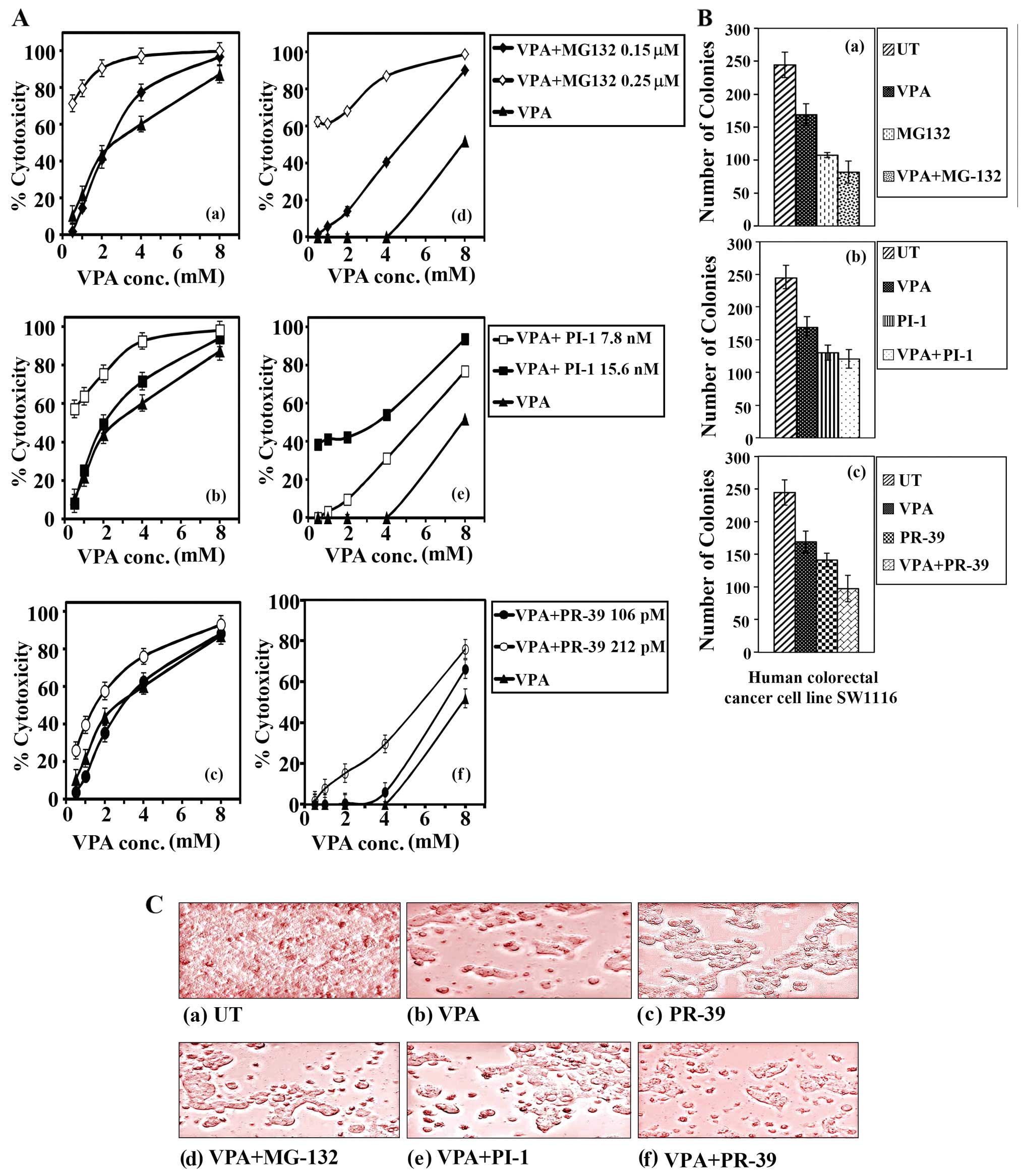
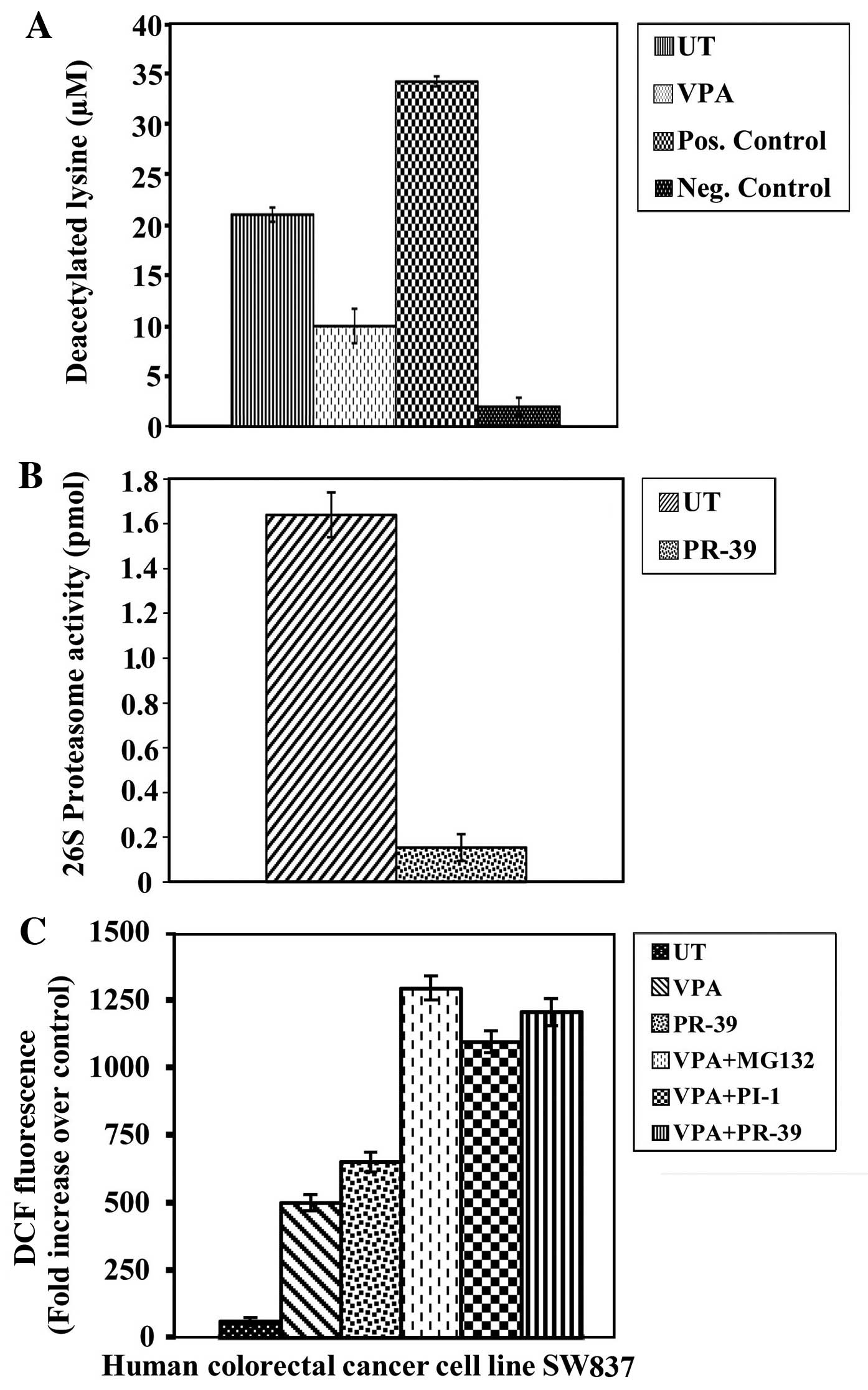
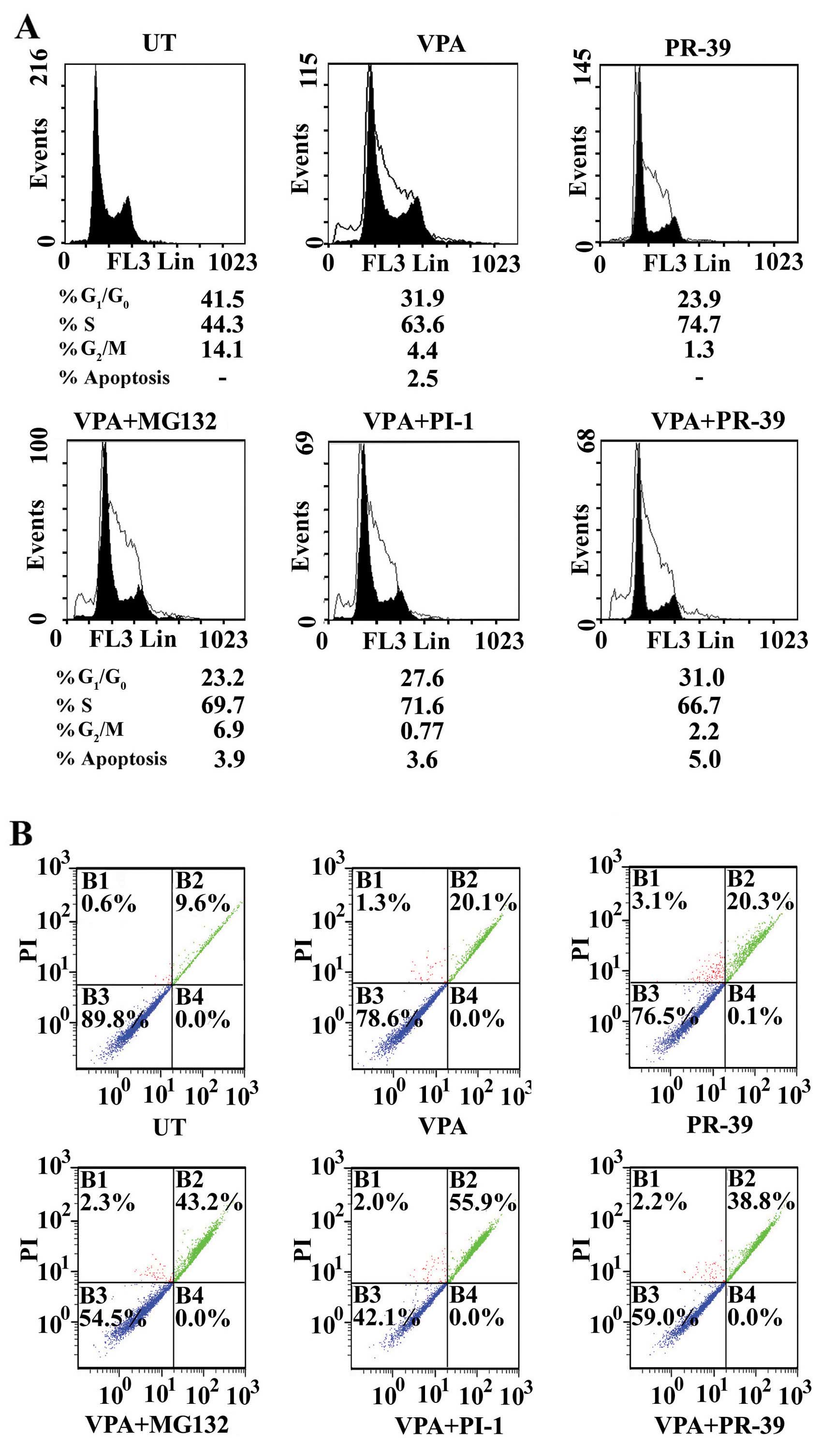
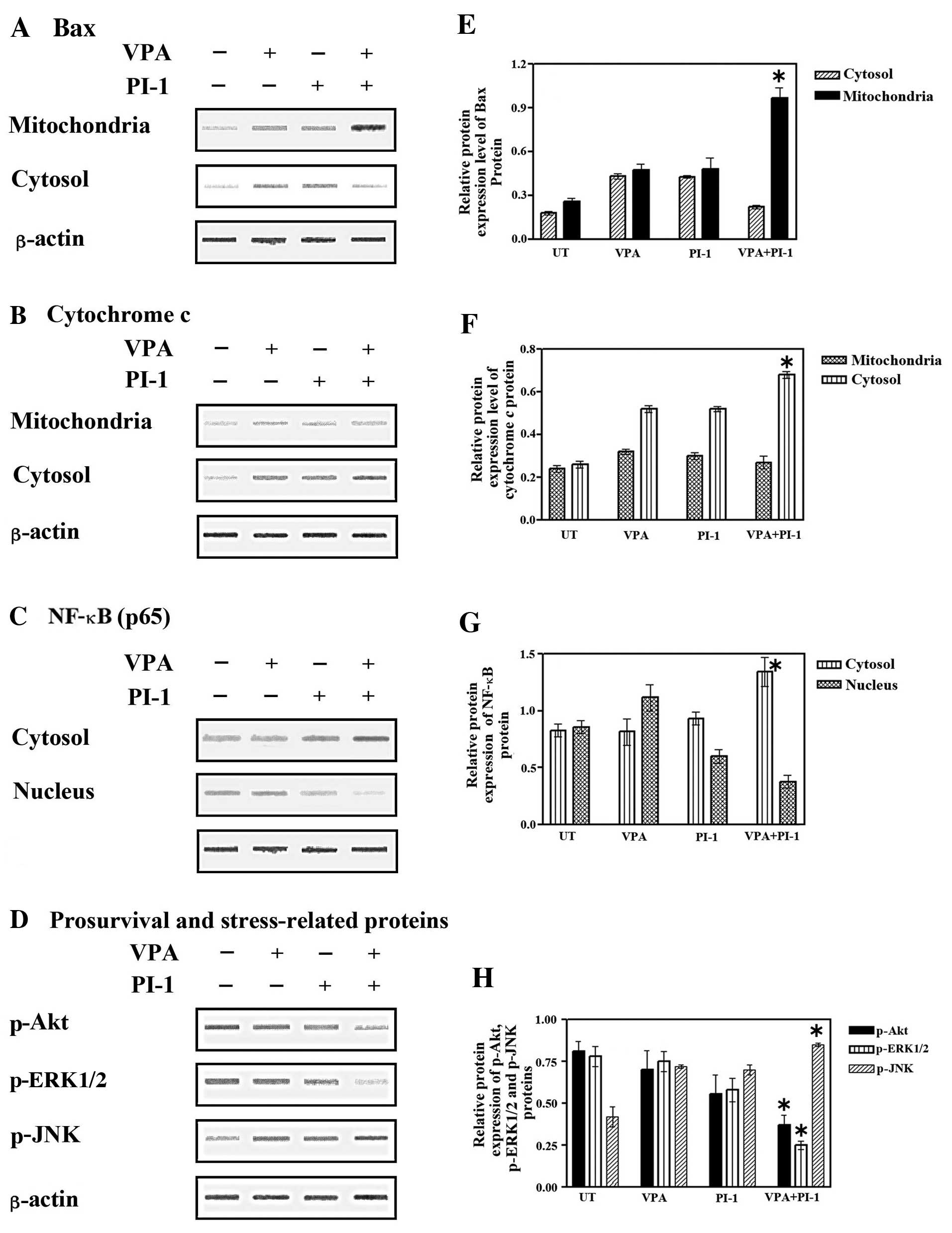
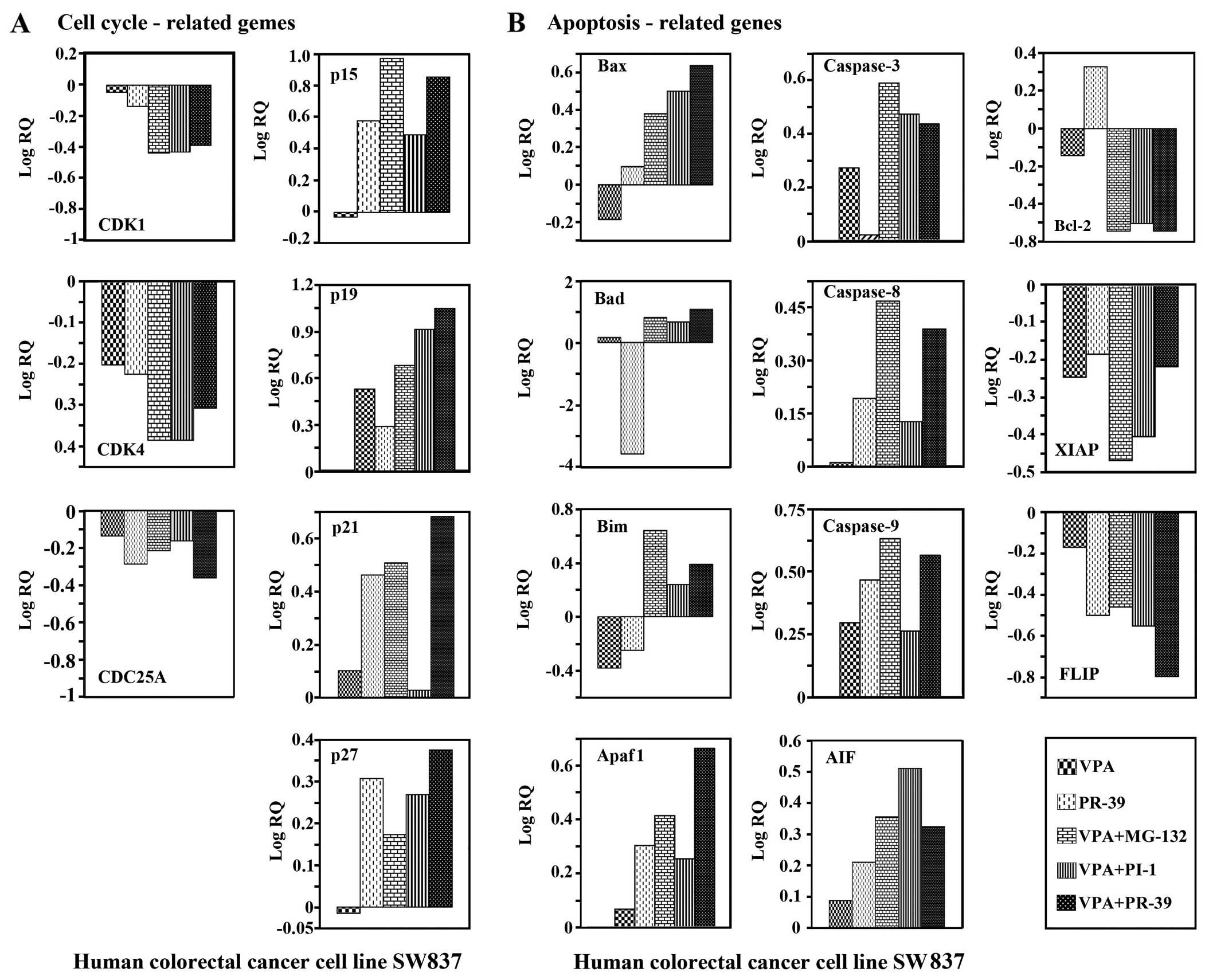
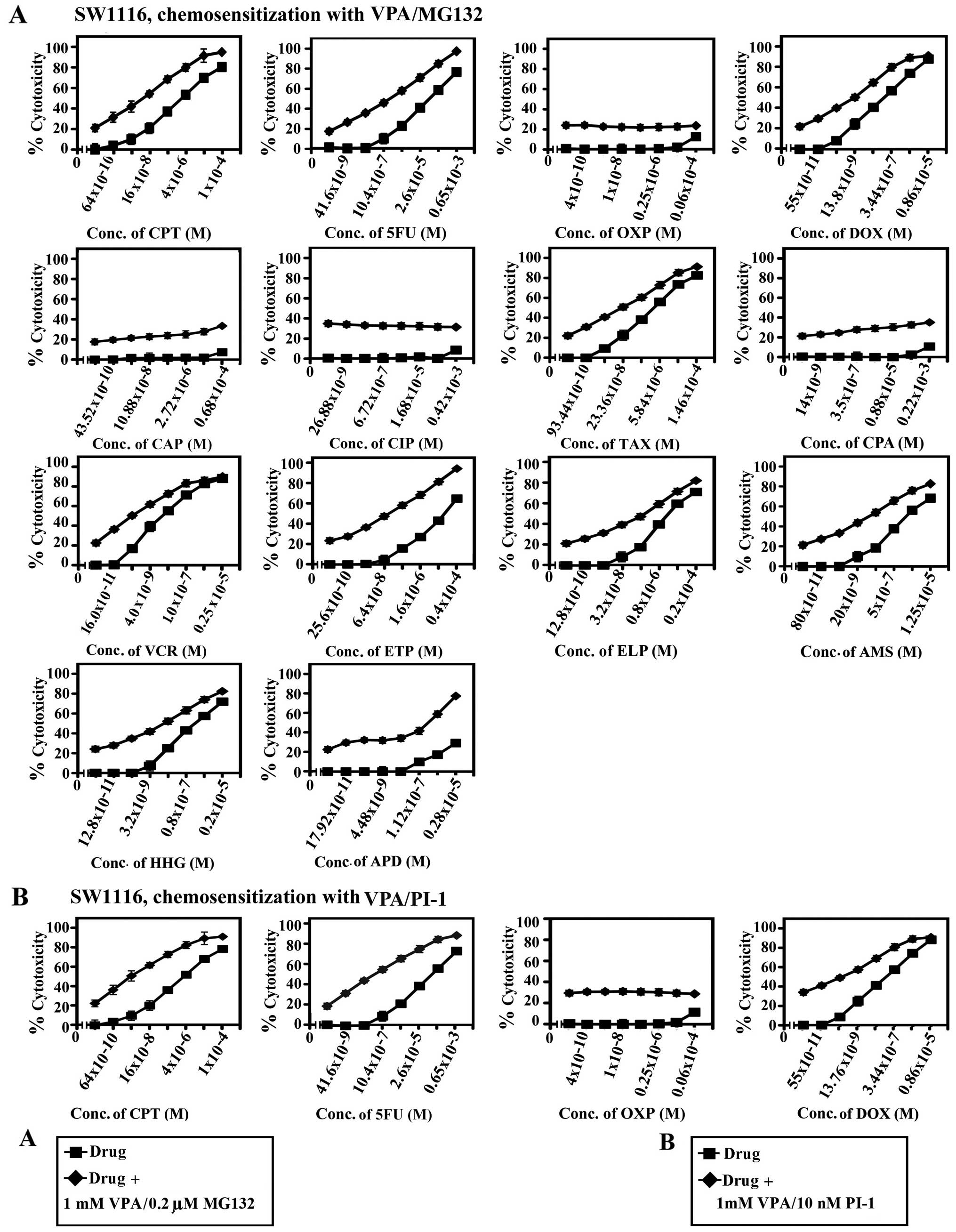
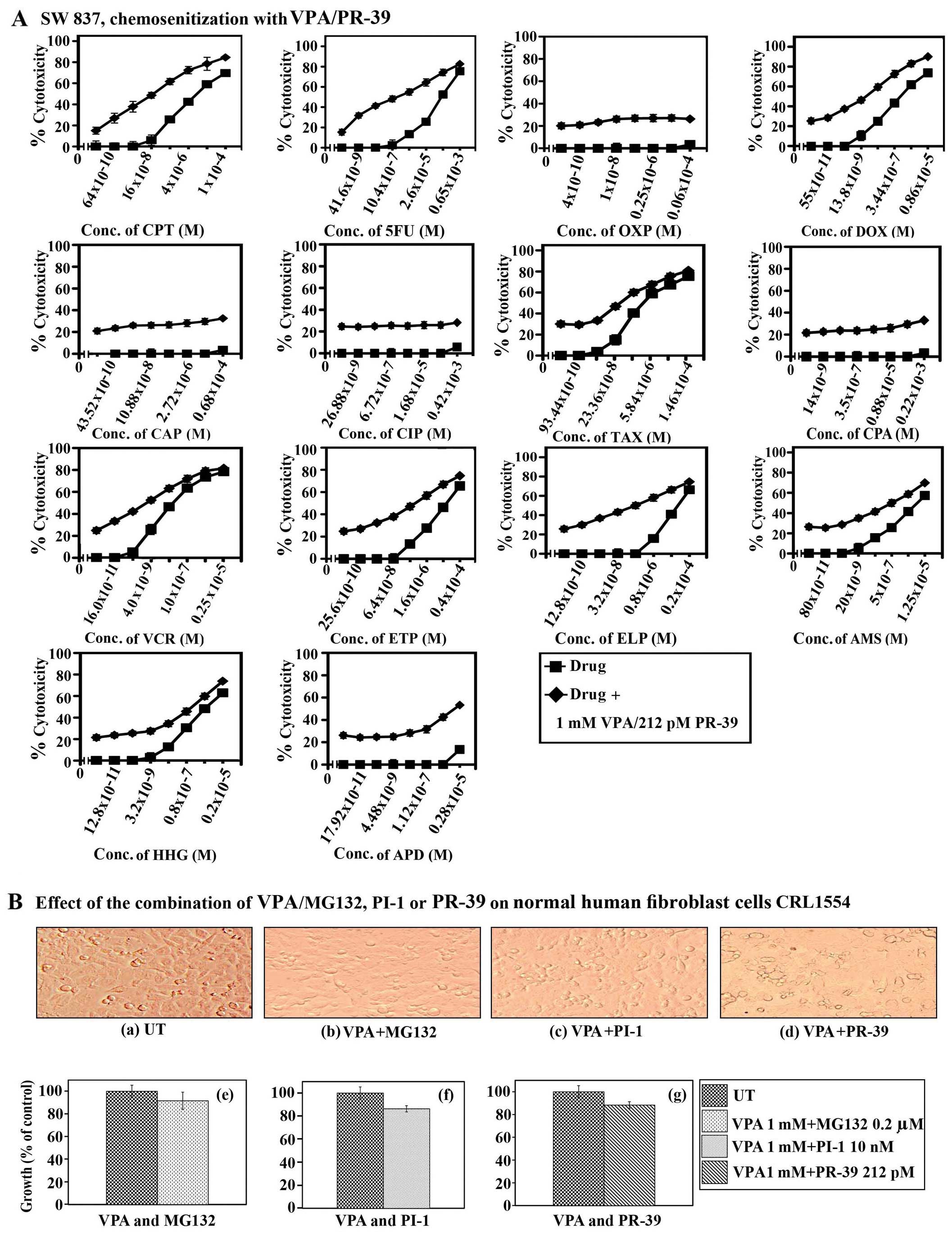
|
1
|
Pitts TM, Morrow M, Kaufman SA, et al:
Vorinostat and bortezomib exert synergistic antiproliferative and
proapoptotic effects in colon cancer cell models. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:342–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, et al:
Valproic acid derivatives: A novel class of HDAC inhibitors
inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J.
20:6969–6978. 2001.
|
|
3
|
Tan J, Cang S, Ma Y, et al: Novel histone
deacetylase inhibitors in clinical trials as anti-cancer agents. J
Hematol Oncol. 3:52010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nolan L, Johnson PWM, Ganesan A, et al:
Will histone deacetylase inhibitors require combination with other
agents to fulfil their therapeutic potential? Br J Cancer.
99:689–694. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dai Y, Chen S, Wang L, et al: Bortezomib
interacts synergistically with belinostat in human acute myeloid
leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells in association
with perturbations in NF-κB and Bim. Br J Haematol. 153:222–235.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adams J: The proteasome: a suitable
antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Orlowski RZ and Kuhn DJ: Proteasome
inhibitors in cancer therapy: lessons from the first decade. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:1649–1657. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bai J, Demirjian A, Sui J, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A and proteasome inhibitor
PS-341 synergistically induce apoptosis in pancreatic cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 4:1245–1253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pei XY, Dai Y and Grant S: Synergistic
induction of oxidative injury and apoptosis in human multiple
myeloma cells by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and histone
deacetylase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3839–3852. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Emanuele S, Lauricella M, Carlisi D, et
al: SAHA induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells and synergistically
interact with proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib. Apoptosis.
12:1327–1338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abaza MS, Al-Safar A, Al-Sawan S, et al:
c-myc anti-sense oligonucleotides sensitize human colorectal cancer
cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Tumour Biol. 29:287–303. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abaza MSI: Augmentation of the anticancer
effects of proteasome inhibitors by combination with sodium
butyrate in human colorectal cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 1:675–693.
2010.
|
|
13
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kwon SH, Ahn SH, Kim YK, et al: Apicidin,
a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces apoptosis and Fas/Fas
ligand expression in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. J
Biol Chem. 277:2073–2080. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Premkumar DR, Jane EP, Agostino NR, et al:
Bortezomib-induced sensitization of malignant human glioma cells to
vorinostat-induced apoptosis depends on reactive oxygen species
production, mitochondrial dysfunction, noxa upregulation, Mcl-1
cleavage, and DNA damage. Mol Carcinog. 52:118–133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Murphy KM, Streips UN and Lock RB: Bcl-2
inhibits a Fas-induced conformational change in the Bax N terminus
and Bax mitochondrial translocation. J Biol Chem. 275:17225–17228.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Knupfer MM, Pulzer F, Schindler I, et al:
Different effects of valproic acid on proliferation and migration
of malignant glioma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 21:347–351.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barbetti V, Gozzini A, Cheloni G, et al:
Time- and residue-specific differences in histone acetylation
induced by VPA and SAHA in AML1/ETO-positive leukemia cells.
Epigenetics. 8:210–219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sztanjnkrycer MD: Valproic acid toxicity:
overview and management. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 40:789–801. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chateauvieux S, Morceau F, Dicato M and
Diederich M: Molecular and therapeutic potential and toxicity of
valproic acid. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:4793642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kostrouchová M, Kostrouch Z and
Kostrouchová M: Valproic acid, a molecular lead to multiple
regulatory pathways. Folia Biol (Praha). 53:37–49. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bastian L, Hof J, Pfau M, et al:
Synergistic activity of bortezomib and HDACi in preclinical models
of B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia via modulation of
p53, PI3K/AKT, and NF-κB. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1445–1457.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stypula-Cyrus Y, Damania D, Kunte DP, et
al: HDAC up-regulation in early colon field carcinogenesis is
involved in cell tumorigenicity through regulation of chromatin
structure. PLoS One. 8:e646002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sidana A, Wang M, Shabbeer S, et al:
Mechanism of growth inhibition of prostate cancer xenografts by
valproic acid. J Biomed Biotech. 2012:1803632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Denlinger C, Keller M, Mayo M, et al:
Combined proteasome and histone deacetylase inhibition in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 127:1078–1086. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Drexler HC, Risau W and Konerding MA:
Inhibition of proteasome function induces programmed cell death in
proliferating endothelial cells. FASEB J. 14:65–77. 2000.
|
|
27
|
Li B and Dou QP: Bax degradation by the
ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent pathway: involvement in tumor
survival and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 97:3850–3855. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, et
al: Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective
antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 59:2615–2622. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chandra J, Niemer I, Gilbreath J, et al:
Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis in glucocorticoid-resistant
chronic lymphocytic leukemic lymphocytes. Blood. 92:4220–4229.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miller CP, Ban K, Dujka ME, et al:
NPI-0052, a novel proteasome inhibitor, induces caspase-8 and
ROS-dependent apoptosis alone and in combination with HDAC
inhibitors in leukemia cells. Blood. 110:267–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Heider U, Metzler I, Kaiser M, et al:
Synergistic interaction of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA
with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in mantle cell lymphoma.
Eur J Haematol. 80:133–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Defoort EN, Kim PM and Winn LM: Valproic
acid increases conservative homologous recombination frequency and
reactive oxygen species formation: a potential mechanism for
valproic acid-induced neural tube defects. Mol Pharmacol.
69:1304–1310. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rahmani M, Reese E, Dai Y, et al:
Coadministration of histone deacetylase inhibitors and perifosine
synergistically induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells through
Akt and ERK1/2 inactivation and the generation of ceramide and
reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 65:2422–2432. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dolado I, Swat A, Ajenjo N, et al:
p38alpha MAP kinase as a sensor of reactive oxygen species in
tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 11:191–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dasmahapatra G, Lembersky D, Son MP, et
al: Carfilzomib interact synergistically with histone deacetylase
inhibitors in mantle cell lymphoma cells in vitro and in
vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1686–1697. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ungerstedt JS, Sowa Y, Xu WS, et al: Role
of thioredoxin in the response of normal and transformed cells to
histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:673–678. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, McMillan-Ward E, Kong J, et al:
Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death independent of
apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell Death Differ.
15:171–182. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Krämer OH, Knauer SK, Zimmermann D, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors and hydroxyurea modulate the cell
cycle and cooperatively induce apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:732–740.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nile D, Huang K, Yin S, et al:
Synergistic/additive interaction of valproic acid with bortezomib
on proliferation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Leuk Lymphoma. 53:2487–2495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Proskuryakov SY, Konoplyannikov AG and
Gabai VL: Necrosis: a specific form of programmed cell death? Exp
Cell Res. 283:1–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hirsch T, Marchetti P, Susin SA, et al:
The apoptosis-necrosis paradox. Apoptogenic proteases activated
after mitochondrial permeability transition determine the mode of
cell death. Oncogene. 15:1573–1581. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Place RF, Noonan EJ and Giardina C: HDACs
and the senescent phenotype of WI-38 cells. BMC Cell Biol.
6:372005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shao Y, Gao Z, Marks PA and Jiang X:
Apoptotic and autophagic cell death induced by histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:18030–18035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li XN, Shu Q, Su JM, et al: Valproic acid
induces growth arrest, apoptosis, and senescence in medulloblastoma
by increasing histone hyperacetylation and regulating expression of
p21Cip1, CDK4, and CMYC. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1912–1922. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science (Washington DC). 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Schendel SL, Montal M and Reed JC: Bcl-2
family proteins as ion-channels. Cell Death Differ. 5:372–380.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bharti AC and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappa B and cancer: its role in prevention and therapy.
Biochem Pharmacol. 64:883–888. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nalepa G and Wade Harper J: Therapeutic
anti-cancer targets upstream of the proteasome. Cancer Treat Rev.
29(Suppl 1): S49–S57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Place RF, Noonan EJ and Giardina C: HDAC
inhibition prevents NF-kappa B activation by suppressing proteasome
activity: Down-regulation of proteasome subunit expression
stabilizes I kappa B alpha. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:394–406. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS and Ahn NG: Signal
transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res.
74:49–139. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, et al:
Inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling synergistically potentiates histone
deacetylase inhibitor-induced growth arrest, apoptosis and
acetylation of histone H3 on p21waf1 promoter in acute myelogenous
leukemia cell. Leukemia. 22:1449–1452. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhang QL, Wang L, Zhang YW, et al: The
proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with the
histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid to
induce T-leukemia/lymphoma cells apoptosis. Leukemia. 23:1507–1514.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shelton JG, Blalock WL, White ER, et al:
Ability of the activated PI3K/Akt oncoproteins to synergize with
MEK1 and induce cell cycle progression and abrogate the
cytokine-dependence of hematopoietic cells. Cell Cycle. 3:503–512.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kawamata N, Chen J and Koeffler HP:
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA; vorinostat) suppresses
translation of cyclin D1 in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Blood.
110:2667–2673. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu C, Rahmani M, Dent P and Grant S: The
hierarchical relationship between MAPK signaling and ROS generation
in human leukemia cells undergoing apoptosis in response to the
proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib. Exp Cell Res. 295:555–566. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yu C, Subler M, Rahmani M, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in BCR/ABL+ cells by histone deacetylase
inhibitors involves reciprocal effects on the RAF/MEK/ERK and JNK
pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:544–551. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yagi Y, Fushida S, Harada S, et al:
Effects of valproic acid on the cell cycle and apoptosis through
acetylation of histone and tubulin in a scirrhous gastric cancer
cell line. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1492010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gatti L, Benedetti V, De Cesare M, et al:
Synergistic interaction between the novel histone deacetylase
inhibitor ST2782 and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in
platinum-sensitive and resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. J Inorg
Biochem. 113:94–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hwang JJ, Kim Ys, Kim T, et al: A novel
histone deacetylase inhibitor, CG200745, potentiates anticancer
effect of docetaxel in prostate cancer via decreasing Mcl-1 and
Bcl-XL. Invest New Drugs. 30:1434–1442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fuino L, Bali P, Wittmann S, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 down-regulates Her-2 and
sensitizes human breast cancer cells to trastuzumab, taxotere,
gemcitabine, and epothilone B. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:971–984.
2003.
|
|
61
|
Huang Y and Waxman S: Enhanced growth
inhibition and differentiation of fluorodeoxyuridine-treated human
colon carcinoma cells by phenylbutyrate. Clin Cancer Res.
4:2503–2509. 1998.
|
|
62
|
Kim MS, Blake M, Baek JH, et al:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases cytotoxicity to
anticancer drugs targeting DNA. Cancer Res. 63:7291–7300.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Maggio SC, Rosato RR, Kramer LB, et al:
The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 interacts synergistically
with fludarabine to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells.
Cancer Res. 64:2590–2600. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Witzig TE, Timm M, Stenson M, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in malignant B cells by phenylbutyrate or
phenylacetate in combination with chemotherapeutic agents. Clin
Cancer Res. 6:681–692. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Linares A, Dalenc F, Balaguer P, et al:
Manipulating protein acetylation in breast cancer: a promising
approach in combination with hormonal therapies. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2011:8569852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Munster PN, Thurn KT, Thomas S, et al: A
phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat
combined with tamoxifen for the treatment of patients with hormone
therapy-resistant breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:1828–1835. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Atmaca A, Al-Batran SE, Maurer A, et al:
Valproic acid (VPA) in patients with refractory advanced cancer: a
dose escalating phase I clinical trial. Br J Cancer. 97:177–182.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M,
Perez-Plascencia C, et al: Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug:
Preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:206–222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Newland SE: The role of bioethics in
international prescription drug market: economics and global
justice. Penn Bioeth J. 2:8–12. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|