|
1
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Nature. 420:868–874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Spagnoli LG, Bonanno E, Sangiorgi G and
Mauriello A: Role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med.
48:1800–1815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
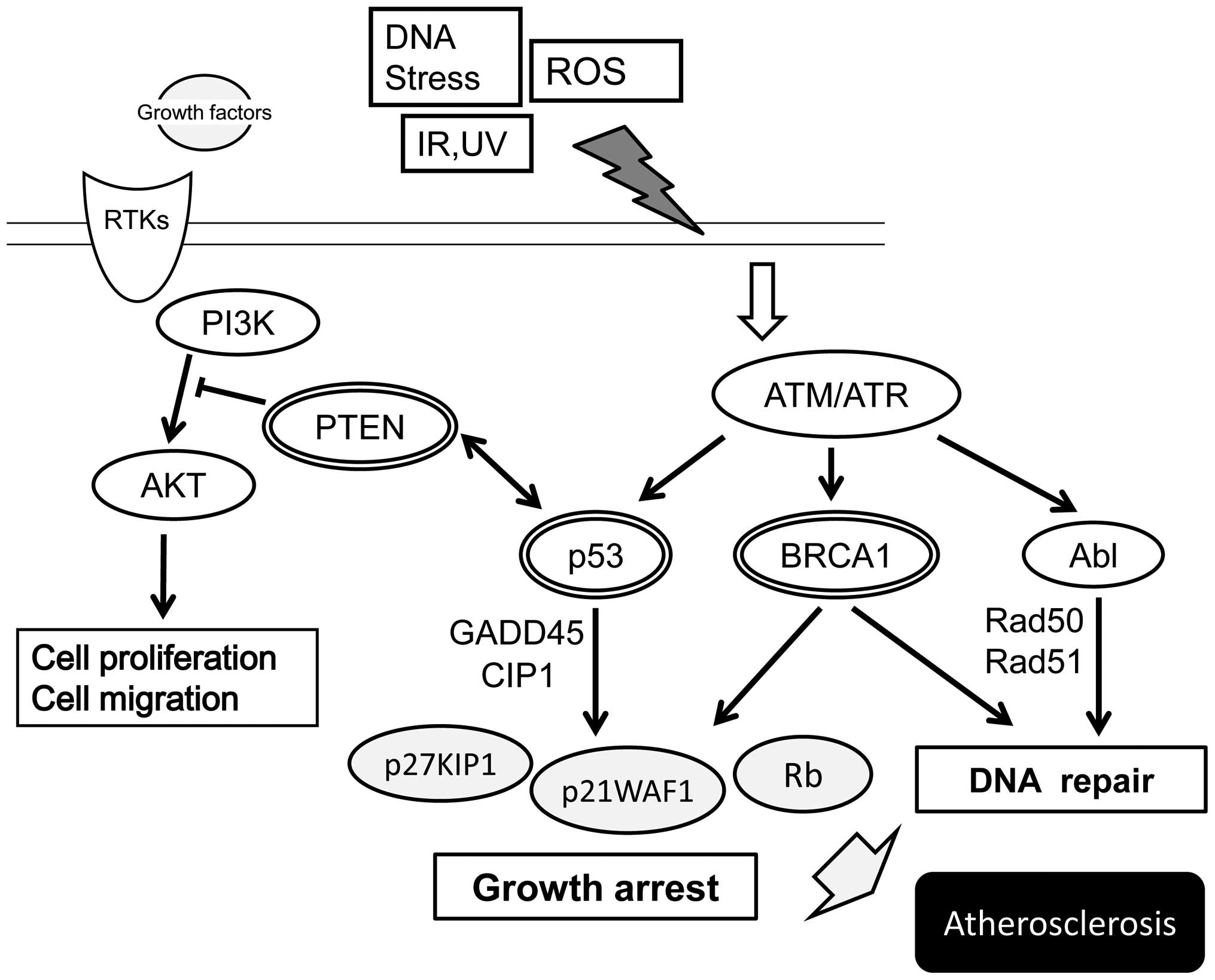
|
Curtiss LK and Tobias PS: The toll of
Toll-like receptors, especially toll-like receptor 2, on murine
atherosclerosis. Curr Drug Targets. 8:1230–1238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cicchi R, Matthäus C, Meyer T, Lattermann
A, Dietzek B, Brehm BR, Popp J and Pavone FS: Characterization of
collagen and cholesterol deposition in atherosclerotic arterial
tissue using non-linear microscopy. J Biophotonics. 7:135–143.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pakala R, Rha SW, Kuchulakanti PK, Cheneau
E, Baffour R and Waksman R: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma; Its role in atherosclerosis and restenosis.
Cardiovasc Radiat Med. 5:44–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bays HE: Adiposopathy, diabetes mellitus,
and primary prevention of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease:
treating ‘sick fat’ through improving fat function with
antidiabetes therapies. Am J Cardiol. 110:B4–B12. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blüher M: Adipose tissue dysfunction in
obesity. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 117:241–250. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Stoll BA: Western nutrition and the
insulin resistance syndrome: a link to breast cancer. Eur J Clin
Nutr. 53:83–87. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kligerman AD, Malik SI and Campbell JA:
Cytogenetic insights into DNA damage and repair of lesions induced
by a monomethylated trivalent arsenical. Mutat Res. 695:2–8. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin FY, Lin YW, Huang CY, Chang YJ, Tsao
NW, Chang NC, Ou KL, Chen TL, Shih CM and Chen YH: GroEL1, a heat
shock protein 60 of Chlamydia pneumoniae, induces lectin-like
oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 expression in
endothelial cells and enhances atherogenesis in
hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Immunol. 186:4405–4414. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dai Y, Mercanti F, Dai D, Wang X, Ding Z,
Pothineni NV and Mehta JL: LOX-1, a bridge between GLP-1R and
mitochondrial ROS generation in human vascular smooth muscle cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 437:62–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dickhout JG, Basseri S and Austin RC:
Macrophage function and its impact on atherosclerotic lesion
composition, progression, and stability: the good, the bad, and the
ugly. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1413–1415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Edlin RS, Tsai S, Yamanouchi D, Wang C,
Liu B and Kent KC: Characterization of primary and restenotic
atherosclerotic plaque from the superficial femoral artery:
potential role of Smad3 in regulation of SMC proliferation. J Vasc
Surg. 49:1289–1295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Humphries SE and Ordovas JM: Genetics and
atherosclerosis: broadening the horizon. Atherosclerosis.
154:517–519. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mercer J and Bennett M: The role of p53 in
atherosclerosis. Cell Cycle. 5:1907–1909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khanna AK: Enhanced susceptibility of
cyclin kinase inhibitor p21 knockout mice to high fat diet induced
atherosclerosis. J Biomed Sci. 15:16–66. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heusch G, Libby P, Gersh B, Yellon D, Böhm
M, Lopaschuk G and Opie L: Cardiovascular remodelling in coronary
artery disease and heart failure. Lancet. 383:1933–1943. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mak AS: p53 in cell invasion, podosomes,
and invadopodia. Cell Adh Migr. Feb 18–2014.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
19
|
Ishii N, Matsumura T, Kinoshita H,
Motoshima H, Kojima K, Tsutsumi A, Kawasaki S, Yano M, Senokuchi T,
Asano T, Nishikawa T and Araki E: Activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase suppresses oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
macrophage proliferation. J Biol Chem. 284:34561–34569. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Anderson JL, Ashwell CM, Smith SC, Shine
R, Smith EC and Taylor RL Jr: Atherosclerosis-susceptible and
atherosclerosis-resistant pigeon aortic cells express different
genes in vivo. Poult Sci. 92:2668–2680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu WM, Scott KA, Thompson M and Dalgleish
AG: Dendritic cell phenotype can be improved by certain
chemotherapies and is associated with alterations to
p21(waf1/cip1.). Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:1553–1561. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HJ, Yoo EK, Kim JY, Choi YK, Lee HJ,
Kim JK, Jeoung NH, Lee KU, Park IS, Min BH, Park KG, Lee CH, Aronow
BJ, Sata M and Lee IK: Protective role of clusterin/apolipoprotein
J against neointimal hyperplasia via antiproliferative effect on
vascular smooth muscle cells and cytoprotective effect on
endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1558–1564.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Obikane H, Abiko Y, Ueno H, Kusumi Y,
Esumi M and Mitsumata M: Effect of endothelial cell proliferation
on atherogenesis: a role of p21(Sdi/Cip/Waf1) in monocyte adhesion
to endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 212:116–122. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Breitenstein A, Akhmedov A, Camici GG,
Lüscher TF and Tanner FC: p27(Kip1) inhibits tissue factor
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 439:559–563. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Conte MS, Owens CD, Belkin M, Creager MA,
Edwards KL, Gasper WJ, Kenagy RD, LeBoeuf RC, Sobel M and Clowes A:
A single nucleotide polymorphism in the p27(Kip1) gene is
associated with primary patency of lower extremity vein bypass
grafts. J Vasc Surg. 57:1179–1185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Díez-Juan A, Pérez P, Aracil M, Sancho D,
Bernad A, Sánchez-Madrid F and Andrés V: Selective inactivation of
p27(Kip1) in hematopoietic progenitor cells increases neointimal
macrophage proliferation and accelerates atherosclerosis. Blood.
103:158–161. 2004.
|
|
27
|
Shahzad K, Thati M, Wang H, Kashif M,
Wolter J, Ranjan S, He T, Zhou Q, Blessing E, Bierhaus A, Nawroth
PP and Isermann B: Minocycline reduces plaque size in diet induced
atherosclerosis via p27(Kip1). Atherosclerosis. 219:74–83. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lange M, Fujikawa T, Koulova A, Kang S,
Griffin MJ, Lassaletta AD, Erat A, Tobiasch E, Bianchi C, Elmadhun
N, Sellke FW and Usheva A: Arterial territory-specific
phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein species and CDK2 promote
differences in the vascular smooth muscle cell response to
mitogens. Cell Cycle. 13:315–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Faber AC and Chiles TC: Inhibition of
cyclin-dependent kinase-2 induces apoptosis in human diffuse large
B-cell lymphomas. Cell Cycle. 6:2982–2989. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma KL, Liu J, Wang CX, Ni J, Zhang Y, Wu
Y, Lv LL, Ruan XZ and Liu BC: Activation of mTOR modulates SREBP-2
to induce foam cell formation through increased retinoblastoma
protein phosphorylation. Cardiovasc Res. 100:450–460. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boesten LS, Zadelaar AS, van Nieuwkoop A,
Hu L, Jonkers J, van de Water B, Gijbels MJ, van der Made I, de
Winther MP, Havekes LM and van Vlijmen BJ: Macrophage
retinoblastoma deficiency leads to enhanced atherosclerosis
development in ApoE-deficient mice. FASEB J. 20:953–955. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen WJ, Lin KH, Lai YJ, Yang SH and Pang
JH: Protective effect of propylthiouracil independent of its
hypothyroid effect on atherogenesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits:
PTEN induction and inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration. Circulation. 110:1313–1319. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan M, Wang X, Zhan Q, Duan X, Yang Q and
Xia J: Association of PTEN genetic polymorphisms with
atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in the Han Chinese population.
J Clin Neurosci. 19:1641–1645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuo HM, Lin CY, Lam HC, Lin PR, Chan HH,
Tseng JC, Sun CK, Hsu TF, Wu CC, Yang CY, Hsu CM and Tai MH: PTEN
overexpression attenuates angiogenic processes of endothelial cells
by blockade of endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor signaling.
Atherosclerosis. 221:341–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bae I, Fan S, Meng Q, Rih JK, Kim HJ, Kang
HJ, Xu J, Goldberg ID, Jaiswal AK and Rosen EM: BRCA1 induces
antioxidant gene expression and resistance to oxidative stress.
Cancer Res. 64:7893–7909. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Singh KK, Shukla PC, Quan A, Al-Omran M,
Lovren F, Pan Y, Brezden-Masley C, Ingram AJ, Stanford WL, Teoh H
and Verma S: BRCA1 is a novel target to improve endothelial
dysfunction and retard atherosclerosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
146:949–960. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Singh KK, Khan R,
Gupta N, Brezden-Masley C, Teoh H, Wheatcroft MD, Al-Omran M and
Verma S: BRCA1 shields vascular smooth muscle cells from oxidative
stress. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 147:1946–1955. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ozaki K, Sato H, Inoue K, Tsunoda T,
Sakata Y, Mizuno H, Lin TH, Miyamoto Y, Aoki A, Onouchi Y, Sheu SH,
Ikegawa S, Odashiro K, Nobuyoshi M, Juo SH, Hori M, Nakamura Y and
Tanaka T: SNPs in BRAP associated with risk of myocardial
infarction in Asian populations. Nat Genet. 41:329–333. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jerome WG: Lysosomes, cholesterol and
atherosclerosis. Clin Lipidol. 5:853–865. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki E, Takahashi M, Oba S and
Nishimatsu H: Oncogene- and oxidative stress-induced cellular
senescence shows distinct expression patterns of proinflammatory
cytokines in vascular endothelial cells. ScientificWorldJournal.
2013:7547352013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Boominathan L: The guardians of the genome
(p53, TA-p73, and TA-p63) are regulators of tumor suppressor miRNAs
network. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:613–639. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
O’Neil N and Rose A: DNA repair. WormBook.
1–12. 2006.
|
|
43
|
Muller PA and Vousden KH: 53 mutations in
cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 15:2–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Conforti F, Sayan AE, Sreekumar R and
Sayan BS: Regulation of p73 activity by post-translational
modifications. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Appella E and Anderson CW:
Post-translational modifications and activation of p53 by genotoxic
stresses. Eur J Biochem. 268:2764–2772. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hock AK and Vousden KH: The role of
ubiquitin modification in the regulation of p53. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mattila KJ, Valtonen VV, Nieminen MS and
Asikainen S: Role of infection as a risk factor for
atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Clin Infect
Dis. 26:719–734. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Razani B, Feng C and Semenkovich CF: p53
is required for chloroquine-induced atheroprotection but not
insulin sensitization. J Lipid Res. 51:1738–1746. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Martinet W, Knaapen MW, De Meyer GR,
Herman AG and Kockx MM: Oxidative DNA damage and repair in
experimental atherosclerosis are reversed by dietary lipid
lowering. Circ Res. 88:733–739. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Georgiev P, Dahm F, Graf R and Clavien PA:
Blocking the path to death: anti-apoptotic molecules in
ischemia/reperfusion injury of the liver. Curr Pharm Des.
12:2911–2921. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsusaka H, Ide T, Matsushima S, Ikeuchi
M, Kubota T, Sunagawa K, Kinugawa S and Tsutsui H: Targeted
deletion of p53 prevents cardiac rupture after myocardial
infarction in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 70:457–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim YC, Kitaura H, Taira T, Iguchi-Ariga
SM and Ariga H: Oxidation of DJ-1-dependent cell transformation
through direct binding of DJ-1 to PTEN. Int J Oncol. 35:1331–1341.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Markiewicz E, Ledran M and Hutchison CJ:
Remodelling of the nuclear lamina and nucleoskeleton is required
for skeletal muscle differentiation in vitro. J Cell Sci.
118:409–420. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wikman H and Kettunen E: Regulation of the
G1/S phase of the cell cycle and alterations in the RB pathway in
human lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 6:515–530. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Smith RC, Branellec D, Gorski DH, Guo K,
Perlman H, Dedieu JF, Pastore C, Mahfoudi A, Denèfle P, Isner JM
and Walsh K: p21CIP1-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation by
overexpression of the gax homeodomain gene. Genes Dev.
11:1674–1689. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Condorelli G, Aycock JK, Frati G and
Napoli C: Mutated p21/WAF/CIP transgene overexpression reduces
smooth muscle cell proliferation, macrophage deposition,
oxidation-sensitive mechanisms, and restenosis in
hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E knockout mice. FASEB J.
15:2162–2170. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Merched AJ and Chan L: Absence of
p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 modulates macrophage differentiation and
inflammatory response and protects against atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 110:3830–3841. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Brader S and Eccles SA: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase signalling pathways in tumor progression, invasion and
angiogenesis. Tumori. 90:2–8. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Musumeci M, Maccari S, Corritore E,
Massimi A, Stati T, Marano G and Catalano L: Signaling
pathway-focused gene expression profiling in pressure overloaded
hearts. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 47:290–295. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ouimet M: Autophagy in obesity and
atherosclerosis: Interrelationships between cholesterol
homeostasis, lipoprotein metabolism and autophagy in macrophages
and other systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1124–1133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yao PM and Tabas I: Free cholesterol
loading of macrophages induces apoptosis involving the fas pathway.
J Biol Chem. 275:23807–23813. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Waters SM, Coyne GS, Kenny DA and Morris
DG: Effect of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on
transcription factor regulation in the bovine endometrium. Mol Biol
Rep. 41:2745–2755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Merched AJ, Williams E and Chan L:
Macrophage-specific p53 expression plays a crucial role in
atherosclerosis development and plaque remodeling. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1608–1614. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lee SJ, Park K, Ha SD, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract inhibits human colon cancer
cells: the role of ERK1/2, G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest and p53
expression. Phytother Res. 24:1870–1876. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lee SJ, Park SS, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract inhibits proliferation and
TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am
J Chin Med. 40:373–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Lu Y, Li CS and Dong Q: Chinese herb
related molecules of cancer-cell-apoptosis: a minireview of
progress between Kanglaite injection and related genes. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 27:312008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li B, Zhao J, Wang CZ, et al: Ginsenoside
Rh2 induces apoptosis and paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal
cancer cells through activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 301:185–192.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Diab-Assaf M, Boltze C,
et al: Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic
cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent
mechanism. Int J Oncol. 25:857–866. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lee SJ, Kim HM, Cho YH, et al: Aqueous
extract of Magnolia officinalis mediates proliferative
capacity, p21WAF1 expression and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity in
human urinary bladder cancer 5637 cells; involvement of p38 MAP
kinase. Oncol Rep. 18:729–736. 2007.
|
|
70
|
Dong LH, Wen JK, Miao SB, et al: Baicalin
inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation through suppressing PDGFRβ-ERK signaling and increase
in p27 accumulation and prevents injury-induced neointimal
hyperplasia. Cell Res. 20:1252–1262. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Way TD, Lee JC, Kuo DH, et al: Inhibition
of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by Saussurea
involucrata, a rare traditional Chinese medicinal herb, in
human hormone-resistant prostate cancer PC-3 cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 58:3356–3365. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hahm ER and Singh SV: Honokiol causes
G0–G1 phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells in
association with suppression of retinoblastoma protein
level/phosphorylation and inhibition of E2F1 transcriptional
activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2686–2695. 2007.
|
|
73
|
Tao R, Lu L, Zhang R, Hu J, Ni J and Shen
W: Triptolide inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and cell cycle progression via attenuation of ERK1/2
and Rb phosphorylation. Exp Mol Pathol. 90:137–142. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shan BE, Zeki K, Sugiura T, Yoshida Y and
Yamashita U: Chinese medicinal herb, Acanthopanax
gracilistylus, extract induces cell cycle arrest of human tumor
cells in vitro. Jpn J Cancer Res. 91:383–389. 2000.
|
|
75
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, et al:
Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells by arresting
cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett.
302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kametani S, Oikawa T, Kojima-Yuasa A, et
al: Mechanism of growth inhibitory effect of cape aloe extract in
ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).
53:540–546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yang P, Cartwright C, Chan D, Vijjeswarapu
M, Ding J and Newman RA: Zyflamend-mediated inhibition of human
prostate cancer PC3 cell proliferation: effects on 12-LOX and Rb
protein phosphorylation. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:228–236. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Liu H, Zang C, Emde A, et al: Anti-tumor
effect of honokiol alone and in combination with other anti-cancer
agents in breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:43–51. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang JY, Della-Fera MA, Rayalam S and
Baile CA: Enhanced effects of xanthohumol plus honokiol on
apoptosis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring).
16:1232–1238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Roy S, Yu Y, Padhye SB, Sarkar FH and
Majumdar AP: Difluorinated-curcumin (CDF) restores PTEN expression
in colon cancer cells by down-regulating miR-21. PLoS One.
8:e685432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yoshida H, Okumura N, Kitagishi Y,
Nishimura Y and Matsuda S: Ethanol extract of rosemary repressed
PTEN expression in K562 culture cells. Int J Appl Boil Pharm
Technol. 2:316–322. 2011.
|
|
82
|
Bosviel R, Dumollard E, Déchelotte P,
Bignon YJ and Bernard-Gallon D: Can soy phytoestrogens decrease DNA
methylation in BRCA1 and BRCA2 oncosuppressor genes in breast
cancer? OMICS. 16:235–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kobayashi K, Nagata E, Sasaki K,
Harada-Shiba M, Kojo S and Kikuzaki H: Increase in secretory
sphingomyelinase activity and specific ceramides in the aorta of
apolipoprotein E knockout mice during aging. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:1192–1196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|