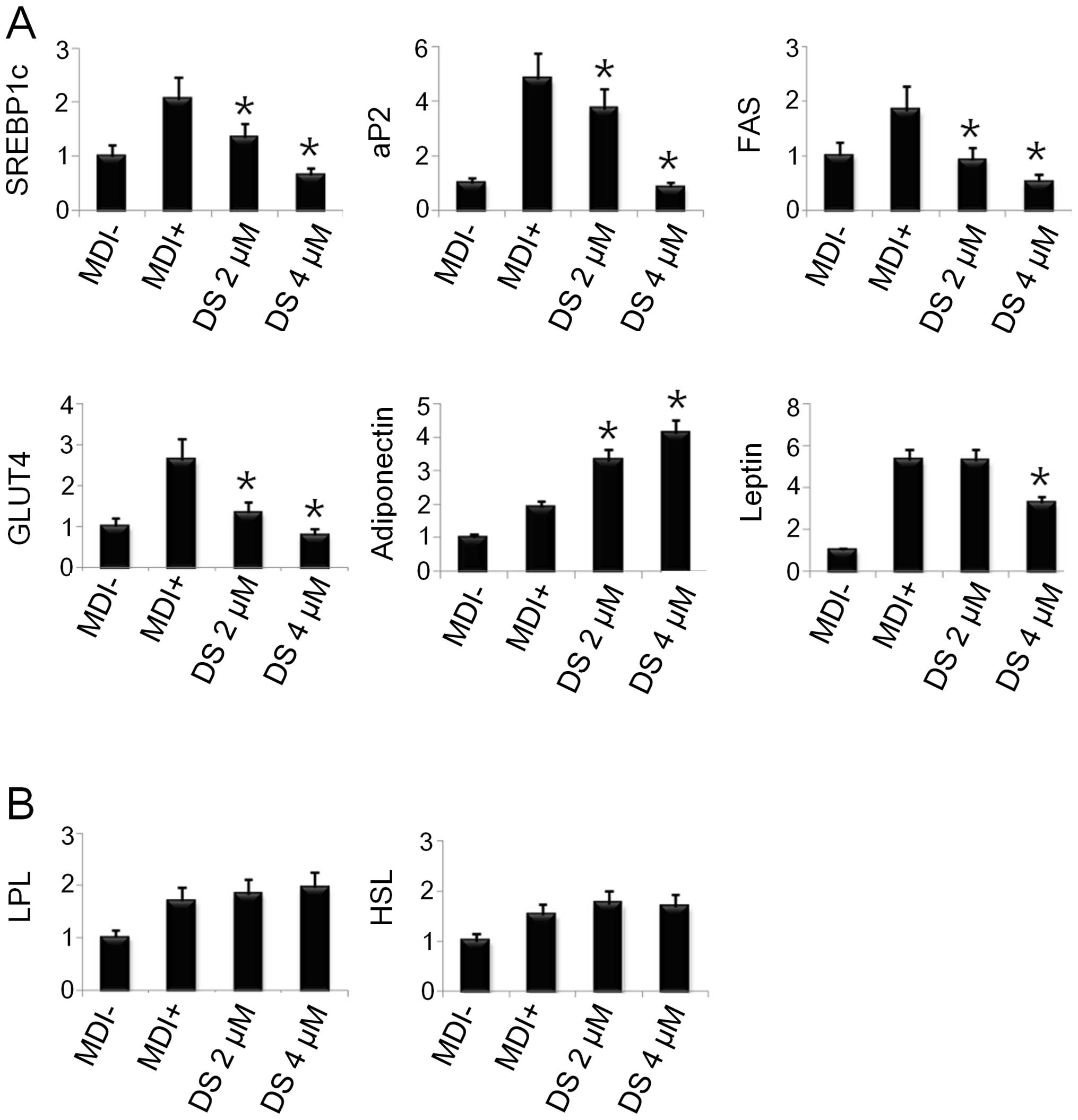
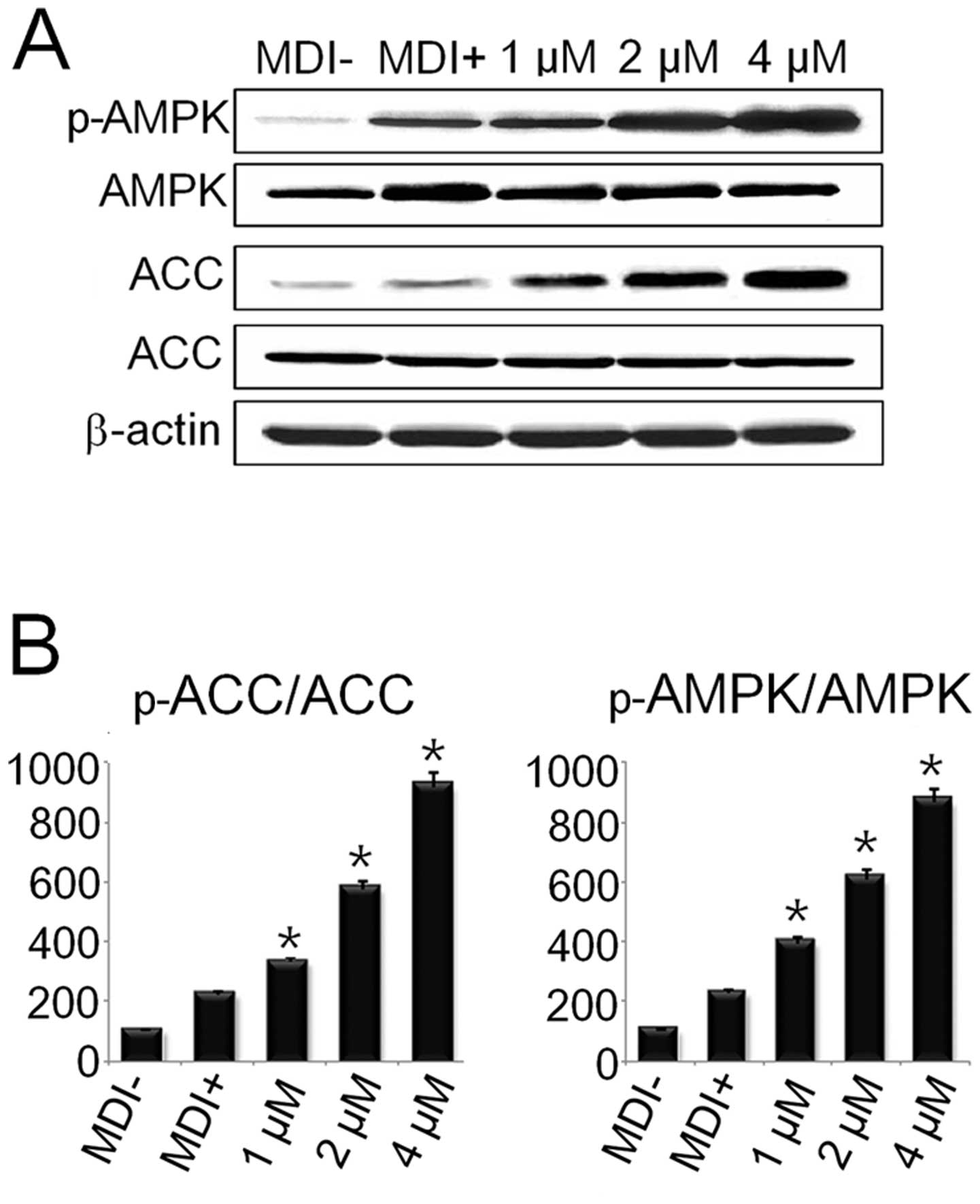
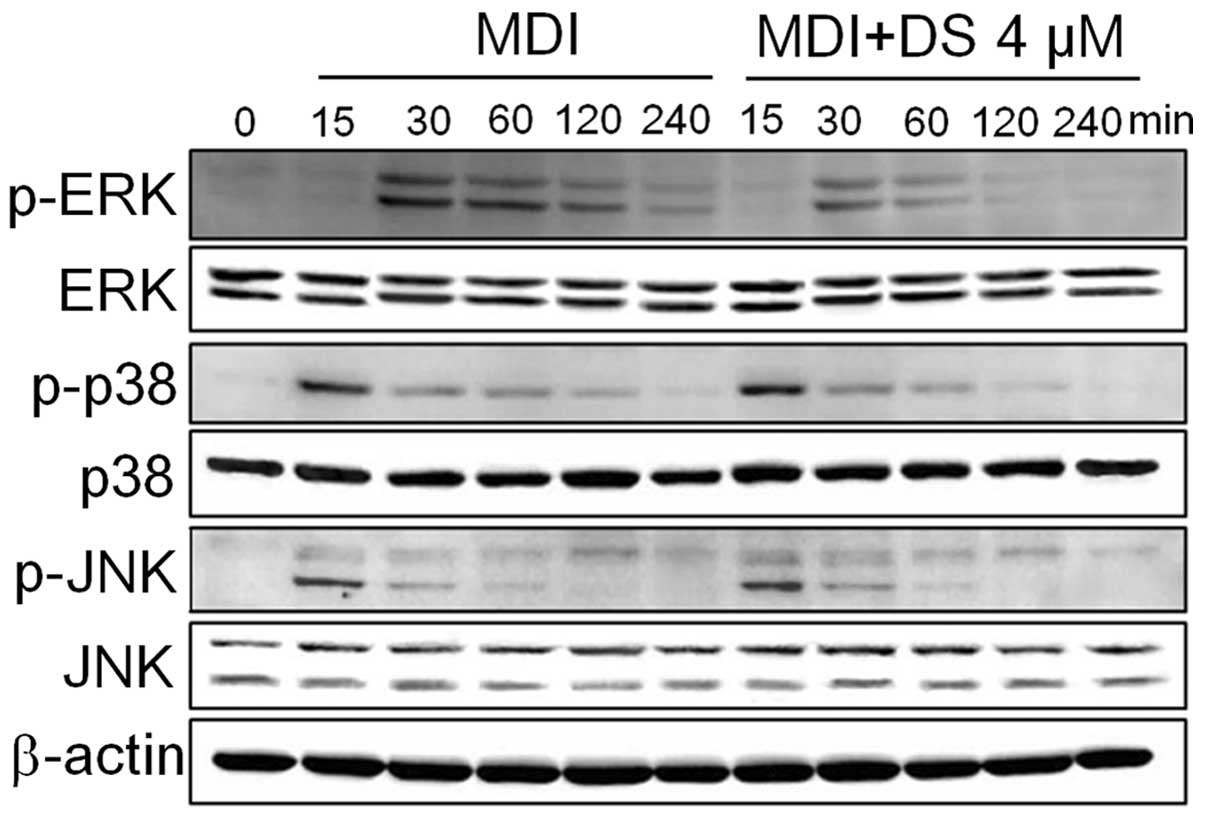
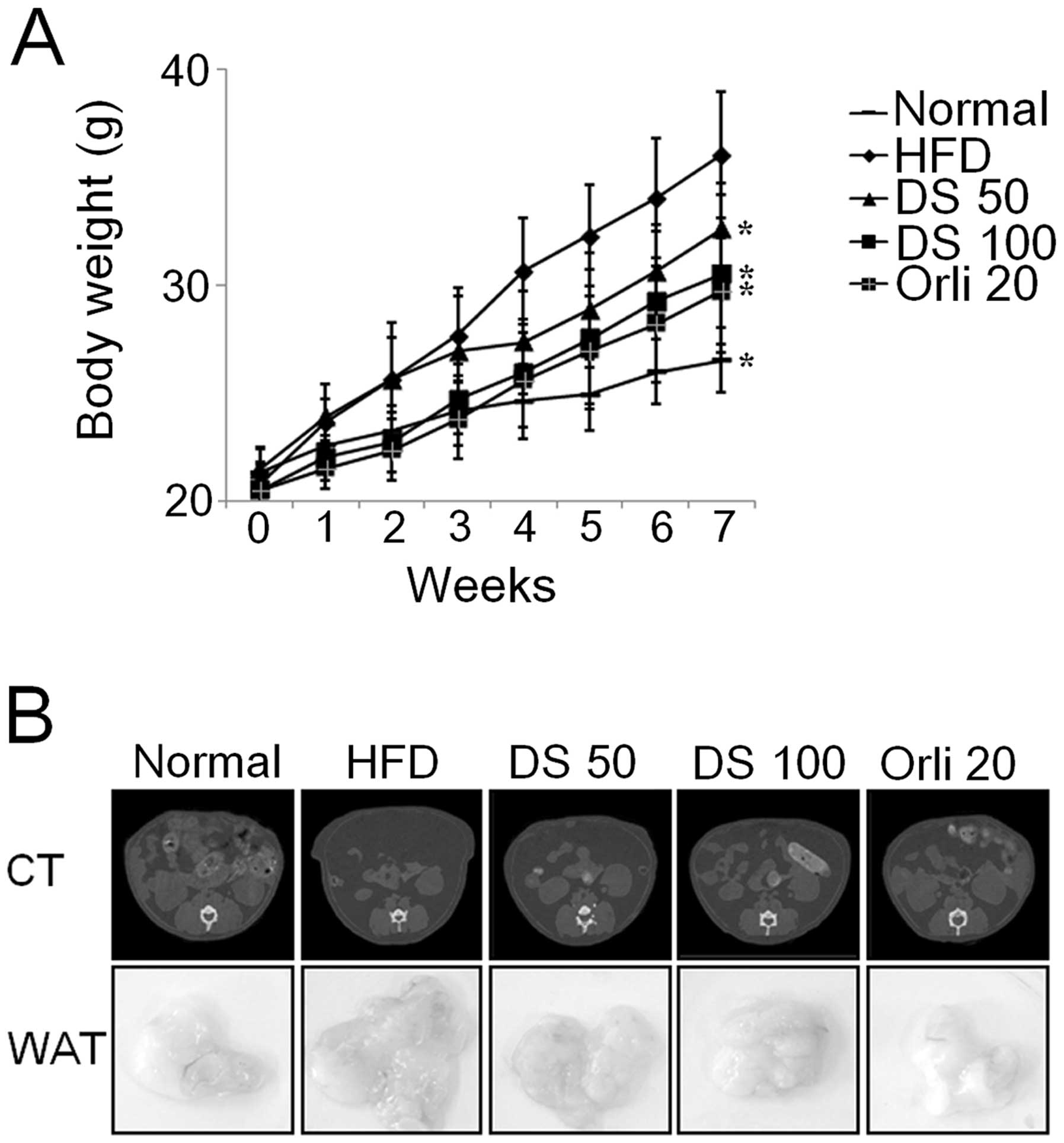
|
1
|
Kopelman PG: Obesity as a medical problem.
Nature. 404:635–643. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwon JY, Seo SG, Heo YS, Yue S, Cheng JX,
Lee KW and Kim KH: Piceatannol, natural polyphenolic stilbene,
inhibits adipogenesis via modulation of mitotic clonal expansion
and insulin receptor-dependent insulin signaling in early phase of
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 287:11566–115678. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Green H and Kehinde O: An established
preadipose cell line and its differentiation in culture II. Factors
affecting the adipose conversion. Cell. 5:19–27. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gregoire FM, Smas CM and Sul HS:
Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev. 78:783–809.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ntambi JM and Young-Cheul K: Adipocyte
differentiation and gene expression. J Nutr. 130:3122S–3126S.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He Y, Li Y, Zhao T, Wang Y and Sun C:
Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through
LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e701352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JO, Lee SK, Kim JH, et al: Metformin
regulates glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation through
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated Cbl/CAP signaling in
3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells. J Biol Chem. 287:44121–44129. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, et al:
AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic
checkpoint. Mol Cell. 18:283–293. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X and Ruderman NB:
AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
26:69–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song XM, Fiedler M, Galuska D, et al:
5-Aminoimidazole 4-carboxamide ribonucleoside treatment improves
glucose homeostasis in insulin-resistant diabetic (ob/ob) mice.
Diabetologia. 45:56–65. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang T, Sawada K, Yamamoto N and Ashida
H: 4-Hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol from Ashitaba (Angelica
keiskei) suppresses differentiation of preadipocytes to
adipocytes via AMPK and MAPK pathways. Mol Nutr Food Res.
57:1729–1740. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Xiao J, Wang NL, Sun B and Cai GP:
Estrogen receptor mediates the effects of pseudoprotodiocsin on
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
299:C128–C138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakamura T, Komori C, Lee Y, Hashimoto F,
Yahara S, Nohara T and Ejima A: Cytotoxic activities of solanum
steroidal glycosides. Biol Pharm Bull. 19:564–566. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cai J, Liu M, Wang Z and Ju Y: Apoptosis
induced by dioscin in Hela cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 25:193–196.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu MJ, Wang Z, Ju Y, Zhou JB, Wang Y and
Wong RN: The mitotic-arresting and apoptosis-inducing effects of
diosgenyl saponins on human leukemia cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:1059–1065. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sata N, Matsunaga S, Fusetani N, Nishikawa
H, Takamura S and Saito T: New antifungal and cytotoxic steroidal
saponins from the bulbs of an elephant garlic mutant. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 62:1904–1911. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ikeda T, Ando J, Miyazono A, et al:
Anti-herpes virus activity of Solanum steroidal glycosides. Biol
Pharm Bull. 23:363–364. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kwon CS, Sohn HY, Kim SH, et al:
Anti-obesity effect of Dioscorea nipponica Makino with
lipase-inhibitory activity in rodents. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
67:1451–1456. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Song MY, Lv N, Kim EK, et al: Antiobesity
activity of aqueous extracts of Rhizoma Dioscoreae Tokoronis on
high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J Med Food. 12:304–309.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bost F, Aouadi M, Caron L and Binétruy B:
The role of MAPKs in adipocyte differentiation and obesity.
Biochimie. 87:51–56. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bray GA and Tartaglia LA: Medicinal
strategies in the treatment of obesity. Nature. 404:672–677.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bray GA: A concise review on the
therapeutics of obesity. Nutrition. 16:953–960. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Christodoulides C and Vidal-Puig A: PPARs
and adipocyte function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 318:61–68. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takahashi S, Tanaka T, Kodama T and Sakai
J: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ (PPARδ), a novel
target site for drug discovery in metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol
Res. 53:501–507. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Tontonoz P, Hu E and Spiegelman BM:
Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a
lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 79:1147–1156. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Darlington GJ, Ross SE and MacDougald OA:
The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem.
273:30057–30060. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao Z, Umek RM and McKnight SL: Regulated
expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of
3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 5:1538–1552. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Z, Rosen ED, Brun R, et al:
Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the
transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity.
Mol Cell. 3:151–158. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu C, Zhu W, Shen CL and Gao W: Green tea
polyphenols reduce body weight in rats by modulating
obesity-related genes. PLoS One. 7:e383322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Warnke I, Goralczyk R, Fuhrer E and
Schwager J: Dietary constituents reduce lipid accumulation in
murine C3H10 T1/2 adipocytes: a novel fluorescent method to
quantify fat droplets. Nutr Metab (Lond). 8:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang XH, Huang B, Choi SK and Seo JS:
Anti-obesity effect of resveratrol-amplified grape skin extracts on
3T3-L1 adipocytes differentiation. Nutr Res Pract. 6:286–293. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yuan G, Jia J, Di L, et al: Effects of
C-reactive protein on adipokines genes expression in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:462–468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alvala R, Alvala M, Sama V, Dharmarajan S,
Ullas JV and BMR: Scientific evidence for traditional claim of
anti-obesity activity of Tecomella undulata bark. J
Ethnopharmacol. 148:441–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wanders D, Graff EC, White BD and Judd RL:
Niacin increases adiponectin and decreases adipose tissue
inflammation in high fat diet-fed mice. PLoS One. 8:e712852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kanagasabapathy G, Malek SN, Mahmood AA,
Chua KH, Vikineswary S and Kuppusamy UR: Beta-glucan-rich extract
from Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) Singer prevents obesity and
oxidative stress in C57BL/6J mice fed on a high-fat diet. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:1852592013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang BB, Zhou G and Li C: AMPK: an
emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell
Metab. 9:407–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tang QQ, Otto TC and Lane MD: Mitotic
clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:44–49. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Engelman JA, Lisanti MP and Scherer PE:
Specific inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase block
3T3-L1 adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 273:32111–32120. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|