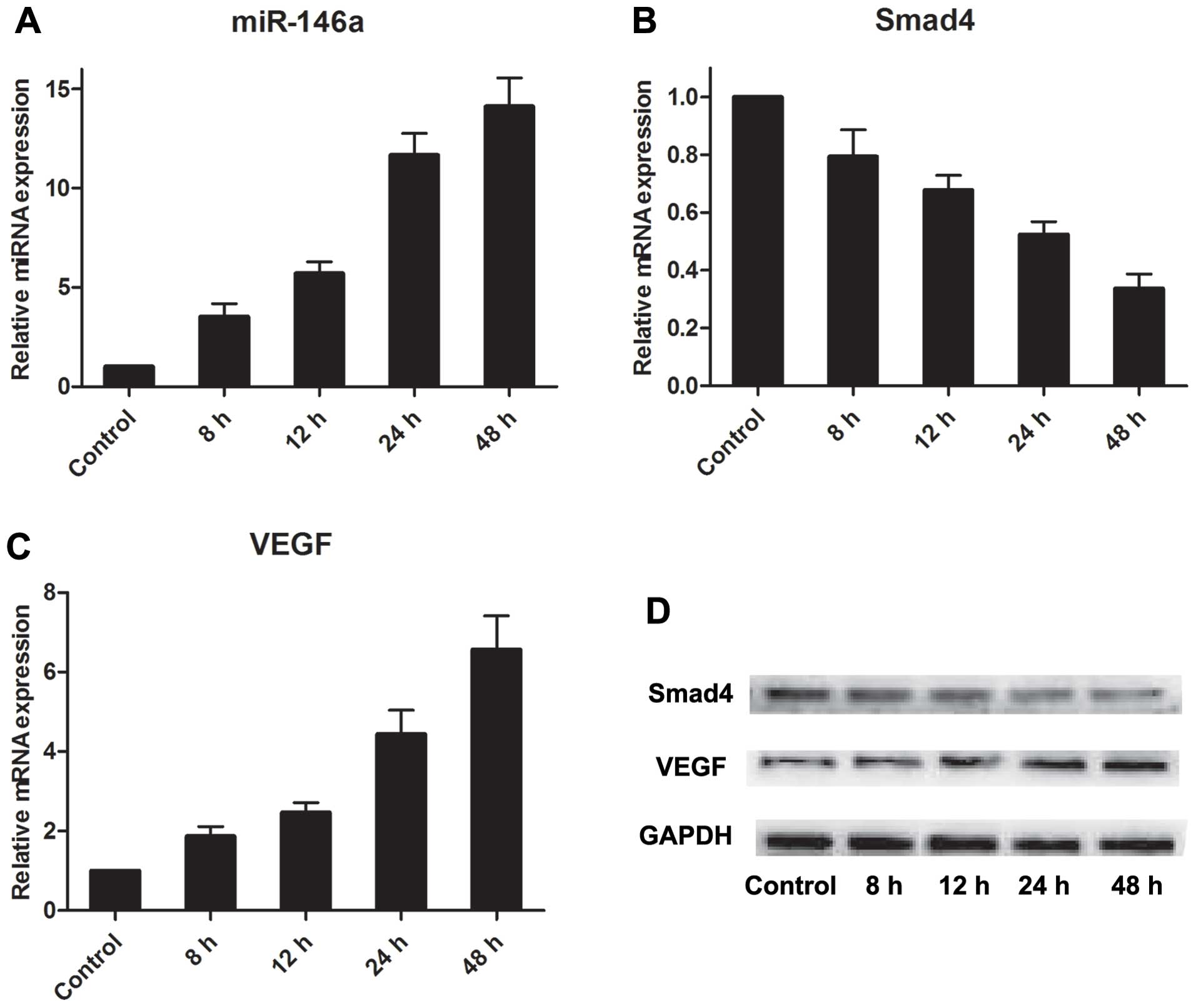
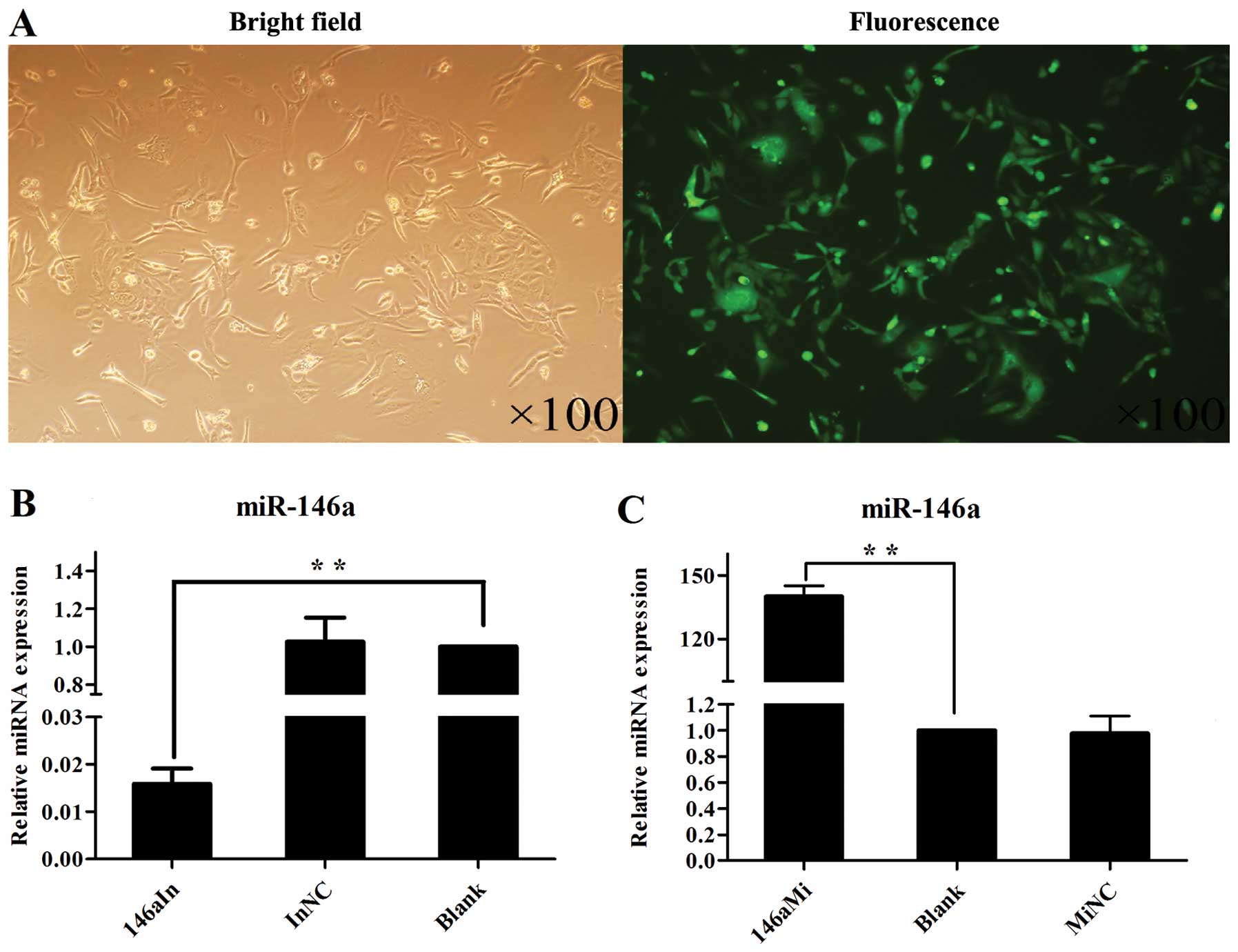
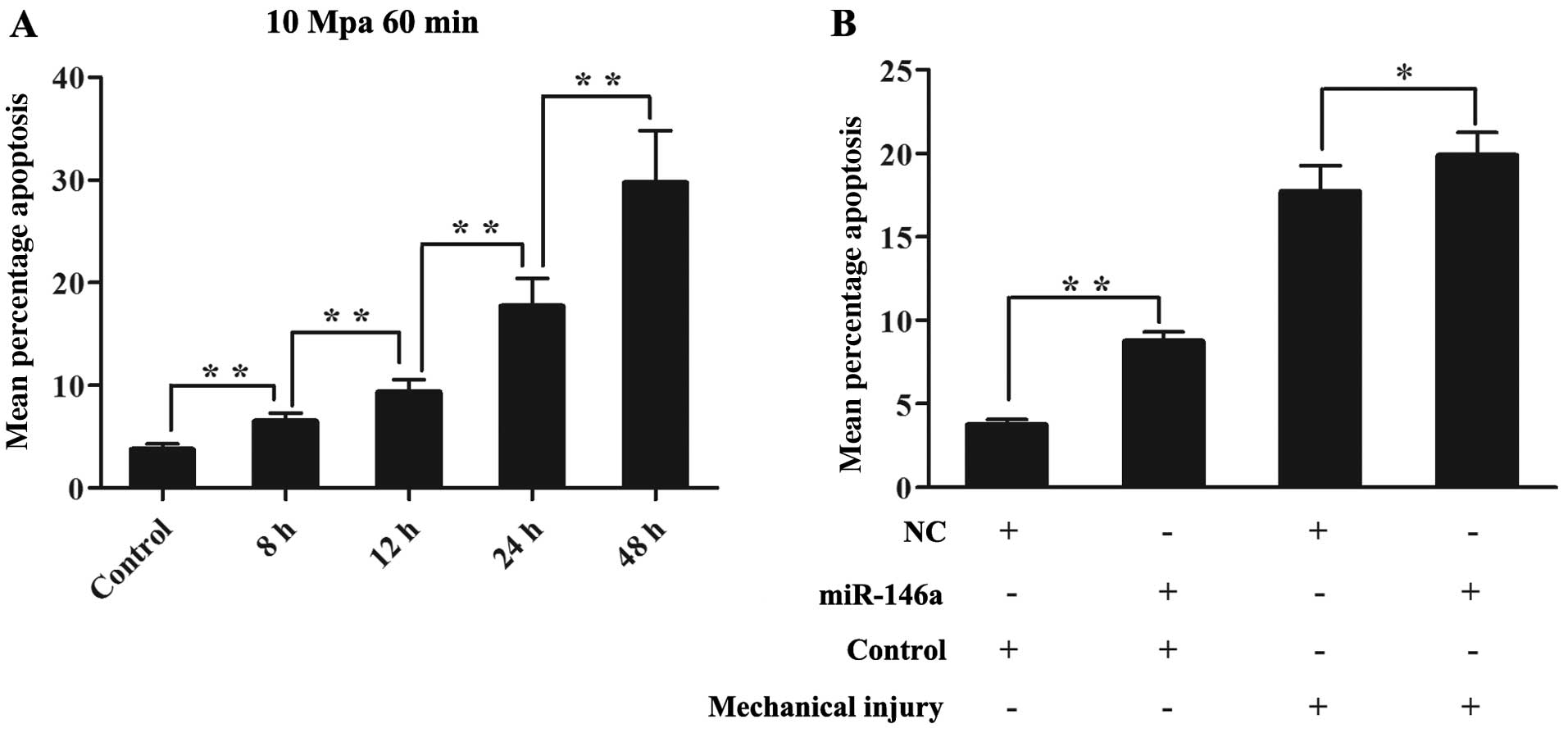
|
1
|
Ashford S and Williard J: Osteoarthritis:
A review. Nurse Pract. 39:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Anderson DD, Chubinskaya S, Guilak F, et
al: Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: improved understanding and
opportunities for early intervention. J Orthop Res. 29:802–809.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin JA and Buckwalter JA:
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: the role of stress induced
chondrocyte damage. Biorheology. 43:517–521. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seol D, McCabe DJ, Choe H, et al:
Chondrogenic progenitor cells respond to cartilage injury.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:3626–3637. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conde J, Scotece M, Gomez R, Lopez V,
Gomez-Reino JJ and Gualillo O: Adipokines and osteoarthritis: novel
molecules involved in the pathogenesis and progression of disease.
Arthritis. 2011:2039012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hogrefe C, Joos H, Maheswaran V, Durselen
L, Ignatius A and Brenner RE: Single impact cartilage trauma and
TNF-alpha: interactive effects do not increase early cell death and
indicate the need for bi-/multidirectional therapeutic approaches.
Int J Mol Med. 30:1225–1232. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Joos H, Hogrefe C, Rieger L, Durselen L,
Ignatius A and Brenner RE: Single impact trauma in human
early-stage osteoarthritic cartilage: implication of prostaglandin
D2 but no additive effect of IL-1β on cell survival. Int J Mol Med.
28:271–277. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leucht F, Durselen L, Hogrefe C, et al:
Development of a new biomechanically defined single impact rabbit
cartilage trauma model for in vivo-studies. J Invest Surg.
25:235–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heraud F, Heraud A and Harmand MF:
Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage.
Ann Rheum Dis. 59:959–965. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Colwell CW Jr, D’Lima DD, Hoenecke HR, et
al: In vivo changes after mechanical injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
391(Suppl): S116–S123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
D’Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Chen PC, Colwell
CW Jr and Lotz MK: Human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to
mechanical injury. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 9:712–719.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tew SR, Kwan AP, Hann A, Thomson BM and
Archer CW: The reactions of articular cartilage to experimental
wounding: role of apoptosis. Arthritis Rheum. 43:215–225. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D’Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Chen PC, Lotz MK
and Colwell CW Jr: Cartilage injury induces chondrocyte apoptosis.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A(Suppl 2): 19–21. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saito Y, Saito H, Liang G and Friedman JM:
Epigenetic alterations and microRNA misexpression in cancer and
autoimmune diseases: a critical review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
Dec 21–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
15
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP and Baltimore D:
MicroRNAs and immunity: tiny players in a big field. Immunity.
26:133–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsai CY, Allie SR, Zhang W and Usherwood
EJ: MicroRNA miR-155 affects antiviral effector and effector Memory
CD8 T cell differentiation. J Virol. 87:2348–2351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, et al:
miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumour suppressors and directly
regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:883–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murphy AJ, Guyre PM and Pioli PA:
Estradiol suppresses NF-kappa B activation through coordinated
regulation of let-7a and miR-125b in primary human macrophages. J
Immunol. 184:5029–5037. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, et al:
Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following
lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles
in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol.
179:5082–5089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Williams AE, Perry MM, Moschos SA,
Larner-Svensson HM and Lindsay MA: Role of miRNA-146a in the
regulation of the innate immune response and cancer. Biochem Soc
Trans. 36:1211–1215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyaki S and Asahara H: Macro view of
microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:543–552.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ceribelli A, Nahid MA, Satoh M and Chan
EK: MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. FEBS Lett. 585:3667–3674.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ammari M, Jorgensen C and Apparailly F:
Impact of microRNAs on the understanding and treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 25:225–233. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goldring MB and Marcu KB: Epigenomic and
microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis,
and osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. 18:109–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Okuhara A, Nakasa T, Shibuya H, et al:
Changes in microRNA expression in peripheral mononuclear cells
according to the progression of osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol.
22:446–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu C, Chen WP and Wang XH: MicroRNA in
osteoarthritis. J Int Med Res. 39:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jones SW, Watkins G, Le Good N, et al: The
identification of differentially expressed microRNA in
osteoarthritic tissue that modulate the production of TNF-alpha and
MMP13. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:464–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P and
Tsezou A: Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify
novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and
inflammatory networks. PLoS One. 3:e37402008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Diaz-Prado S, Cicione C, Muinos-Lopez E,
et al: Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal
and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
13:1442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang JH, Shih KS, Wu YW, Wang AW and Yang
CR: Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase microRNA-146a
expression and enhance negative regulation of interleukin-1beta
signaling in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1987–1996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, et al:
Expression of microRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:1035–1041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Okubo A, et al:
Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue.
Arthritis Rheum. 58:1284–1292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
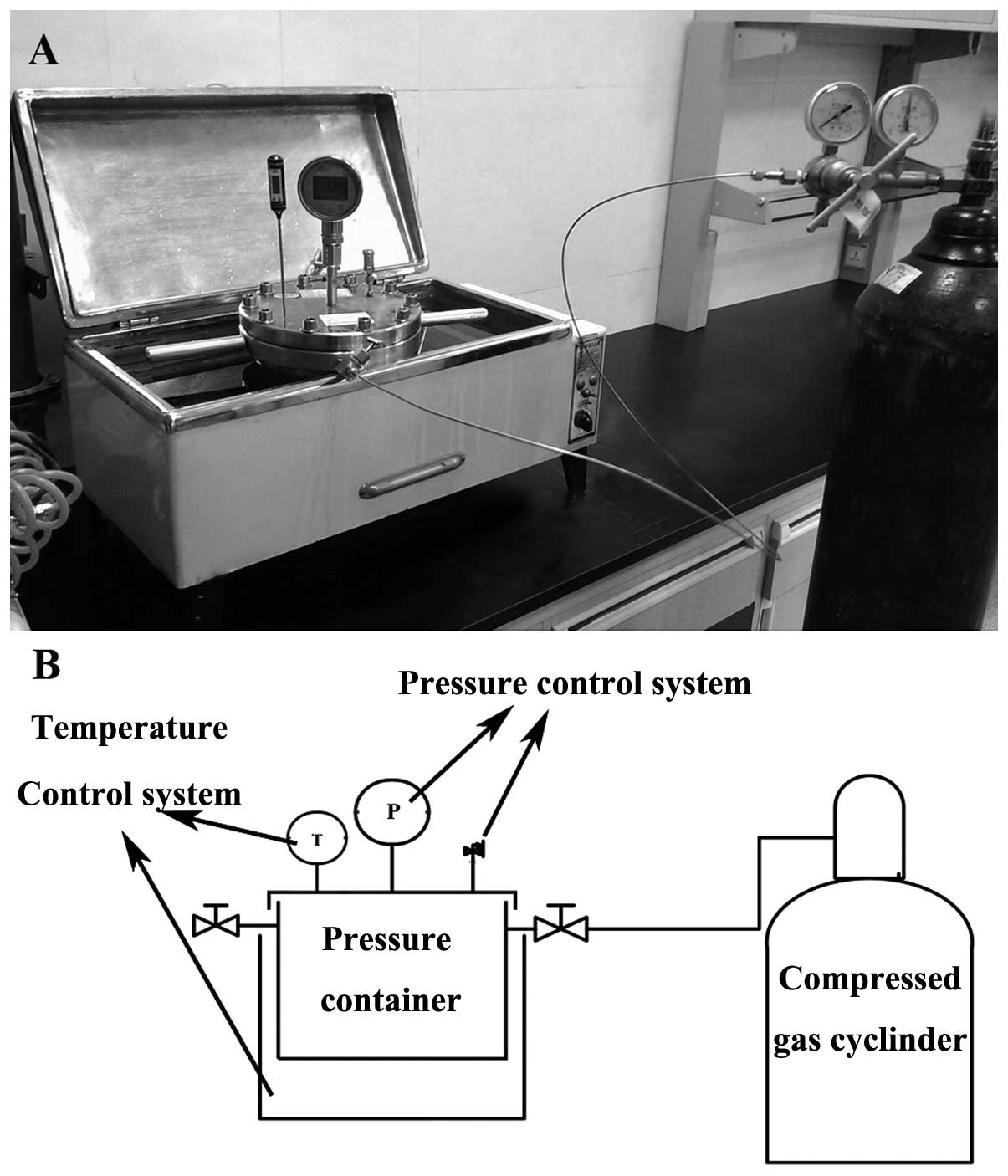
Ma Baoan and Jin Lei: Multifunctional
constant-temperature high pressure hydrostatic pressure loading
device in in-vitro cell culture. China, utility model patent No. CN
203229539 U. Filed May 16, 2013; issued October 9, 2013.
|
|
37
|
Hashimoto S, Nishiyama T, Hayashi S, et
al: Role of p53 in human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to shear
strain. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2340–2349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moon MH, Jeong JK, Lee YJ, Seol JW and
Park SY: Sphingosine-1-phosphate inhibits interleukin-1β-induced
inflammation in human articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med.
30:1451–1458. 2012.
|
|
39
|
Takebe K, Nishiyama T, Hayashi S, et al:
Regulation of p38 MAPK phosphorylation inhibits chondrocyte
apoptosis in response to heat stress or mechanical stress. Int J
Mol Med. 27:329–335. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Storch A, Burkhardt K, Ludolph AC and
Schwarz J: Protective effects of riluzole on dopamine neurons:
involvement of oxidative stress and cellular energy metabolism. J
Neurochem. 75:2259–2269. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36:D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bottoni A, Zatelli MC, Ferracin M, et al:
Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs by microarray:
a possible role for microRNA genes in pituitary adenomas. J Cell
Physiol. 210:370–377. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weatherall JM, Mroczek K, McLaurin T, Ding
B and Tejwani N: Post-traumatic ankle arthritis. Bull Hosp Jt Dis.
2013. 71:104–112. 2013.
|
|
45
|
Lee JH, Fitzgerald JB, Dimicco MA and
Grodzinsky AJ: Mechanical injury of cartilage explants causes
specific time-dependent changes in chondrocyte gene expression.
Arthritis Rheum. 52:2386–2395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Douville NJ, Zamankhan P, Tung YC, et al:
Combination of fluid and solid mechanical stresses contribute to
cell death and detachment in a microfluidic alveolar model. Lab
Chip. 11:609–619. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Levin A, Burton-Wurster N, Chen CT and
Lust G: Intercellular signaling as a cause of cell death in
cyclically impacted cartilage explants. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
9:702–711. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Honda K, Ohno S, Tanimoto K, et al: The
effects of high magnitude cyclic tensile load on cartilage matrix
metabolism in cultured chondrocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 79:601–609.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fermor B, Weinberg JB, Pisetsky DS,
Misukonis MA, Banes AJ and Guilak F: The effects of static and
intermittent compression on nitric oxide production in articular
cartilage explants. J Orthop Res. 19:729–737. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Millward-Sadler SJ, Wright MO, Davies LW,
Nuki G and Salter DM: Mechanotransduction via integrins and
interleukin-4 results in altered aggrecan and matrix
metalloproteinase 3 gene expression in normal, but not
osteoarthritic, human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.
43:2091–2099. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
D’Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Chen PC, Colwell
CW Jr and Lotz MK: Impact of mechanical trauma on matrix and cells.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. (391 Suppl): S90–S99. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wenger R, Hans MG, Welter JF, Solchaga LA,
Sheu YR and Malemud CJ: Hydrostatic pressure increases apoptosis in
cartilage-constructs produced from human osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. Front Biosci. 11:1690–1695. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Islam N, Haqqi TM, Jepsen KJ, et al:
Hydrostatic pressure induces apoptosis in human chondrocytes from
osteoarthritic cartilage through up-regulation of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha, inducible nitric oxide synthase, p53, c-myc, and
bax-alpha, and suppression of bcl-2. J Cell Biochem. 87:266–278.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sharif M, Whitehouse A, Sharman P, Perry M
and Adams M: Increased apoptosis in human osteoarthritic cartilage
corresponds to reduced cell density and expression of caspase-3.
Arthritis Rheum. 50:507–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Loening AM, James IE, Levenston ME, et al:
Injurious mechanical compression of bovine articular cartilage
induces chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 381:205–212.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cho YS: Perspectives on the therapeutic
modulation of an alternative cell death, programmed necrosis
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 33:1401–1406. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang W, Lin M, Li X, et al: Icariin
promotes bone formation via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction
pathway in the hFOB 1.19 human osteoblastic cell line. Int J Mol
Med. 30:889–895. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang XM, Huang GW, Tian ZH, Ren DL and
Wilson JX: Folate stimulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cell
proliferation in fetal neural stem cells. Nutr Neurosci.
12:226–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Imamichi Y, Waidmann O, Hein R,
Eleftheriou P, Giehl K and Menke A: TGF beta-induced focal complex
formation in epithelial cells is mediated by activated ERK and JNK
MAP kinases and is independent of Smad4. Biol Chem. 386:225–236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zuscik MJ, Hilton MJ, Zhang X, Chen D and
O’Keefe RJ: Regulation of chondrogenesis and chondrocyte
differentiation by stress. J Clin Invest. 118:429–438. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chiquet M, Gelman L, Lutz R and Maier S:
From mechanotransduction to extracellular matrix gene expression in
fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:911–920. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Agarwal S, Deschner J, Long P, et al: Role
of NF-kappaB transcription factors in antiinflammatory and
proinflammatory actions of mechanical signals. Arthritis Rheum.
50:3541–3548. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dossumbekova A, Anghelina M, Madhavan S,
et al: Biomechanical signals inhibit IKK activity to attenuate
NF-kappaB transcription activity in inflamed chondrocytes.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:3284–3296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Perera PM, Wypasek E, Madhavan S, et al:
Mechanical signals control SOX-9, VEGF, and c-Myc expression and
cell proliferation during inflammation via integrin-linked kinase,
B-Raf, and ERK1/2-dependent signaling in articular chondrocytes.
Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R1062010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Carlevaro MF, Cermelli S, Cancedda R and
Descalzi Cancedda F: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in
cartilage neovascularization and chondrocyte differentiation:
auto-paracrine role during endochondral bone formation. J Cell Sci.
113:59–69. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chen C, Sun MZ, Liu S, et al: Smad4
mediates malignant behaviors of human ovarian carcinoma cell
through the effect on expressions of E-cadherin, plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 and VEGF. BMB Rep. 43:554–560. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Schwarte-Waldhoff I and Schmiegel W: Smad4
transcriptional pathways and angiogenesis. Int J Gastrointest
Cancer. 31:47–59. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Volpert OV, Bouck NP,
et al: Smad4/DPC4-mediated tumor suppression through suppression of
angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:9624–9629. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chowdhury TT, Bader DL and Lee DA: Dynamic
compression counteracts IL-1 beta-induced release of nitric oxide
and PGE2 by superficial zone chondrocytes cultured in agarose
constructs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 11:688–696. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Nugent GE, Aneloski NM, Schmidt TA,
Schumacher BL, Voegtline MS and Sah RL: Dynamic shear stimulation
of bovine cartilage biosynthesis of proteoglycan 4. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:1888–1896. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nam J, Aguda BD, Rath B and Agarwal S:
Biomechanical thresholds regulate inflammation through the
NF-kappaB pathway: experiments and modeling. PLoS One. 4:e52622009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
McNulty AL, Estes BT, Wilusz RE, Weinberg
JB and Guilak F: Dynamic loading enhances integrative meniscal
repair in the presence of interleukin-1. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
18:830–838. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|