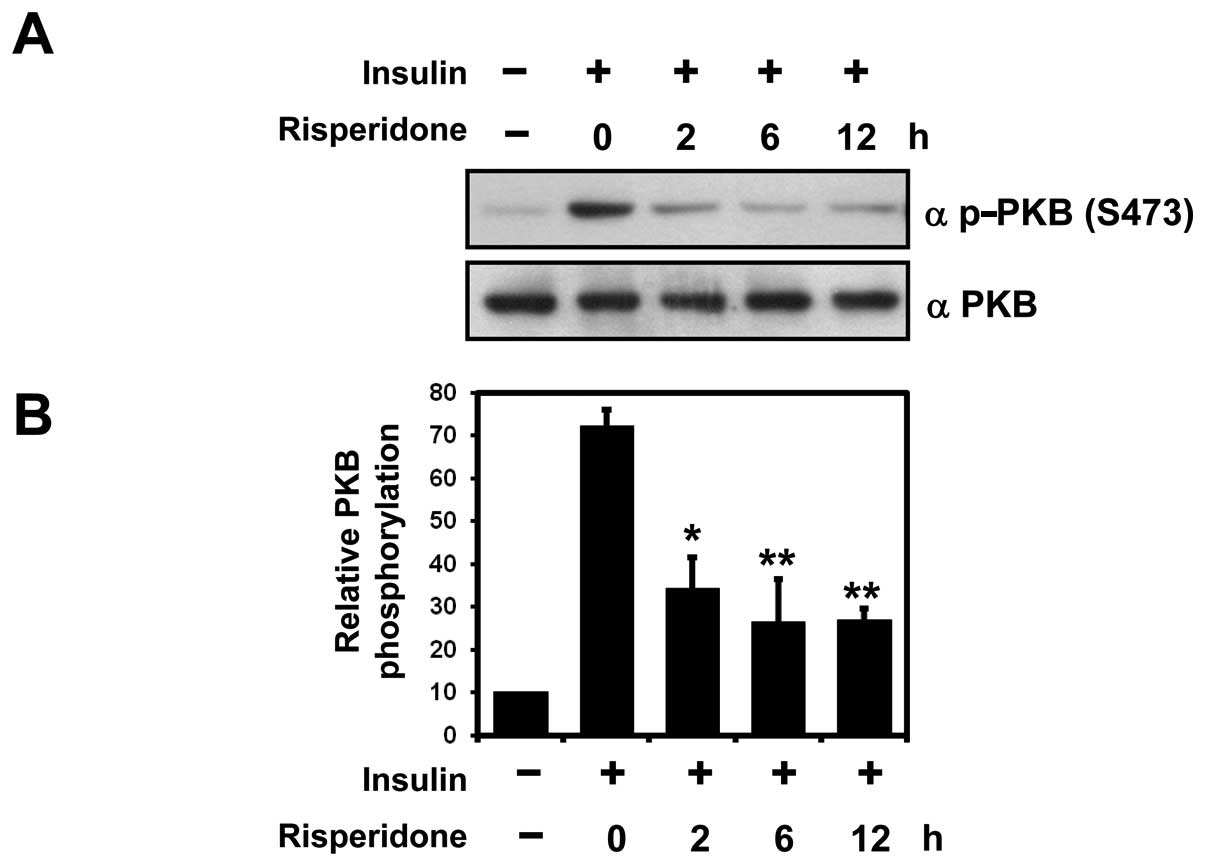
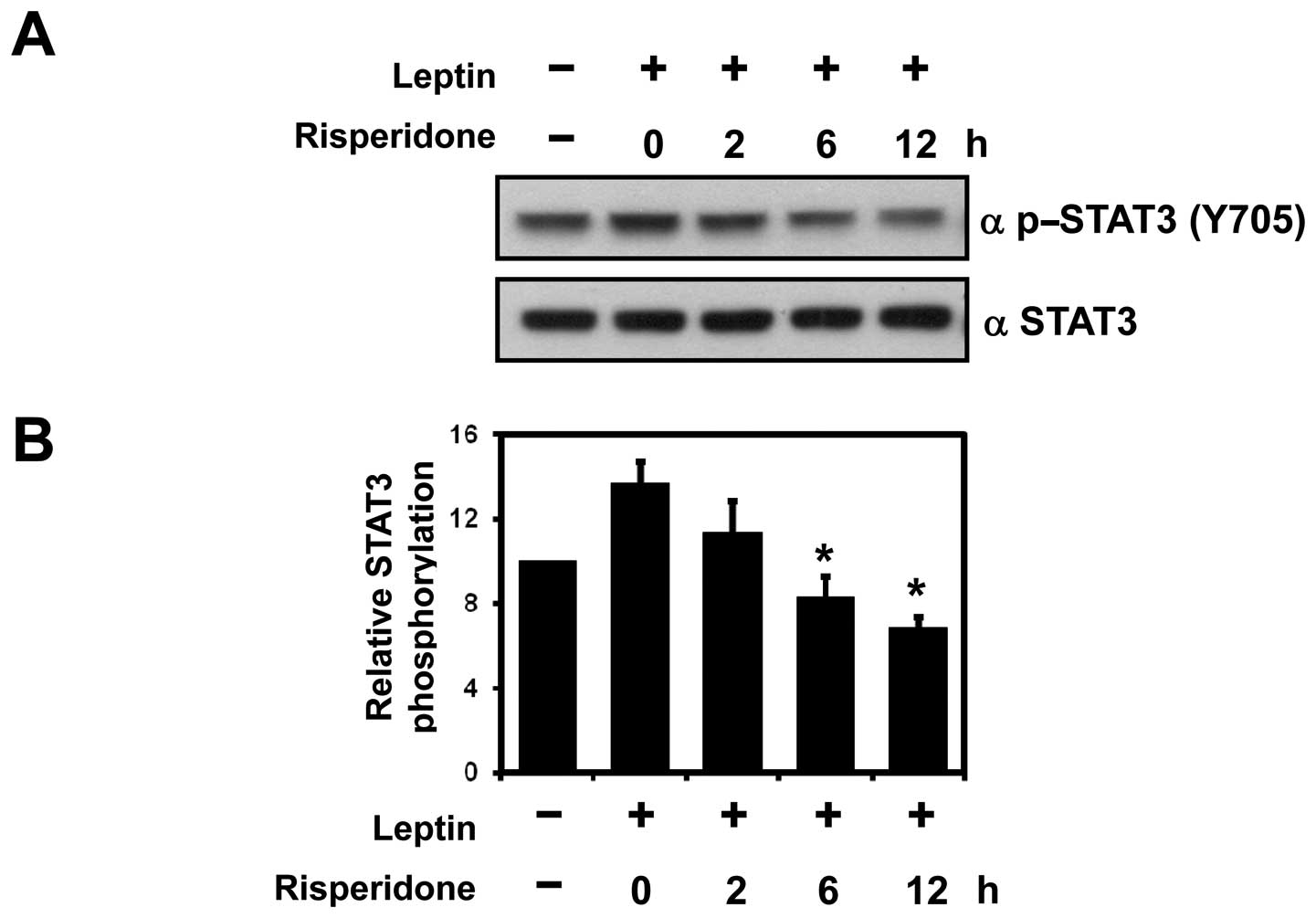
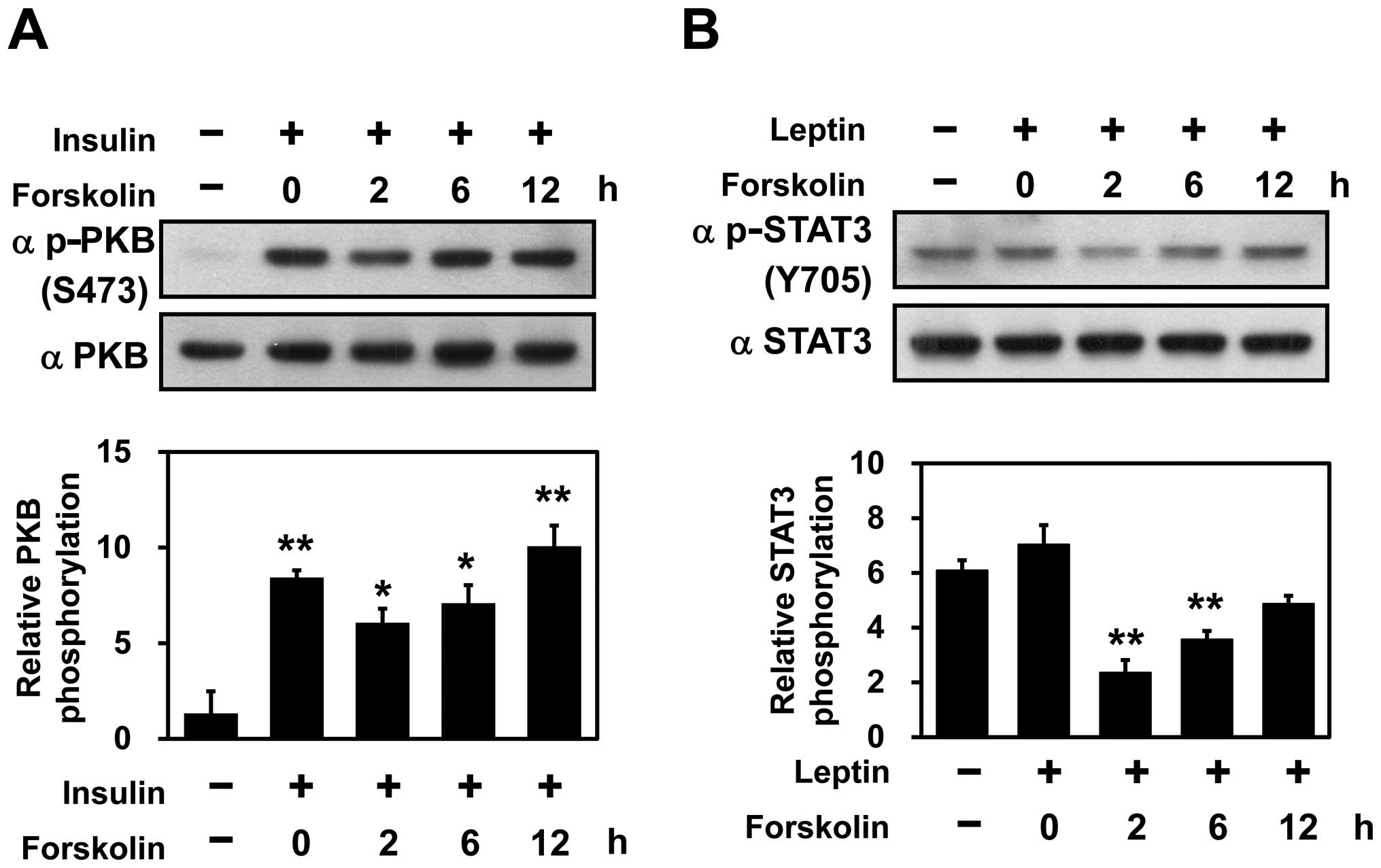
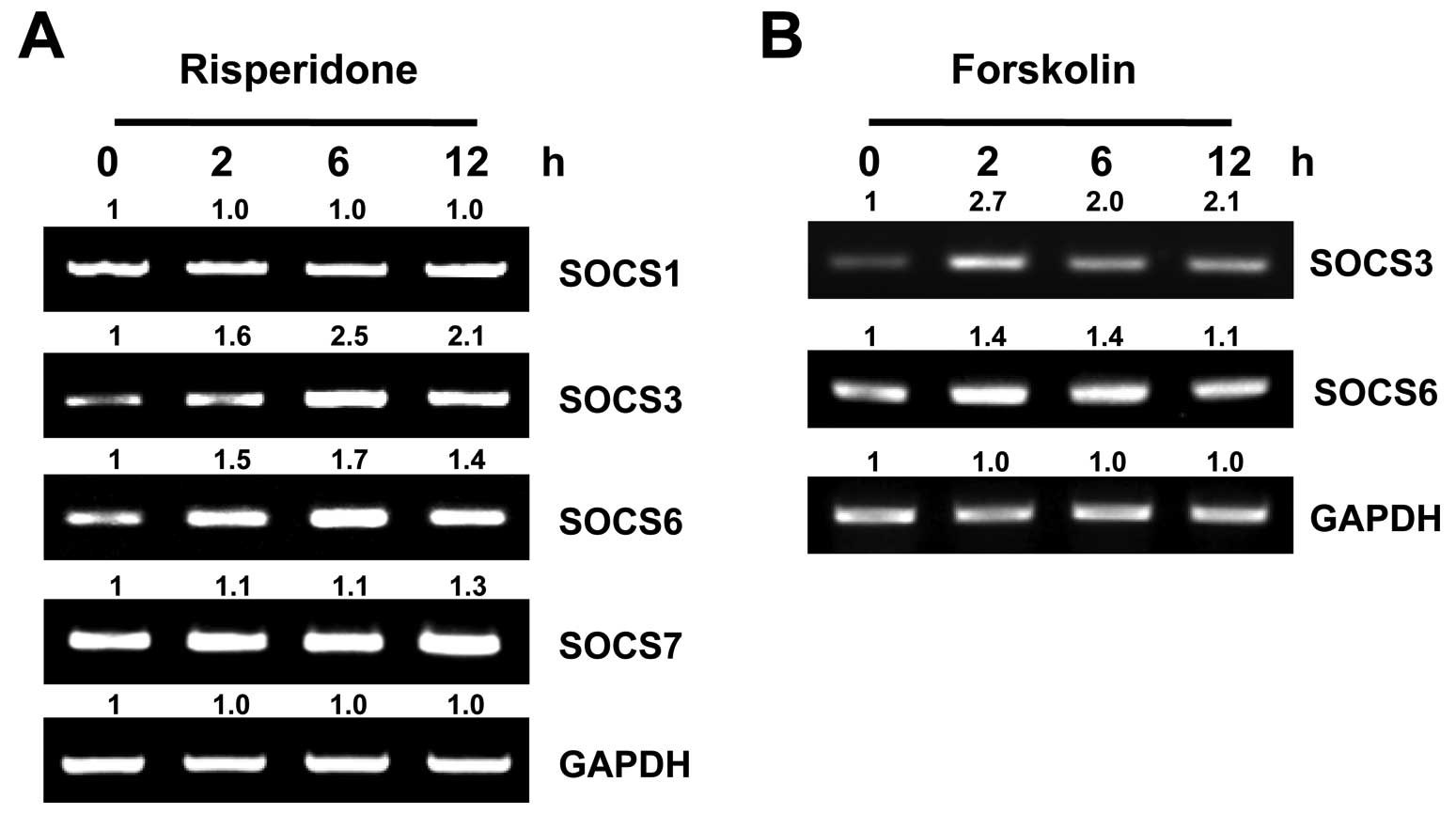
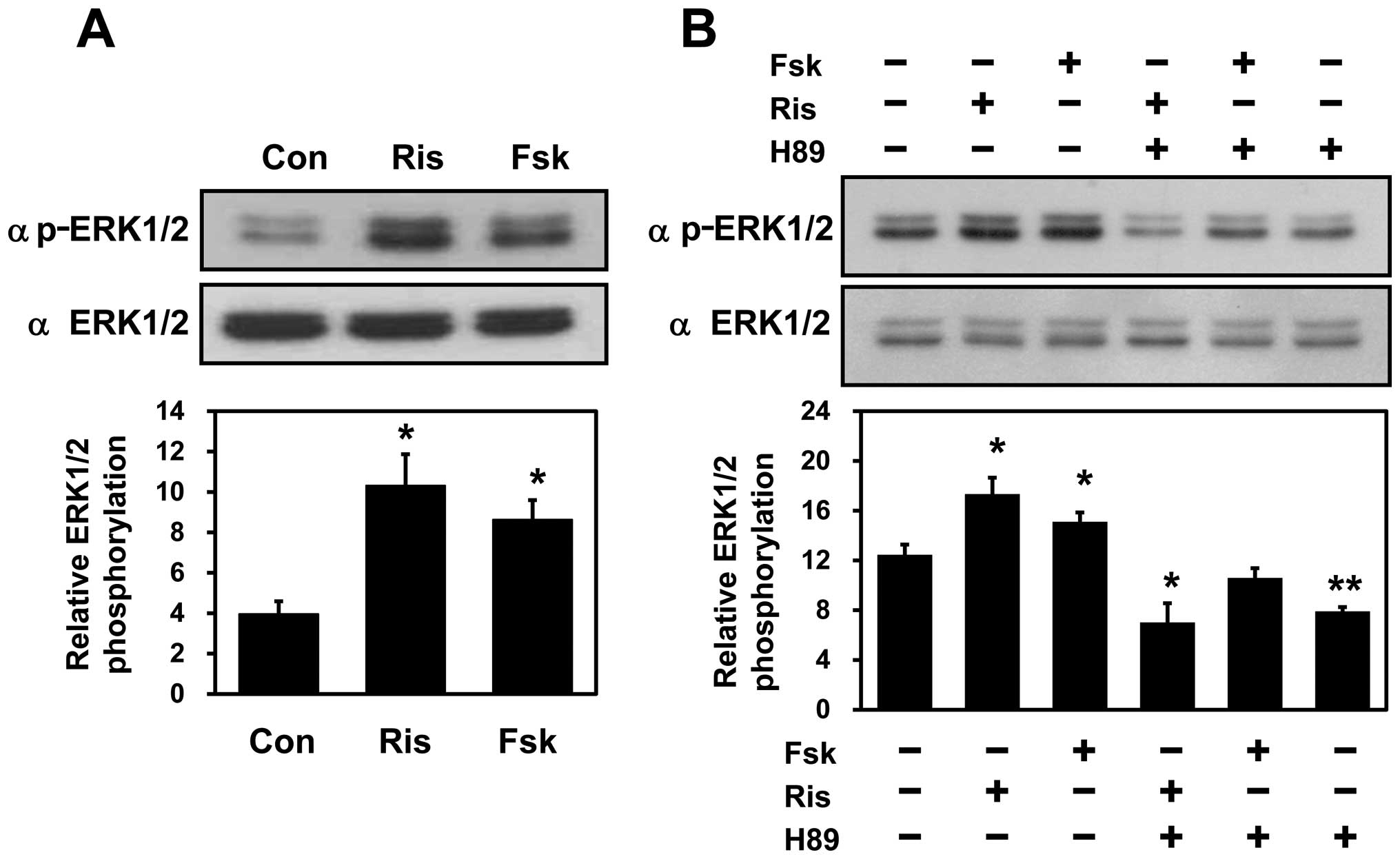
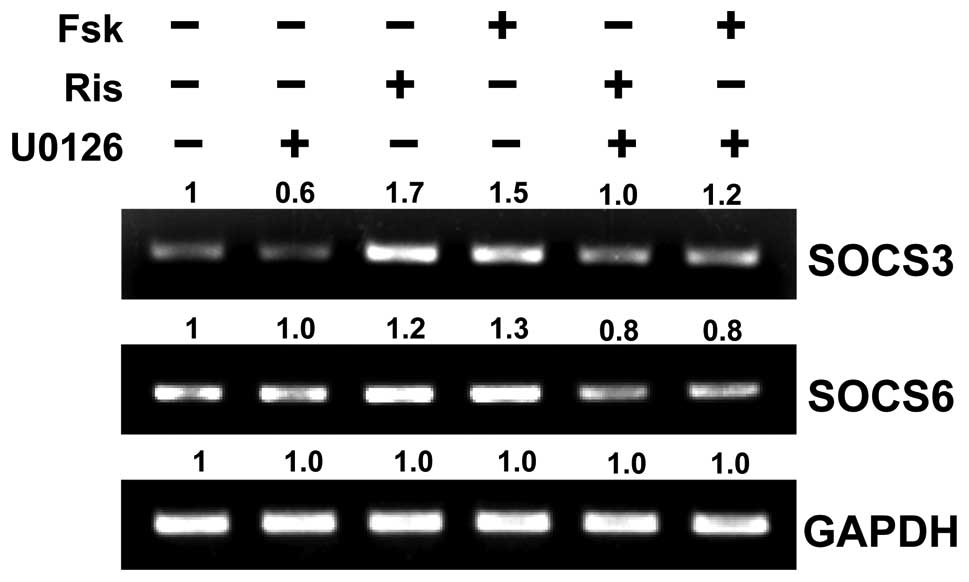
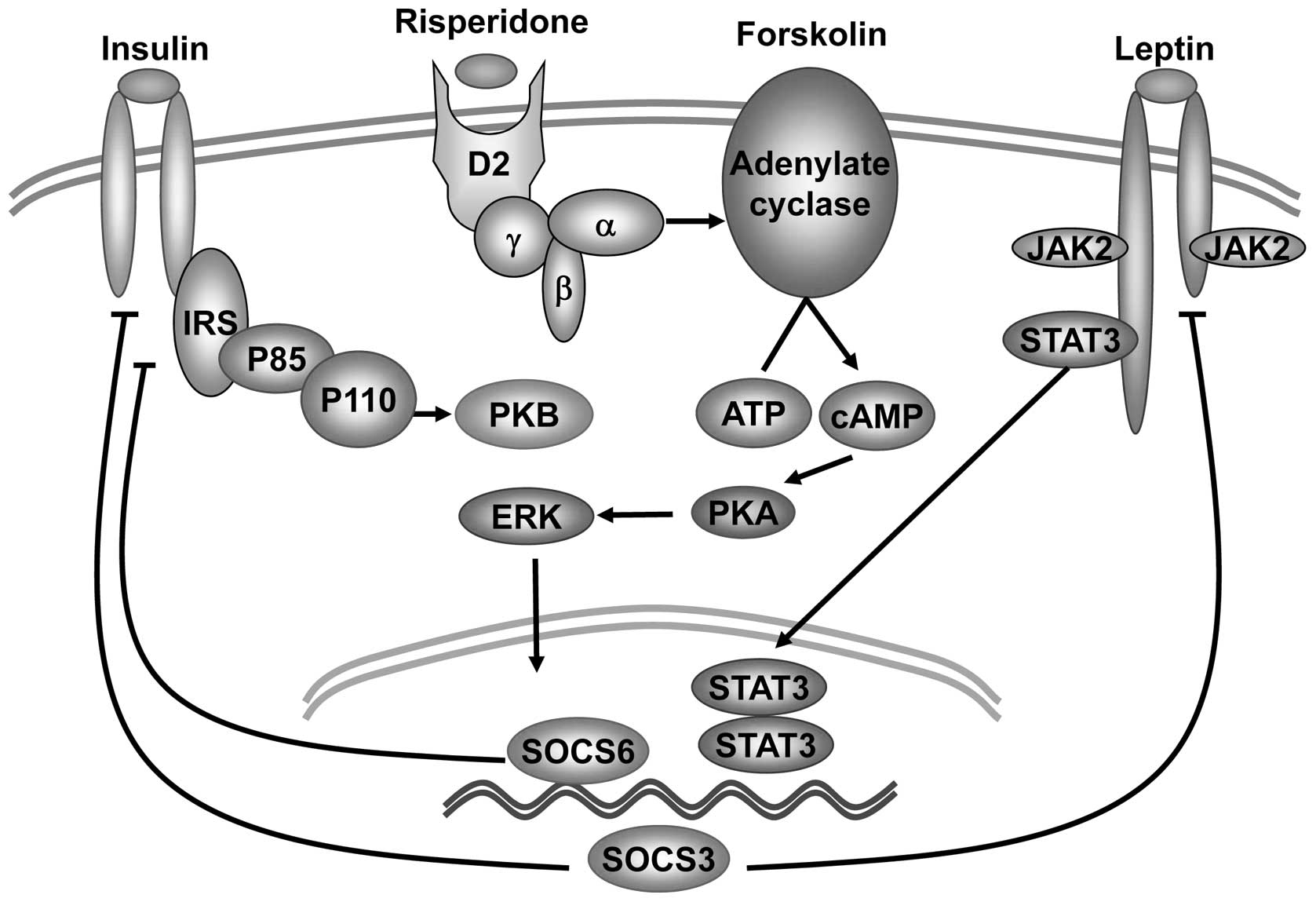
|
1
|
Lett TA, Wallace TJ, Chowdhury NI, Tiwari
AK, Kennedy JL and Muller DJ: Pharmacogenetics of
antipsychotic-induced weight gain: review and clinical
implications. Mol Psychiatry. 17:242–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Citrome L, Jaffe A, Levine J and
Lindenmayer JP: Dosing of quetiapine in schizophrenia: how clinical
practice differs from registration studies. J Clin Psychiatry.
66:1512–1516. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Melkersson KI, Dahl ML and Hulting AL:
Guidelines for prevention and treatment of adverse effects of
antipsychotic drugs on glucose-insulin homeostasis and lipid
metabolism. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 175:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scheen AJ and De Hert MA: Abnormal glucose
metabolism in patients treated with antipsychotics. Diabetes Metab.
33:169–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grace AA: Gating of information flow
within the limbic system and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 31:330–341. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Narendran R, Slifstein M, Guillin O, et
al: Dopamine (D2/3) receptor agonist positron emission tomography
radiotracer [11C]-(+)-PHNO is a D3 receptor preferring agonist in
vivo. Synapse. 60:485–495. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Masi G, Cosenza A, Mucci M and Brovedani
P: Open trial of risperidone in 24 young children with pervasive
developmental disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry.
40:1206–1214. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nasrallah H: A review of the effect of
atypical antipsychotics on weight. Psychoneuroendocrinology.
28(Suppl 1): 83–96. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Claus A, Bollen J, De Cuyper H, et al:
Risperidone versus haloperidol in the treatment of chronic
schizophrenic inpatients: a multicentre double-blind comparative
study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 85:295–305. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Owens DG: Extrapyramidal side effects and
tolerability of risperidone: a review. J Clin Psychiatry. 55:29–35.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morton GJ: Hypothalamic leptin regulation
of energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism. J Physiol.
583:437–443. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niswender KD, Baskin DG and Schwartz MW:
Insulin and its evolving partnership with leptin in the
hypothalamic control of energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 15:362–369. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hemmings BA and Restuccia DF: PI3K-PKB/Akt
pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0111892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Coppari R and Bjorbaek C: Leptin
revisited: its mechanism of action and potential for treating
diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:692–708. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Obici S, Feng Z, Morgan K, Stein D,
Karkanias G and Rossetti L: Central administration of oleic acid
inhibits glucose production and food intake. Diabetes. 51:271–275.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kloek C, Haq AK, Dunn SL, Lavery HJ, Banks
AS and Myers MG Jr: Regulation of Jak kinases by intracellular
leptin receptor sequences. J Biol Chem. 277:41547–41555. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Myers MG Jr: Leptin receptor signaling and
the regulation of mammalian physiology. Recent Prog Horm Res.
59:287–304. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
White DW, Kuropatwinski KK, Devos R,
Baumann H and Tartaglia LA: Leptin receptor (OB-R) signaling.
Cytoplasmic domain mutational analysis and evidence for receptor
homo-oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 272:4065–4071. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Starr R, Willson TA, Viney EM, Murray LJ,
Rayner JR, Jenkins BJ, Gonda TJ, Alexander WS, Metcalf D, Nicola NA
and Hilton DJ: A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of
signalling. Nature. 387:917–921. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoshimura A, Nishinakamura H, Matsumura Y
and Hanada T: Negative regulation of cytokine signaling and immune
responses by SOCS proteins. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:100–110. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE and
Lieberman JA: Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of
pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Mol
Psychiatry. 10:79–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friedman JM and Halaas JL: Leptin and the
regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 395:763–770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Spiegelman BM and Flier JS: Obesity and
the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 104:531–543. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nilsson CL and Eriksson E: Haloperidol
increases prolactin release and cyclic AMP formation in vitro:
inverse agonism at dopamine D2 receptors? J Neural Transm Gen Sect.
92:213–220. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Insel PA and Ostrom RS: Forskolin as a
tool for examining adenylyl cyclase expression, regulation, and G
protein signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 23:305–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sands WA, Woolson HD, Milne GR, Rutherford
C and Palmer TM: Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP
(Epac)-mediated induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3
(SOCS-3) in vascular endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol.
26:6333–6346. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Banks AS, Li J, McKeag L, et al: Deletion
of SOCS7 leads to enhanced insulin action and enlarged islets of
Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 115:2462–2471. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mooney RA, Senn J, Cameron S, et al:
Suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 and -6 associate with and
inhibit the insulin receptor. A potential mechanism for
cytokine-mediated insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 276:25889–25893.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, et al:
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3), a potential mediator
of interleukin-6-dependent insulin resistance in hepatocytes. J
Biol Chem. 278:13740–13746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ueki K, Kondo T and Kahn CR: Suppressor of
cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance
through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor
substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol.
24:5434–5446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wojtal KA, Hoekstra D and van Ijzendoorn
SC: cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and the dynamics of epithelial
cell surface domains: moving membranes to keep in shape. Bioessays.
30:146–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stork PJ and Schmitt JM: Crosstalk between
cAMP and MAP kinase signaling in the regulation of cell
proliferation. Trends Cell Biol. 12:258–266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Metzger BE, Buchanan TA, Coustan DR, et
al: Summary and recommendations of the Fifth International
Workshop-Conference on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes
Care. 30(Suppl 2): S251–S260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, et al:
Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic
schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 353:1209–1223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tran PV, Hamilton SH, Kuntz AJ, et al:
Double-blind comparison of olanzapine versus risperidone in the
treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. J Clin
Psychopharmacol. 17:407–418. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Csernansky JG, Miller JP, McKeel D and
Morris JC: Relationships among cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in
dementia of the Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord.
16:144–149. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akam E and Strange PG: Inverse agonist
properties of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol.
67:2039–2045. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seeman P, Schwarz J, Chen JF, et al:
Psychosis pathways converge via D2high dopamine receptors. Synapse.
60:319–346. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Albert PR, Neve KA, Bunzow JR and Civelli
O: Coupling of a cloned rat dopamine-D2 receptor to inhibition of
adenylyl cyclase and prolactin secretion. J Biol Chem.
265:2098–2104. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang BH, Son H, Kim SH, Nam JH, Choi JH
and Lee JS: Phosphorylation of ERK and CREB in cultured hippocampal
neurons after haloperidol and risperidone administration.
Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 58:262–267. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Howard JK and Flier JS: Attenuation of
leptin and insulin signaling by SOCS proteins. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 17:365–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bjorbak C, Lavery HJ, Bates SH, et al:
SOCS3 mediates feedback inhibition of the leptin receptor via
Tyr985. J Biol Chem. 275:40649–40657. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rui L, Yuan M, Frantz D, Shoelson S and
White MF: SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 block insulin signaling by
ubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRS1 and IRS2. J Biol Chem.
277:42394–42398. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Laroche-Joubert N, Marsy S, Michelet S,
Imbert-Teboul M and Doucet A: Protein kinase A-independent
activation of ERK and H,K-ATPase by cAMP in native kidney cells:
role of Epac I. J Biol Chem. 277:18598–18604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yee WM and Worley PF: Rheb interacts with
Raf-1 kinase and may function to integrate growth factor- and
protein kinase A-dependent signals. Mol Cell Biol. 17:921–933.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Richards JS: New signaling pathways for
hormones and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate action in
endocrine cells. Mol Endocrinol. 15:209–218. 2001.
|