|
1
|
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A and Wendon
J: Acute liver failure. Lancet. 376:190–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fiegel HC, Lange C, Kneser U, et al: Fetal
and adult liver stem cells for liver regeneration and tissue
engineering. J Cell Mol Med. 10:577–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wigg AJ, Gunson BK and Mutimer DJ:
Outcomes following liver transplantation for seronegative acute
liver failure: experience during a 12-year period with more than
100 patients. Liver Transpl. 11:27–34. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
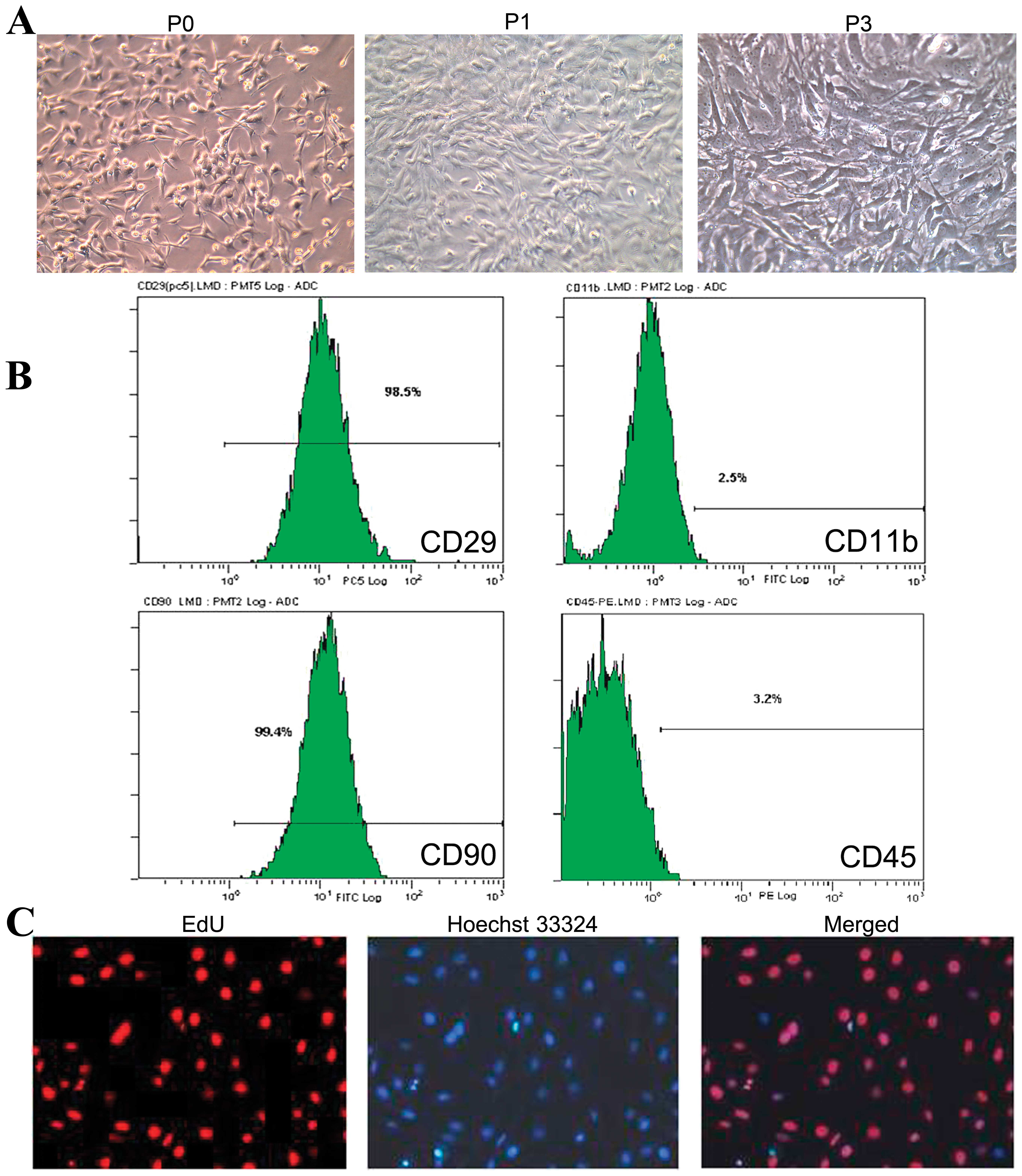
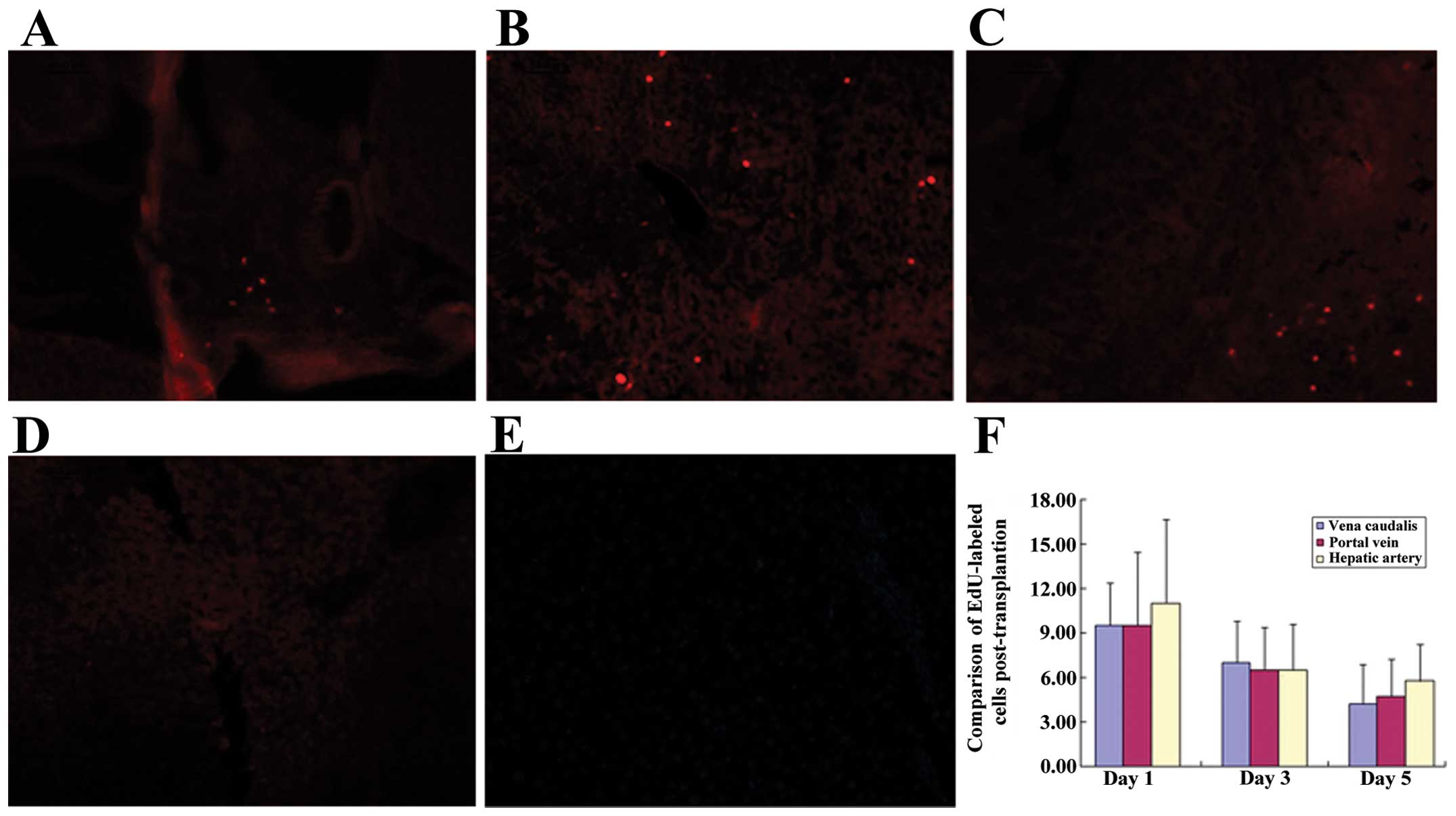
|
Le Blanc K and Pittenger M: Mesenchymal
stem cells: progress toward promise. Cytotherapy. 7:36–45.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cantz T, Manns MP and Ott M: Stem cells in
liver regeneration and therapy. Cell Tissue Res. 331:271–282. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stutchfield BM, Forbes SJ and Wigmore SJ:
Prospects for stem cell transplantation in the treatment of hepatic
disease. Liver Transpl. 16:827–836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
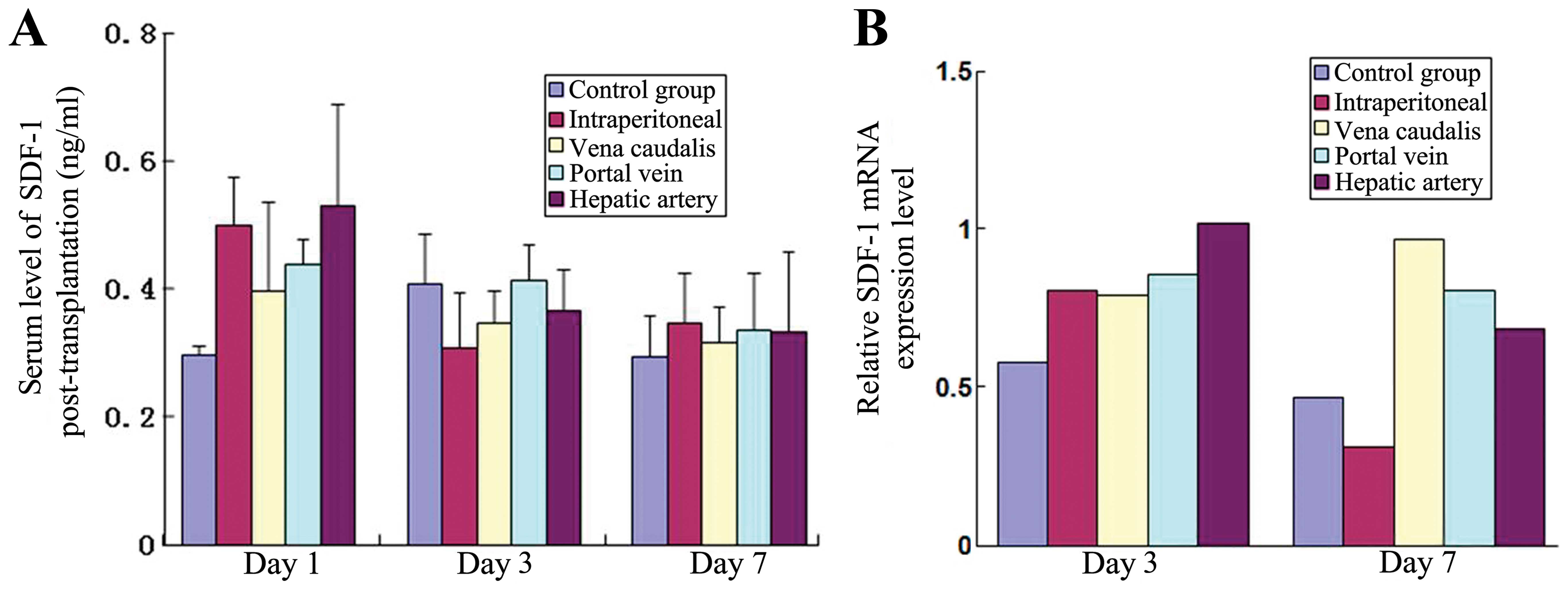
7
|
Aurich I, Mueller LP, Aurich H, et al:
Functional integration of hepatocytes derived from human
mesenchymal stem cells into mouse livers. Gut. 56:405–415. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aurich H, Sgodda M, Kaltwasser P, et al:
Hepatocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human
adipose tissue in vitro promotes hepatic integration in vivo. Gut.
58:570–581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al:
Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a source of human
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 46:219–228. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beaudry P, Hida Y, Udagawa T, et al:
Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to accelerated liver
regeneration. J Pediatr Surg. 42:1190–1198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, et al: Stem
cell therapy for liver disease: parameters governing the success of
using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology.
134:2111–2121. 2121.e1–3. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bajek A, Olkowska J and Drewa T:
Mesenchymal stem cells as a therapeutic tool in tissue and organ
regeneration. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 65:124–132. 2011.(In
Polish).
|
|
13
|
Zhou P, Hohm S, Olusanya Y, Hess DA and
Nolta J: Human progenitor cells with high aldehyde dehydrogenase
activity efficiently engraft into damaged liver in a novel model.
Hepatology. 49:1992–2000. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cho KA, Ju SY, Cho SJ, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells showed the highest potential for the regeneration of
injured liver tissue compared with other subpopulations of the bone
marrow. Cell Biol Int. 33:772–777. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang M, Shang Z, Zhang X and Jia C:
Therapeutic effect of different channels of BMSCs transplantation
on liver cirrhosis in rat. China Modern Doctor. 48:7–9. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Xiong Q, Feng J, Wang J, et al: Comparison
among curative effects of three different transplantation
approaches of mesenchymal stem cells on rat model of cirrhosis. J
Third Mil Med Univ. 33:804–808. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Zhao W, Li JJ, Cao DY, et al: Intravenous
injection of mesenchymal stem cells is effective in treating liver
fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:1048–1058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao H, Yang J, Yu J, et al: Therapeutic
potential of transplanted placental mesenchymal stem cells in
treating Chinese miniature pigs with acute liver failure. BMC Med.
10:562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim SJ, Park KC, Lee JU, Kim KJ and Kim
DG: Therapeutic potential of adipose tissue-derived stem cells for
liver failure according to the transplantation routes. J Korean
Surg Soc. 81:176–186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li F, Hu X, Zhao HM, et al: Influence of
different infusion methods of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem
cells on acute tubular necrosis. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu
Linchuang Kangfu. 14:7470–7473. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Zonta S, De Martino M, Bedino G, et al:
Which is the most suitable and effective route of administration
for mesenchymal stem cell-based immunomodulation therapy in
experimental kidney transplantation: endovenous or arterial?
Transplant Proc. 42:1336–1340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang GQ, Fang CH and Chi DZ: Hepatocyte
growth factor induces differentiation of adult rat mesenchymal stem
cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.
43:716–720. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Lin G, Huang YC, Shindel AW, et al:
Labeling and tracking of mesenchymal stromal cells with EdU.
Cytotherapy. 11:864–873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ichai P and Samuel D: Etiology and
prognosis of fulminant hepatitis in adults. Liver Transpl. 14(Suppl
2): S67–S79. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pathikonda M and Munoz SJ: Acute liver
failure. Ann Hepatol. 9:7–14. 2010.
|
|
26
|
Podoll AS, DeGolovine A and Finkel KW:
Liver support systems - a review. ASAIO J. 58:443–449. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiodt FV, et
al: Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17
tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med.
137:947–954. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lysy PA, Campard D, Smets F, Najimi M and
Sokal EM: Stem cells for liver tissue repair: current knowledge and
perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 14:864–875. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Campsen J, Blei AT, Emond JC, et al:
Outcomes of living donor liver transplantation for acute liver
failure: the adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation
cohort study. Liver Transpl. 14:1273–1280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fisher RA and Strom SC: Human hepatocyte
transplantation: worldwide results. Transplantation. 82:441–449.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bruzzone P and Strom SC: Historical
aspects of hepatocyte transplantation. Transplant Proc.
38:1179–1180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu YM, Joseph B, Berishvili E, Kumaran V
and Gupta S: Hepatocyte transplantation and drug-induced
perturbations in liver cell compartments. Hepatology. 47:279–287.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kisseleva T, Gigante E and Brenner DA:
Recent advances in liver stem cell therapy. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 26:395–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Baksh D, Song L and Tuan RS: Adult
mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and
application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 8:301–316.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et
al: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult
marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Flohr TR, Bonatti H Jr, Brayman KL and
Pruett TL: The use of stem cells in liver disease. Curr Opin Organ
Transplant. 14:64–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K,
Mohyeddin-Bonab M, et al: Phase I trial of autologous bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with
decompensated liver cirrhosis. Arch Iran Med. 10:459–466.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al:
Rapid hepatic fate specification of adipose-derived stem cells and
their therapeutic potential for liver failure. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:70–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al:
Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position
statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al:
Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.
Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Mosca JD, Moorman
M and Gerson SL: Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures
of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and stromal cells.
J Cell Physiol. 176:57–66. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hung SC, Chen NJ, Hsieh SL, Li H, Ma HL
and Lo WH: Isolation and characterization of size-sieved stem cells
from human bone marrow. Stem Cells. 20:249–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jin SZ, Meng XW, Han MZ, Sun X, Sun LY and
Liu BR: Stromal cell derived factor-1 enhances bone marrow
mononuclear cell migration in mice with acute liver failure. World
J Gastroenterol. 15:2657–2664. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Peled A, Petit I, Kollet O, et al:
Dependence of human stem cell engraftment and repopulation of
NOD/SCID mice on CXCR4. Science. 283:845–848. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reca R, Mastellos D, Majka M, et al:
Functional receptor for C3a anaphylatoxin is expressed by normal
hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, and C3a enhances their
homing-related responses to SDF-1. Blood. 101:3784–3793. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Forte G, Minieri M, Cossa P, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem cells:
proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells.
24:23–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jia C: Advances in the regulation of liver
regeneration. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:105–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST and Tay SS:
Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the
migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the
brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells. 22:415–427. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ozaki Y, Nishimura M, Sekiya K, et al:
Comprehensive analysis of chemotactic factors for bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 16:119–129. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Salem HK and Thiemermann C: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: current understanding and clinical status. Stem
Cells. 28:585–596. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, Ghiran
I, Glodek AM and Silberstein LE: Human bone marrow stromal cells
express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine
receptors. Stem Cells. 24:1030–1041. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lapidot T: Mechanism of human stem cell
migration and repopulation of NOD/SCID and B2mnull NOD/SCID mice.
The role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions. Ann NY Acad Sci. 938:83–95.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Son BR, Marquez-Curtis LA, Kucia M, et al:
Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in
vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-1-CXCR4 and hepatocyte
growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloproteinases.
Stem Cells. 24:1254–1264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sordi V, Malosio ML, Marchesi F, et al:
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express a restricted set of
functionally active chemokine receptors capable of promoting
migration to pancreatic islets. Blood. 106:419–427. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|