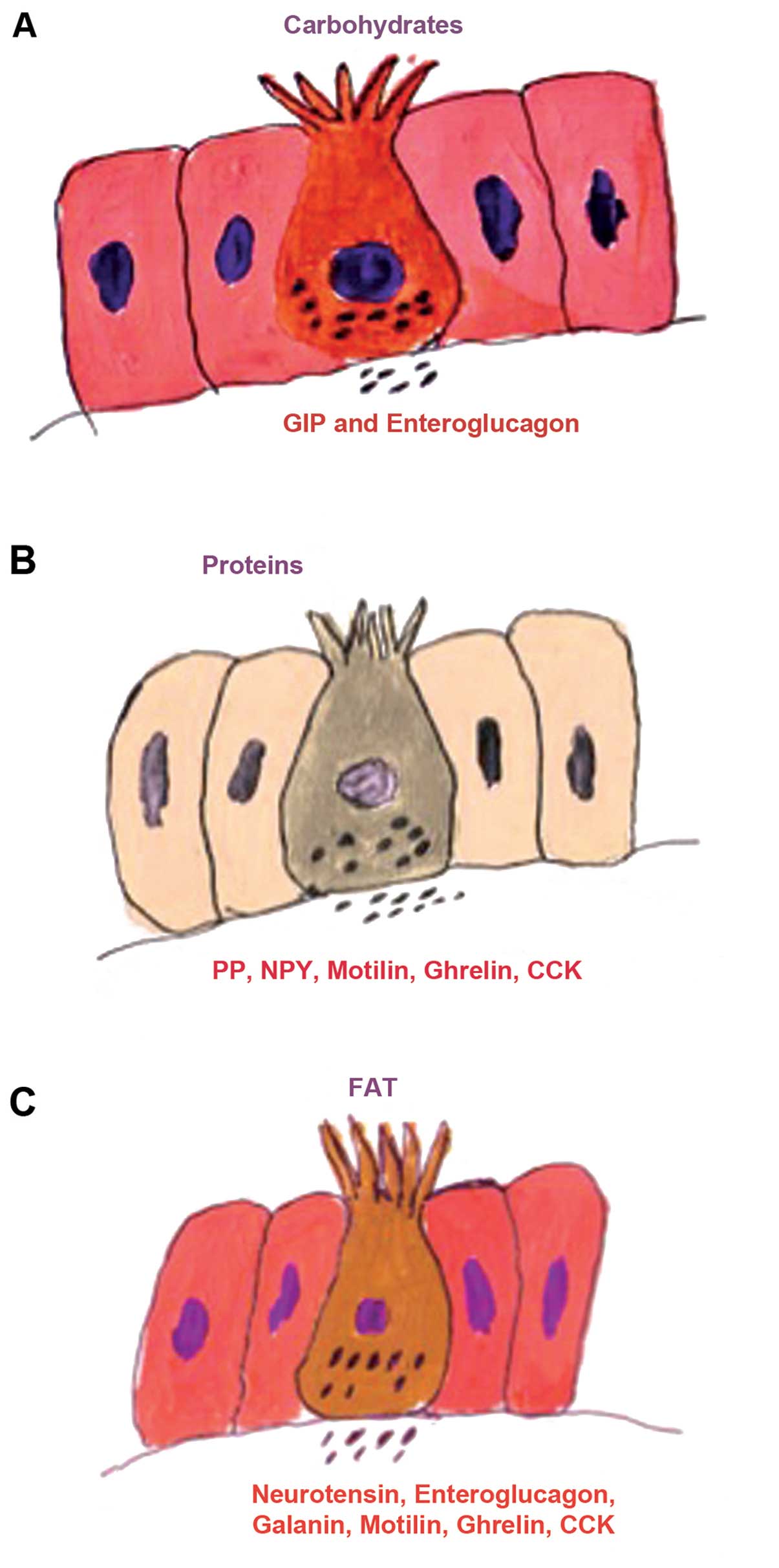
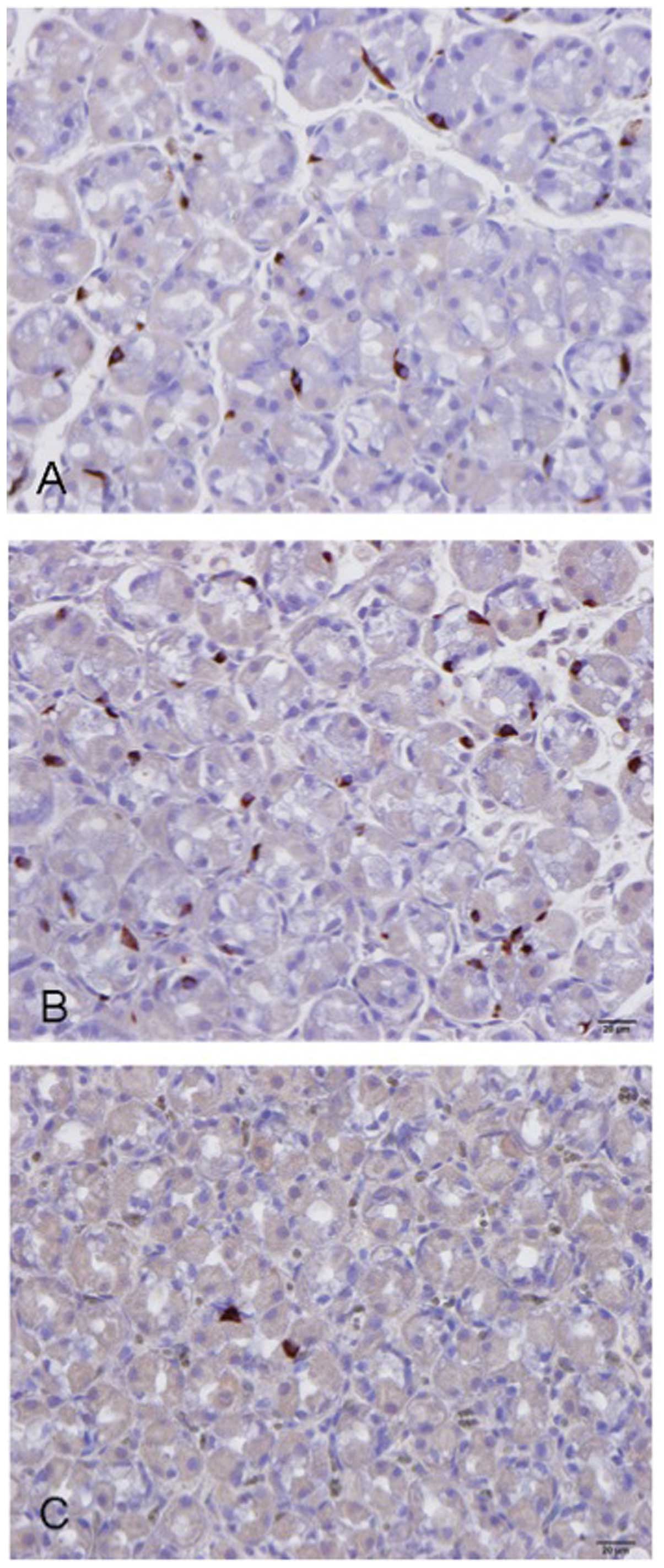
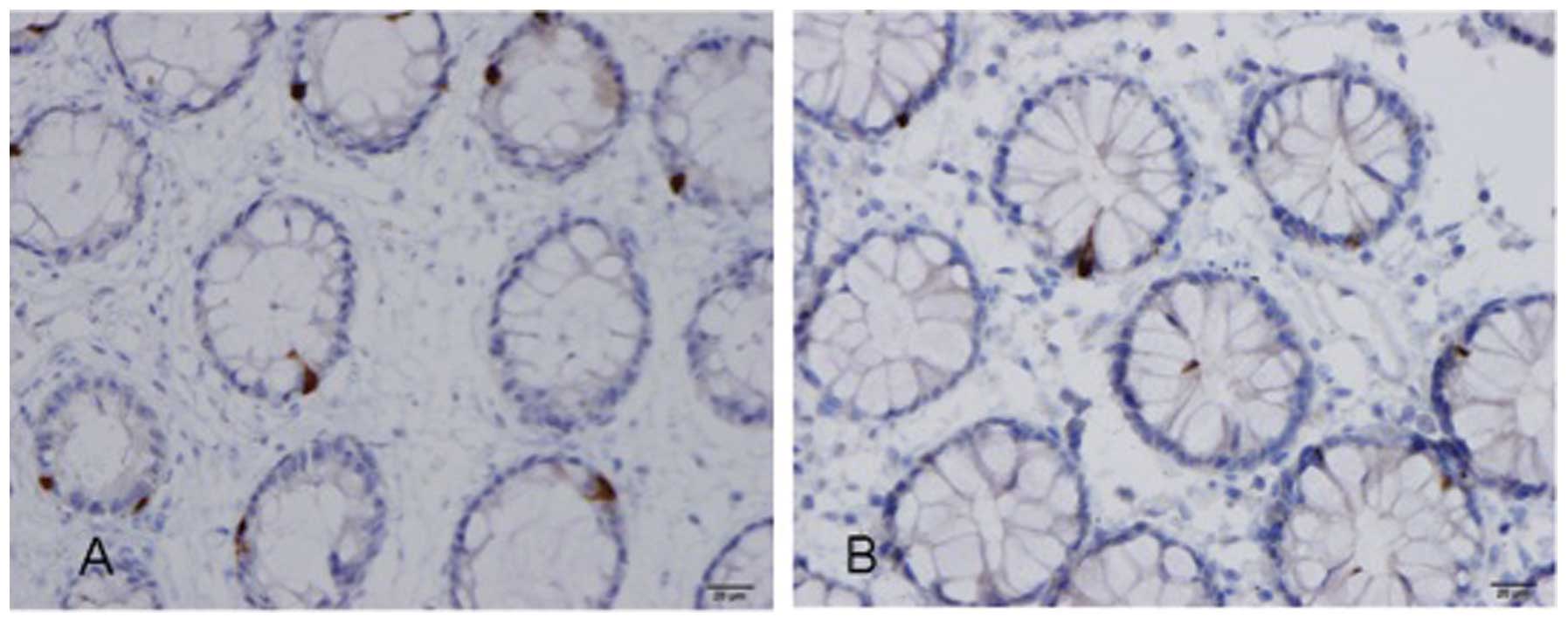
|
1
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Irritable bowel syndrome: diagnosis, pathogenesis and
treatment options. Nova Science Publishers Inc.; New York: 2012
|
|
2
|
Thompson WG: A world view of IBS.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Camilleri M and Spiller RC: Saunders;
Philadelphia and London: pp. 17–26. 2002
|
|
3
|
Agreus L, Svardsudd K, Nyren O and Tibblin
G: Irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia in the general
population: overlap and lack of stability over time.
Gastroenterology. 109:671–680. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson WG, Irvine EJ, Pare P, Ferrazzi S
and Rance L: Functional gastrointestinal disorders in Canada: first
population-based survey using Rome II criteria with suggestions for
improving the questionnaire. Dig Dis Sci. 47:225–235. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kennedy TM, Jones RH, Hungin AP,
O’Flanagan H and Kelly P: Irritable bowel syndrome,
gastro-oesophageal reflux, and bronchial hyper-responsiveness in
the general population. Gut. 43:770–774. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, et al: U.S.
householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig Dis Sci.
38:1569–1580. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Talley NJ, Gabriel SE, Harmsen WS,
Zinsmeister AR and Evans RW: Medical costs in community subjects
with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 109:1736–1741.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hungin AP, Whorwell PJ, Tack J and Mearin
F: The prevalence, patterns and impact of irritable bowel syndrome:
an international survey of 40,000 subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
17:643–650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jones R and Lydeard S: Irritable bowel
syndrome in the general population. BMJ. 304:87–90. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bordie AK: Functional disorders of the
colon. J Indian Med Assoc. 58:451–456. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O’Keefe EA, Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR and
Jacobsen SJ: Bowel disorders impair functional status and quality
of life in the elderly: a population-based study. J Gerontol A Biol
Sci Med Sci. 50:M184–M189. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Everhart JE and Renault PF: Irritable
bowel syndrome in office-based practice in the United States.
Gastroenterology. 100:998–1005. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wilson S, Roberts L, Roalfe A, Bridge P
and Singh S: Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome: a community
survey. Br J Gen Pract. 54:495–502. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Quigley EM, Locke GR, Mueller-Lissner S,
et al: Prevalence and management of abdominal cramping and pain: a
multinational survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 24:411–419. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harvey RF, Salih SY and Read AE: Organic
and functional disorders in 2000 gastroenterology outpatients.
Lancet. 1:632–634. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Spiller R, Aziz Q, Creed F, et al:
Guidelines on the irritable bowel syndrome: mechanisms and
practical management. Gut. 56:1770–1798. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD,
Houghton LA, Mearin F and Spiller RC: Functional bowel disorders.
Gastroenterology. 130:1480–1491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thompson WG and Heaton KW: Functional
bowel disorders in apparently healthy people. Gastroenterology.
79:283–288. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miller V, Whitaker K, Morris JA and
Whorwell PJ: Gender and irritable bowel syndrome: the male
connection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 38:558–560. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whitehead WE, Burnett CK, Cook EW III and
Taub E: Impact of irritable bowel syndrome on quality of life. Dig
Dis Sci. 41:2248–2253. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gralnek IM, Hays RD, Kilbourne A, Naliboff
B and Mayer EA: The impact of irritable bowel syndrome on
health-related quality of life. Gastroenterology. 119:654–660.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
El-Salhy M: Irritable bowel syndrome:
diagnosis and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5151–5163.
2012.
|
|
23
|
Simren M, Mansson A, Langkilde AM, et al:
Food-related gastrointestinal symptoms in the irritable bowel
syndrome. Digestion. 63:108–115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nanda R, James R, Smith H, Dudley CR and
Jewell DP: Food intolerance and the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut.
30:1099–1104. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bohn L, Storsrud S, Tornblom H, Bengtsson
U and Simren M: Self-reported food-related gastrointestinal
symptoms in IBS are common and associated with more severe symptoms
and reduced quality of life. Am J Gastroenterol. 108:634–641. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jarrett M, Heitkemper MM, Bond EF and
Georges J: Comparison of diet composition in women with and without
functional bowel disorder. Gastroenterol Nurs. 16:253–258. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saito YA, Locke GR III, Weaver AL,
Zinsmeister AR and Talley NJ: Diet and functional gastrointestinal
disorders: a population-based case-control study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 100:2743–2748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Williams EA, Nai X and Corfe BM: Dietary
intakes in people with irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol.
11:92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ostgaard H, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Diet and effects of diet management on quality of life
and symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med
Rep. 5:1382–1390. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Böhn L, Störsrud S and Simrén M: Nutrient
intake in patients with irritable bowel syndrome compared with the
general population. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
25:23-e212013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ligaarden SC, Lydersen S and Farup PG:
Diet in subjects with irritable bowel syndrome: a cross-sectional
study in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:612012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
El-Salhy M, Ostgaard H, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: The role of diet in the pathogenesis
and management of irritable bowel syndrome (Review). Int J Mol Med.
29:723–731. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dizdar V, Spiller R, Singh G, et al:
Relative importance of abnormalities of CCK and 5-HT (serotonin) in
Giardia-induced post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome and
functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 31:883–891.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Monsbakken KW, Vandvik PO and Farup PG:
Perceived food intolerance in subjects with irritable bowel
syndrome - etiology, prevalence and consequences. Eur J Clin Nutr.
60:667–672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vesa TH, Seppo LM, Marteau PR, Sahi T and
Korpela R: Role of irritable bowel syndrome in subjective lactose
intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr. 67:710–715. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Geissler C: Human Nutrition. Geissler C
and Powers H: Elsevier; Churchill Livingstone: 2005
|
|
37
|
Wald A and Rakel D: Behavioral and
complementary approaches for the treatment of irritable bowel
syndrome. Nutr Clin Pract. 23:284–292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heizer WD, Southern S and McGovern S: The
role of diet in symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in adults: a
narrative review. J Am Diet Assoc. 109:1204–1214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morcos A, Dinan T and Quigley EM:
Irritable bowel syndrome: role of food in pathogenesis and
management. J Dig Dis. 10:237–246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eswaran S, Tack J and Chey WD: Food: the
forgotten factor in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol
Clin North Am. 40:141–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Austin GL, Dalton CB, Hu Y, et al: A very
low-carbohydrate diet improves symptoms and quality of life in
diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 7:706–708. e7012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barrett JS and Gibson PR: Fermentable
oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols
(FODMAPs) and nonallergic food intolerance: FODMAPs or food
chemicals? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 5:261–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Barrett JS: Extending our knowledge of
fermentable, short-chain carbohydrates for managing
gastrointestinal symptoms. Nutr Clin Pract. 28:300–306. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Biesiekierski JR, Rosella O, Rose R, et
al: Quantification of fructans, galacto-oligosacharides and other
short-chain carbohydrates in processed grains and cereals. J Hum
Nutr Diet. 24:154–176. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Roest RH, Dobbs BR, Chapman BA, et al:
The low FODMAP diet improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients
with irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective study. Int J Clin
Pract. 67:895–903. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Staudacher HM, Whelan K, Irving PM and
Lomer MC: Comparison of symptom response following advice for a
diet low in fermentable carbohydrates (FODMAPs) versus standard
dietary advice in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Hum
Nutr Diet. 24:487–495. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bijkerk CJ, Muris JW, Knottnerus JA, Hoes
AW and de Wit NJ: Systematic review: the role of different types of
fibre in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 19:245–251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ford AC, Talley NJ, Spiegel BM, et al:
Effect of fibre, antispasmodics, and peppermint oil in the
treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ. 337:a23132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Francis CY and Whorwell PJ: Bran and
irritable bowel syndrome: time for reappraisal. Lancet. 344:39–40.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bijkerk CJ, de Wit NJ, Muris JW, Whorwell
PJ, Knottnerus JA and Hoes AW: Soluble or insoluble fibre in
irritable bowel syndrome in primary care? Randomised placebo
controlled trial. BMJ. 339:b31542009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kassinen A, Krogius-Kurikka L, Makivuokko
H, et al: The fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients
differs significantly from that of healthy subjects.
Gastroenterology. 133:24–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Si JM, Yu YC, Fan YJ and Chen SJ:
Intestinal microecology and quality of life in irritable bowel
syndrome patients. World J Gastroenterol. 10:1802–1805.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
El-Salhy M, Seim I, Chopin L, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Irritable bowel syndrome: the role of
gut neuroendocrine peptides. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:2783–2800.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gunawardene AR, Corfe BM and Staton CA:
Classification and functions of enteroendocrine cells of the lower
gastrointestinal tract. Int J Exp Pathol. 92:219–231. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
May CL and Kaestner KH: Gut endocrine cell
development. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 323:70–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Mawe GM, Coates MD and Moses PL: Review
article: intestinal serotonin signalling in irritable bowel
syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:1067–1076. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wade PR, Chen J, Jaffe B, Kassem IS,
Blakely RD and Gershon MD: Localization and function of a 5-HT
transporter in crypt epithelia of the gastrointestinal tract. J
Neurosci. 16:2352–2364. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gershon MD and Tack J: The serotonin
signaling system: from basic understanding to drug development for
functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology. 132:397–414. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gershon MD: 5-Hydroxytryptamine
(serotonin) in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Opin Endocrinol
Diabetes Obes. 20:14–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gershon MD: Serotonin is a sword and a
shield of the bowel: serotonin plays offense and defense. Trans Am
Clin Climatol Assoc. 123:268–280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
El-Salhy M, Mazzawi T, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: The role of peptide YY in
gastrointestinal diseases and disorders (Review). Int J Mol Med.
31:275–282. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dubrasquet M, Bataille D and Gespach C:
Oxyntomodulin (glucagon-37 or bioactive enteroglucagon): a potent
inhibitor of pentagastrin-stimulated acid secretion in rats. Biosci
Rep. 2:391–395. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schjoldager BT, Baldissera FG, Mortensen
PE, Holst JJ and Christiansen J: Oxyntomodulin: a potential hormone
from the distal gut. Pharmacokinetics and effects on gastric acid
and insulin secretion in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 18:499–503. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Schjoldager B, Mortensen PE, Myhre J,
Christiansen J and Holst JJ: Oxyntomodulin from distal gut. Role in
regulation of gastric and pancreatic functions. Dig Dis Sci.
34:1411–1419. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dakin CL, Small CJ, Batterham RL, et al:
Peripheral oxyntomodulin reduces food intake and body weight gain
in rats. Endocrinology. 145:2687–2695. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wynne K, Park AJ, Small CJ, et al:
Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin reduces body weight in overweight and
obese subjects: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
Diabetes. 54:2390–2395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Camilleri M: Peripheral mechanisms in
irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. 367:1626–1635. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Jianu CS, Fossmark R, Syversen U, Hauso O
and Waldum HL: A meal test improves the specificity of chromogranin
A as a marker of neuroendocrine neoplasia. Tumour Biol. 31:373–380.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sandstrom O and El-Salhy M: Ageing and
endocrine cells of human duodenum. Mech Ageing Dev. 108:39–48.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
El-Salhy M: Ghrelin in gastrointestinal
diseases and disorders: a possible role in the pathophysiology and
clinical implications (Review). Int J Mol Med. 24:727–732. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tolhurst G, Reimann F and Gribble FM:
Intestinal sensing of nutrients. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 309–335.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lee J, Cummings BP, Martin E, et al:
Glucose sensing by gut endocrine cells and activation of the vagal
afferent pathway is impaired in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 302:R657–R666.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Parker HE, Reimann F and Gribble FM:
Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient-stimulated incretin
secretion. Expert Rev Mol Med. 12:e12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Raybould HE: Nutrient sensing in the
gastrointestinal tract: possible role for nutrient transporters. J
Physiol Biochem. 64:349–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
San Gabriel A, Nakamura E, Uneyama H and
Torii K: Taste, visceral information and exocrine reflexes with
glutamate through umami receptors. J Med Invest. 56(Suppl):
S209–S217. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rudholm T, Wallin B, Theodorsson E,
Naslund E and Hellstrom PM: Release of regulatory gut peptides
somatostatin, neurotensin and vasoactive intestinal peptide by acid
and hyperosmolal solutions in the intestine in conscious rats.
Regul Pept. 152:8–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sternini C, Anselmi L and Rozengurt E:
Enteroendocrine cells: a site of ‘taste’ in gastrointestinal
chemosensing. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 15:73–78.
2008.
|
|
78
|
Sternini C: Taste receptors in the
gastrointestinal tract. IV. Functional implications of bitter taste
receptors in gastrointestinal chemosensing. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G457–G461. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Buchan AM: Nutrient Tasting and Signaling
Mechanisms in the Gut III. Endocrine cell recognition of luminal
nutrients. Am J Physiol. 277:G1103–G1107. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Montero-Hadjadje M, Elias S, Chevalier L,
et al: Chromogranin A promotes peptide hormone sorting to mobile
granules in constitutively and regulated secreting cells: role of
conserved N- and C-terminal peptides. J Biol Chem. 284:12420–12431.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Shooshtarizadeh P, Zhang D, Chich JF, et
al: The antimicrobial peptides derived from
chromogranin/secretogranin family, new actors of innate immunity.
Regul Pept. 165:102–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Rindi G, Inzani F and Solcia E: Pathology
of gastrointestinal disorders. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
39:713–727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Seim I, El-Salhy M, Hausken T, Gundersen D
and Chopin L: Ghrelin and the brain-gut axis as a pharmacological
target for appetite control. Curr Pharm Des. 18:768–775. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wendelbo I, Mazzawi T and El-Salhy M:
Increased serotonin transporter immunoreactivity intensity in the
ileum of patients with irritable bowel disease. Mol Med Rep.
9:180–184. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
El-Salhy M, Wendelbo IH and Gundersen D:
Reduced chromogranin A cell density in the ileum of patients with
irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 7:1241–1244. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
El-Salhy M, Vaali K, Dizdar V and Hausken
T: Abnormal small-intestinal endocrine cells in patients with
irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 55:3508–3513. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
El-Salhy M, Mazzawi T, Gundersen D and
Hausken T: Chromogranin A cell density in the rectum of patients
with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 6:1223–1225. 2012.
|
|
88
|
El-Salhy M, Lomholt-Beck B and Hausken T:
Chromogranin A as a possible tool in the diagnosis of irritable
bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 45:1435–1439. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
El-Salhy M, Lillebo E, Reinemo A and
Salmelid L: Ghrelin in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Int
J Mol Med. 23:703–707. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
El-Salhy M, Hatlebakk JG, Gundersen D and
Hausken T: Endocrine cells in the gastric oxyntic mucosa of
patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2013.
|
|
91
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Ostgaard H,
Lomholt-Beck B, Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Low densities of
serotonin and peptide YY cells in the colon of patients with
irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 57:873–878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Chromogranin a cell density as a diagnostic marker for
lymphocytic colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 57:3154–3159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Gastric endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa ofpatients
with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2013.
|
|
94
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Gastric antral endocrine cells in patients with
irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013.
|
|
95
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH and Hausken T:
Chromogranin A cells in the stomach of patients with sporadic
irritable bowel syndrome. Histol Histopathol. 2013.
|
|
96
|
Sjolund K, Ekman R and Wierup N:
Covariation of plasma ghrelin and motilin in irritable bowel
syndrome. Peptides. 31:1109–1112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang SH, Dong L, Luo JY, et al: Decreased
expression of serotonin in the jejunum and increased numbers of
mast cells in the terminal ileum in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 13:6041–6047. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Park JH, Rhee PL, Kim G, et al:
Enteroendocrine cell counts correlate with visceral
hypersensitivity in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable
bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 18:539–546. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Coates MD, Mahoney CR, Linden DR, et al:
Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content and decreased
serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable
bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 126:1657–1664. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
El-Salhy M, Wendelbo I and Gundersen D:
Serotonin and serotonin transporter in the rectum of patients with
irritable bowel disease. Mol Med Rep. 8:451–455. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Hotoleanu C, Popp R, Trifa AP, Nedelcu L
and Dumitrascu DL: Genetic determination of irritable bowel
syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 14:6636–6640. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Whorwell PJ, McCallum M, Creed FH and
Roberts CT: Non-colonic features of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut.
27:37–40. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Locke GR III, Zinsmeister AR, Talley NJ,
Fett SL and Melton LJ III: Familial association in adults with
functional gastrointestinal disorders. Mayo Clin Proc. 75:907–912.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kalantar JS, Locke GR III, Zinsmeister AR,
Beighley CM and Talley NJ: Familial aggregation of irritable bowel
syndrome: a prospective study. Gut. 52:1703–1707. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kanazawa M, Endo Y, Whitehead WE, Kano M,
Hongo M and Fukudo S: Patients and nonconsulters with irritable
bowel syndrome reporting a parental history of bowel problems have
more impaired psychological distress. Dig Dis Sci. 49:1046–1053.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Morris-Yates A, Talley NJ, Boyce PM,
Nandurkar S and Andrews G: Evidence of a genetic contribution to
functional bowel disorder. Am J Gastroenterol. 93:1311–1317. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Levy RL, Jones KR, Whitehead WE, Feld SI,
Talley NJ and Corey LA: Irritable bowel syndrome in twins: heredity
and social learning both contribute to etiology. Gastroenterology.
121:799–804. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Lembo A, Zaman M, Jones M and Talley NJ:
Influence of genetics on irritable bowel syndrome,
gastro-oesophageal reflux and dyspepsia: a twin study. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 25:1343–1350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wojczynski MK, North KE, Pedersen NL and
Sullivan PF: Irritable bowel syndrome: a co-twin control analysis.
Am J Gastroenterol. 102:2220–2229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Bengtson MB, Ronning T, Vatn MH and Harris
JR: Irritable bowel syndrome in twins: genes and environment. Gut.
55:1754–1759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Mohammed I, Cherkas LF, Riley SA, Spector
TD and Trudgill NJ: Genetic influences in irritable bowel syndrome:
a twin study. Am J Gastroenterol. 100:1340–1344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Akiho H, Ihara E and Nakamura K: Low-grade
inflammation plays a pivotal role in gastrointestinal dysfunction
in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol.
1:97–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wouters MM and Boeckxstaens GE:
Neuroimmune mechanisms in functional bowel disorders. Neth J Med.
69:55–61. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kuwahara A, Kuramoto H and Kadowaki M:
5-HT activates nitric oxide-generating neurons to stimulate
chloride secretion in guinea pig distal colon. Am J Physiol.
275:G829–G834. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gershon MD: Plasticity in serotonin
control mechanisms in the gut. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 3:600–607.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Zar S, Benson MJ and Kumar D:
Food-specific serum IgG4 and IgE titers to common food antigens in
irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 100:1550–1557. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zar S, Kumar D and Benson MJ: Food
hypersensitivity and irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol
Ther. 15:439–449. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Park MI and Camilleri M: Is there a role
of food allergy in irritable bowel syndrome and functional
dyspepsia? A systematic review. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
18:595–607. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Uz E, Turkay C, Aytac S and Bavbek N: Risk
factors for irritable bowel syndrome in Turkish population: role of
food allergy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 41:380–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Dainese R, Galliani EA, De Lazzari F, Di
Leo V and Naccarato R: Discrepancies between reported food
intolerance and sensitization test findings in irritable bowel
syndrome patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 94:1892–1897. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Bischoff S and Crowe SE: Gastrointestinal
food allergy: new insights into pathophysiology and clinical
perspectives. Gastroenterology. 128:1089–1113. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Murch S: Allergy and intestinal
dysmotility--evidence of genuine causal linkage? Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 22:664–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gui XY: Mast cells: a possible link
between psychological stress, enteric infection, food allergy and
gut hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:980–989. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Teufel M, Biedermann T, Rapps N, et al:
Psychological burden of food allergy. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3456–3465. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Walker MM and Talley NJ: Functional
gastrointestinal disorders and the potential role of eosinophils.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 37:383–395. vi2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Petitpierre M, Gumowski P and Girard JP:
Irritable bowel syndrome and hypersensitivity to food. Ann Allergy.
54:538–540. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Tobin MC, Moparty B, Farhadi A, DeMeo MT,
Bansal PJ and Keshavarzian A: Atopic irritable bowel syndrome: a
novel subgroup of irritable bowel syndrome with allergic
manifestations. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 100:49–53. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Atkinson W, Sheldon TA, Shaath N and
Whorwell PJ: Food elimination based on IgG antibodies in irritable
bowel syndrome: a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 53:1459–1464.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Whorwell PJ: The growing case for an
immunological component to irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Exp
Allergy. 37:805–807. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Hunter JO: Food elimination in IBS: the
case for IgG testing remains doubtful. Gut. 54:1203author reply
1203. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Beyer K and Teuber SS: Food allergy
diagnostics: scientific and unproven procedures. Curr Opin Allergy
Clin Immunol. 5:261–266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Choung RS, Branda ME, Chitkara D, et al:
Longitudinal direct medical costs associated with constipation in
women. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 33:251–260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Ortolani C, Bruijnzeel-Koomen C, Bengtsson
U, et al: Controversial aspects of adverse reactions to food.
European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (EAACI)
Reactions to Food Subcommittee. Allergy. 54:27–45. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Frissora CL and Koch KL: Symptom overlap
and comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other conditions.
Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 7:264–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
El-Salhy M, Lomholt-Beck B and Gundersen
D: The prevalence of celiac disease in patients with irritable
bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 4:403–405. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Catassi C, Kryszak D, Louis-Jacques O, et
al: Detection of Celiac disease in primary care: a multicenter
case-finding study in North America. Am J Gastroenterol.
102:1454–1460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al:
Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in
the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med.
163:286–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
van der Wouden EJ, Nelis GF and Vecht J:
Screening for coeliac disease in patients fulfilling the Rome II
criteria for irritable bowel syndrome in a secondary care hospital
in The Netherlands: a prospective observational study. Gut.
56:444–445. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Locke GR III, Murray JA, Zinsmeister AR,
Melton LJ III and Talley NJ: Celiac disease serology in irritable
bowel syndrome and dyspepsia: a population-based case-control
study. Mayo Clin Proc. 79:476–482. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Hin H, Bird G, Fisher P, Mahy N and Jewell
D: Coeliac disease in primary care: case finding study. BMJ.
318:164–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Shahbazkhani B, Forootan M, Merat S, et
al: Coeliac disease presenting with symptoms of irritable bowel
syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 18:231–235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Korkut E, Bektas M, Oztas E, Kurt M,
Cetinkaya H and Ozden A: The prevalence of celiac disease in
patients fulfilling Rome III criteria for irritable bowel syndrome.
Eur J Intern Med. 21:389–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Sanders DS, Patel D, Stephenson TJ, et al:
A primary care cross-sectional study of undiagnosed adult coeliac
disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:407–413. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Verdu EF, Armstrong D and Murray JA:
Between celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome: the ‘no man’s
land’ of gluten sensitivity. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:1587–1594.
2009.
|
|
145
|
Wahnschaffe U, Schulzke JD, Zeitz M and
Ullrich R: Predictors of clinical response to gluten-free diet in
patients diagnosed with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel
syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:844–850; quiz 769. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Carroccio A, Mansueto P, Iacono G, et al:
Non-celiac wheat sensitivity diagnosed by double-blind
placebo-controlled challenge: exploring a new clinical entity. Am J
Gastroenterol. 107:1898–1906; quiz 1907. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Aziz I and Sanders DS: Emerging concepts:
from coeliac disease to non-coeliac gluten sensitivity. Proc Nutr
Soc. 71:576–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Newnham ED: Does gluten cause
gastrointestinal symptoms in subjects without coeliac disease? J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26(Suppl 3): S132–S134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Biesiekierski JR, Peters SL, Newnham ED,
Rosella O, Muir JG and Gibson PR: No effects of gluten in patients
with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity after dietary
reduction of fermentable, poorly absorbed, short-chain
carbohydrates. Gastroenterology. 145:320–328. e3232013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Mazzawi T, Hausken T, Gundersen D and
El-Salhy M: Effects of dietary guidance on the symptoms, quality of
life and habitual dietary intake of patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 8:845–852. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
El-Salhy M, Lilbo E, Reinemo A, Salmeøid L
and Hausken T: Effects of a health program comprising reassurance,
diet management, probiotic administration and regular exercise on
symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Gastroenterol Insights. 2:21–26. 2010.
|
|
152
|
Posserud I, Syrous A, Lindstrom L, Tack J,
Abrahamsson H and Simren M: Altered rectal perception in irritable
bowel syndrome is associated with symptom severity.
Gastroenterology. 133:1113–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Ritchie J: Pain from distension of the
pelvic colon by inflating a balloon in the irritable colon
syndrome. Gut. 14:125–132. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Mertz H, Naliboff B, Munakata J, Niazi N
and Mayer EA: Altered rectal perception is a biological marker of
patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology.
109:40–52. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Whitehead WE and Palsson OS: Is rectal
pain sensitivity a biological marker for irritable bowel syndrome:
psychological influences on pain perception. Gastroenterology.
115:1263–1271. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Whitehead WE, Holtkotter B, Enck P, et al:
Tolerance for rectosigmoid distention in irritable bowel syndrome.
Gastroenterology. 98:1187–1192. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Bouin M, Plourde V, Boivin M, et al:
Rectal distention testing in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of pain
sensory thresholds. Gastroenterology. 122:1771–1777. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Bradette M, Delvaux M, Staumont G,
Fioramonti J, Bueno L and Frexinos J: Evaluation of colonic sensory
thresholds in IBS patients using a barostat. Definition of optimal
conditions and comparison with healthy subjects. Dig Dis Sci.
39:449–457. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Camilleri M, McKinzie S, Busciglio I, et
al: Prospective study of motor, sensory, psychologic, and autonomic
functions in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:772–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Costantini M, Sturniolo GC, Zaninotto G,
et al: Altered esophageal pain threshold in irritable bowel
syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 38:206–212. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Trimble KC, Farouk R, Pryde A, Douglas S
and Heading RC: Heightened visceral sensation in functional
gastrointestinal disease is not site-specific. Evidence for a
generalized disorder of gut sensitivity. Dig Dis Sci. 40:1607–1613.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Zighelboim J, Talley NJ, Phillips SF,
Harmsen WS and Zinsmeister AR: Visceral perception in irritable
bowel syndrome. Rectal and gastric responses to distension and
serotonin type 3 antagonism. Dig Dis Sci. 40:819–827. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Accarino AM, Azpiroz F and Malagelada JR:
Selective dysfunction of mechanosensitive intestinal afferents in
irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 108:636–643. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Kanazawa M, Hongo M and Fukudo S: Visceral
hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 26(Suppl 3): S119–S121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Whorwell PJ, Clouter C and Smith CL:
Oesophageal motility in the irritable bowel syndrome. Br Med J
(Clin Res Ed). 282:1101–1102. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Clouse RE and Eckert TC: Gastrointestinal
symptoms of patients with esophageal contraction abnormalities. Dig
Dis Sci. 31:236–240. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Soffer EE, Scalabrini P, Pope CE II and
Wingate DL: Effect of stress on oesophageal motor function in
normal subjects and in patients with the irritable bowel syndrome.
Gut. 29:1591–1594. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Lind CD: Motility disorders in the
irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 20:279–295.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Lee OY: Asian motility studies in
irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 16:120–130.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
van Wijk HJ, Smout AJ, Akkermans LM,
Roelofs JM and ten Thije OJ: Gastric emptying and dyspeptic
symptoms in the irritable bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol.
27:99–102. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Charles F, Phillips SF, Camilleri M and
Thomforde GM: Rapid gastric emptying in patients with functional
diarrhea. Mayo Clin Proc. 72:323–328. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Caballero-Plasencia AM,
Valenzuela-Barranco M, Herrerias-Gutierrez JM and Esteban-Carretero
JM: Altered gastric emptying in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Eur J Nucl Med. 26:404–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Portincasa P, Moschetta A, Baldassarre G,
Altomare DF and Palasciano G: Pan-enteric dysmotility, impaired
quality of life and alexithymia in a large group of patients
meeting ROME II criteria for irritable bowel syndrome. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:2293–2299. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Stanghellini V, Tosetti C, Barbara G, et
al: Dyspeptic symptoms and gastric emptying in the irritable bowel
syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 97:2738–2743. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Leahy A, Besherdas K, Clayman C, Mason I
and Epstein O: Abnormalities of the electrogastrogram in functional
gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 94:1023–1028. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Evans PR, Bak YT, Shuter B, Hoschl R and
Kellow JE: Gastroparesis and small bowel dysmotility in irritable
bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 42:2087–2093. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Nielsen OH, Gjorup T and Christensen FN:
Gastric emptying rate and small bowel transit time in patients with
irritable bowel syndrome determined with 99mTc-labeled pellets and
scintigraphy. Dig Dis Sci. 31:1287–1291. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Narducci F, Bassotti G, Granata MT, et al:
Colonic motility and gastric emptying in patients with irritable
bowel syndrome. Effect of pretreatment with octylonium bromide. Dig
Dis Sci. 31:241–246. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Acharya U, Waite N, Howlett P, Tanner AR
and Smith CL: Failure to demonstrate altered gastric emptying in
irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 28:889–892. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|