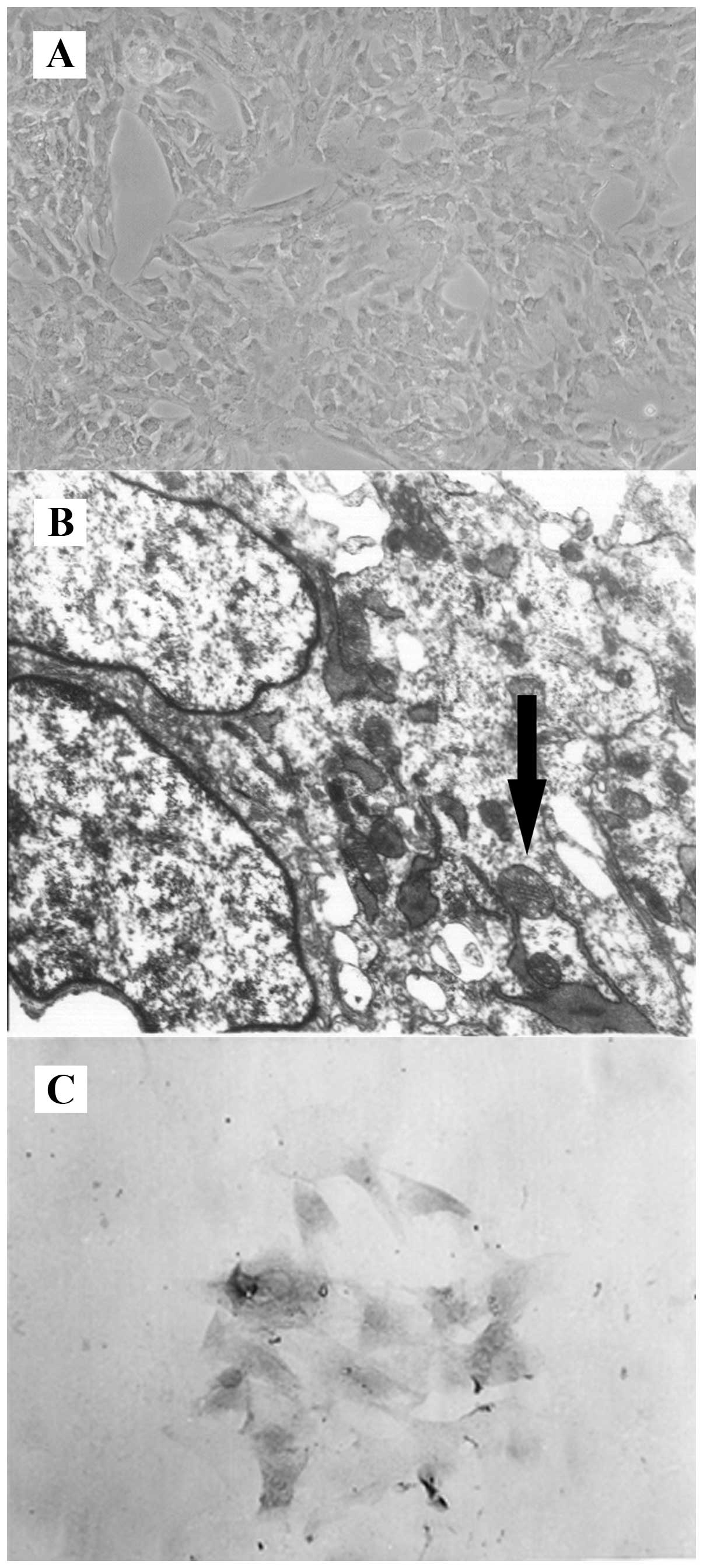
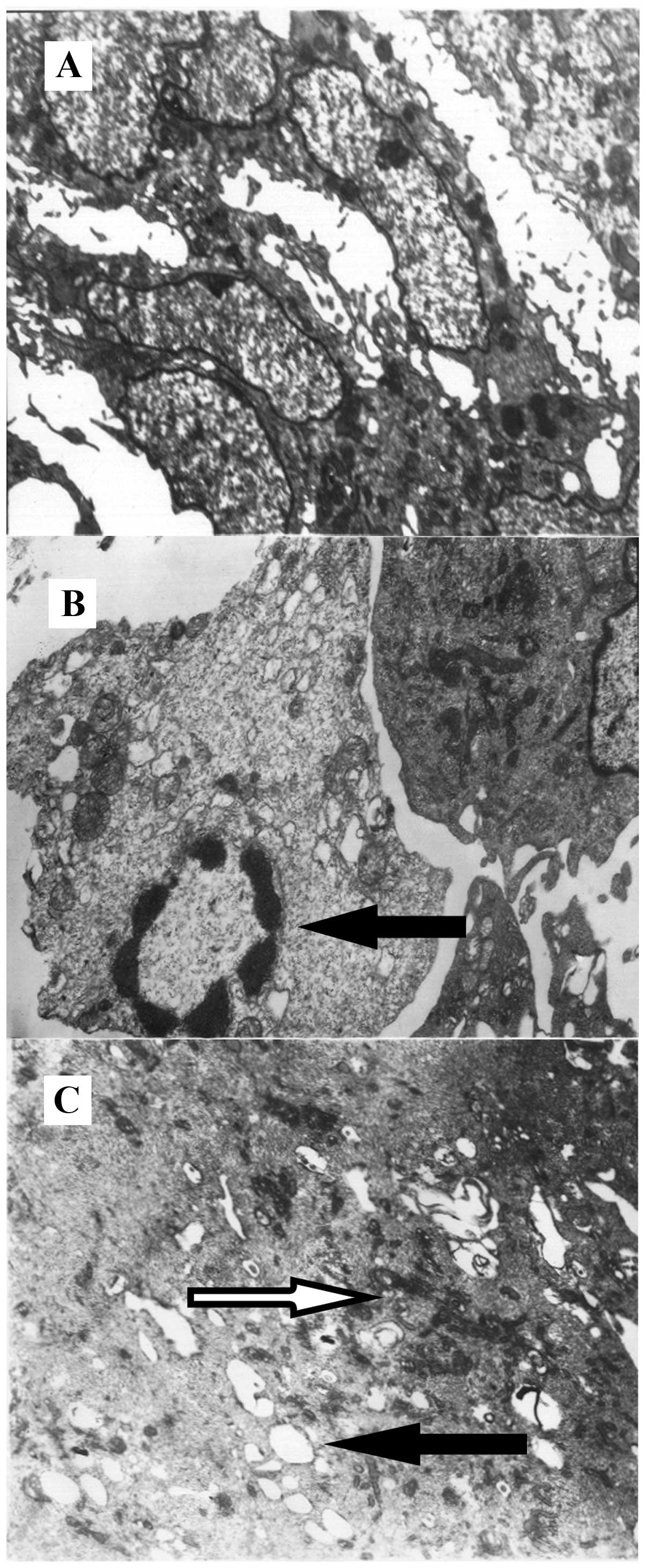
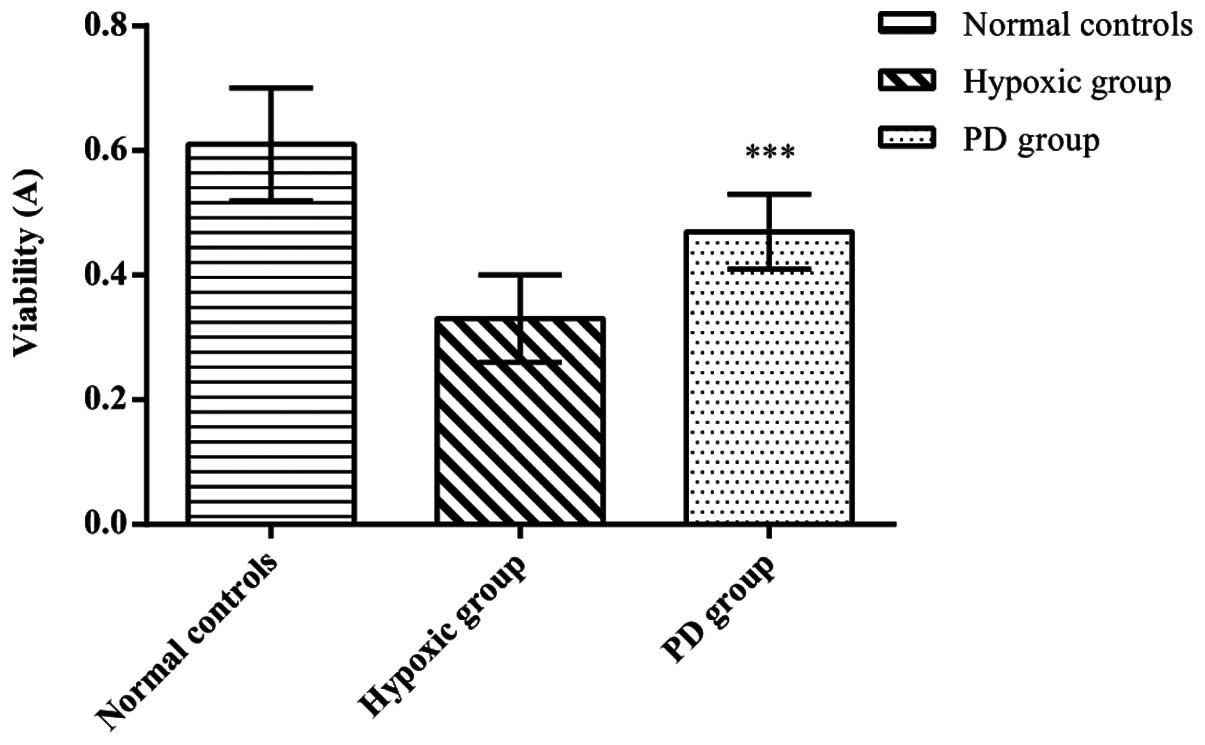
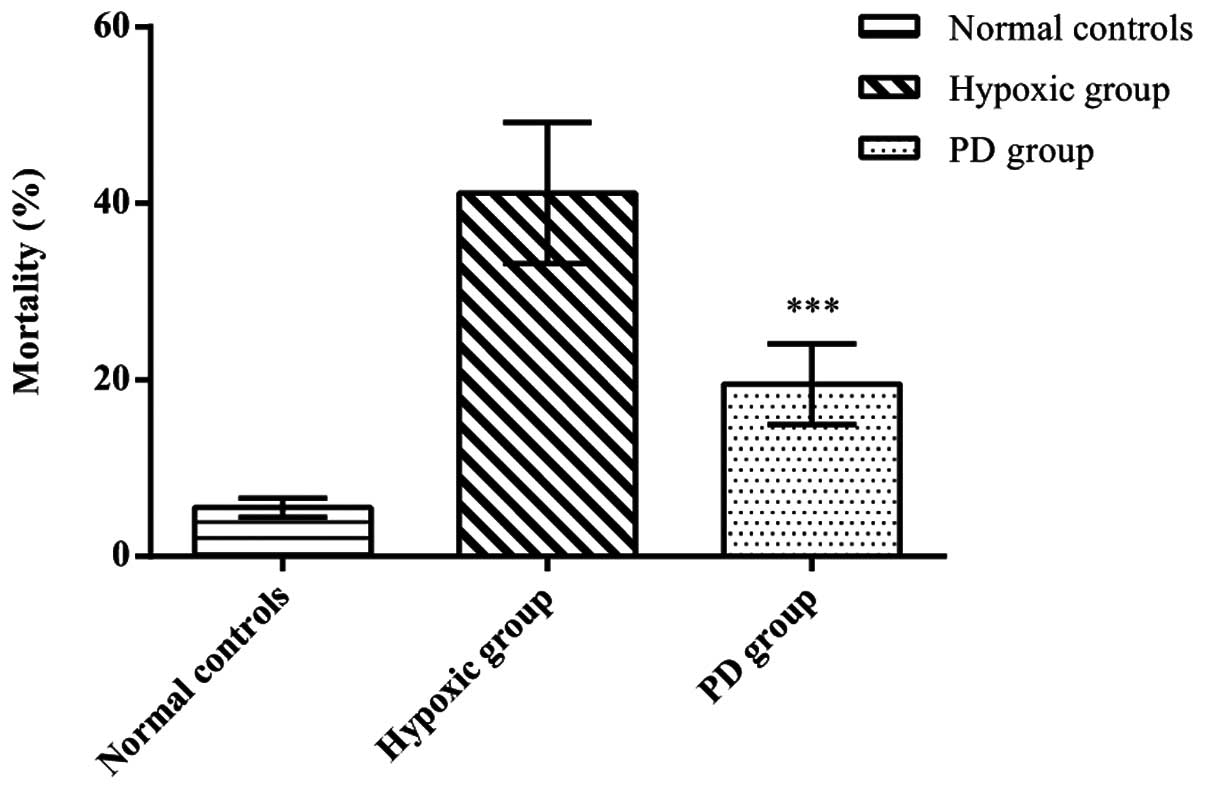
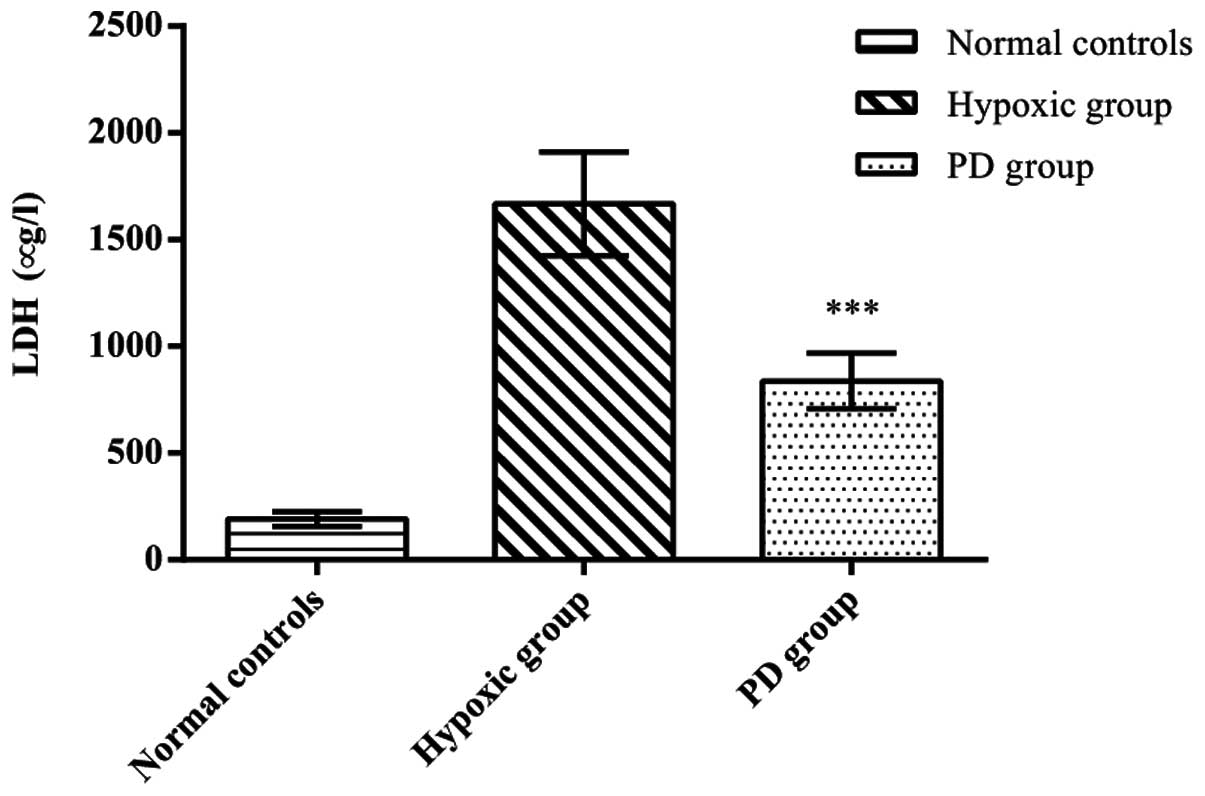
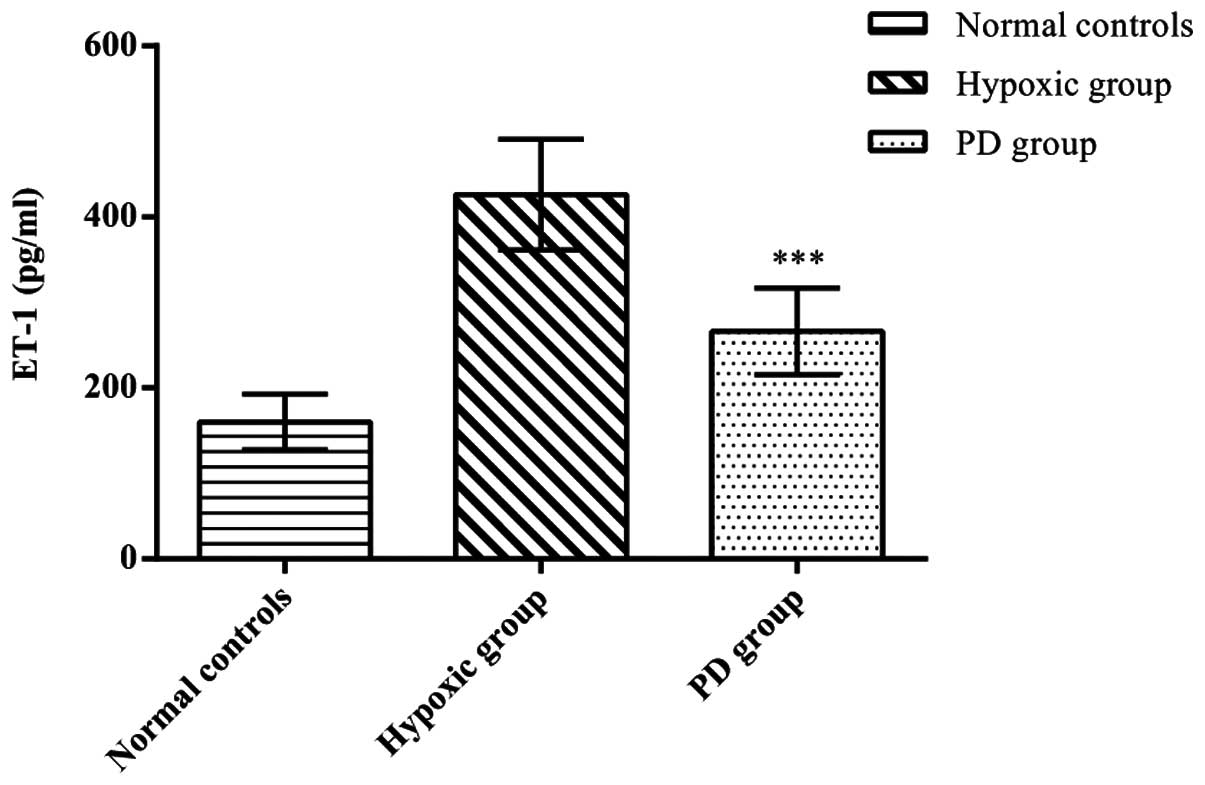
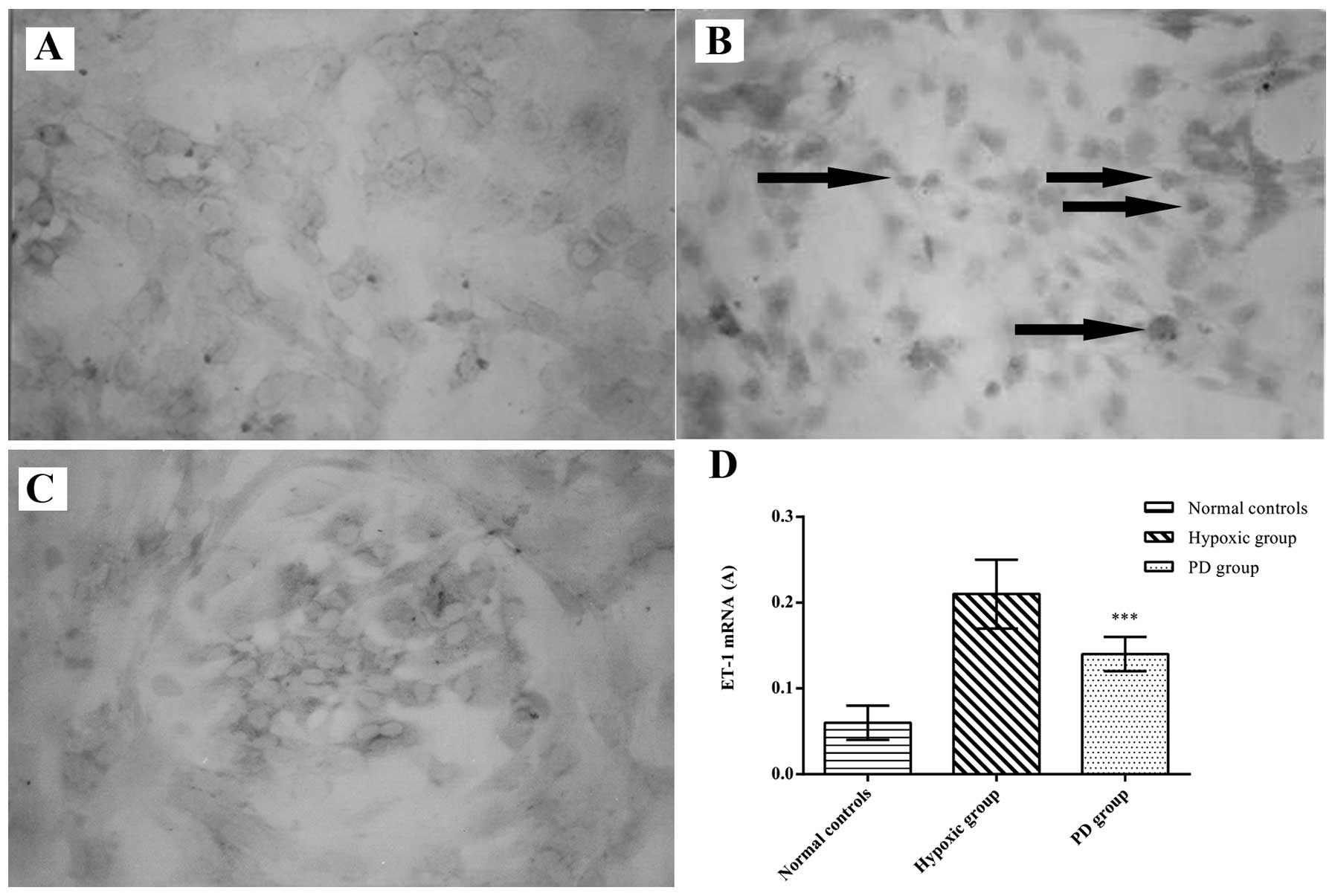
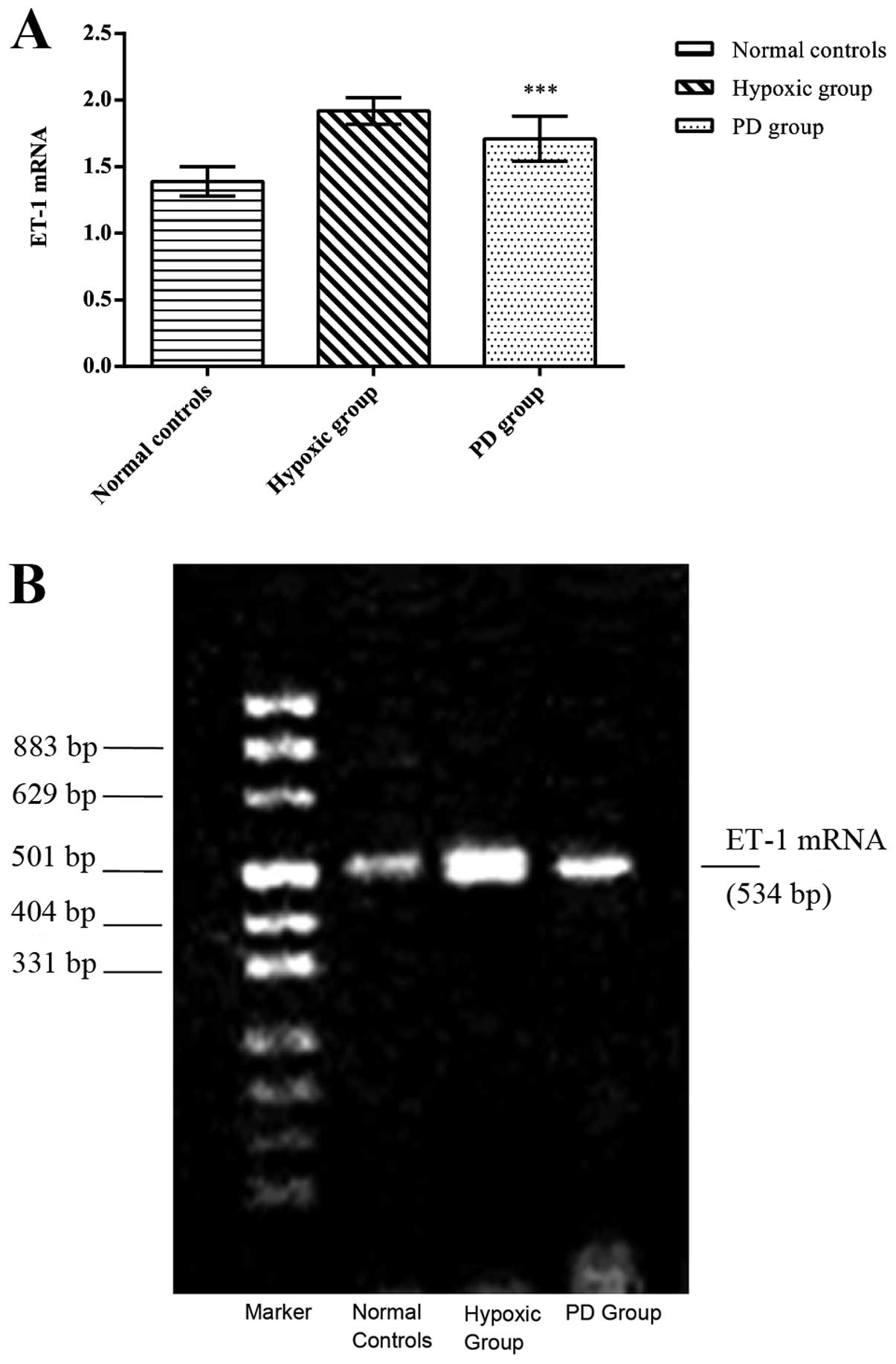
|
1
|
Shostak HDC, Lemasters JJ, Edgell CJ, et
al: Role of ICE-like proteases in endothelial cell hypoxic and
reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 231:844–847. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo J, Martinez J, Yin X, et al: Hypoxia
induces angiogenic factors in brain microvascular endothelial
cells. Microvasc Res. 83:138–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faller DV: Endothelial cell responses to
hypoxic stress. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 26:74–84. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lo AC, Chen AY, Hung VK, et al:
Endothelin-1 overexpression leads to further water accumulation and
brain edema after middle cerebral artery occlusion via aquaporin 4
expression in astrocytic end-feet. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
25:998–1011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kourembanas S, Marsden PA, Mcquillan LP,
et al: Hypoxia induced endothelin gene expression and secretion in
cultured human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 88:1054–1060. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fernandez N, Monge L, Garcia-Villalon AL,
et al: Endothelin-1-induced in vitro cerebral venoconstriction is
mediated by endothelin ETA receptors. Eur-J-Pharmacol. 294:483–490.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moldes O, Sobrino T, Blanco M, et al:
Neuroprotection afforded by antagonists of endothelin-1 receptors
in experimental stroke. Neuropharmacology. 63:1279–1285. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maguire JJ, Kuc RE, Doherty AM, et al:
Potency of 155080, an orally active ETA receptor antagonist,
determined for human endothelin receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
26(suppl 3): S362–S364. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagy Z, Vastag M, Kolev K, et al: Human
cerebral microvessel endothelial cell culture as a model system to
study the blood-brain interface in ischemic/hypoxic conditions.
Cell Mol Neurobiol. 25:201–210. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagy Z, Vastag M, Skopal J, et al: Human
brain microvessel endothelial cell culture as a model system to
study vascular factors of ischemic brain. Keio J Med. 45:200–206.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wenbin Wu, Changlin HU and Weixue TANG:
Microvascular endothelial cell culture of Wistar rat cerebral
cortex. Journal of Chongqing Medical University. 27:151–152.
2002.
|
|
12
|
Martinez-Orgado J, Gonzalez R, Alonso MJ,
et al: Endothelial factors and autoregulation during pressure
changes in isolated newborn piglet cerebral arteries. Pediatr-Res.
44:161–167. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Korzeniewski C and Callewaert DM: An
enzyme-release assay for natural cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods.
64:313–320. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel TR, Galbraith S, McAuley MA and
McCulloch J: Endothelin-mediated vascular tone following focal
cerebral ischaemia in the cat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
16:679–687. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goodwin AT, Smolenski RT, Gray CC,
Jayakumar J, Amrani M and Yacoub MH: Role of endogenous endothelin
on coronary reflow after cardioplegic arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 122:1167–1173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, McCarron RM, Golech S, et al:
ET-1- and NO-mediated signal transduction pathway in human brain
capillary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
284:C243–C249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang CZ, Winardi D, Lin CL, et al:
Attenuation of hemolysate-induced cerebrovascular endothelial cell
injury and of production of endothelin-1 and big endothelin-1 by an
endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Surg Neurol. 58:181–187.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schaller BJ: The role of endothelin in
stroke: experimental data and underlying pathophysiology. Arch Med
Sci. 2:1462006.
|
|
19
|
Ergul A: Endothelin-1 and diabetic
complications: focus on the vasculature. Pharmacol Res. 63:477–482.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamashita K, Discher DJ, Hu J, Bishopric
NH and Webster KA: Molecular regulation of the endothelin-1 gene by
hypoxia. Contributions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1, activator
protein-1, GATA-2, AND p300/CBP. J Biol Chem. 276:12645–12653.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moreau P, d’Uscio LV, Shaw S, Takase H,
Barton M and Lüscher TF: Angiotensin II increases tissue endothelin
and induces vascular hypertrophy: reversal by ET(A)-receptor
antagonist. Circulation. 96:1593–1597. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barton M, d’Uscio LV, Shaw S, Meyer P,
Moreau P and Lüscher TF: ET(A) receptor blockade prevents increased
tissue endothelin-1, vascular hypertrophy, and endothelial
dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension.
31:499–504. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lüscher Thomas F and Barton Matthias:
Endothelins and endothelin receptor antagonists: therapeutic
considerations for a novel class of cardiovascular drugs.
Circulation. 102:2434–2440. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Terese PR and Nilsson GE: Endothelin
induced cerebral vasoconstriction in rainbow trout, detected in a
novel in vitro preparation. Neurosci Lett. 325:195–198. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaundal RK, Deshpande TA, Gulati A, et al:
Targeting endothelin receptors for pharmacotherapy of ischemic
stroke: current scenario and future perspectives. Drug Discov
Today. 17:793–804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takasu A, Matsushima S, Takino M, et al:
Effect of an endothelin-1 antagonist, BQ-485, on cerebral oxygen
metabolism after complete global cerebral ischemia in dogs.
Resuscitation. 34:65–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leung JW, Chung SS and Chung SK:
Endothelial endothelin-1 over-expression using receptor tyrosine
kinase tie-1 promoter leads to more severe vascular permeability
and blood brain barrier breakdown after transient middle cerebral
artery occlusion. Brain Res. 1266:121–129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Legos JJ, Lenhard SC, Haimbach RE, et al:
selective ET(A) receptor antagonism: perfusion/diffusion MRI used
to define treatable stroke model, time to treatment and mechanism
of protection. Exp Neurol. 212:53–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khatibi NH, Lee LK, Zhou Y, et al:
Endothelin receptor-A (ETa) inhibition fails to improve neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. Acta Neurochir Suppl.
111:207–212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Danielyan L, Mueller L, Proksch B, et al:
Similar protective effects of BQ-123 and erythropoietin on survival
of neural cells and generation of neurons upon hypoxic injury. Eur
J Cell Biol. 84:907–913. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Doherty AM, Patt WC, Repine J, et al:
Structure-activity relationships of a novel series of orally active
nonpeptide ETA and ETA/B endothelin receptor-selective antagonists.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 26(suppl 3): S358–S361. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Friedrich B, Gerald W and Stephen H:
Defective intracellular calcium handling in monocrotaline-induced
right ventricular hypertrophy: protective effect of long-term
endothelin-A receptor blockade with
2-benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-yl-3-benzyl-4-(4-methoxy-phenyl-)-4-oxobut-2-enoate-sodium
(PD 155080). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 300:442–449. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spiers JP, Kelso EJ, McDermott BJ,
Scholfield CN and Silke B: Endothelin-1 mediated inhibition of the
acetylcholine-activated potassium current from rabbit isolated
atrial cardiomyocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 119:1427–1437. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wanecek M, Oldner A, Sundin P, Alving K,
Weitzberg E and Rudehill A: Effects on haemodynamics by selective
endothelin ET(B) receptor and combined endothelin ET(A)/ET(B)
receptor antagonism during endotoxin shock. Eur J Pharmacol.
386:235–245. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Potter GS, Johnson RJ and Fink GD: Role of
endothelin in hypertension of experimental chronic renal failure.
Hypertension. 30:1578–1584. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|