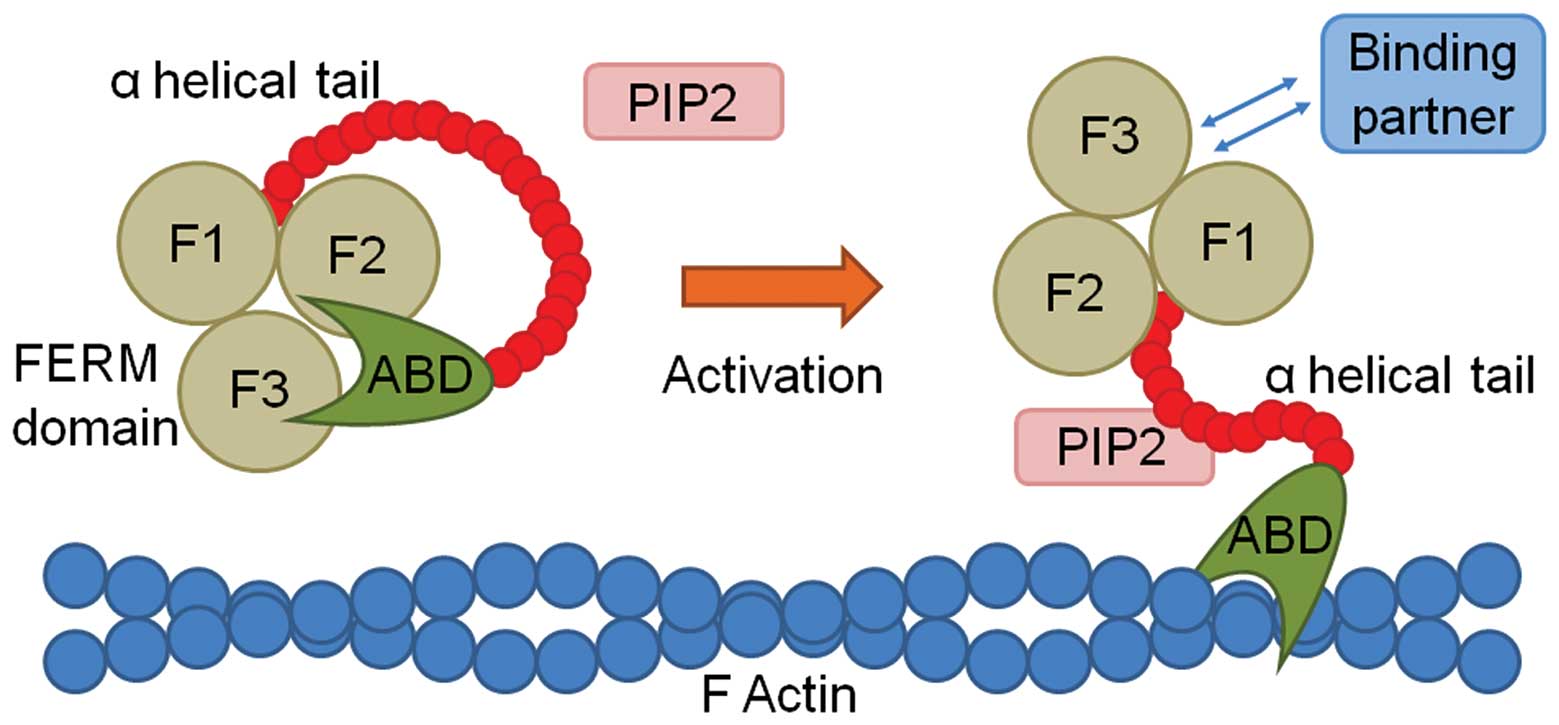
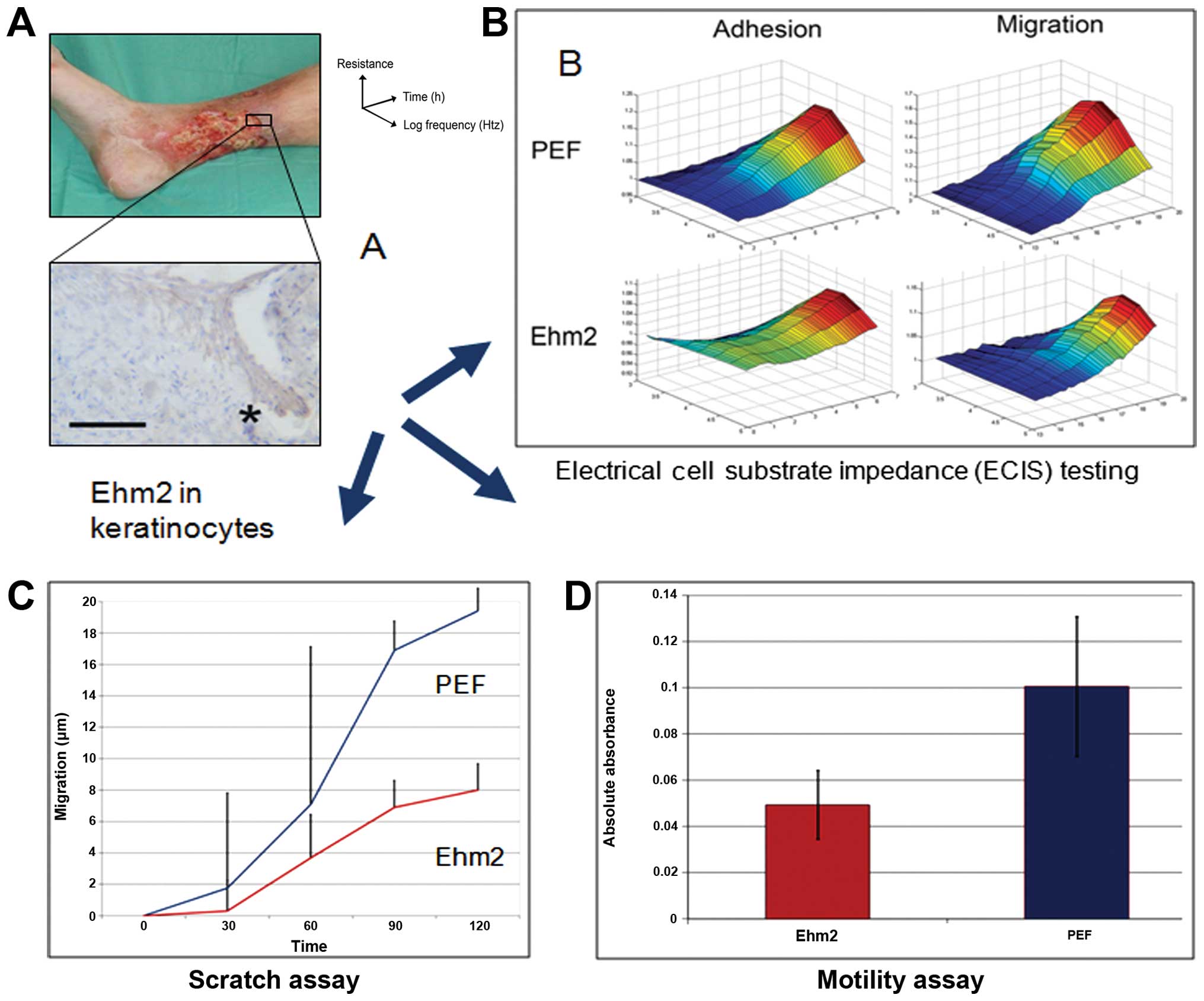
|
1
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van ’t Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mehlen P and Puisieux A: Metastasis: a
question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:449–458. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arnoux V, Come C, Kusewitt D, Hudson L and
Savagner P: Cutaneous Wound Reepithelializaton: A partial and
reversible EMT. Rise and Fall of Epithelial Phenotype: Concepts of
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Savagner P: Springer; Berlin:
pp. 111–134. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yan CL, Grimm WA, Garner WL, et al:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human skin wound healing is
induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha through bone morphogenic
protein-2. Am J Pathol. 176:2247–2258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Virchow R: Aetiologie der neoplastischen
Geschwulste/ Pathogenie der neoplastischen Geschwulste. Die
Krankhaften Geschwülste. Verlag von August Hirschwald; Berlin: pp.
57–101. 1863
|
|
7
|
Dolberg DS, Hollingsworth R, Hertle M and
Bissell MJ: Wounding and its role in RSV-mediated tumor formation.
Science. 230:676–678. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Martinsgreen M, Boudreau N and Bissell MJ:
Inflammation is responsible for the development of wound-induced
tumors in chickens infected with Rous sarcoma virus. Cancer Res.
54:4334–4341. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dvorak HF: Tumors: wounds that do not
heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound
healing. N Engl J Med. 315:1650–1659. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schafer M and Werner S: Cancer as an
overhealing wound: an old hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Bio. 9:628–638. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Antsiferova M and Werner S: The bright and
the dark sides of activin in wound healing and cancer. J Cell Sci.
125:3929–3937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grose R: Common ground in the
transcriptional profiles of wounds and tumors. Genome Biol.
5:2282004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pedersen TX, Leethanakul C, Patel V, et
al: Laser capture microdissection-based in vivo genomic profiling
of wound keratinocytes identifies similarities and differences to
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 22:3964–3976. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang HY, Sneddon JB, Alizadeh AA, et al:
Gene expression signature of fibroblast serum response predicts
human cancer progression: similarities between tumors and wounds.
PLoS Biol. 2:72004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Eming SA, Brachvogel B, Odorisio T and
Koch M: Regulation of angiogenesis: wound healing as a model. Prog
Histochem Cytochem. 42:115–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Midwood KS, Williams LV and Schwarzbauer
JE: Tissue repair and the dynamics of the extracellular matrix. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:1031–1037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martin P: Wound healing--aiming for
perfect skin regeneration. Science. 276:75–81. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pollard TD and Borisy GG: Cellular
motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments.
Cell. 112:453–465. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mellman I and Nelson WJ: Coordinated
protein sorting, targeting and distribution in polarized cells. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:833–845. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Small JV, Stradal T, Vignal E and Rottner
K: The lamellipodium: where motility begins. Trends Cell Biol.
12:112–120. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bugyi B and Carlier MF: Control of actin
filament treadmilling in cell motility. Annu Rev Biophys.
39:449–470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
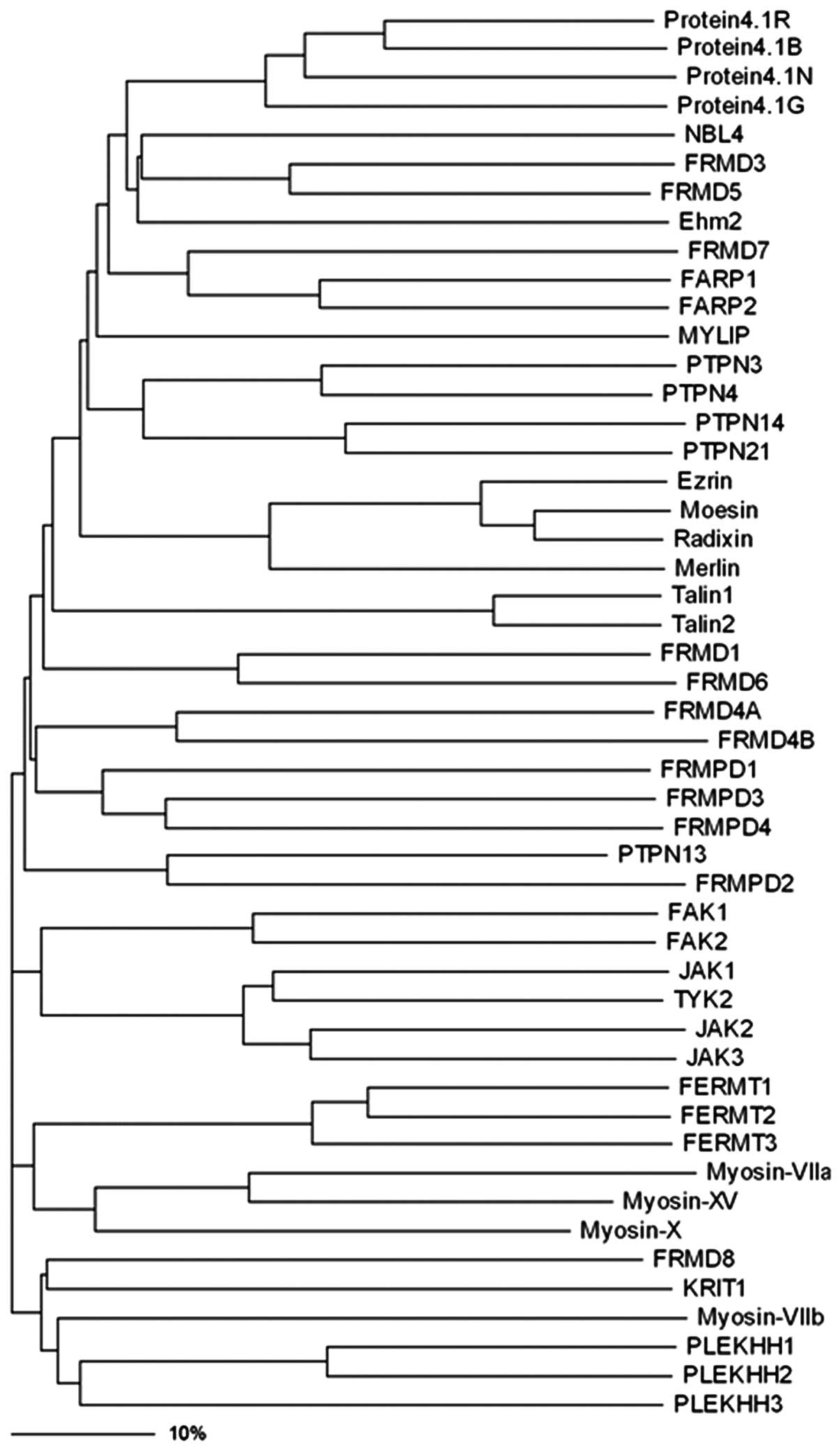
Yu H, Zhang Y, Ye L and Jiang WG: The FERM
family proteins in cancer invasion and metastasis. Frontiers in
bioscience: a journal and virtual library. 16:1536–1550. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chishti AH, Kim AC, Marfatia SM, et al:
The FERM domain: a unique module involved in the linkage of
cytoplasmic proteins to the membrane. Trends Biochem Sci.
23:281–282. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leto TL and Marchesi VT: A structural
model of human erythrocyte protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 259:4603–4608.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tyler JM, Hargreaves WR and Branton D:
Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and
electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation
between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
76:5192–5196. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shiffer KA and Goodman SR: Protein 4.1:
its association with the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 81:4404–4408. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bretscher A: Purification of the
intestinal microvillus cytoskeletal proteins villin, fimbrin, and
ezrin. Methods Enzymol. 134:24–37. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsukita S and Hieda Y: A new 82-kD barbed
end-capping protein (radixin) localized in the cell-to-cell
adherens junction: purification and characterization. J Cell Biol.
108:2369–2382. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lankes WT and Furthmayr H: Moesin: a
member of the protein 4.1-talin-ezrin family of proteins. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 88:8297–8301. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Singhrao SK, et al:
Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation and translocation of ezrin by
hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 217:1062–1069. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun CX, Robb VA and Gutmann DH: Protein
4.1 tumor suppressors: getting a FERM grip on growth regulation. J
Cell Sci. 115:3991–4000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takeuchi K, Kawashima A, Nagafuchi A and
Tsukita S: Structural diversity of band 4.1 superfamily members. J
Cell Sci. 107:1921–1928. 1994.
|
|
33
|
Conboy J, Kan YW, Shohet SB and Mohandas
N: Molecular cloning of protein 4.1, a major structural element of
the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
83:9512–9516. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smith WJ, Nassar N, Bretscher A, Cerione
RA and Karplus PA: Structure of the active N-terminal domain of
Ezrin. Conformational and mobility changes identify keystone
interactions. J Biol Chem. 278:4949–4956. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shimizu T, Seto A, Maita N, Hamada K,
Tsukita S and Hakoshima T: Structural basis for neurofibromatosis
type 2. Crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain. J Biol Chem.
277:10332–10336. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pearson MA, Reczek D, Bretscher A and
Karplus PA: Structure of the ERM protein moesin reveals the FERM
domain fold masked by an extended actin binding tail domain. Cell.
101:259–270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gautreau A, Louvard D and Arpin M: ERM
proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical
actin organization and cell growth signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
14:104–109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bretscher A: Purification of an
80,000-dalton protein that is a component of the isolated
microvillus cytoskeleton, and its localization in nonmuscle cells.
J Cell Biol. 97:425–432. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Franck Z, Gary R and Bretscher A: Moesin,
like ezrin, colocalizes with actin in the cortical cytoskeleton in
cultured cells, but its expression is more variable. J Cell Sci.
105:219–231. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sato N, Funayama N, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura
S and Tsukita S and Tsukita S: A gene family consisting of ezrin,
radixin and moesin. Its specific localization at actin
filament/plasma membrane association sites. J Cell Sci.
103:131–143. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Louvet-Vallee S: ERM proteins: From
cellular architecture to cell signaling. Biol Cell. 92:305–316.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nowak D, Mazur AJ, Popow-Wozniak A,
Radwanska A, Mannherz HG and Malicka-Blaszkiewicz M: Subcellular
distribution and expression of cofilin and ezrin in human colon
adenocarcinoma cell lines with different metastatic potential. Eur
J Histochem. 54:142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sarrio D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Dotor A,
Calero F, Hardisson D and Palacios J: Abnormal ezrin localization
is associated with clinicopathological features in invasive breast
carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Tr. 98:71–79. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lankes W, Griesmacher A, Grunwald J,
Schwartzalbiez R and Keller R: A heparin-binding protein involved
in inhibition of smooth-muscle cell proliferation. Biochem J.
251:831–842. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Amieva MR and Furthmayr H: Subcellular
localization of moesin in dynamic filopodia, retraction fibers, and
other structures involved in substrate exploration, attachment, and
cell-cell contacts. Exp Cell Res. 219:180–196. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lallemand D and Arpin M: Moesin/ezrin: a
specific role in cell metastasis? Pigm Cell Melanoma Res. 23:6–7.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He M, Cheng Y, Li W, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor C promotes cervical cancer metastasis via
up-regulation and activation of RhoA/ROCK-2/moesin cascade. BMC
Cancer. 10:2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Amieva MR, Wilgenbus KK and Furthmayr H:
Radixin is a component of hepatocyte microvilli in situ. Exp Cell
Res. 210:140–144. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hamada K, Shimizu T, Matsui T, Tsukita S
and Hakoshima T: Structural basis of the membrane-targeting and
unmasking mechanisms of the radixin FERM domain. Embo J.
19:4449–4462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Loebrich S, Bahring R, Katsuno T, Tsukita
S and Kneussel M: Activated radixin is essential for GABAA receptor
alpha5 subunit anchoring at the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO J.
25:987–999. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Elliott BE, Meens JA, SenGupta SK, Louvard
D and Arpin M: The membrane cytoskeletal crosslinker ezrin is
required for metastasis of breast carcinoma cells. Breast Cancer
Research. 7:365–373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Khanna C, Wan XL, Bose S, et al: The
membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma
metastasis. Nat Med. 10:182–186. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu YL, Khan J, Khanna C, Helman L, Meltzer
PS and Merlino G: Expression profiling identifies the cytoskeletal
organizer ezrin and the developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key
metastatic regulators. Nat Med. 10:175–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kang YK, Hong SW, Lee H and Kim WH:
Prognostic implications of ezrin expression in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 49:798–804. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Deng XY, Tannehill-Gregg SH, Nadella MVP,
et al: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and ezrin are
up-regulated in human lung cancer bone metastases. Clin Exp
Metastas. 24:107–119. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Meng YX, Lu ZH, Yu SN, Zhang QA, Ma YH and
Chen J: Ezrin promotes invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
cells. J Transl Med. 8:2010.
|
|
57
|
Federici C, Brambilla D, Lozupone F, et
al: Pleiotropic function of ezrin in human metastatic melanomas.
Int J Cancer. 124:2804–2812. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou BB, Leng J, Hu M, et al: Ezrin is a
key molecule in the metastasis of MOLT4 cells induced by
CCL25/CCR9. Leuk Res. 34:769–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Morales FC, Molina JR, Hayashi Y and
Georgescu MM: Overexpression of ezrin inactivates NF2 tumor
suppressor in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 12:528–539. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cui YZ, Wu JM, Zong MJ, et al: Proteomic
profiling in pancreatic cancer with and without lymph node
metastasis. Int J Cancer. 124:1614–1621. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Estecha A, Sanchez-Martin L, Puig-Kroger
A, et al: Moesin orchestrates cortical polarity of melanoma tumour
cells to initiate 3D invasion. J Cell Sci. 122:3492–3501. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jensen PV and Larsson LI: Actin
microdomains on endothelial cells: association with CD44, ERM
proteins, and signaling molecules during quiescence and wound
healing. Histochem Cell Biol. 121:361–369. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ng T, Parsons M, Hughes WE, et al: Ezrin
is a downstream effector of trafficking PKC-integrin complexes
involved in the control of cell motility. EMBO J. 20:2723–2741.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Haas MA, Vickers JC and Dickson TC:
Binding partners L1 cell adhesion molecule and the
ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins are involved in development and
the regenerative response to injury of hippocampal and cortical
neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 20:1436–1444. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Haas MA, Vickers JC and Dickson TC: Rho
kinase activates ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins and mediates
their function in cortical neuron growth, morphology and motility
in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 85:34–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tsuda M, Makino Y, Iwahara T, et al: Crk
associates with ERM proteins and promotes cell motility toward
hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 279:46843–46850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Crepaldi T, Gautreau A, Comoglio PM,
Louvard D and Arpin M: Ezrin is an effector of hepatocyte growth
factor-mediated migration and morphogenesis in epithelial cells. J
Cell Biol. 138:423–434. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hashimoto S, Amaya F, Matsuyama H, et al:
Dysregulation of lung injury and repair in moesin-deficient mice
treated with intratracheal bleomycin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 295:L566–L574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Okayama T, Kikuchi S, Ochiai T, et al:
Attenuated response to liver injury in moesin-deficient mice:
impaired stellate cell migration and decreased fibrosis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1782:542–548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Takakuwa Y: Regulation of red cell
membrane protein interactions: implications for red cell function.
Curr Opin Hematol. 8:80–84. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Holzwarth G, Yu J and Steck TL:
Heterogeneity in the conformation of different protein fractions
from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Supramol Struct. 4:161–168.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Diakowski W, Grzybek M and Sikorski AF:
Protein 4.1, a component of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton and
its related homologue proteins forming the protein 4.1/FERM
superfamily. Folia Histochem Cyto. 44:231–248. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mattagajasingh SN, Huang SC, Hartenstein
JS and Benz EJ: Characterization of the interaction between protein
4.1R and ZO-2. A possible link between the tight junction and the
actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 275:30573–30585. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Yamakawa H, Ohara R, Nakajima D, Nakayama
M and Ohara O: Molecular characterization of a new member of the
protein 4.1 family (brain 4.1) in rat brain. Mol Brain Res. 74:247.
1999.
|
|
75
|
Tchernia G, Mohandas N and Shohet SB:
Deficiency of skeletal membrane protein band 4.1 in homozygous
hereditary elliptocytosis. Implications for erythrocyte membrane
stability. J Clin Invest. 68:454–460. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Shi ZT, Afzal V, Coller B, et al: Protein
4.1R-deficient mice are viable but have erythroid membrane skeleton
abnormalities. J Clin Invest. 103:331–340. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Salomao M, Zhang XH, Yang Y, et al:
Protein 4.1R-dependent multiprotein complex: New insights into the
structural organization of the red blood cell membrane. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:8026–8031. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Nunomura W and Takakuwa Y: Regulation of
protein 4.1R interactions with membrane proteins by Ca2+ and
calmodulin. Front Biosci. 11:1522–1539. 2006.
|
|
79
|
Pinder JC, Gardner B and Gratzer WB:
Interaction of protein 4.1 with the red cell membrane: effects of
phosphorylation by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
210:478–482. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Horne WC, Prinz WC and Tang EK:
Identification of two cAMP-dependent phosphorylation sites on
erythrocyte protein 4.1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1055:87–92. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Eder PS, Soong CJ and Tao M:
Phosphorylation reduces the affinity of protein 4.1 for spectrin.
Biochemistry. 25:1764–1770. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Krauss SW, Larabell CA, Lockett S, et al:
Structural protein 4.1 in the nucleus of human cells: dynamic
rearrangements during cell division. J Cell Biol. 137:275–289.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mattagajasingh SN, Huang SC, Hartenstein
JS, Snyder M, Marchesi VT and Benz EJ: A nonerythroid isoform of
protein 4.1R interacts with the nuclear mitotic apparatus (NuMA)
protein. J Cell Biol. 145:29–43. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Perez-Ferreiro CM, Luque CM and Correas I:
4.1R proteins associate with interphase microtubules in human T
cells: a 4.1R constitutive region is involved in tubulin binding. J
Biol Chem. 276:44785–44791. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Krauss SW, Heald R, Lee G, et al: Two
distinct domains of protein 4.1 critical for assembly of functional
nuclei in vitro. J Biol Chem. 277:44339–44346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yang SM, Guo XH, Debnath G, Mohandas N and
An XL: Protein 4.1R links E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to the
cytoskeleton through its direct interaction with beta-catenin and
modulates adherens junction integrity. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1788:1458–1465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chen L, Hughes RA, Baines AJ, Conboy J,
Mohandas N and An X: Protein 4.1R regulates cell adhesion,
spreading, migration and motility of mouse keratinocytes by
modulating surface expression of beta1 integrin. J Cell Sci.
124:2478–2487. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ruiz-Sáenz A, Kremer L, Alonso MA, Millan
J and Correas I: Protein 4.1R regulates cell migration and IQGAP1
recruitment to the leading edge. J Cell Sci. 124:2529–2538.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hashimoto Y, Shindo-Okada N, Tani M,
Takeuchi K, Toma H and Yokota J: Identification of genes
differentially expressed in association with metastatic potential
of K-1735 murine melanoma by messenger RNA differential display.
Cancer Res. 56:5266–5271. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shimizu K, Nagamachi Y, Tani M, et al:
Molecular cloning of a novel NF2/ERM/4.1 superfamily gene, ehm2,
that is expressed in high-metastatic K1735 murine melanoma cells.
Genomics. 65:113–120. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chauhan S, Pandey R, Way JF, et al:
Androgen regulation of the human FERM domain encoding gene EHM2 in
a cell model of steroid-induced differentiation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 310:421–432. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cress AE and Nagle RB: Cell Adhesion and
Cytoskeletal Molecules in Metastasis. (Series: Cancer Metastasis -
Biology and Treatment). 9. Springer; Dordrecht: 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Hoover KB and Bryant PJ: Drosophila
Yurt is a new protein-4.1-like protein required for epithelial
morphogenesis. Dev Genes Evol. 212:230–238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wang J, Cai Y, Penland R, Chauhan S,
Miesfeld RL and Ittmann M: Increased expression of the
metastasis-associated gene Ehm2 in prostate cancer. Prostate.
66:1641–1652. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Schulz WA, Ingenwerth M, Djuidje CE, Hader
C, Rahnenfuhrer J and Engers R: Changes in cortical cytoskeletal
and extracellular matrix gene expression in prostate cancer are
related to oncogenic ERG deregulation. BMC Cancer. 10:5052010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Dhanasekaran SM, Barrette TR, Ghosh D, et
al: Delineation of prognostic biomarkers in prostate cancer.
Nature. 412:822–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Luo JH, Yu YP, Cieply K, et al: Gene
expression analysis of prostate cancers. Mol Carcinog. 33:25–35.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Luo J, Duggan DJ, Chen Y, et al: Human
prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: molecular
dissection by gene expression profiling. Cancer Res. 61:4683–4688.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yu H, Ye L, Mansel RE, Zhang Y and Jiang
WG: Clinical implications of the influence of Ehm2 on the
aggressiveness of breast cancer cells through regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1501–1512. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Bosanquet DC, Ye L, Harding KG and Jiang
WG: Expressed in high metastatic cells (Ehm2) is a positive
regulator of keratinocyte adhesion and motility: The implication
for wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 71:115–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Reid BJ, Li X, Galipeau PC and Vaughan TL:
Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma: time for a new
synthesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:87–101. 2010.
|
|
102
|
De Minicis S, Marzioni M, Saccomanno S, et
al: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis
leading to liver cancer. Transl Gastrointest Cancer. 1:88–94.
2011.
|
|
103
|
Mountford RA, Brown P, Salmon PR,
Alvarenga C, Neumann CS and Read AE: Gastric cancer detection in
gastric ulcer disease. Gut. 21:9–17. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Jess T, Rungoe C and Peyrin-Biroulet L:
Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a
meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:639–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Malka D, Hammel P, Maire F, et al: Risk of
pancreatic adenocarcinoma in chronic pancreatitis. Gut. 51:849–852.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kerr-Valentic MA, Samimi K, Rohlen BH,
Agarwal JP and Rockwell WB: Marjolin’s ulcer: modern analysis of an
ancient problem. Plast Reconstr Surg. 123:184–191. 2009.
|
|
107
|
Pasternack GR, Anderson RA, Leto TL and
Marchesi VT: Interactions between protein 4.1 and band 3. An
alternative binding site for an element of the membrane skeleton. J
Biol Chem. 260:3676–3683. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Hemming NJ, Anstee DJ, Mawby WJ, Reid ME
and Tanner MJ: Localization of the protein 4.1-binding site on
human erythrocyte glycophorins C and D. Biochem J. 299:191–196.
1994.
|
|
109
|
Marfatia SM, Leu RA, Branton D and Chishti
AH: Identification of the protein 4.1 binding interface on
glycophorin C and p55, a homologue of the Drosophila
discs-large tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem. 270:715–719.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Reczek D, Berryman M and Bretscher A:
Identification of EBP50: A PDZ-containing phosphoprotein that
associates with members of the ezrin-radixin-moesin family. J Cell
Biol. 139:169–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nunomura W, Takakuwa Y, Tokimitsu R,
Krauss SW, Kawashima M and Mohandas N: Regulation of CD44-protein
4.1 interaction by Ca2+ and calmodulin. Implications for
modulation of CD44-ankyrin interaction. J Biol Chem.
272:30322–30328. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Heiska L, Alfthan K, Gronholm M, Vilja P,
Vaheri A and Carpen O: Association of ezrin with intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 and -2 (ICAM-1 and ICAM-2). Regulation by
phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem.
273:21893–21900. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Darmellah A, Rucker-Martin C and Feuvray
D: ERM proteins mediate the effects of Na+/H+
exchanger (NHE1) activation in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res.
81:294–300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Niggli V, Andreoli C, Roy C and Mangeat P:
Identification of a phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate-binding
domain in the N-terminal region of ezrin. FEBS Lett. 376:172–176.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Tanaka T, Kadowaki K, Lazarides E and
Sobue K: Ca2(+)-dependent regulation of the spectrin/actin
interaction by calmodulin and protein 4.1. J Biol Chem.
266:1134–1140. 1991.
|
|
116
|
Weinman EJ, Steplock D, Wade JB and
Shenolikar S: Ezrin binding domain-deficient NHERF attenuates
cAMP-mediated inhibition of Na(+)/H(+) exchange in OK cells. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 281:F374–F380. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|