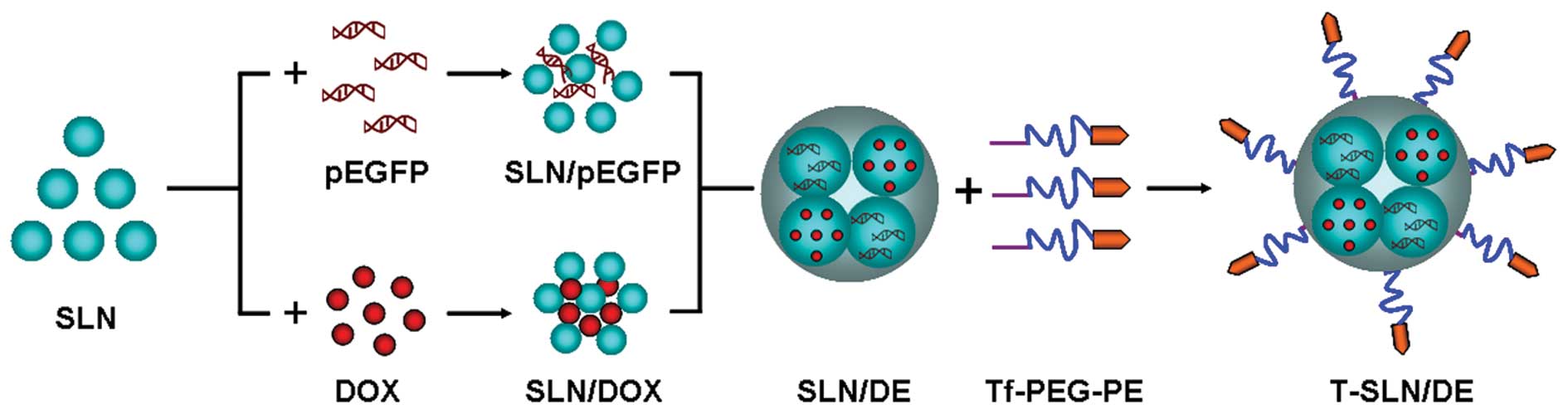
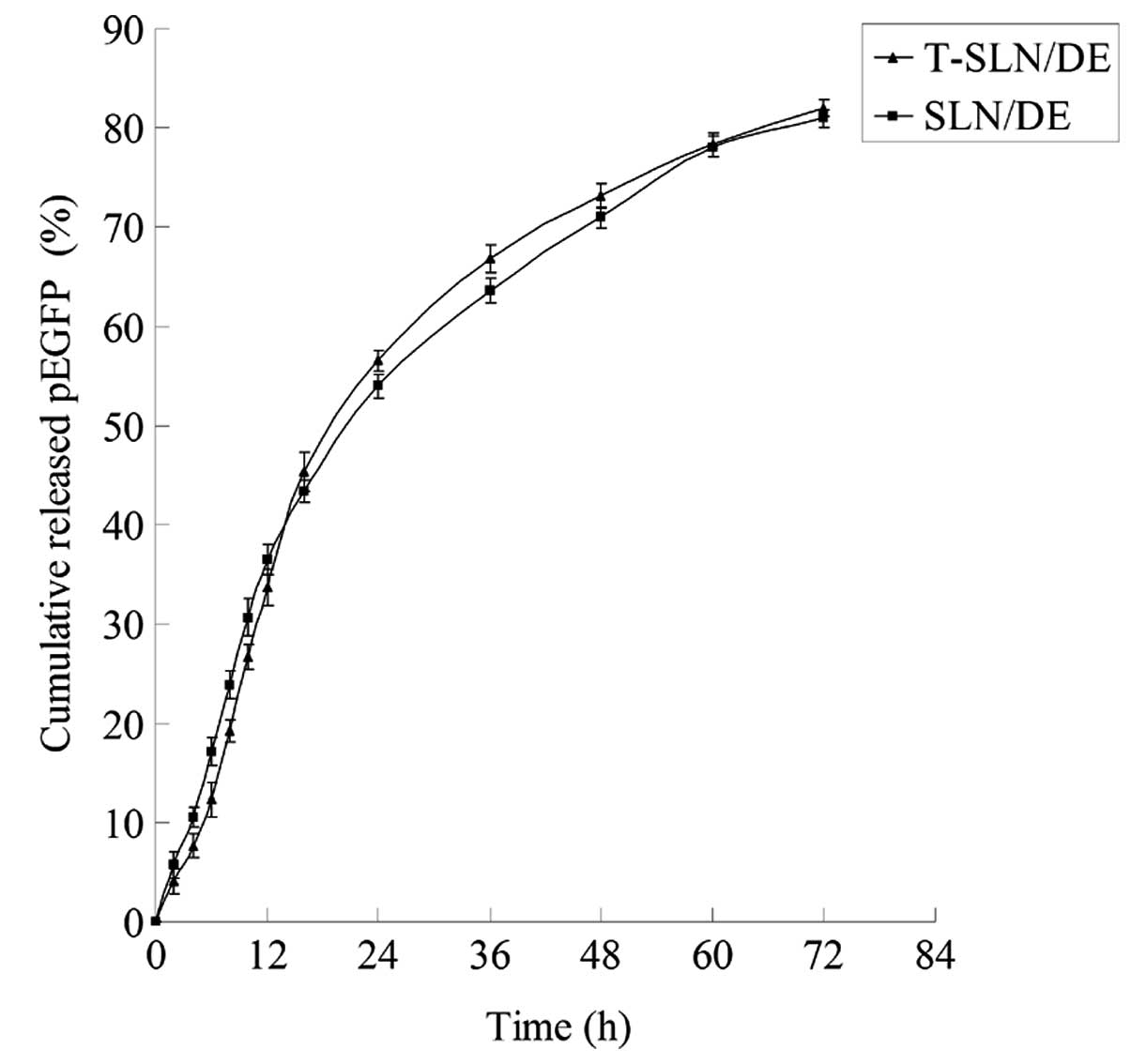
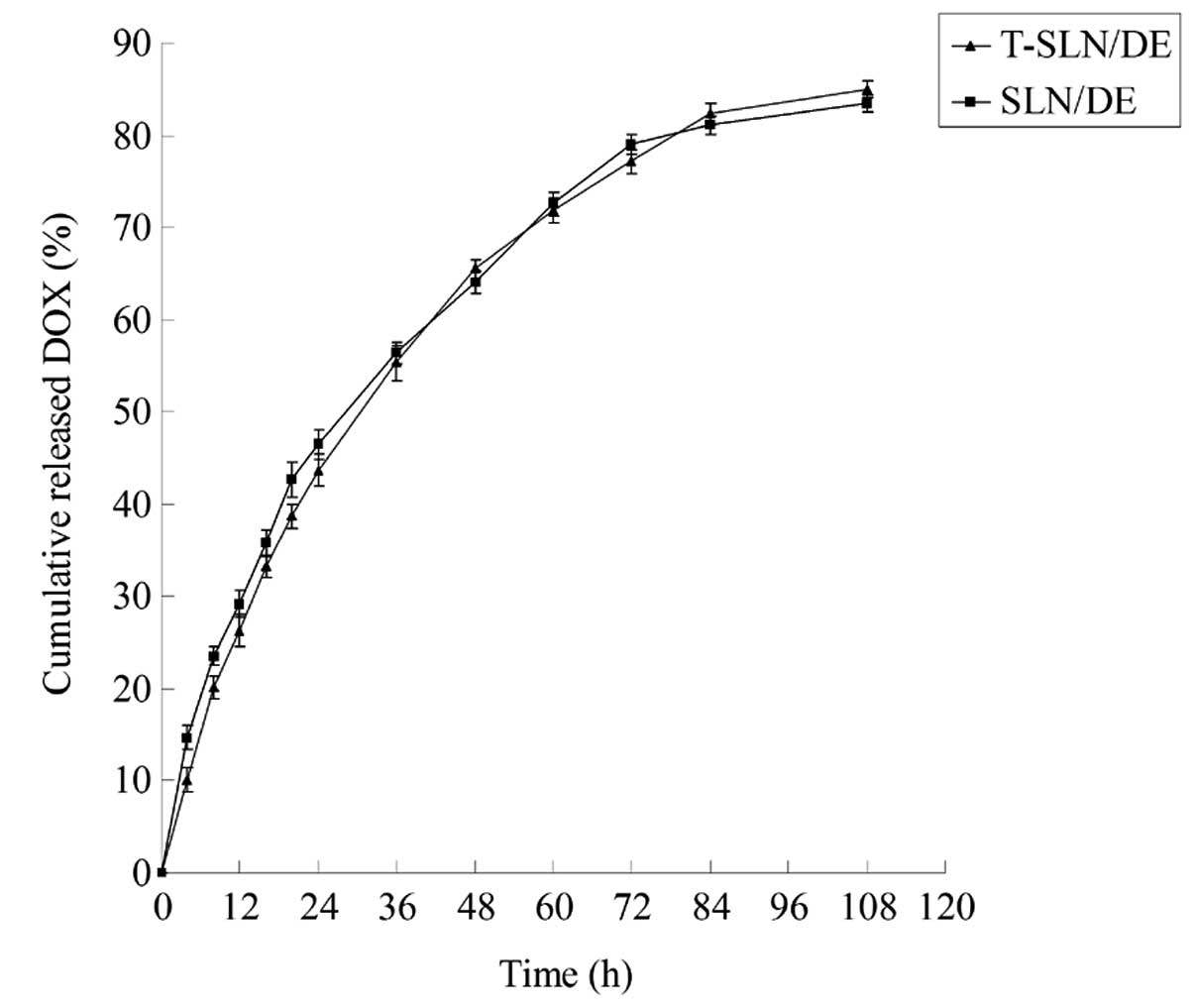
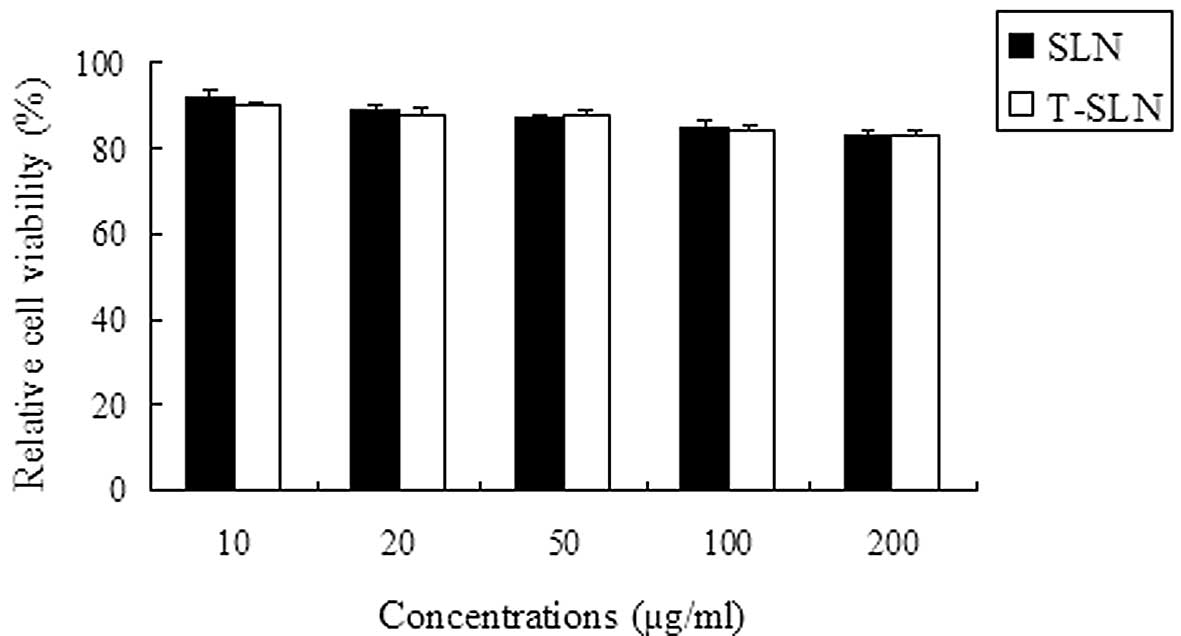
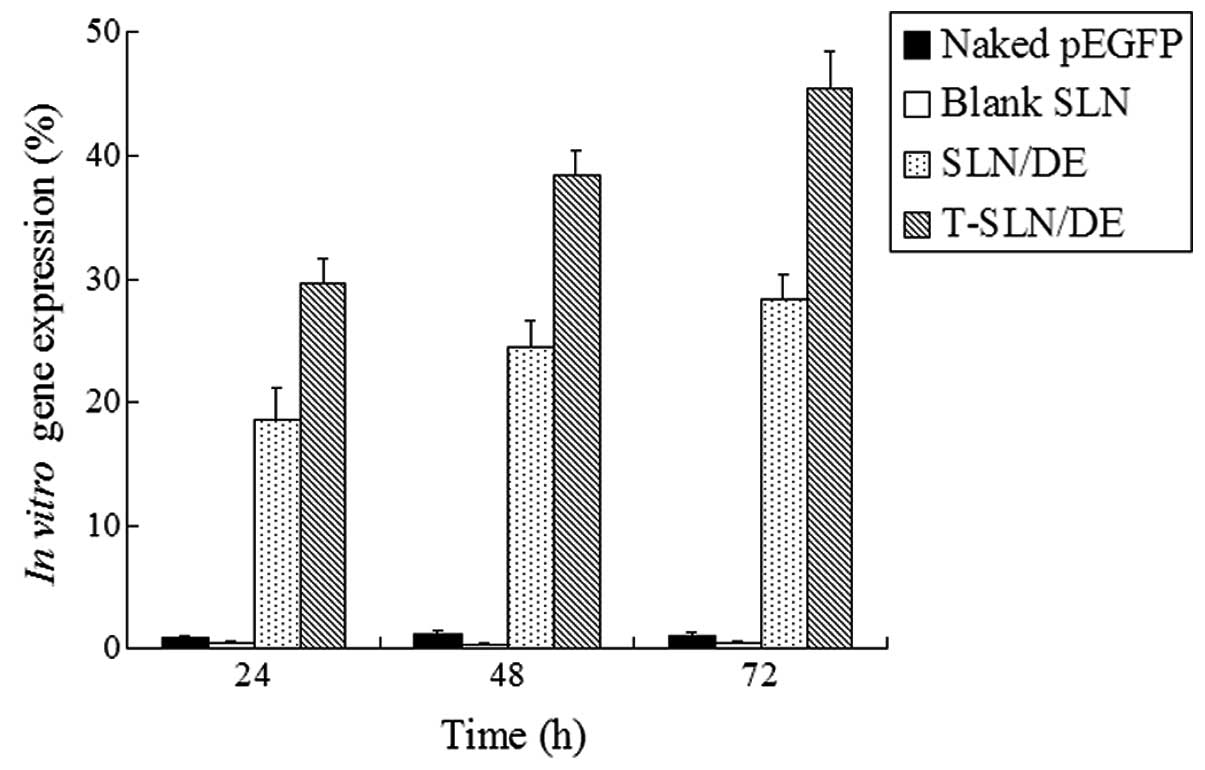
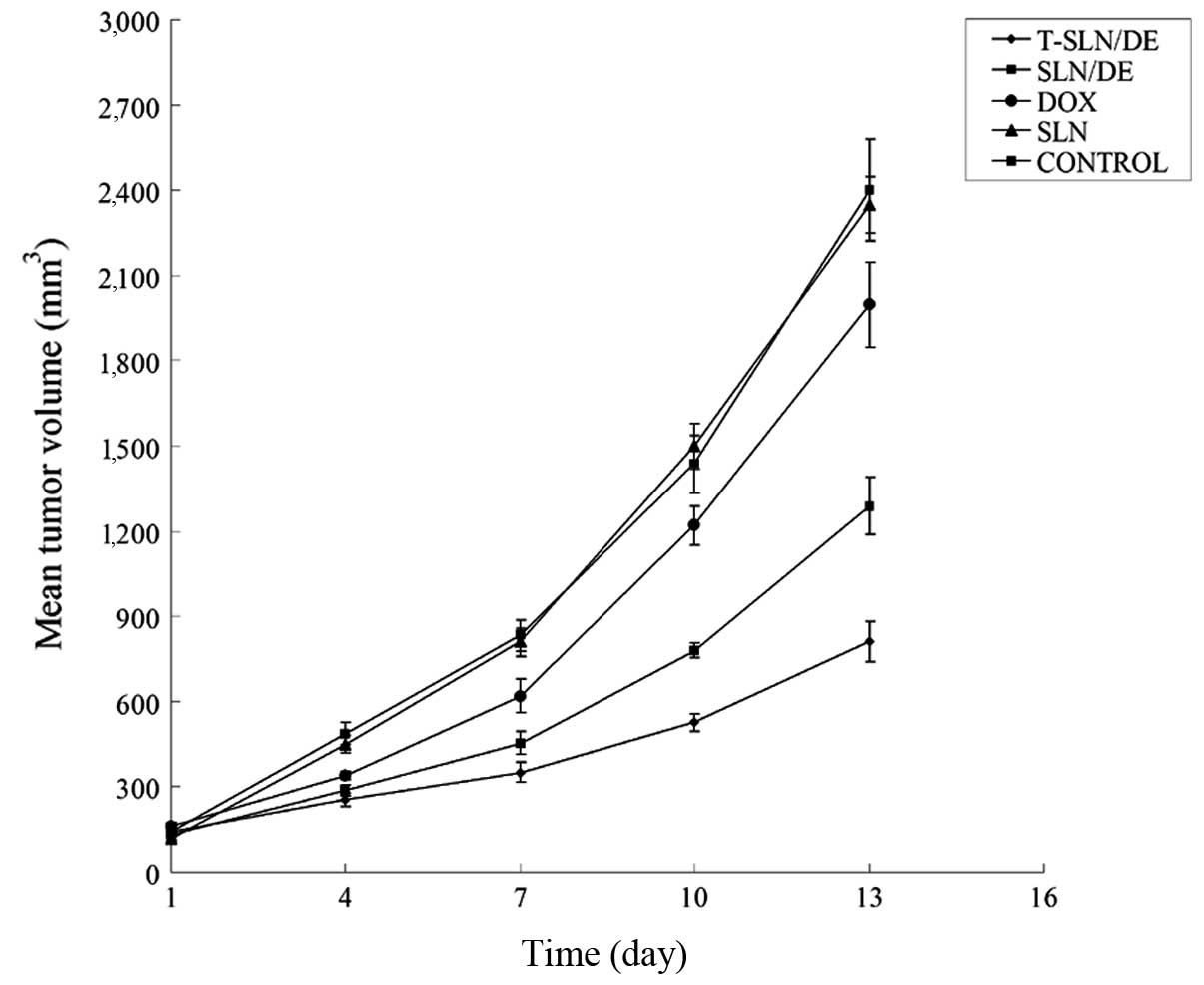
|
1
|
Shepherd FA, Bunn PA and Paz-Ares L: Lung
cancer in 2013: state of the art therapy for metastatic disease. Am
Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 339–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sundaram S, Trivedi R, Durairaj C, Ramesh
R, Ambati BK and Kompella UB: Targeted drug and gene delivery
systems for lung cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7299–7308.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jamel A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kawabata A, Baoum A, Ohta N, Jacquez S,
Seo GM, Berkland C and Tamura M: Intratracheal administration of a
nanoparticle-based therapy with the angiotensin II type 2 receptor
gene attenuates lung cancer growth. Cancer Res. 72:2057–2067. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bajelan E, Haeri A, Vali AM, Ostad SN and
Dadashzadeh S: Co-delivery of doxorubicin and PSC 833 (Valspodar)
by stealth nanoliposomes for efficient overcoming of multidrug
resistance. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 15:568–582. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brannon-Peppas L and Blanchette JO:
Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 56:1649–1659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gottesman MM, Fojo T and Bates SE:
Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu C, Liu F, Feng L, Li M, Zhang J and
Zhang N: The targeted co-delivery of DNA and doxorubicin to tumor
cells via multifunctional PEI-PEG based nanoparticles.
Biomaterials. 34:2547–2564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng C, Zheng M, Gong P, Deng J, Yi H,
Zhang P, Zhang Y, Liu P, Ma Y and Cai L: Polypeptide cationic
micelles mediated co-delivery of docetaxel and siRNA for
synergistic tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 34:3431–3438. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loh XJ, Ong SJ, Tung YT and Choo HT:
Co-delivery of drug and DNA from cationic dual-responsive micelles
derived from poly(DMAEMA-co-PPGMA). Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol
Appl. 33:4545–4550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao J, Mi Y and Feng SS: Targeted
co-delivery of docetaxel and siPlk1 by herceptin-conjugated vitamin
E TPGS based immunomicelles. Biomaterials. 34:3411–3421. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shim G, Han SE, Yu YH, et al: Trilysinoyl
oleylamide-based cationic liposomes for systemic co-delivery of
siRNA and an anticancer drug. J Control Release. 155:60–66. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Z, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Chen L, Lin L and
Li Y: The characteristics and performance of a multifunctional
nanoassembly system for the co-delivery of docetaxel and iSur-pDNA
in a mouse hepatocellular carcinoma model. Biomaterials.
31:916–922. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu B, Ji M, Song X, et al: Co-delivery of
docetaxel and endostatin by a biodegradable nanoparticle for the
synergistic treatment of cervical cancer. Nanoscale Res Lett.
7:6662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaneshiro TL and Lu ZR: Targeted
intracellular codelivery of chemotherapeutics and nucleic acid with
a well-defined dendrimer-based nanoglobular carrier. Biomaterials.
30:5660–5666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang Z, Sun C, Yin Z, Zhou F, Ge L, Liu X
and Kong F: Comparison of two kinds of nanomedicine for targeted
gene therapy: premodified or postmodified gene delivery systems.
Int J Nanomedicine. 7:2019–2031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Zhou F, Ge L, Liu X and Kong F:
Transferrin-PEG-PE modified dexamethasone conjugated cationic lipid
carrier mediated gene delivery system for tumor-targeted
transfection. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:2513–2522. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Kong F, Ge L, Liu X, Huang N and Zhou F:
Mannan-modified PLGA nanoparticles for targeted gene delivery. Int
J Photoenergy. 2012:9267542012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kong F, Zhou F, Ge L, Liu X and Wang Y:
Mannosylated liposomes for targeted gene delivery. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:1079–1089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Olbrich C, Bakowsky U, Lehr CM, Müller RH
and Kneuer C: Cationic solid-lipid nanoparticles can efficiently
bind and transfect plasmid DNA. J Control Release. 77:345–355.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vighi E, Ruozi B, Montanari M, Battini R
and Leo E: Re-dispersible cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs)
freeze-dried without cryoprotectors: characterization and ability
to bind the pEGFP-plasmid. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 67:320–328. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bellocq NC, Pun SH, Jensen GS and Davis
ME: Transferrin-containing, cyclodextrin polymer-based particles
for tumor-targeted gene delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 14:1122–1132.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H and Qian ZM: Transferrin/transferrin
receptor-mediated drug delivery. Med Res Rev. 22:225–250. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maruyama K: Intracellular targeting
delivery of liposomal drugs to solid tumors based on EPR effects.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 63:161–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torchilin VP: Multifunctional
nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 58:1532–1555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Torchilin VP: Recent advances with
liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
4:145–160. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lukyanov AN, Gao Z, Mazzola L and
Torchilin VP: Polyethylene glycol-diacyllipid micelles demonstrate
increased acculumation in subcutaneous tumors in mice. Pharm Res.
19:1424–1429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miao J, Du YZ, Yuan H, Zhang XG and Hu FQ:
Drug resistance reversal activity of anticancer drug loaded solid
lipid nanoparticles in multi-drug resistant cancer cells. Colloids
Surf B Biointerfaces. 110:74–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao X, Wang B, Wei X, et al: Preparation,
characterization and application of star-shaped PCL/PEG micelles
for the delivery of doxorubicin in the treatment of colon cancer.
Int J Nanomedicine. 8:971–982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Men K, Liu W, Li L, et al: Delivering
instilled hydrophobic drug to the bladder by a cationic
nanoparticle and thermo-sensitive hydrogel composite system.
Nanoscale. 4:6425–6433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang BL, Gao X, Men K, et al: Treating
acute cystitis with biodegradable micelle-encapsulated quercetin.
Int J Nanomedicine. 7:2239–2247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li P, Liu D, Miao L, Liu C, Sun X, Liu Y
and Zhang N: A pH-sensitive multifunctional gene carrier assembled
via layer-by-layer technique for efficient gene delivery. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:925–939. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jia Y, Yuan M, Yuan H, et al:
Co-encapsulation of magnetic Fe3O4
nanoparticles and doxorubicin into biodegradable PLGA nanocarriers
for intratumoral drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:1697–1708.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He SN, Li YL, Yan JJ, Zhang W, Du YZ, Yu
HY, Hu FQ and Yuan H: Ternary nanoparticles composed of cationic
solid lipid nanoparticles, protamine, and DNA for gene delivery.
Int J Nanomedicine. 8:2859–2869. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mehnert W and Mäder K: Solid lipid
nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 47:165–196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Singh M: Transferrin as a targeting ligand
for liposomes and anticancer drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 5:443–451.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|