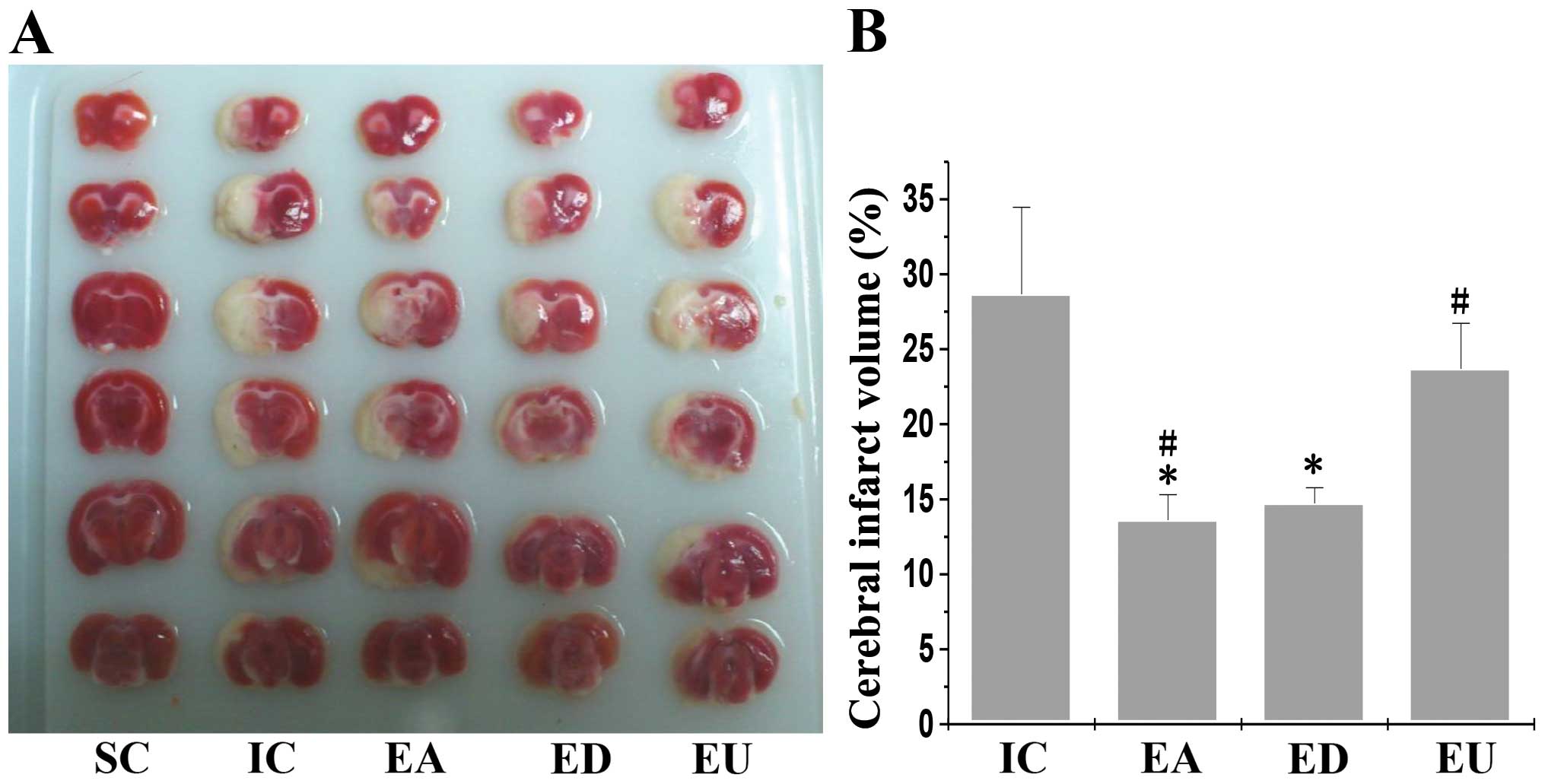
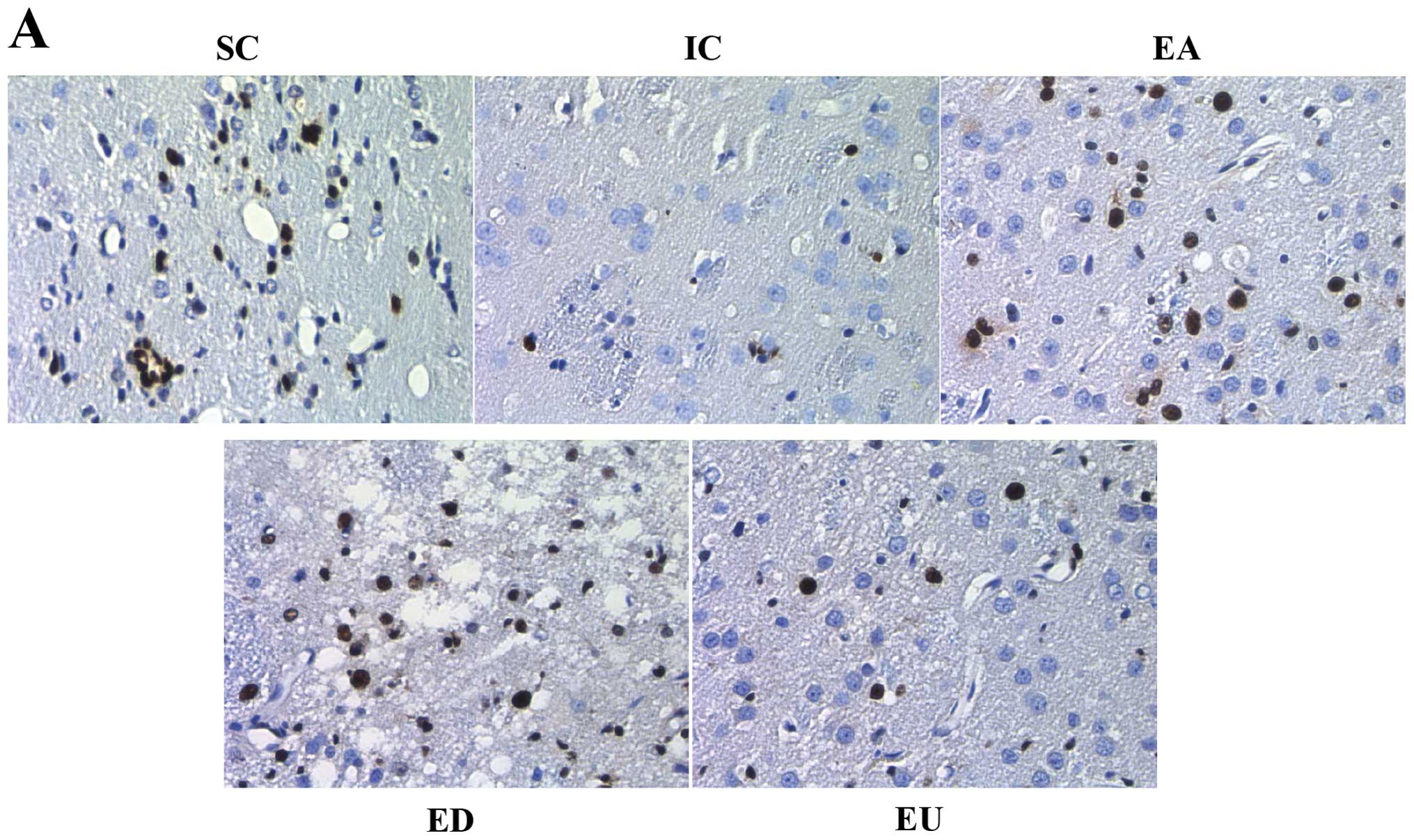
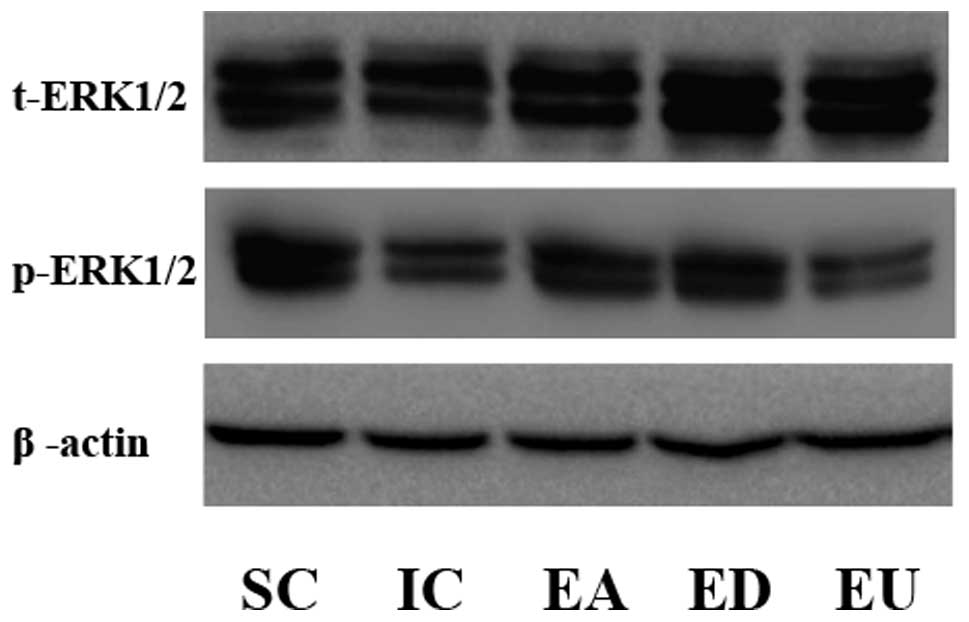
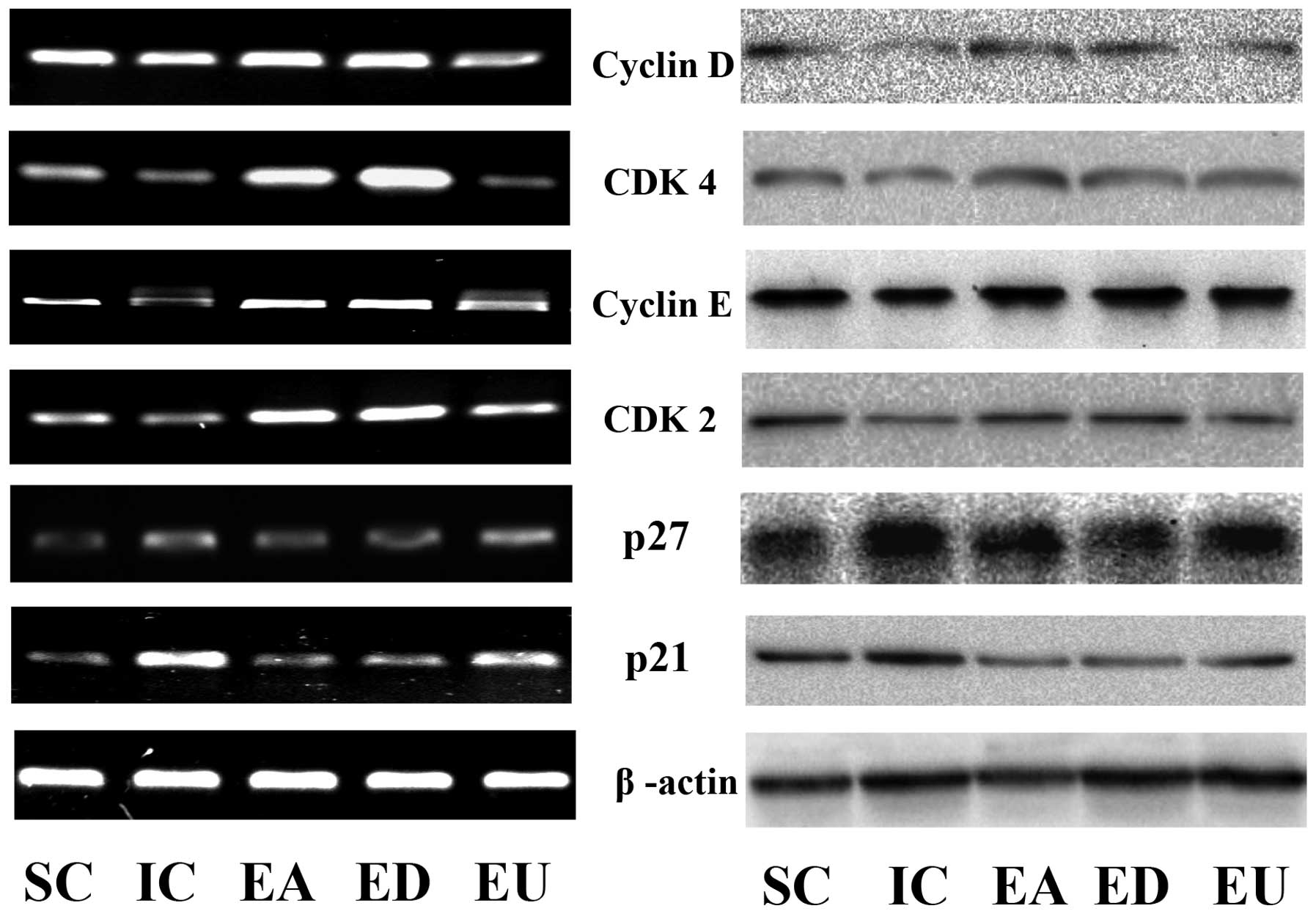
|
1
|
The Chinese medical association of
neurology, cerebrovascular epidemiology group of acute ischemic
stroke treatment guidelines writing group. China’s acute ischaemic
stroke treatment guidelines. Chinese General Practice. 4013–4017.
2010.
|
|
2
|
Diener HC, Foerch C, Riess H, et al:
Treatment of acute ischaemic stroke with thrombolysis or
thrombectomy in patients receiving anti-thrombotic treatment.
Lancet Neurol. 12:677–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Flynn RW, MacWalter RS and Doney AS: The
cost of cerebral ischaemia. Neuropharmacology. 55:250–256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hong J, Wu G, Zou Y, et al:
Electroacupuncture promotes neurological functional recovery via
the retinoic acid signaling pathway in rats following cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Med. 31:225–231.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Le W, Liu Y, Wang Q, et al: Effect of
scalp-acupuncture on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats of
proliferation and differentiation intervention neural stem cell. J
Hubei Univ Trad Chin Med. 2:12–15. 2013.
|
|
6
|
Tao J, Xue XH, Chen LD, et al:
Electroacupuncture improves neurological deficits and enhances
proliferation and differentiation of endogenous nerve stem cells in
rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res. 32:198–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kawano T, Fukunaga K, Takeuchi Y, et al:
Neuroprotective effect of sodium orthovanadate on delayed neuronal
death after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil hippocampus. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 21:1268–1280. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pignataro G, Meller R, Inoue K, et al: In
vivo and in vitro characterization of a novel neuroprotective
strategy for stroke: ischemic postconditioning. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 28:232–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bao XM and Shu SY: The stereotaxic atlas
of the rat brain. People’s Medical Publishing House; pp. 7–35.
1991
|
|
10
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al:
Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion craniectomy in rats.
Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie G, Yang S, Chen A, et al:
Electroacupuncture at Quchi and Zusanli treats cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of ERK signaling.
Exp Ther Med. 5:1593–1597. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li ZR: The subject of experimental
acupuncture and moxibustion. Chinese Press of Traditional Chinese
Medicine; Beijing: 2003
|
|
13
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, et al: Rat
middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and
development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 17:472–476. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xue X, You Y, Tao J, Ye X, et al:
Electro-acupuncture at points of Zusanli and Quchi exerts
anti-apoptotic effect through the modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurosci Lett. 558:14–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Y-Y, Liu Z-S, Wang S, et al: The
influence of electroacupuncture acupoints on the protein expression
of β-EP and glu hypathalamus in rats with cerebral ischemia
reperfusion injury. Chin J Bas Med Trad Chin Med. 16:1030–1033.
2010.
|
|
16
|
Xiao YY, Du L, Hong BK, et al: Study the
acupuncture at acupoint of Zusanli effects in the brain magnetic
resonance imaging. Sichuan Zhongyi. 25:98–101. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Qi JP, Xia YL, et al: The response
of human motor cortex to acupuncture of S36 and G34 as revealed by
functional MRI. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil. 26:472–475. 2004.
|
|
18
|
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF and Hu XJ:
Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable
to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical
validation. Stroke. 26:627–634. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, et al:
Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain
protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11569–11574. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sawe N, Steinberg G and Zhao H: Dual roles
of the MAPK/ERK1/2 cell signaling pathway after stroke. J Neurosci
Res. 86:1659–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sironi L, Banfi C, Brioschi M, et al:
Activation of NF-κB and ERK1/2 after permanent focal ischemia is
abolished by simvastatin treatment. Neurobiol Dis. 22:445–451.
2006.
|
|
22
|
Meller R, Stevens SL, Minami M, et al:
Neuroprotection by osteopontin in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
25:217–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen WY and Chang MS: IL-20 is regulated
by hypoxia-inducible factor and up-regulated after experimental
ischemic stroke. J Immunol. 182:5003–5012. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dang ZC and Lowik CW: Differential effects
of PD98059 and U0126 on osteogenesis and adipogenesis. J Cell
Biochem. 92:525–533. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim TJ and Yun YP: Potent inhibition of
serum-stimulated responses in vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by
2-chloro-3-(4-hexylphenyl)-amino-1,4-naphthoquinone, a newly
synthesized 1,4-naphthoquinone derivative. Biol Pharm Bull.
30:121–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wharton SB, Williams GH, Stoeber K, et al:
Expression of Ki67, PCNA and the chromosome replication licensing
protein Mcm2 in glial cells of the aeing human hippocampus
increases with the burden of Alzheimer-type pathology. Neurosci
Lett. 383:33–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang B, Gao Y, Xiao Z, et al: ERK1/2
prootes proliferation and inhibits neuronal differentiation of
neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett. 461:252–257. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng Q, Huang S, Zhang A, et al: Y-box
protein 1 stimulates mesangial cell proliferation via activation of
ERK1/2. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 113:e16–e25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Osaki LH, Figueiredo PM, Alvares EP and
Gama P: EGFR is involved in control of gastric cell proliferation
through activation of MAPK and Src signaling pathways
inearly-weaned rats. Cell Prolif. 44:174–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sah JF, Balasubramanian S, Eckert RL and
Rorke EA: Epigallo-catechin-3-gallate inhibits epidermal growth
factor receptor signaling pathway. Evidence for direct inhibition
of ERK1/2 and AKT kinases. J Biol Chem. 279:12755–12762. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|