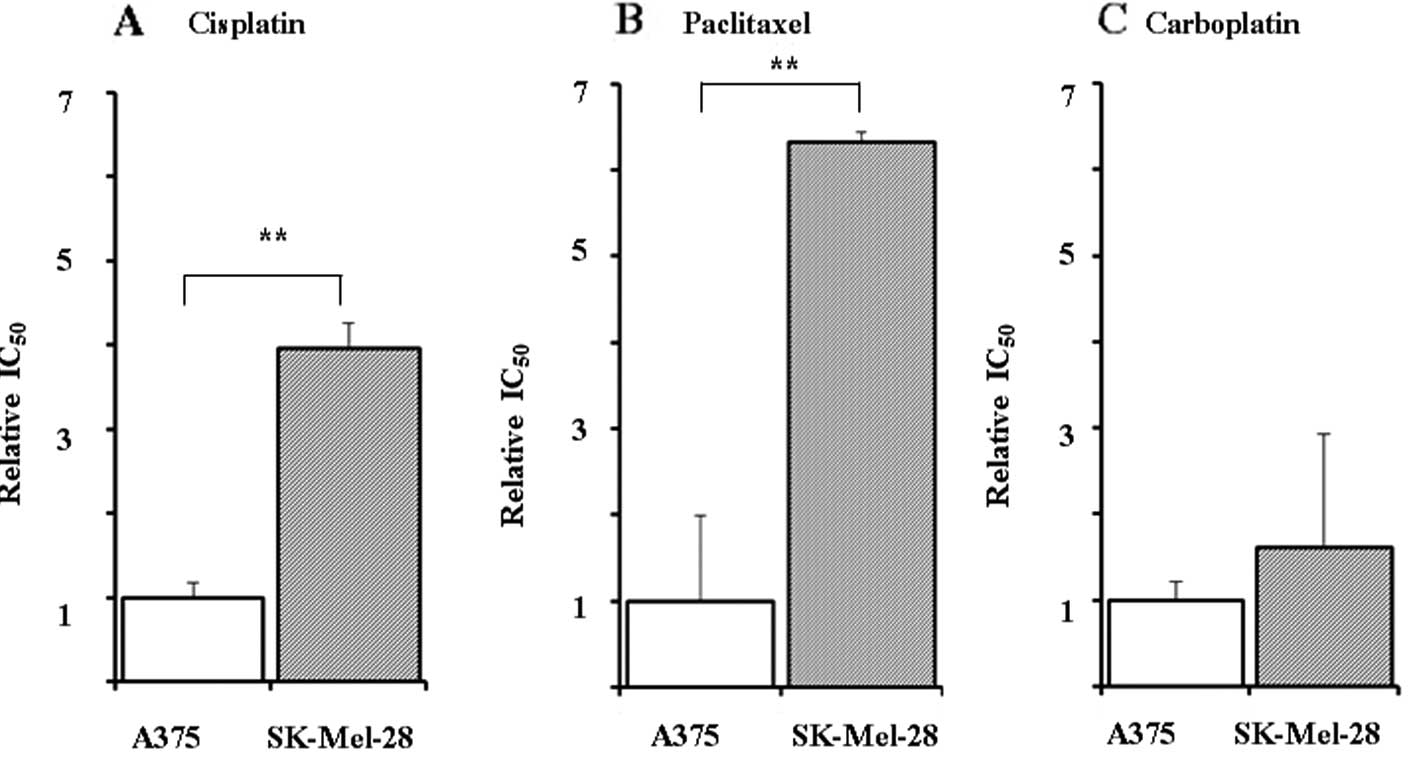
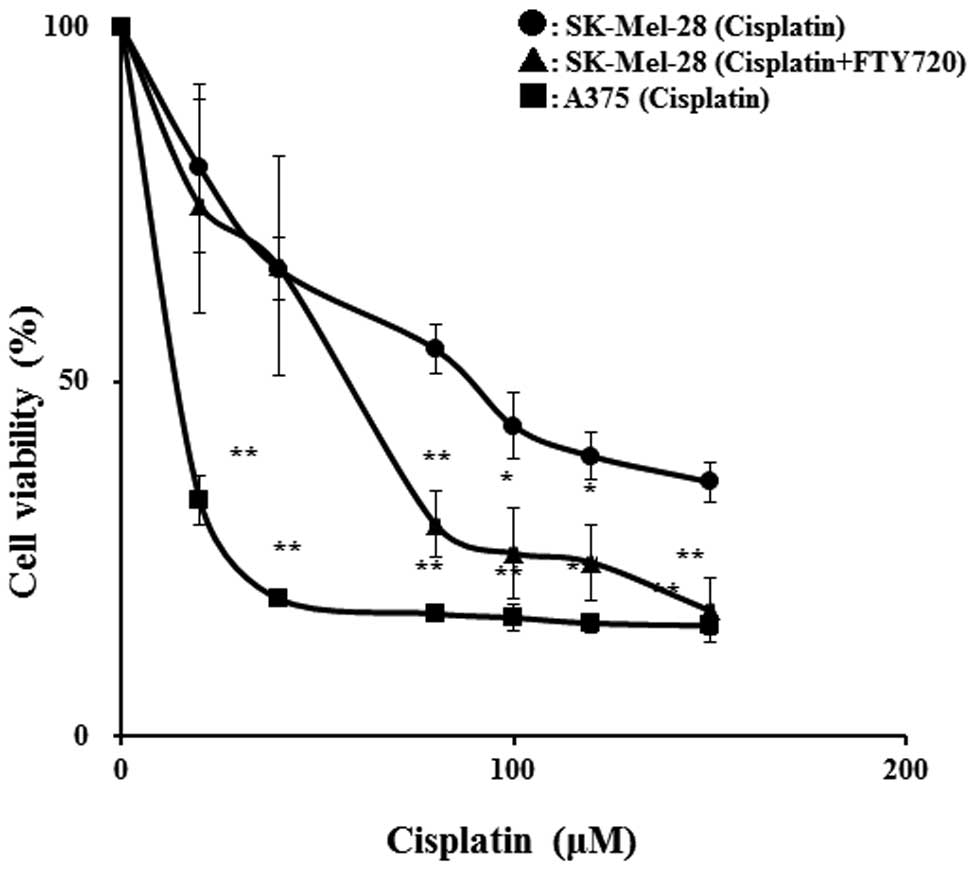
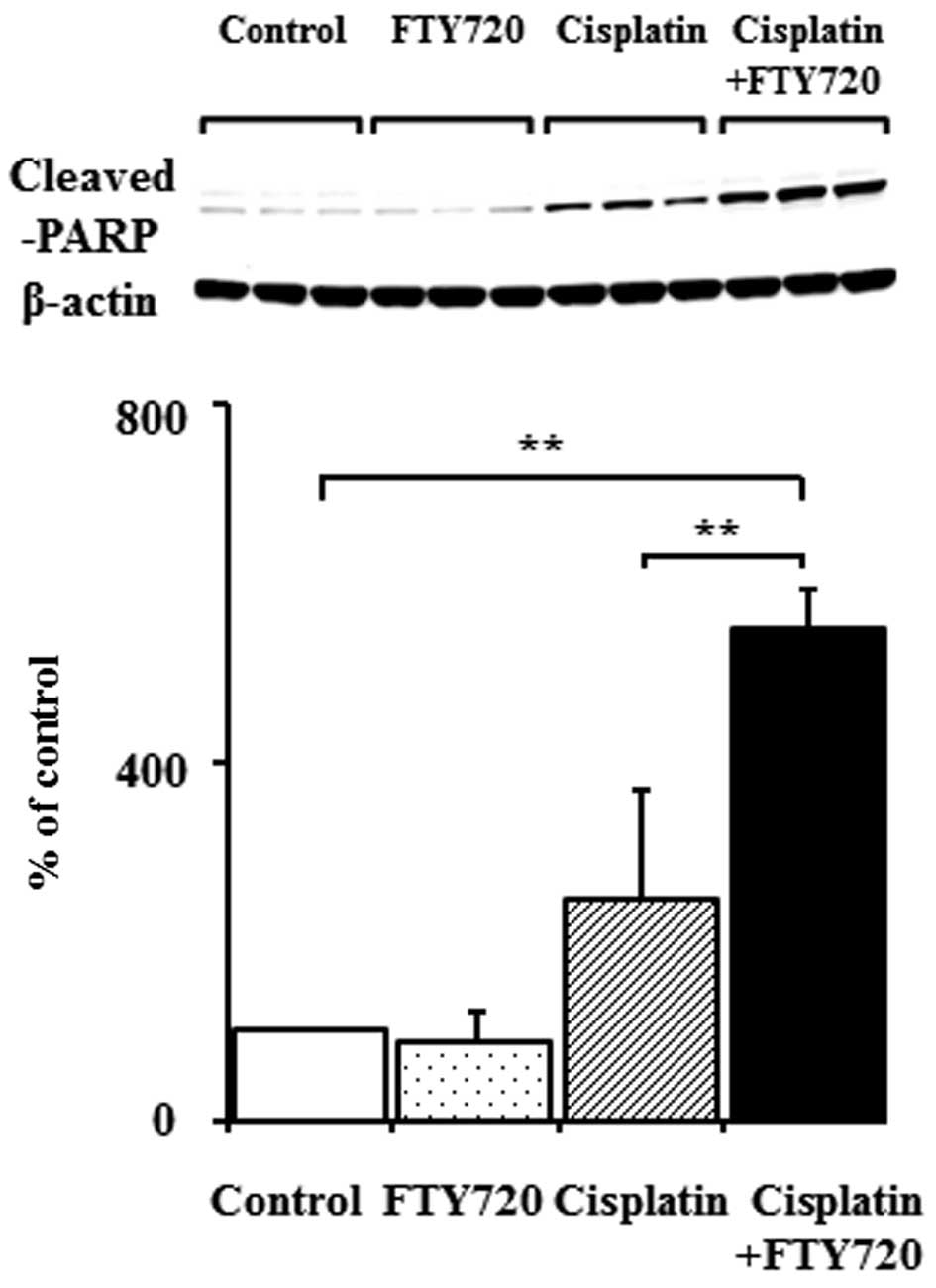
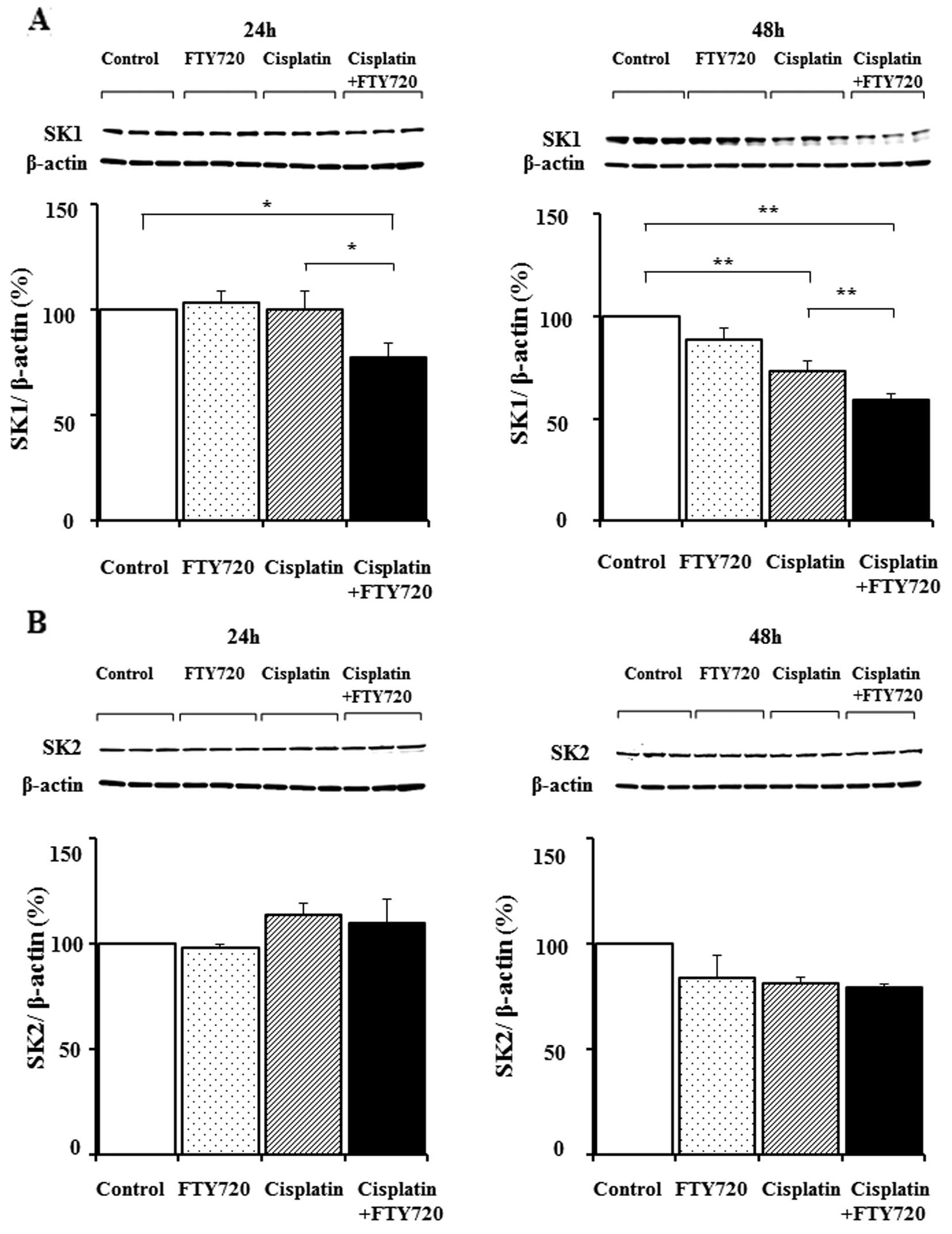
|
1
|
Taha TA, Hannun YA and Obeid LM:
Sphingosine kinase: biochemical and cellular regulation and role in
disease. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:113–131. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ogretmen B and Hannun YA: Biologically
active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:604–616. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olivera A, Kohama T, Edsall LC, et al:
Sphingosine kinase expression increases intracellular
sphingosine-1-phosphate and promotes cell growth and survival. J
Cell Biol. 147:545–558. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xia P, Wang L, Gamble JR and Vadas MA:
Activation of sphingosine kinase by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
inhibits apoptosis in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
274:34499–34505. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spiegel S and Milstien S:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:397–407. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xia P, Gamble JR, Wang L, et al: An
oncogenic role of sphingosine kinase. Curr Biol. 10:1527–1530.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ho JW, Man K, Sun CK, Lee TK, Poon RT and
Fan ST: Effects of a novel immunomodulating agent, FTY720, on tumor
growth and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:1430–1438. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pchejetski D, Doumerc N, Golzio M, et al:
Chemosensitizing effects of sphingosine kinase-1 inhibition in
prostate cancer cell and animal models. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:1836–1845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
French KJ, Schrecengost RS, Lee BD, et al:
Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human sphingosine kinase.
Cancer Res. 63:5962–5969. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shida D, Takabe K, Kapitonov D, Milstien S
and Spiegel S: Targeting SphK1 as a new strategy against cancer.
Curr Drug Targets. 9:662–673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vadas M, Xia P, McCaughan G and Gamble J:
The role of sphingosine kinase 1 in cancer: oncogene or
non-oncogene addiction? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1781:442–447. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Azuma H, Takahara S, Horie S, Muto S,
Otsuki Y and Katsuoka Y: Induction of apoptosis in human bladder
cancer cells in vitro and in vivo caused by FTY720 treatment. J
Urol. 169:2372–2377. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ubai T, Azuma H, Kotake Y, et al: FTY720
induced Bcl-associated and Fas-independent apoptosis in human renal
cancer cells in vitro and significantly reduced in vivo tumor
growth in mouse xenograft. Anticancer Res. 27:75–88.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Billich A, Bornancin F, Dévay P,
Mechtcheriakova D, Urtz N and Baumruker T: Phosphorylation of the
immunomodulatory drug FTY720 by sphingosine kinases. J Biol Chem.
278:47408–47415. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang JD, Takahara S, Nonomura N, Ichimaru
N, Toki K and Azuma H: Early induction of apoptosis in
androgen-independent prostate cancer cell line by FTY720 requires
caspase-3 activation. Prostate. 40:50–55. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pereira FV, Arruda DC, Figueiredo CR, et
al: FTY720 induces apoptosis in B16F10-NEX2 murine melanoma cells,
limits metastatic development in vivo, and modulates the immune
system. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 68:1018–1027. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
LaMontagne K, Littlewood-Evans A, Schnell
C, et al: Antagonism of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors by FTY720
inhibits angiogenesis and tumor vascularization. Cancer Res.
66:221–231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tonelli F, Lim KG, Loveridge C, et al:
FTY720 and (S)-FTY720 vinylphosphonate inhibit sphingosine kinase 1
and promote its proteasomal degradation in human pulmonary artery
smooth muscle, breast cancer and androgen-independent prostate
cancer cells. Cell Signal. 22:1536–1542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sukocheva O, Wadham C, Holmes A, et al:
Estrogen transactivates EGFR via the sphingosine 1-phosphate
receptor Edg-3: the role of sphingosine kinase-1. J Cell Biol.
173:301–310. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shida D, Fang X, Kordula T, et al:
Cross-talk between LPA1 and epidermal growth factor receptors
mediates up-regulation of sphingosine kinase 1 to promote gastric
cancer cell motility and invasion. Cancer Res. 68:6569–6577. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Paugh BS, Paugh SW, Bryan L, et al: EGF
regulates plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) by a pathway
involving c-Src, PKCdelta, and sphingosine kinase 1 in glioblastoma
cells. FASEB J. 22:455–465. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nemoto S, Nakamura M, Osawa Y, et al:
Sphingosine kinase isoforms regulate oxaliplatin sensitivity of
human colon cancer cells through ceramide accumulation and Akt
activation. J Biol Chem. 84:10422–10432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kawahara S, Otsuji Y, Nakamura M, et al:
Sphingosine kinase 1 plays a role in the upregulation of CD44
expression through extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling
in human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 24:473–483. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guillermet-Guibert J, Davenne L,
Pchejetski D, et al: Targeting the sphingolipid metabolism to
defeat pancreatic cancer cell resistance to the chemotherapeutic
gemcitabine drug. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:809–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fuereder T, Hoeflmayer D, Jaeger-Lansky A,
et al: Sphingosine kinase 1 is a relevant molecular target in
gastric cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 22:245–252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pchejetski D, Bohler T, Brizuela L, et al:
FTY720 (fingolimod) sensitizes prostate cancer cells to
radiotherapy by inhibition of sphingosine kinase-1. Cancer Res.
70:8651–8661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heffernan-Stroud LA, Helke KL, Jenkins RW,
De Costa AM, Hannun YA and Obeid LM: Defining a role for
sphingosine kinase 1 in p53-dependent tumors. Oncogene.
31:1166–1175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taha TA, Osta W, Kozhaya L, et al:
Down-regulation of sphingosine kinase-1 by DNA damage: dependence
on proteases and p53. J Biol Chem. 279:20546–20554. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rudolf K, Cervinka M and Rudolf E: Dual
inhibition of topoisomerases enhances apoptosis in melanoma cells.
Neoplasma. 57:316–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang L, et al: S1PR1 is an
effective target to block STAT3 signaling in activated B cell-like
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 120:1458–1465. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong YB, Yang HL, Elliott MJ and McMasters
KM: Adenovirus-mediated E2F-1 gene transfer sensitizes melanoma
cells to apoptosis induced by topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer
Res. 62:1776–1783. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim D, Cheng GZ, Lindsley CW, Yang H and
Cheng JQ: Targeting the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway
for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 6:1250–1258.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meier F, Schittek B, Busch S, et al: The
RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways present molecular
targets for the effective treatment of advanced melanoma. Front
Biosci. 10:2986–3001. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sinnberg T, Lasithiotakis K, Niessner H,
et al: Inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling sensitizes melanoma
cells to cisplatin and temozolomide. J Invest Dermatol.
129:1500–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Powlas J, Shi Y, et al: Rapamycin
inhibits Akt-mediated oncogenic transformation and tumor growth.
Anticancer Res. 24:2697–2704. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun SY, Rosenberg LM, Wang X, et al:
Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways by rapamycin-mediated
mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition. Cancer Res. 65:7052–7208.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Francipane MG and Lagasse E: mTOR pathway
in colorectal cancer: an update (Review). Oncotarget. 15:49–66.
2014.
|
|
38
|
Rosa R, Marciano R, Malapelle U, et al:
Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression contributes to cetuximab
resistance in human colorectal cancer models. Clin Cancer Res.
19:138–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|