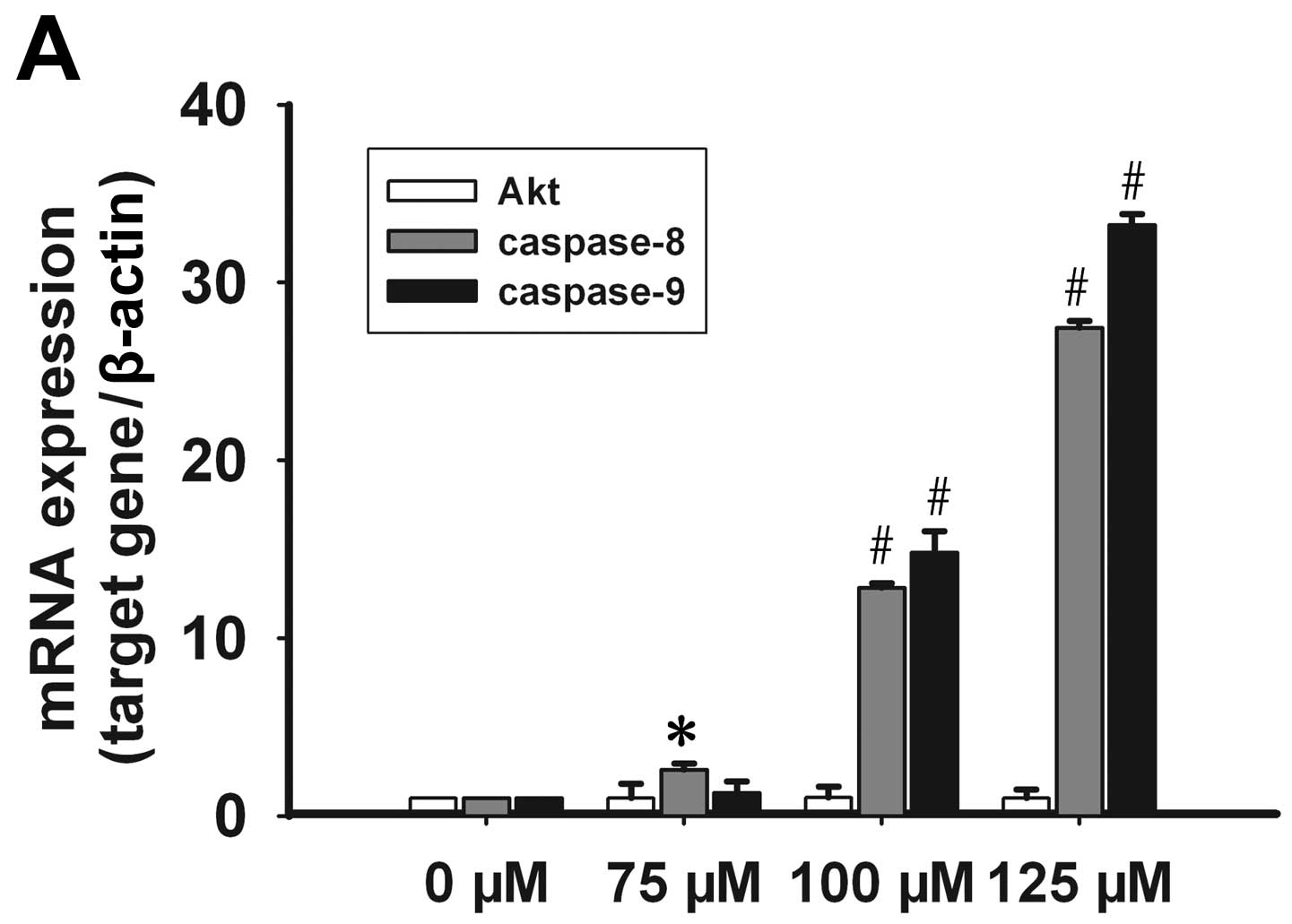
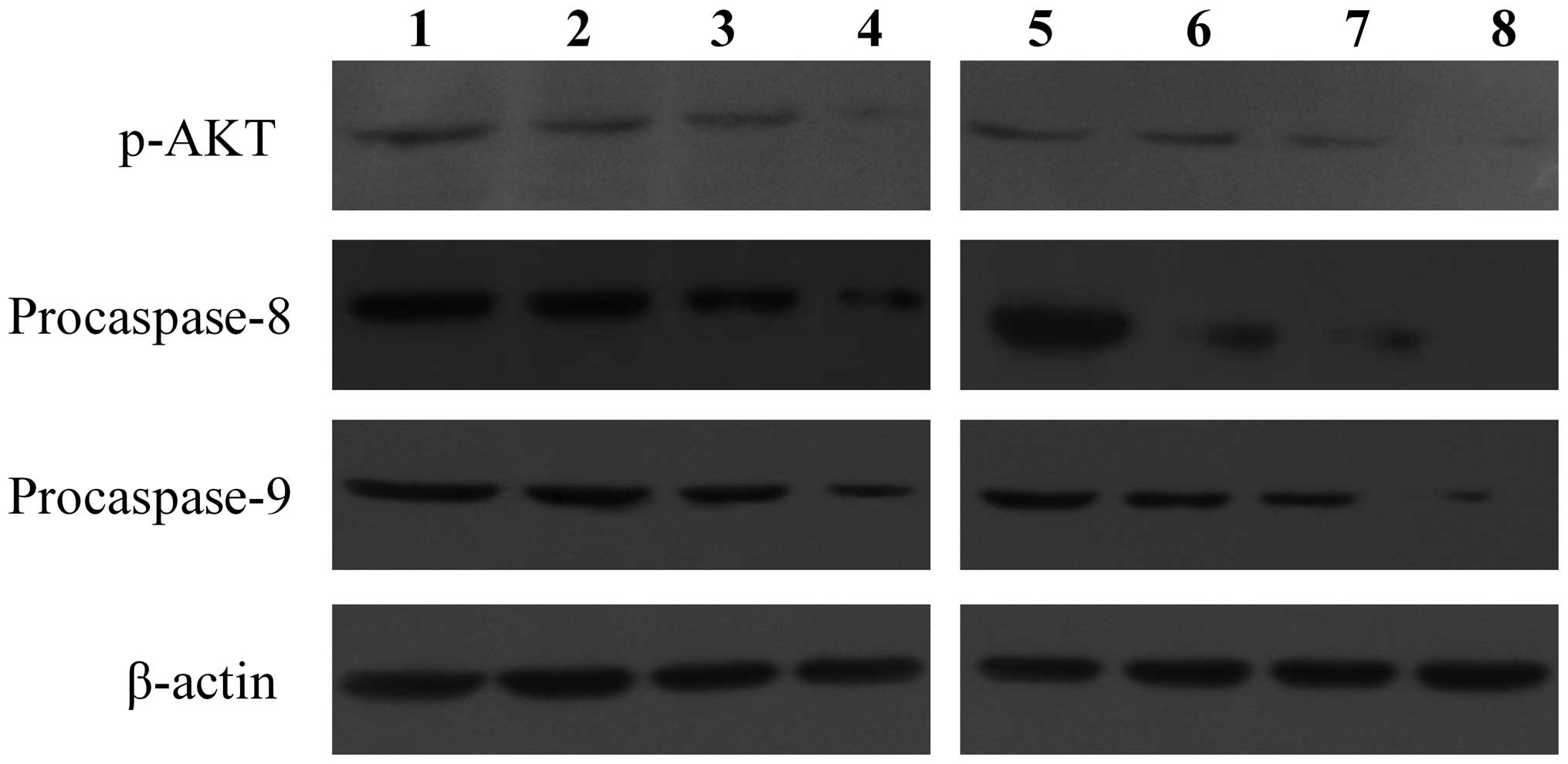
|
1
|
Saukkonen K, Rintahaka J, Sivula A, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastric carcinogenesis. APMIS. 111:915–925.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jones DA, Carlton DP, McIntyre TM,
Zimmerman GA and Prescott SM: Molecular cloning of human
prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase type II and demonstration of
expression in response to cytokines. J Biol Chem. 268:9049–9054.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sarkar FH, Adsule S, Li Y and Padhye S:
Back to the future: COX-2 inhibitors for chemoprevention and cancer
therapy. Mini Rev Med Chem. 7:599–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Duan L, Wu AH, Sullivan-Halley J and
Bernstein L: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of
esophageal and gastric adenocarcinomas in Los Angeles County.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:126–134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fu SL, Wu YL, Zhang YP, Qiao MM and Chen
Y: Anti-cancer effects of COX-2 inhibitors and their correlation
with angiogenesis and invasion in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:1971–1974. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lo AC, Woo TT, Wong RL and Wong D:
Apoptosis and other cell death mechanisms after retinal detachment:
implications for photoreceptor rescue. Ophthalmologica. 226(Suppl
1): 10–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su M, Mei Y and Sinha S: Role of the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. J Oncol.
2013:1027352013.
|
|
8
|
Qadri SS, Wang JH, Coffey JC, et al:
Surgically induced accelerated local and distant tumor growth is
significantly attenuated by selective COX-2 inhibition. Ann Thorac
Surg. 79:990–995. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grösch S, Maier TJ, Schiffmann S and
Geisslinger G: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-independent
anticarcinogenic effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 98:736–747. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baek JY, Hur W, Wang JS, Bae SH and Yoon
SK: Selective COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398, suppresses cellular
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via cell
cycle arrest. World J Gastroenterol. 13:1175–1181. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jendrossek V: Targeting apoptosis pathways
by celecoxib in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan XM, Jiang XH, Gu Q, et al: Inhibition
of Akt/PKB by a COX-2 inhibitor induces apoptosis in gastric cancer
cells. Digestion. 73:75–83. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim N, Kim CH, Ahn DW, et al: Anti-gastric
cancer effects of Celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, through
inhibition of Akt signaling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:480–487.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patru CL, Surlin V, Georgescu I and Patru
E: Current issues in gastric cancer epidemiology. Rev Med Chir Soc
Med Nat Iasi. 117:199–204. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Futagami S, Suzuki K, Hiratsuka T, et al:
Chemopreventive effect of Celecoxib in gastric cancer.
Inflammopharmacology. 15:1–4. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Willoughby DA, Moore AR and Colville-Nash
PR: COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 and the future treatment of chronic
inflammatory disease. Lancet. 355:646–648. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, et al:
The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and
adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis.
30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y and Liu BA: Enhanced proliferation,
invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
nicotine-promoted gastric cancer by periostin. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:2674–2680. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fulda S: Caspase-8 in cancer biology and
therapy. Cancer Lett. 281:128–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Würstle ML, Laussmann MA and Rehm M: The
central role of initiator caspase-9 in apoptosis signal
transduction and the regulation of its activation and activity on
the apoptosome. Exp Cell Res. 318:1213–1220. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Allan LA and Clarke PR: Apoptosis and
autophagy: Regulation of caspase-9 by phosphorylation. FEBS J.
276:6063–6073. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
White E, Karp C, Strohecker AM, Guo Y and
Mathew R: Role of autophagy in suppression of inflammation and
cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 22:212–217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lorin S, Hamaï A, Mehrpour M and Codogno
P: Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
23:361–379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Helgason GV, Holyoake TL and Ryan KM: Role
of autophagy in cancer prevention, development and therapy. Essays
Biochem. 55:133–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie BS, Zhao HC, Yao SK, et al: Autophagy
inhibition enhances etoposide-induced cell death in human hepatoma
G2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 27:599–606. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu B, Wu JM, Li J, et al: Polygonatum
cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell
apoptosis and autophagy via blocking Ras-Raf and PI3K-Akt signaling
pathways. Biochimie. 92:1934–1938. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ye B, Jiang LL, Xu HT, Zhou DW and Li ZS:
Expression of PI3K/AKT pathway in gastric cancer and its blockade
suppresses tumor growth and metastasis. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:627–636. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin X, Zhang X, Wang Q, et al: Perifosine
downregulates MDR1 gene expression and reverses multidrug-resistant
phenotype by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in a
human breast cancer cell line. Neoplasma. 59:248–256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang XH, Xu ZY, Gong YB, et al: Bufalin
reverses HGF-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR mutant lung
cancer cells via blockage of Met/PI3k/Akt pathway and induction of
apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2438592013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, et al:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Falasca M: PI3K/Akt signalling pathway
specific inhibitors: a novel strategy to sensitize cancer cells to
anti-cancer drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 16:1410–1416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Garcia-Echeverria C and Sellers WR: Drug
discovery approaches targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer.
Oncogene. 27:5511–5526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Lin Y, Yang H, Deng Q, Chen and He
J: The expression of p33(ING1), p53, and autophagy-related gene
Beclin1 in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol.
32:1113–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng Y, Ren X, Zhang Y, et al: eEF-2
kinase dictates cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis induced
by Akt inhibition, thereby modulating cytotoxicity of novel Akt
inhibitor MK-2206. Cancer Res. 71:2654–2663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Djavaheri-Mergny M, Maiuri MC and Kroemer
G: Cross talk between apoptosis and autophagy by caspase-mediated
cleavage of Beclin 1. Oncogene. 29:1717–1719. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|