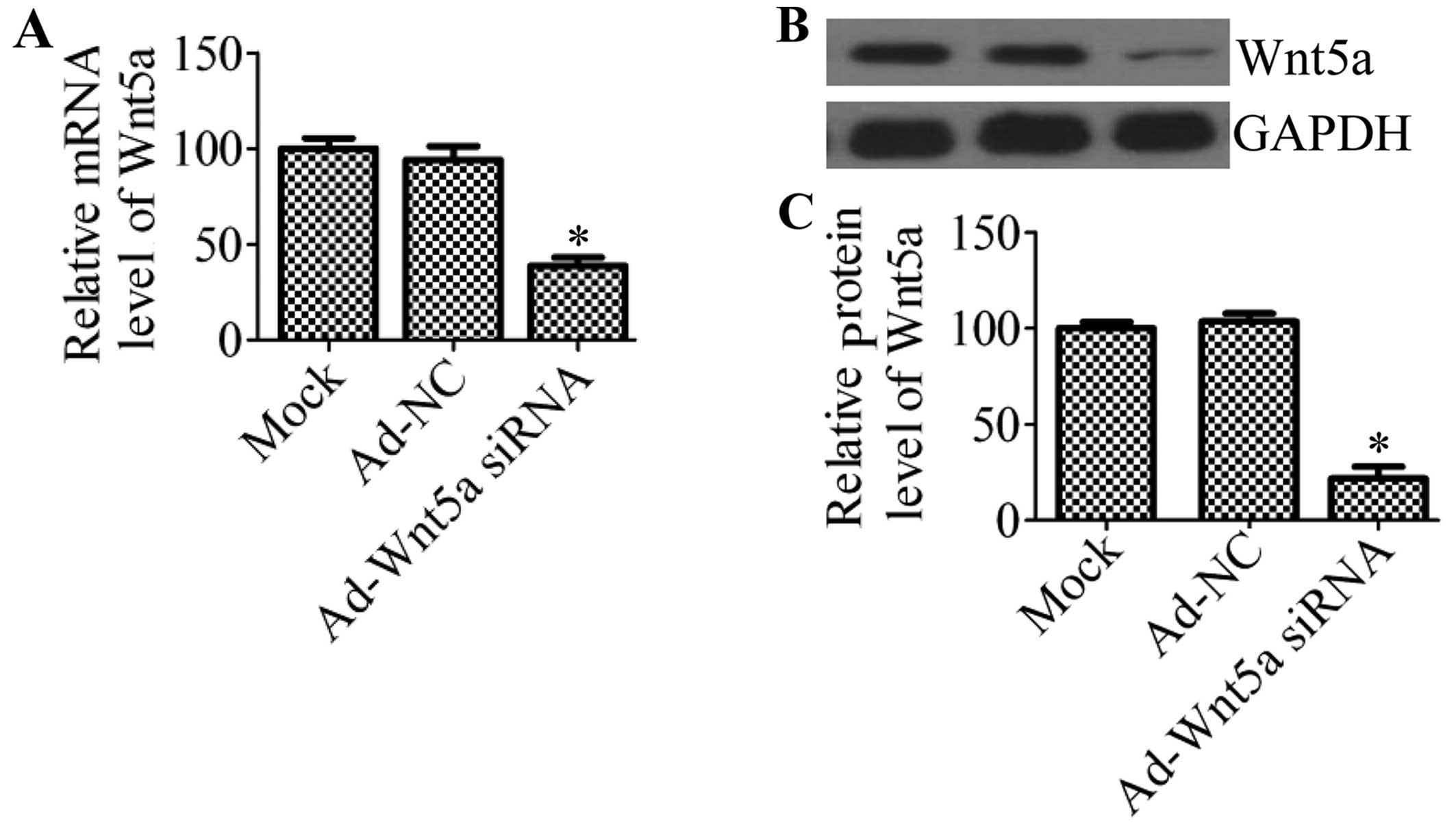
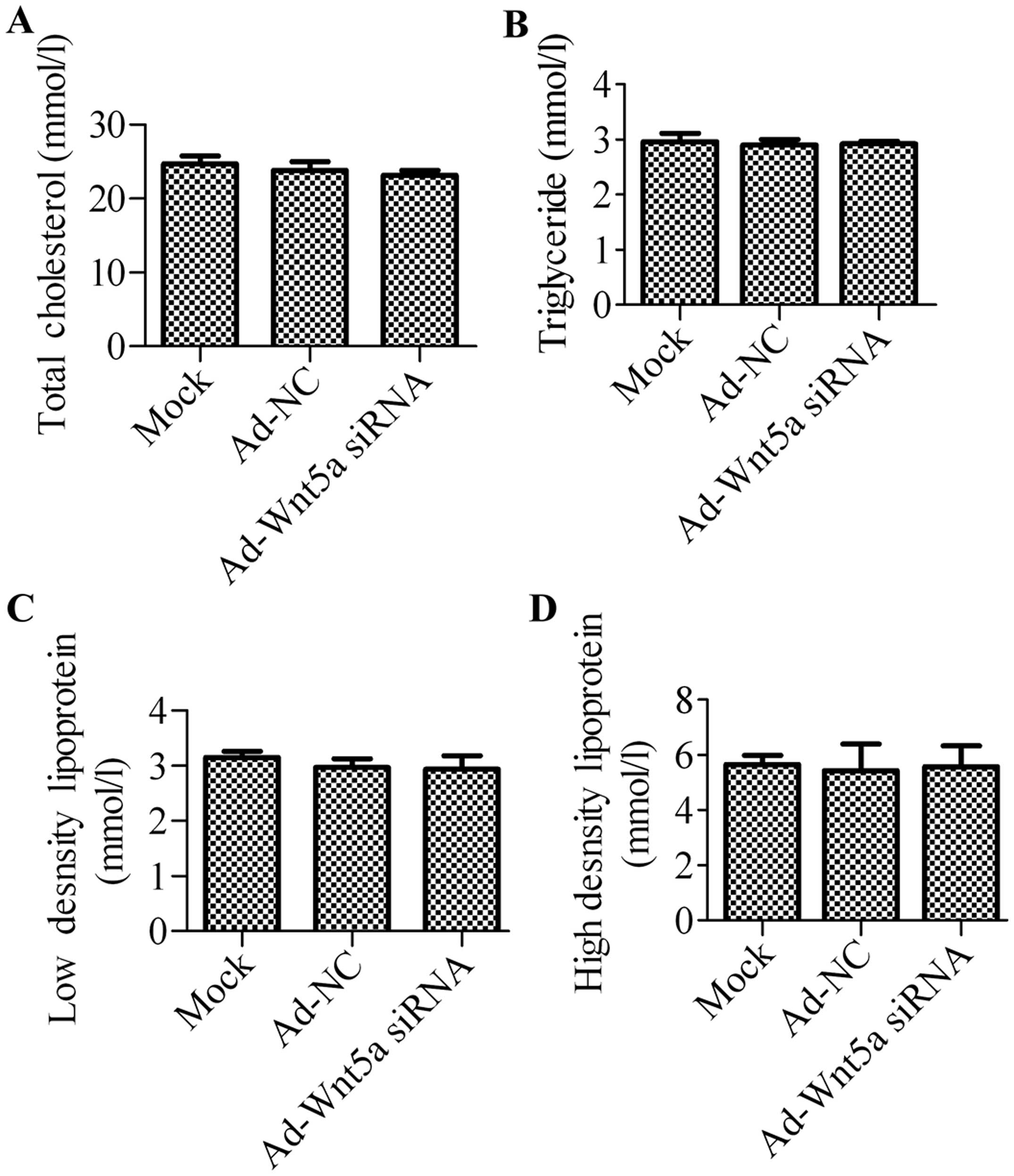
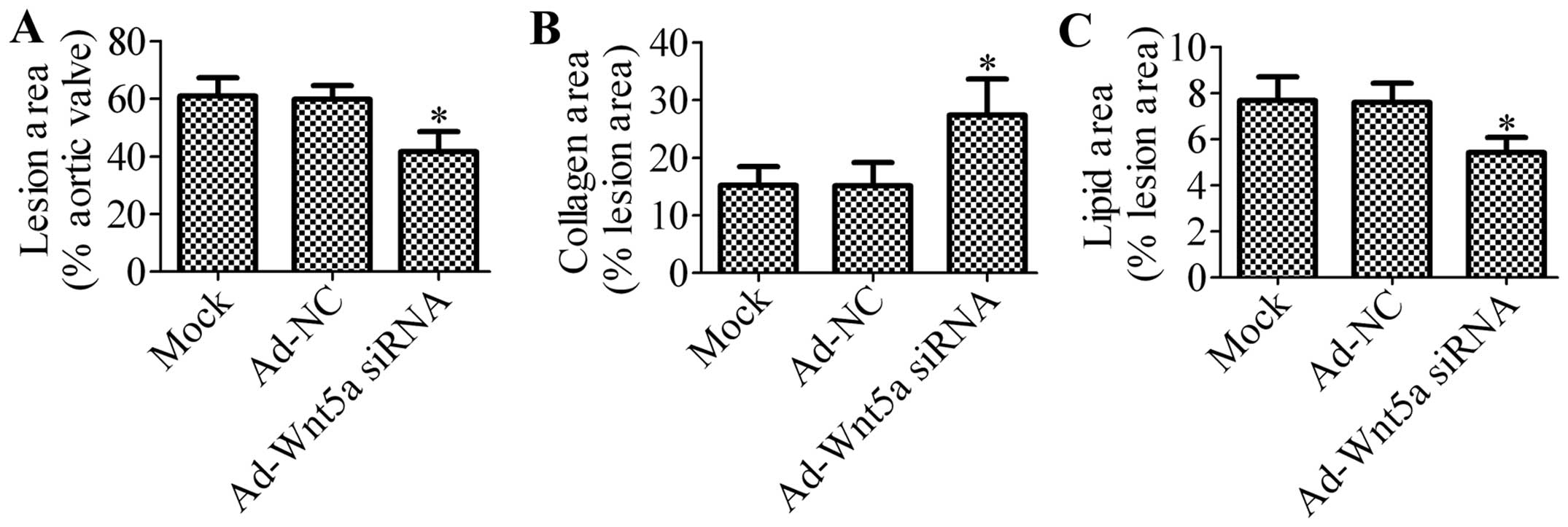
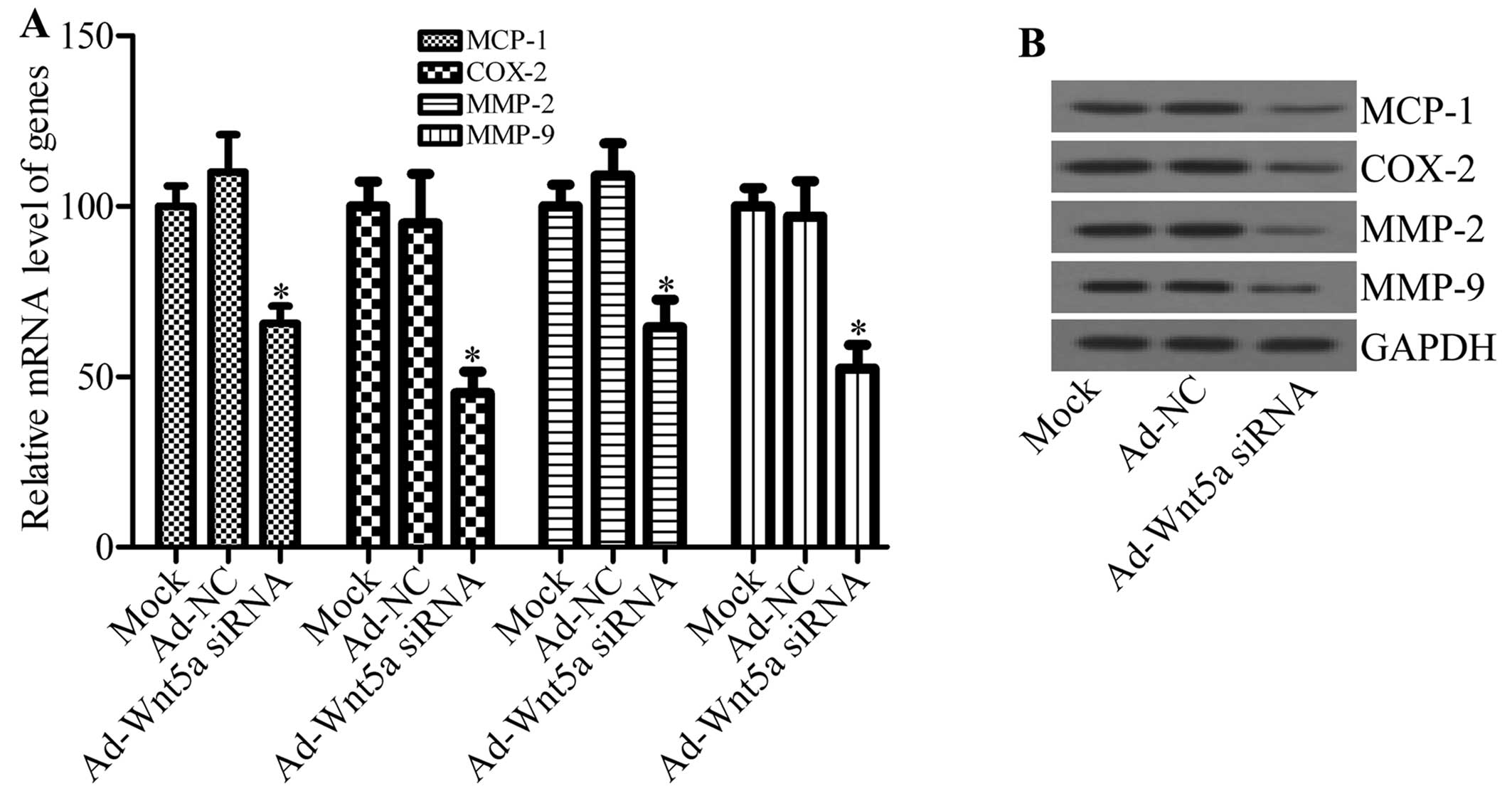
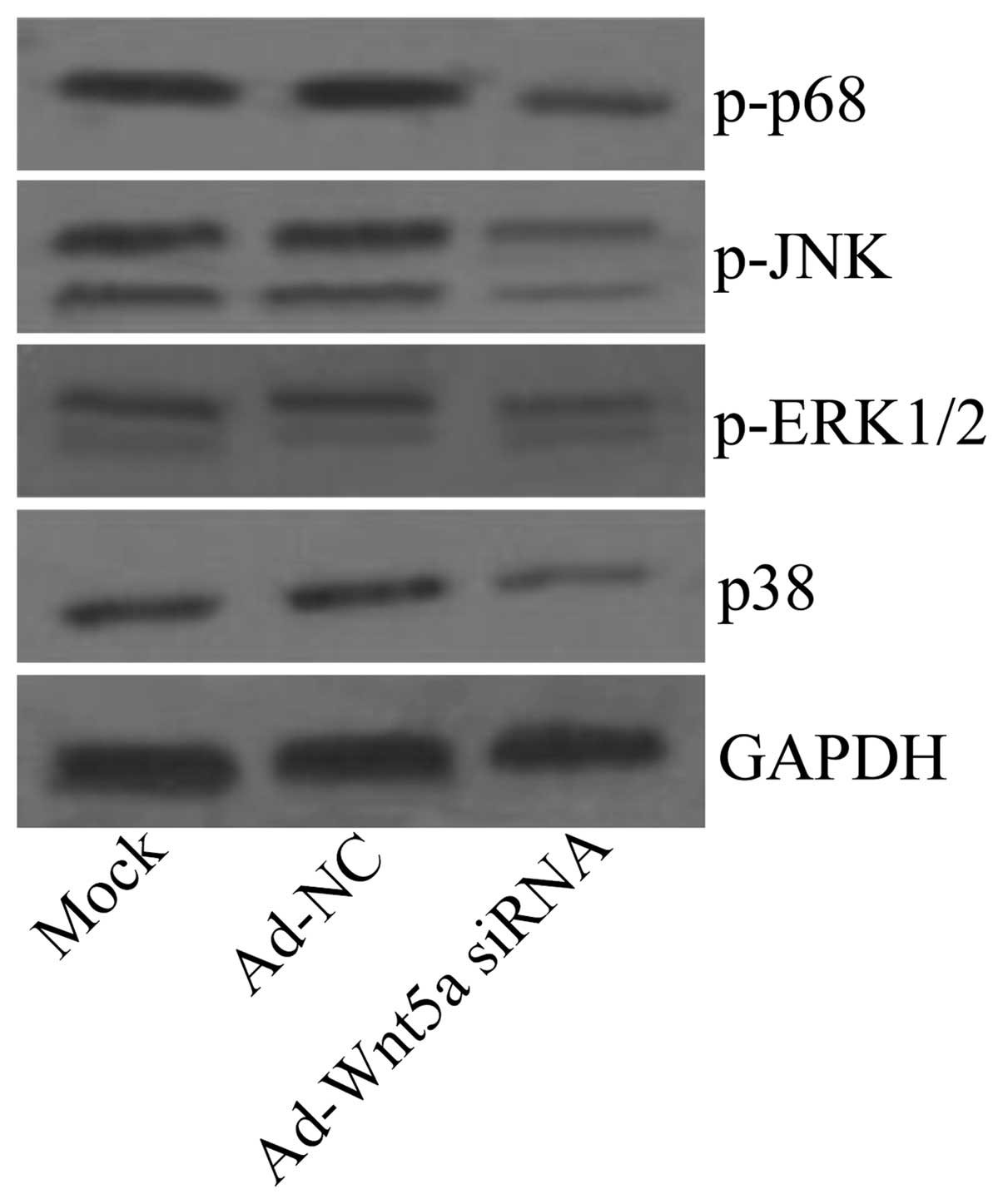
|
1
|
Glass CK and Witztum JL: Atherosclerosis.
the road ahead. Cell. 104:503–516. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li AC and Glass CK: The macrophage foam
cell as a target for therapeutic intervention. Nat Med.
8:1235–1242. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H, Sato A and
Matsumoto S: Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in
diseases. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 204:17–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sen M, Lauterbach K, El-Gabalawy H, et al:
Expression and function of wingless and frizzled homologs in
rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:2791–2796. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Christman MA II, Goetz DJ, Dickerson E, et
al: Wnt5a is expressed in murine and human atherosclerotic lesions.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 294:H2864–H2870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reischl J, Schwenke S, Beekman JM, et al:
Increased expression of Wnt5a in psoriatic plaques. J Invest
Dermatol. 127:163–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pereira C, Schaer DJ, Bachli EB, Kurrer MO
and Schoedon G: Wnt5A/CaMKII signaling contributes to the
inflammatory response of macrophages and is a target for the
antiinflammatory action of activated protein C and interleukin-10.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:504–510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Halleskog C, Dijksterhuis JP, Kilander MB,
et al: Heterotrimeric G protein-dependent WNT-5A signaling to
ERK1/2 mediates distinct aspects of microglia proinflammatory
transformation. J Neuroinflammation. 9:1112012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim J, Kim J, Kim DW, Ha Y, et al: Wnt5a
induces endothelial inflammation via beta-catenin-independent
signaling. J Immunol. 185:1274–1282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung YS, Lee HY, Kim SD, et al: Wnt5a
stimulates chemotactic migration and chemokine production in human
neutrophils. Exp Mol Med. 45:e272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malgor R, Bhatt PM, Connolly BA, et al:
Wnt5a, TLR2 and TLR4 are elevated in advanced human atherosclerotic
lesions. Inflamm Res. 63:277–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan X, Baxter RC, Perbal B and Firth SM:
The aminoterminal insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding domain
of IGF binding protein-3 cannot be functionally substituted by the
structurally homologous domain of CCN3. Endocrinology.
147:5268–5274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Hansson GK:
Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from pathophysiology to practice.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:2129–2138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kutuk O and Basaga H: Inflammation meets
oxidation: NF-kappaB as a mediator of initial lesion development in
atherosclerosis. Trends Mol Med. 9:549–557. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan ED and Riches DW: IFN-gamma + LPS
induction of iNOS is modulated by ERK, JNK/SAPK, and p38(mapk) in a
mouse macrophage cell line. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
280:C441–C450. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schönbeck U, Sukhova GK, Graber P, Coulter
S and Libby P: Augmented expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human
atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 155:1281–1291.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burleigh ME, Babaev VR, Oates JA, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes early atherosclerotic lesion formation in
LDL receptor-deficient mice. Circulation. 105:1816–1823. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burleigh ME, Babaev VR, Yancey PG, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes early atherosclerotic lesion formation in
ApoE-deficient and C57BL/6 mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 39:443–452.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gosling J, Slaymaker S, Gu L, et al: MCP-1
deficiency reduces susceptibility to atherosclerosis in mice that
overexpress human apolipoprotein B. J Clin Invest. 103:773–778.
1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Falk E: Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 47(Suppl 8): C7–C12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Davies MJ: The pathophysiology of acute
coronary syndromes. Heart. 83:361–366. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schaar JA, Muller JE, Falk E, et al:
Terminology for high-risk and vulnerable coronary artery plaques.
Report of a meeting on the vulnerable plaque, June 17 and 18, 2003,
Santorini, Greece. Eur Heart J. 25:1077–1082. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ylä-Herttuala S, Bentzon JF, Daemen M, et
al: Stabilisation of atherosclerotic plaques. Position paper of the
European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working Group on
atherosclerosis and vascular biology. Thromb Haemost. 106:1–19.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, et al: From
vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions
and risk assessment strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108:1664–1672.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Newby AC: Metalloproteinase expression in
monocytes and macrophages and its relationship to atherosclerotic
plaque instability. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:2108–2114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bond M, Fabunmi RP, Baker AH and Newby AC:
Synergistic upregulation of metalloproteinase-9 by growth factors
and inflammatory cytokines: an absolute requirement for
transcription factor NF-kappa B. FEBS Lett. 435:29–34. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Zhang R, Xu Y, et al: Genistein
inhibits the development of atherosclerosis via inhibiting
NF-kappaB and VCAM-1 expression in LDLR knockout mice. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 86:777–784. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Muslin AJ: MAPK signalling in
cardiovascular health and disease: molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets. Clin Sci (Lond). 115:203–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|