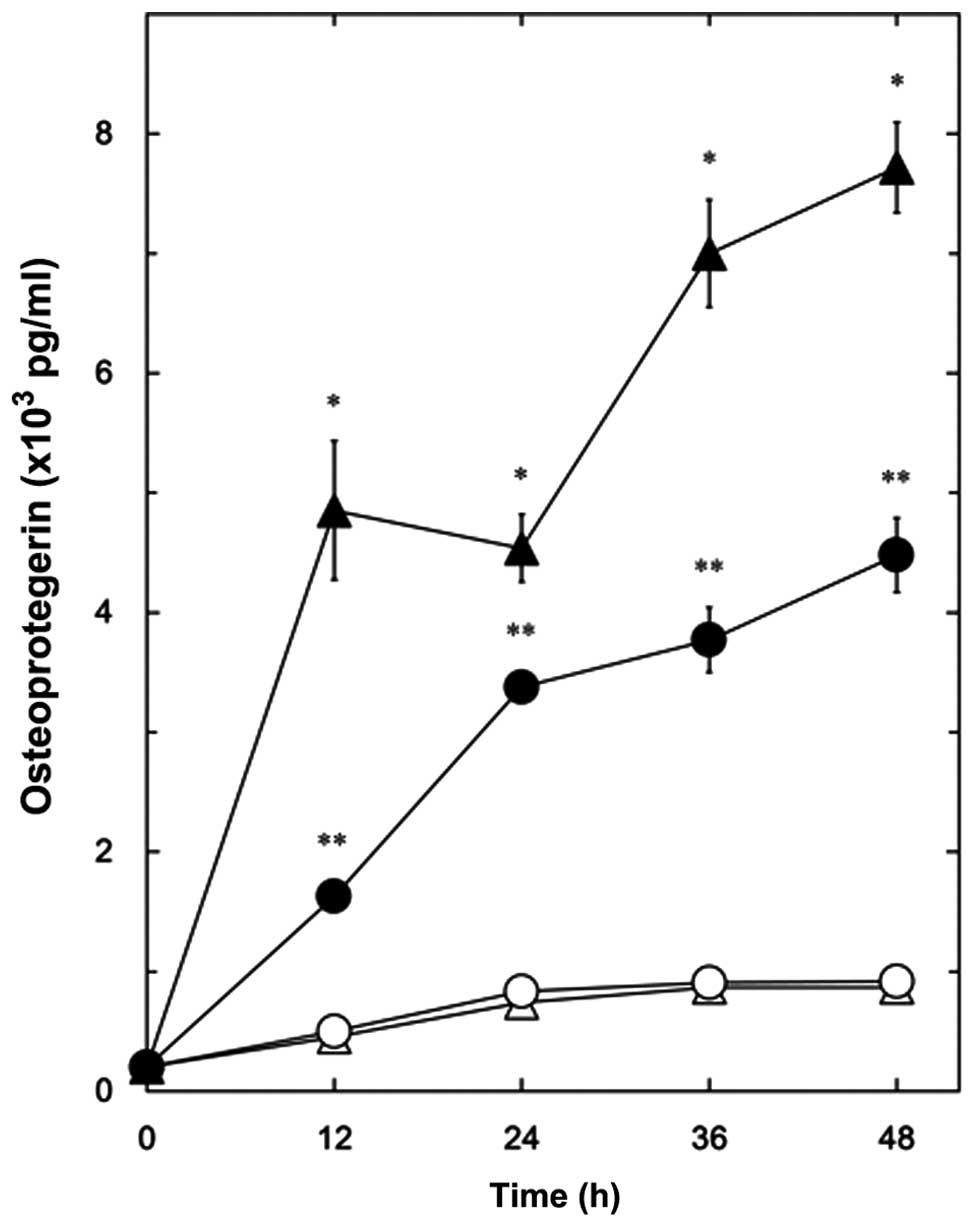
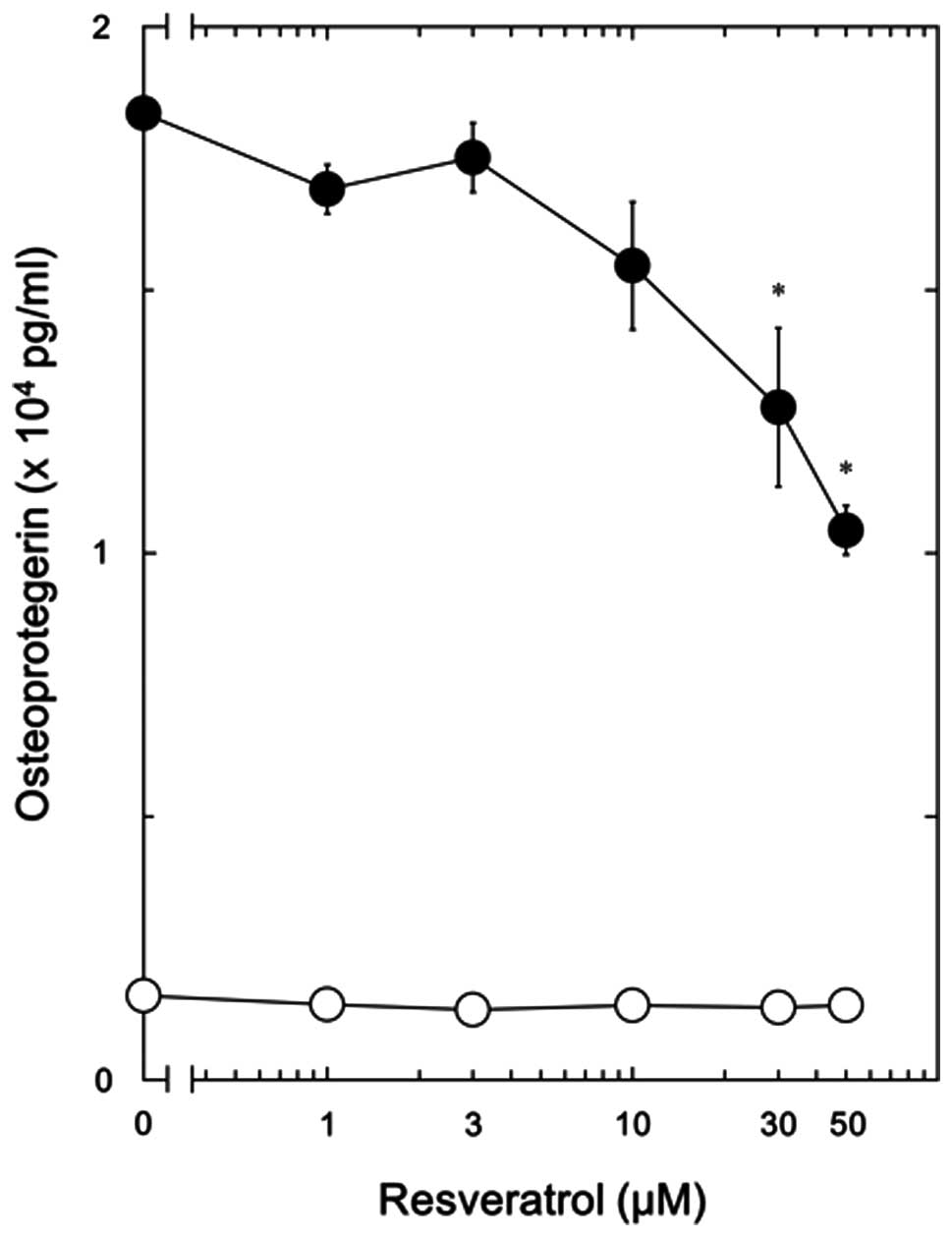
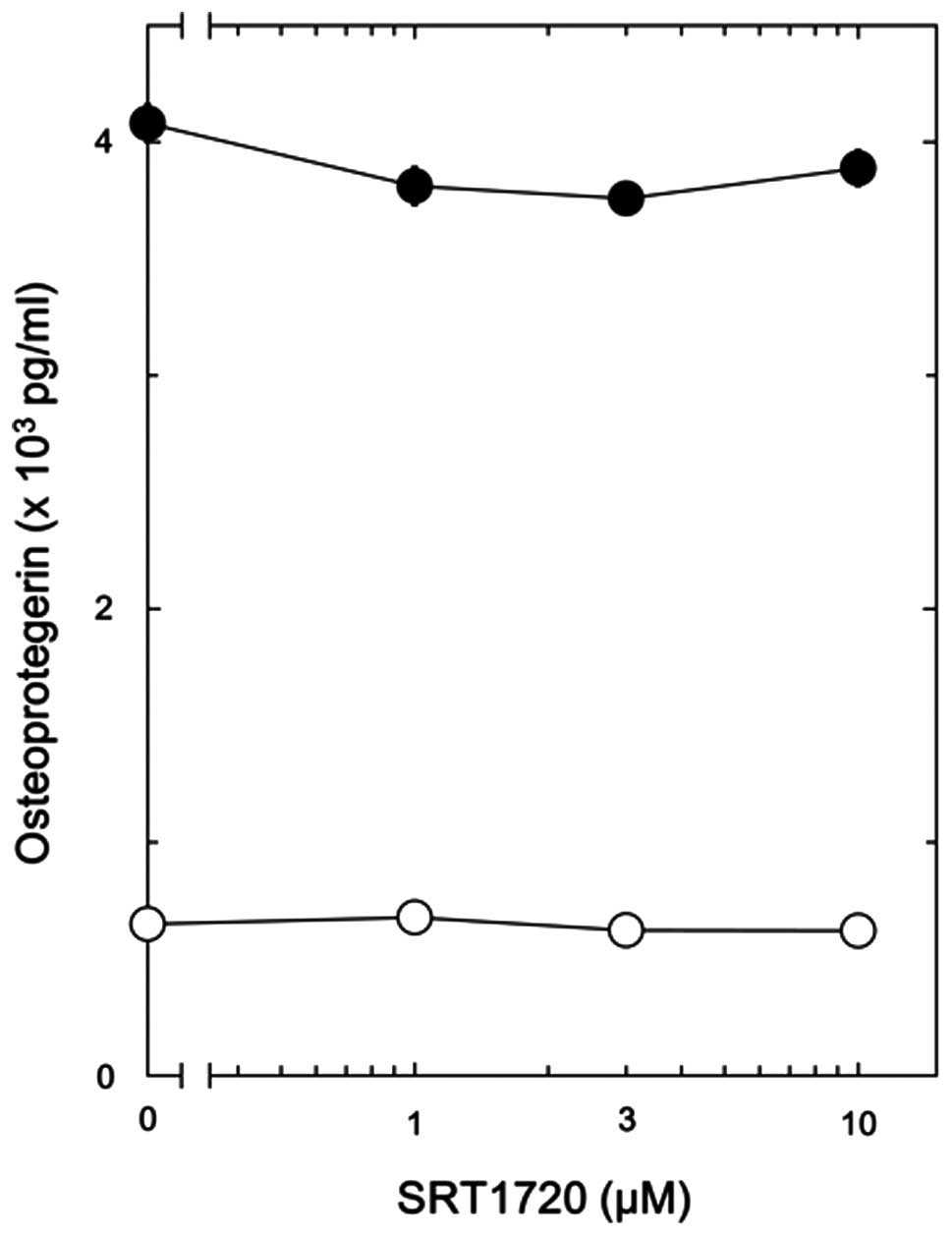
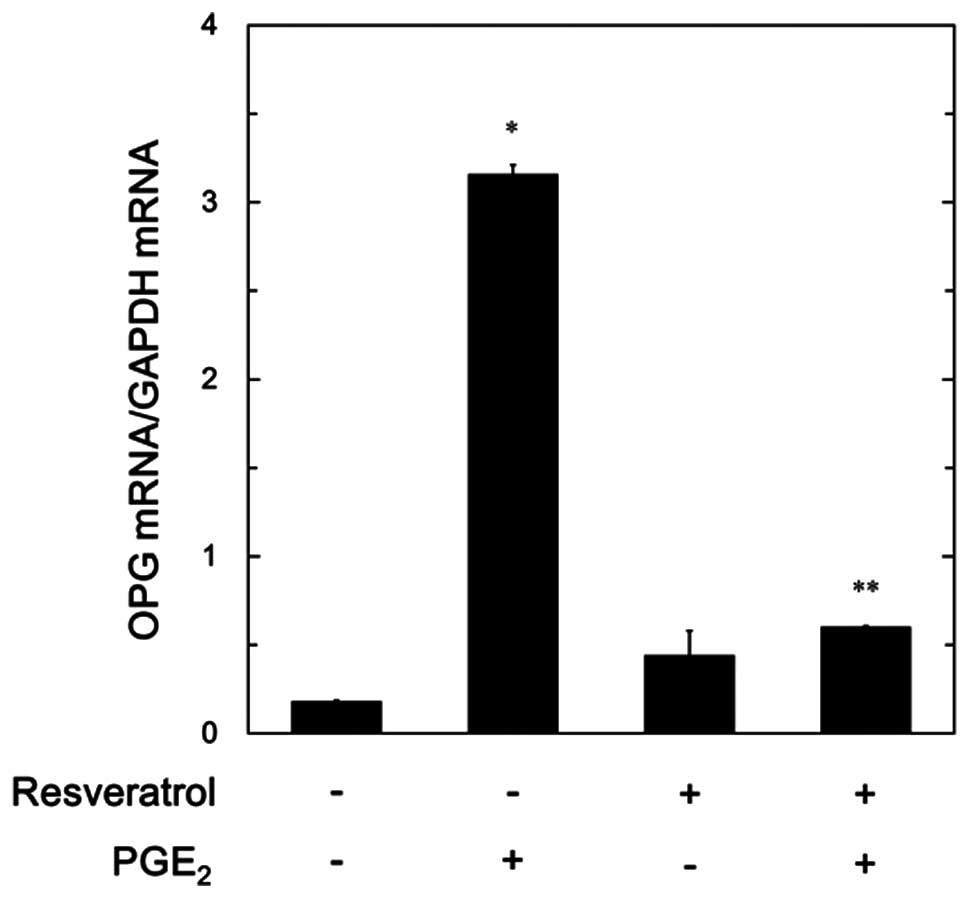
|
1
|
Karsenty G and Wagner EF: Reaching a
genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev
Cell. 2:389–406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parfitt AM: Targeted and nontargeted bone
remodeling: relationship to basic multicellular unit origination
and progression. Bone. 30:5–7. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T,
Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G,
Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D,
Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R
and Boyle WJ: Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in
the regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Yasuda H, Mizuno
A, Itoh K, Ueno Y, Shinki T, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ, Higashio K
and Suda T: Osteoprotegerin produced by osteoblasts is an important
regulator in osteoclast development and function. Endocrinology.
141:3478–3484. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwan TS, Padrines M, Théoleyre S, Heymann
D and Fortun Y: IL-6, RANKL, TNF-α/IL-1: interrelations in bone
resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:49–60.
2004.
|
|
6
|
Nijiweide PJ, Burger EH and Feyen JH:
Cells of bone: proliferation, differentiation, and hormonal
regulation. Physiol Rev. 66:855–886. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith WL: The eicosanoids and their
biochemical mechanisms of action. Biochem J. 259:315–324.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blackwell KA, Raisz LG and Pilbeam CC:
Prostaglandins in bone: bad cop, good cop? Trends Endocrinol Metab.
21:294–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kozawa O, Suzuki A, Tokuda H, Kaida T and
Uematsu T: Interleukin-6 synthesis induced by prostaglandin
E2: cross-talk regulation by protein kinase C. Bone.
22:355–360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tokuda H, Kozawa O, Niwa M, Matsuno H,
Kato K and Uematsu T: Mechanism of prostaglandin
E2-stimulated heat shock protein 27 induction in
osteoblasts-like MC3T3-E1 cells. J Endocrinol. 172:271–281.
2002.
|
|
11
|
Frémont L: Biological effects of
resveratrol. Life Sci. 66:663–673. 2000.
|
|
12
|
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson
HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K,
Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M,
Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, Le Couteur D,
Shaw RJ, Navas P, Puigserver P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R and Sinclair
DA: Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a
high-calorie diet. Nature. 444:337–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Timmers S, Auwerx J and Schrauwen P: The
journey of resveratrol from yeast to human. Aging. 4:146–158.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kondo A, Otsuka T, Kuroyanagi G, Yamamoto
N, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Mizutani J, Kozawa O and Tokuda H:
Resveratrol inhibits BMP-4-stimulated VEGF synthesis in
osteoblasts: Suppression of S6 kinase. Int J Mol Med. 33:1013–1018.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sudo H, Kodama H, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S and
Kasai S: In vivo differentiation and calcification in a new clonal
osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J Cell
Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kozawa O, Tokuda H, Miwa M, Kotoyori J and
Oiso Y: Cross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and
phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2
in osteoblast-like cells. Exp Cell Res. 198:130–134. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kato K, Ito H, Hasegawa K, Inaguma Y,
Kozawa O and Asano T: Modulation of the stress-induced synthesis of
hsp27 and αB-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 glioma cells. J
Neurochem. 66:946–950. 1996.
|
|
19
|
Milne JC, Lambert PD, Schenk S, Carney DP,
Smith JJ and Gagne DJ: Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as
therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature.
450:712–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways
activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 81:807–869.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alessi DR: PD98059 is a specific inhibitor
of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in vitro and
in vivo. J Biol Chem. 270:27489–27494. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cuenda A, Rouse J, Doza YN, Meier R, Cohen
P, Gallagher TF, Young PR and Lee JC: SB203580 is a specific
inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular
stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 364:229–233. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O’Leary
EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala L, Peierce S, Satoh Y,
Bhagwat SS, Manning SM and Anderson DW: SP600125, an
anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal Kinase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:13681–13686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB and Johnson
GL: Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a
three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev. 79:143–180.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mader I, Wabitsch M, Debatin KM,
Fischer-Posovsky P and Fulda S: Identification of a novel
proapoptotic function of resveratrol in fat cells:
SIRT1-independent sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FASEB
J. 24:1997–2009. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang A, Liu M, Liu X, Dong LQ, Glickman
RD, Slaga TJ, Zhou Z and Liu F: Up-regulation of adiponectin by
resveratrol: the essential roles of the Akt/FOXO1 and AMP-activated
protein kinase signaling pathways and DsbA-L. J Biol Chem.
286:60–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|