|
1
|
Luehr M, Bachet J, Mohr FW and Etz CD:
Modern temperature management in aortic surgery: the dilemma of
moderate hypothermia. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 45:27–39. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Griepp RB and Di Luozzo G: Hypothermia for
aortic surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 145(Suppl 3): S56–S58.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
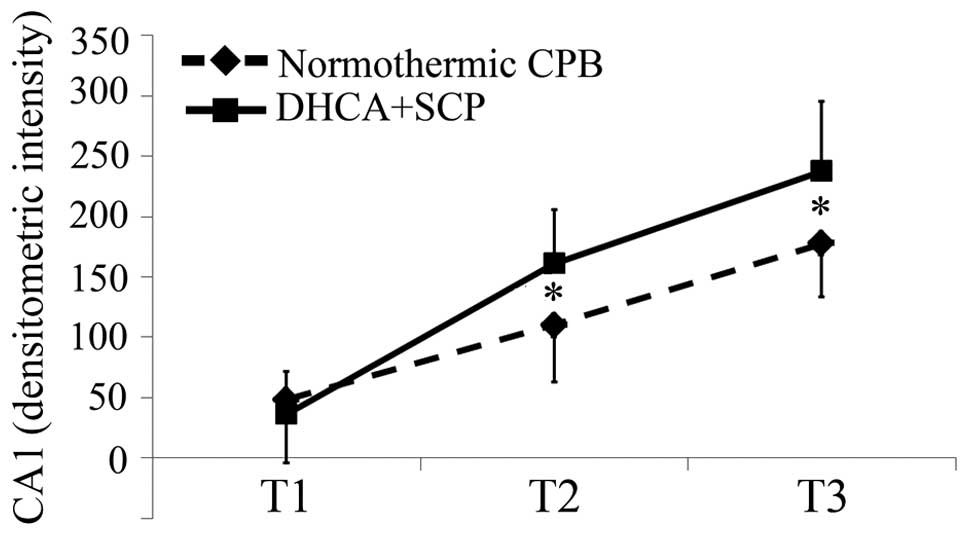
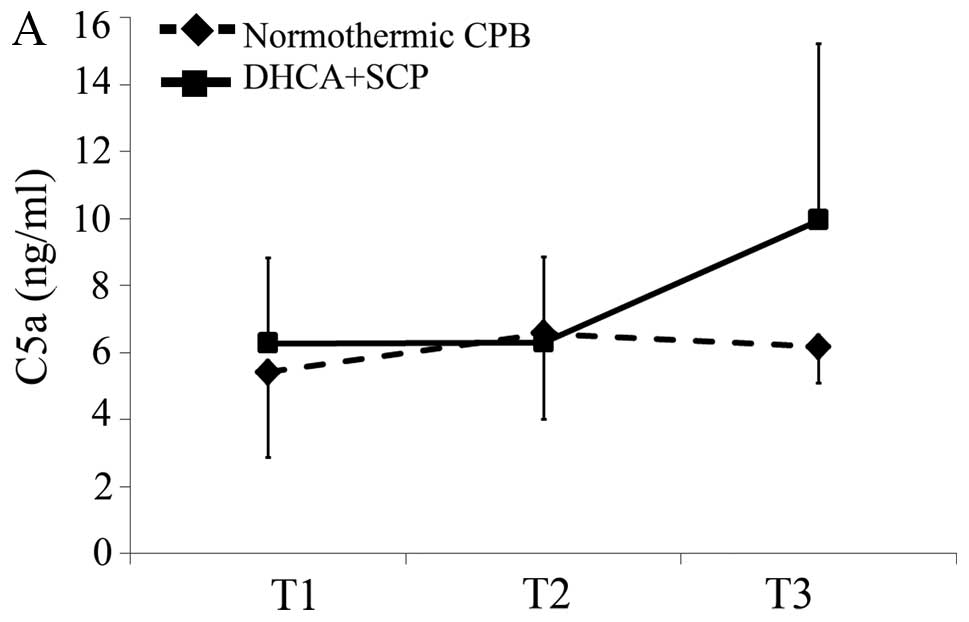
|
|
3
|
Goldstein DJ, DeRosa CM, Mongero LB,
Weinberg AD, Michler RE, Rose EA, Oz MC and Smith CR: Safety and
efficacy of aprotinin under conditions of deep hypothermia and
circulatory arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 110:1615–1621. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minatoya K, Ogino H, Matsuda H, Sasaki H,
Tanaka H, Kobayashi J, Yagihara T and Kitamura S: Evolving
selective cerebral perfusion for aortic arch replacement: high flow
rate with moderate hypothermic circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg.
86:1827–1831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu L, Candille SI, Choi Y, Xie D, Jiang L,
Li-Pook-Than J, Tang H and Snyder M: Variation and genetic control
of protein abundance in humans. Nature. 499:79–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pottiez G, Wiederin J, Fox HS and
Ciborowski P: Comparison of 4-plex to 8-plex iTRAQ quantitative
measurements of proteins in human plasma samples. J Proteome Res.
11:774–3781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Satoh K, Maniwa T, Oda T and Matsumoto K:
Proteomic profiling for the identification of serum diagnostic
biomarkers for abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms. Proteome
Sci. 11:272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lancaster TS, Jefferson SJ, Hunter JC,
Lopez V, Van Eyk JE, Lakatta EG and Korzick DH: Quantitative
proteomic analysis reveals novel mitochondrial targets of estrogen
deficiency in the aged female rat heart. Physiol Genomics.
44:957–969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT and
Thomas PD: Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER
classification system. Nat Protoc. 8:1551–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, et al:
Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet.
25:25–29. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kelly RF, Cabrera JA, Ziemba EA, Crampton
M, Anderson LB, McFalls EO and Ward HB: Continued depression of
maximal oxygen consumption and mitochondrial proteomic expression
despite successful coronary artery bypass grafting in a swine model
of hibernation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 141:261–268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kourliouros A, Yin X, Didangelos A,
Hosseini MT, Valencia O, Mayr M and Jahangiri M: Substrate
modifications precede the development of atrial fibrillation after
cardiac surgery: a proteomic study. Ann Thorac Surg. 92:104–110.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lynn DJ, Chan C, Naseer M, Yau M, Lo R,
Sribnaia A, Ring G, Que J, Wee K, Winsor GL, Laird MR, Breuer K,
Foroushani AK, Brinkman FS and Hancock RE: Curating the innate
immunity interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 4:1172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Salama A, Hugo F, Heinrich D, Höge R,
Müller R, Kiefel V, Mueller-Eckhardt C and Bhakdi S: Deposition of
terminal C5b-9 complement complexes on erythrocytes and leukocytes
during cardiopulmonary bypass. N Engl J Med. 318:408–414. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kouchoukos NT, Blackstone EH, Doty DB,
Hanley FL and Karp RB: Hypothermia, circulatory arrest, and
cardiopulmonary bypass. Kirklin/Barratt-Boyes, Cardiac Surgery:
Morphology, Diagnostic Criteria, Natural History, Techniques,
Results, and Indications. 3rd edition. Churchill Livingstone;
Philadelphia, PA: pp. 91–96. 2003
|
|
16
|
Marcheix B, Carrier M, Martel C, Cossette
M, Pellerin M, Bouchard D and Perrault LP: Effect of pericardial
blood processing on postoperative inflammation and the complement
pathways. Ann Thorac Surg. 85:530–535. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Videm V, Mollnes TE, Garred P and
Svennevig JL: Biocompatibility of extracorporeal circulation. In
vitro comparison of heparin-coated and uncoated oxygenator
circuits. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 101:654–660. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mahmood S, Bilal H, Zaman M and Tang A: Is
a fully heparin-bonded cardiopulmonary bypass circuit superior to a
standard cardiopulmonary bypass circuit? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac
Surg. 14:406–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thiara AS, Mollnes TE, Videm V, Anderson
VY, Svennevig K, Kolset SO and Fiane AE: Biocompatibility and
pathways of initial complement pathway activation with Phisio- and
PMEA-coated cardiopulmonary bypass circuits during open heart
surgery. Perfusion. 26:107–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gabriel EA, Montevilla FM, Chida VV, Dias
FN, Montoya CV, Otsubo H, Pires ZF and Nogaroto SL: Experimental
research with synthetic copolymer-coated cardiopulmonary bypass
circuits: inflammatory and thrombogenicity analysis. Artif Organs.
36:110–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Smith PK, Shernan SK, Chen JC, Carrier M,
Verrier ED, Adams PX, Todaro TG, Muhbaier LH and Levy JH;
PRIMO-CABG II Investigators. Effects of C5 complement inhibitor
pexelizumab on outcome in high-risk coronary artery bypass
grafting: combined results from the PRIMO-CABG I and II trials. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 142:89–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baig K, Nassar R, Craig DM, Quick G Jr,
Jiang HX, Frank MM, Lodge AJ, Anderson PA and Jaggers J: Complement
factor 1 inhibitor improves cardiopulmonary function in neonatal
cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 83:1477–1483. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Umstead TM, Lu CJ, Freeman WM, et al: The
kinetics of cardiopulmonary bypass: a dual-platform proteomics
study of plasma biomarkers in pediatric patients undergoing
cardiopulmonary bypass. Artif Organs. 36:E1–E20. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anderson NL, Polanski M, Pieper R, Gatlin
T, Tirumalai RS, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Adkins JN, Pounds JG,
Fagan R and Lobley A: The human plasma proteome: a nonredundant
list developed by combination of four separate sources. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 3:311–326. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chello M, Mastroroberto P, Romano R,
Ascione R, Pantaleo D and De Amicis V: Complement and neutrophil
activation during cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized comparison
of hypothermic and normothermic circulation. Euro J Cardiothorac
Surg. 11:162–168. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Polderman KH: Mechanisms of action,
physiological effects, and complications of hypothermia. Crit Care
Med. 37(Suppl 7): 186–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bisschops LL, Hoedemaekers CW, Mollnes TE
and van der Hoeven JG: Rewarming after hypothermia after cardiac
arrest shifts the inflammatory balance. Crit Care Med.
40:1136–1142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oda T, Shimizu K, Yamaguchi A, Satoh K and
Matsumoto K: Hypothermia produces rat liver proteomic changes as in
hibernating mammals but decreases endoplasmic reticulum chaperones.
Cryobiology. 65:104–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ehrnthaller C, Ignatius A, Gebhard F and
Hurber-Lang M: New insights of an old defense system: structure,
function, and clinical relevance of the complement system. Mol Med.
17:317–329. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rauen U, Petrat F, Li T and de Groot H:
Hypothermia injury/cold-induced apoptosis-evidence of an increase
in chelatable iron causing oxidative injury in spite of low
O2−/H2O2formation.
FASEB J. 14:1953–1964. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao BB, Clermont A, Rook S, Fonda SJ,
Srinivasan VJ, Wojtkowski M, Fujimoto JG, Avery RL, Arigg PG,
Bursell SE, Aiello LP and Feener EP: Extracellular carbonic
anhydrase mediates hemorrhagic retinal and cerebral vascular
permeability through prekallikrein activation. Nat Med. 13:181–188.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kramer MD, Schaefer BM and Reinartz J:
Network interactions of the complement system with other serum
mediator systems. The Complement System. Rother K, Till GO and
Hansch GM: 2nd revised edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin;
Heidelberg: pp. 324–341. 1998
|
|
33
|
Kaplan AP and Ghebrehiwet B: The plasma
bradykinin-forming pathways and its interrelationships with
complement. Mol Immunol. 47:2161–2169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tapryal N, Mukhopadhyay C, Das D, Fox PL
and Mukhopadhyay CK: Reactive oxygen species regulate ceruloplasmin
by a novel mRNA decay mechanism involving its 3′-untranslated
region: implications in neurodegenerative diseases. J Biol Chem.
284:1873–1883. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chapman AL, Mocatta TJ, Shiva S, Seidel A,
Chen B, Khalilova I, Paumann-Page ME, Jameson GN, Winterbourn CC
and Kettle AJ: Ceruloplasmin is an endogenous inhibitor of
myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 288:6465–6477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|