|
1
|
Wilber CG: Toxicology of selenium: a
review. Clin Toxicol. 17:171–230. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Smith AM and Picciano MF: Evidence for
increased selenium requirement for the rat during pregnancy and
lactation. J Nutr. 116:1068–1079. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang GQ, Chen JS, Wen ZM, Ge KY, Zhu LZ,
Chen XC and Chen XS: The role of selenium in Keshan disease. Adv
Nutr Res. 6:203–231. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Rij AM, Thomson CD, McKenzie JM and
Robinson MF: Selenium deficiency in total parenteral nutrition. Am
J Clin Nutr. 32:2076–2085. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schwarz K and Foltz CM: Selenium as an
integral part of factor 3 against dietary necrotic liver
degeneration. J Am Chem Soc. 79:3292–3293. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Reddy PG, Morill JL, Minocha HC and
Stevenson JS: Vitamin E is immunostimulatory in calves. J Dairy
Sci. 70:993–999. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Birringer M, Pilawa S and Flohé L: Trends
in selenium biochemistry. Nat Prod Rep. 19:693–718. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Carlson BA, Novoselov SV, Kumaraswamy E,
Lee BJ, Anver MR, Gladyshev VN and Hatfield DL: Specific excision
of the selenocysteine tRNA[Ser]Sec (Trsp) gene in mouse liver
demonstrates an essential role of selenoproteins in liver function.
J Biol Chem. 279:8011–8017. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Berry MJ, Banu L, Chen YY, Mandel SJ,
Kieffer JD, Harney JW and Larsen PR: Recognition of UGA as a
selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase requires sequences in the
3′ untransalated region. Nature. 353:273–276. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kryukov GV, Castellano S, Novoselov SV,
Lobanov AV, Zehtab O, Guigó R and Gladyshev VN: Characterization of
mammalian selenoproteomes. Science. 300:1439–1443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korotkov KV, Novoselov SV, Hatfield DL and
Gladyshev VN: Mammalian selenoprotein in which selenocysteine (Sec)
incorporation is supported by a new form of Sec insertion sequence
element. Mol Cell Biol. 22:1402–1411. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Müller WE, Borejko A, Brandt D, et al:
Selenium affects biosilica formation in the demosponge Suberites
domuncula. Effect on gene expression and spicule formation. FEBS J.
272:3838–3852. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hwang DY, Sin JS, Kim MS, et al:
Overexpression of human selenoprotein M differentially regulates
the concentrations of antioxidants and H2O2,
the activity of antioxidant enzymes, and the composition of white
blood cells in a transgenic rat. Int J Mol Med. 21:169–179.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J and Berry MJ: Selenium and
selenoproteins in the brain and brain diseases (Review). J
Neurochem. 86:1–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ramaekers VT, Calomme M, Vanden Berghe D
and Makropoulos W: Selenium deficiency triggering intractable
seizures. Neuropediatrics. 25:217–223. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Imam SZ, el-Yazal J, Newport GD, Itzhak Y,
Cadet JL, Slikker W Jr and Ali SF: Methamphetamine-induced
dopaminergic neurotoxicity: role of peroxynitrite and
neuroprotective role of antioxidants and peroxynitrite
decomposition catalysts. Ann NY Acad Sci. 939:366–380. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zafar KS, Siddiqui A, Sayeed I, Ahmad M,
Salim S and Islam F: Dose-dependent protective effect of selenium
in rat model of Parkinson’s disease: neurobehavioral and
neurochemical evidences. J Neurochem. 84:438–446. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takizawa S, Matsushima K, Shinohara Y,
Ogawa S, Komatsu N, Utsunomiya H and Watanabe K:
Immunohistochemical localization of glutathione peroxidase in
infarcted human brain. J Neurol Sci. 122:66–73. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saijoh K, Saito N, Lee MJ, Fujii M,
Kobayashi T and Sumino K: Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a
bovine selenoprotein P-like protein containing 12 selenocysteines
and a (His-Pro) rich domain insertion, and its regional expression.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 30:301–311. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim IY, Shin JH and Seong JK: Mouse
phenogenomics, toolbox for functional annotation of human genome.
BMB Rep. 43:79–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schomburg L, Schweizer U, Holtmann B,
Flohé L, Sendtner M and Köhrle J: Gene disruption discloses role of
selenoprotein P in selenium delivery to target tissues. Biochem J.
370:397–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hill KE, Zhou J, McMahan WJ, Motley AK,
Atkins JF, Gesteland RF and Burk RF: Deletion of selenoprotein P
alters distribution of selenium in the mouse. J Biol Chem.
278:13640–13646. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang DY, Seo SJ, Kim YK, et al: Selenium
acts as an insulin-like molecule for the downregulation of diabetic
symptoms via endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin signalling
proteins in diabetes-induced non-obese diabetic mice. J Biosci.
32:723–735. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yim SY, Chae KR, Shim SB, et al: ERK
activation induced by selenium treatment significantly
downregulates beta/gamma-secretase activity and Tau phosphorylation
in the transgenic rat overexpressing human selenoprotein M. Int J
Mol Med. 24:91–96. 2009.
|
|
25
|
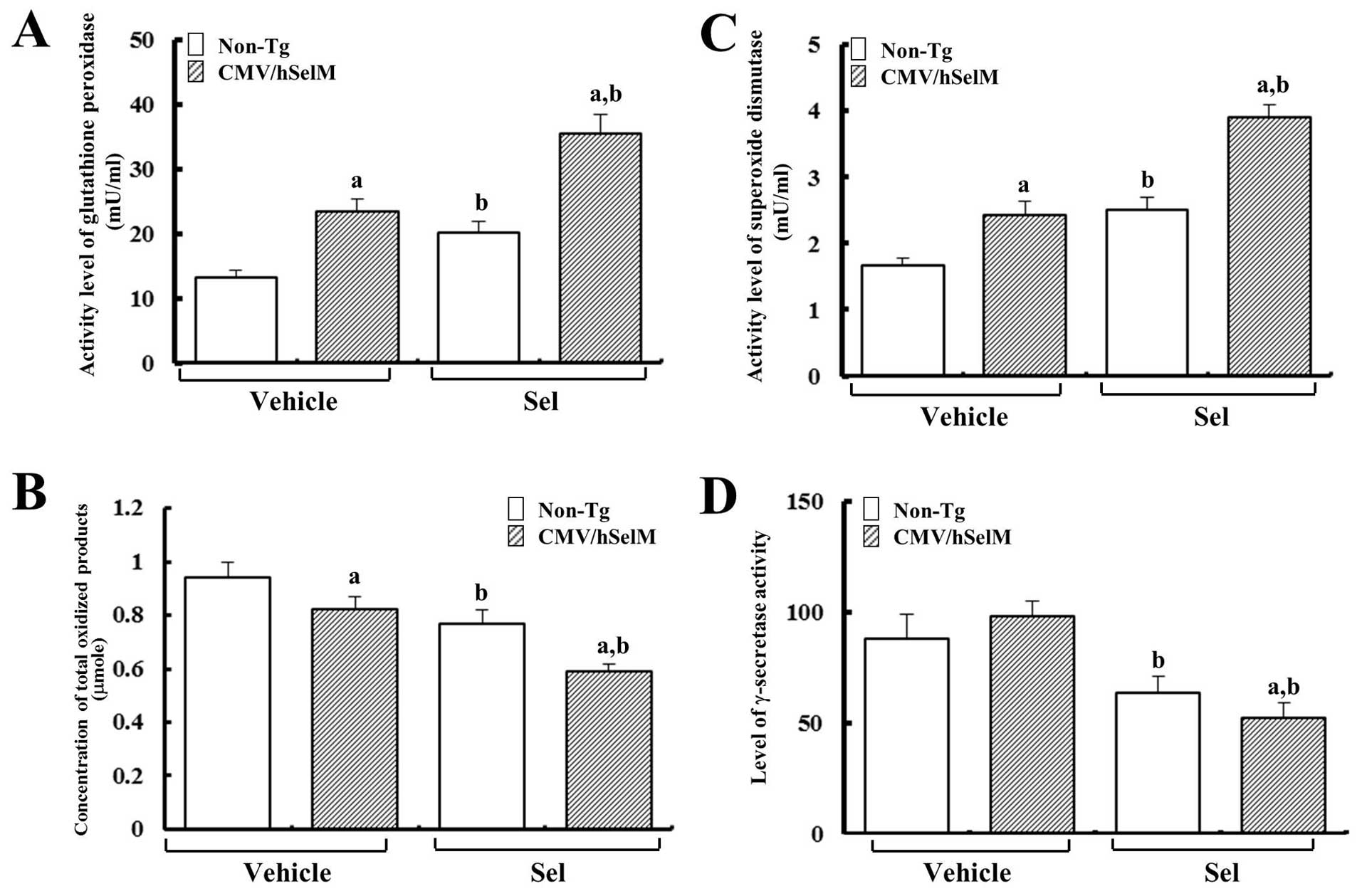
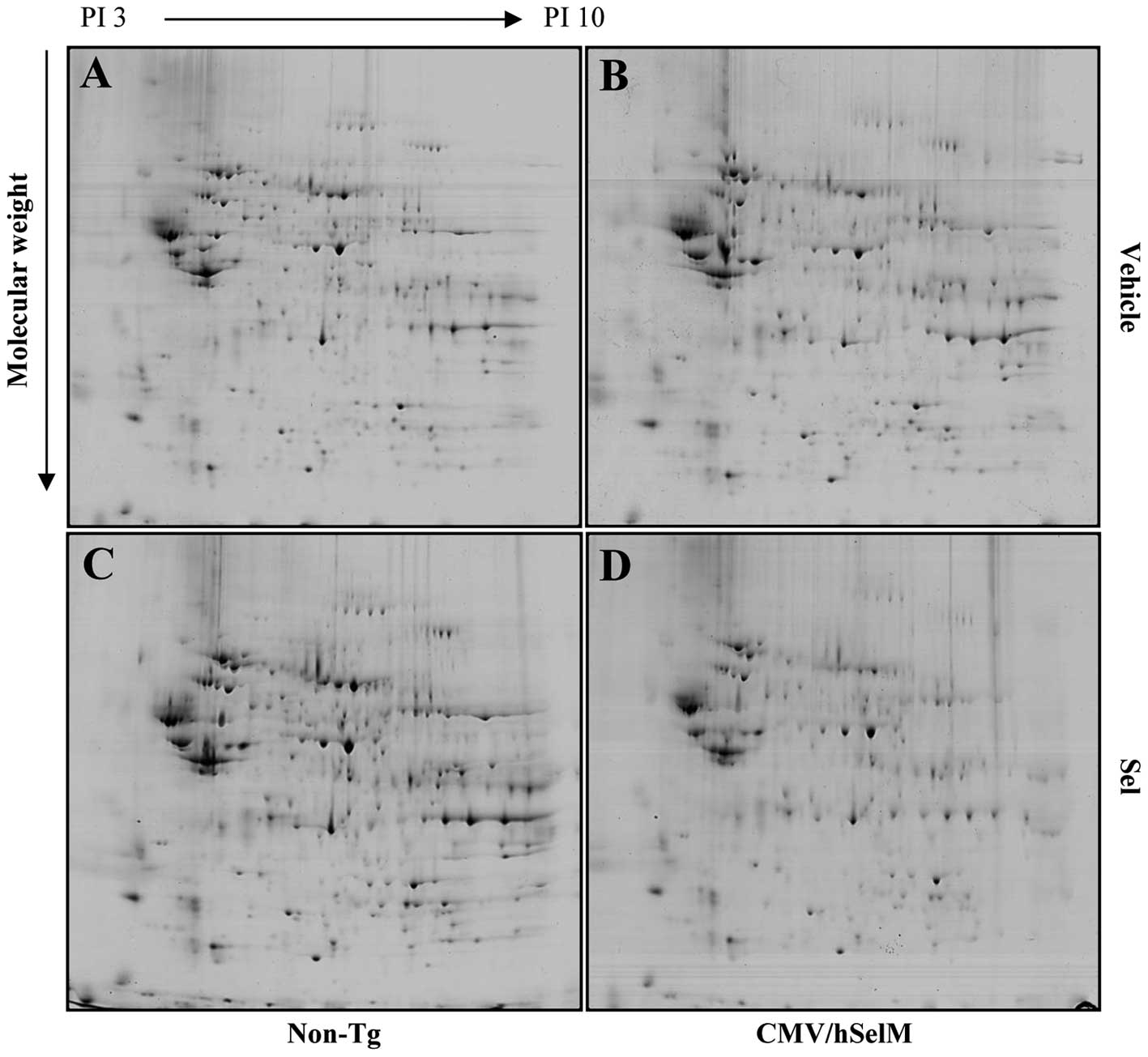
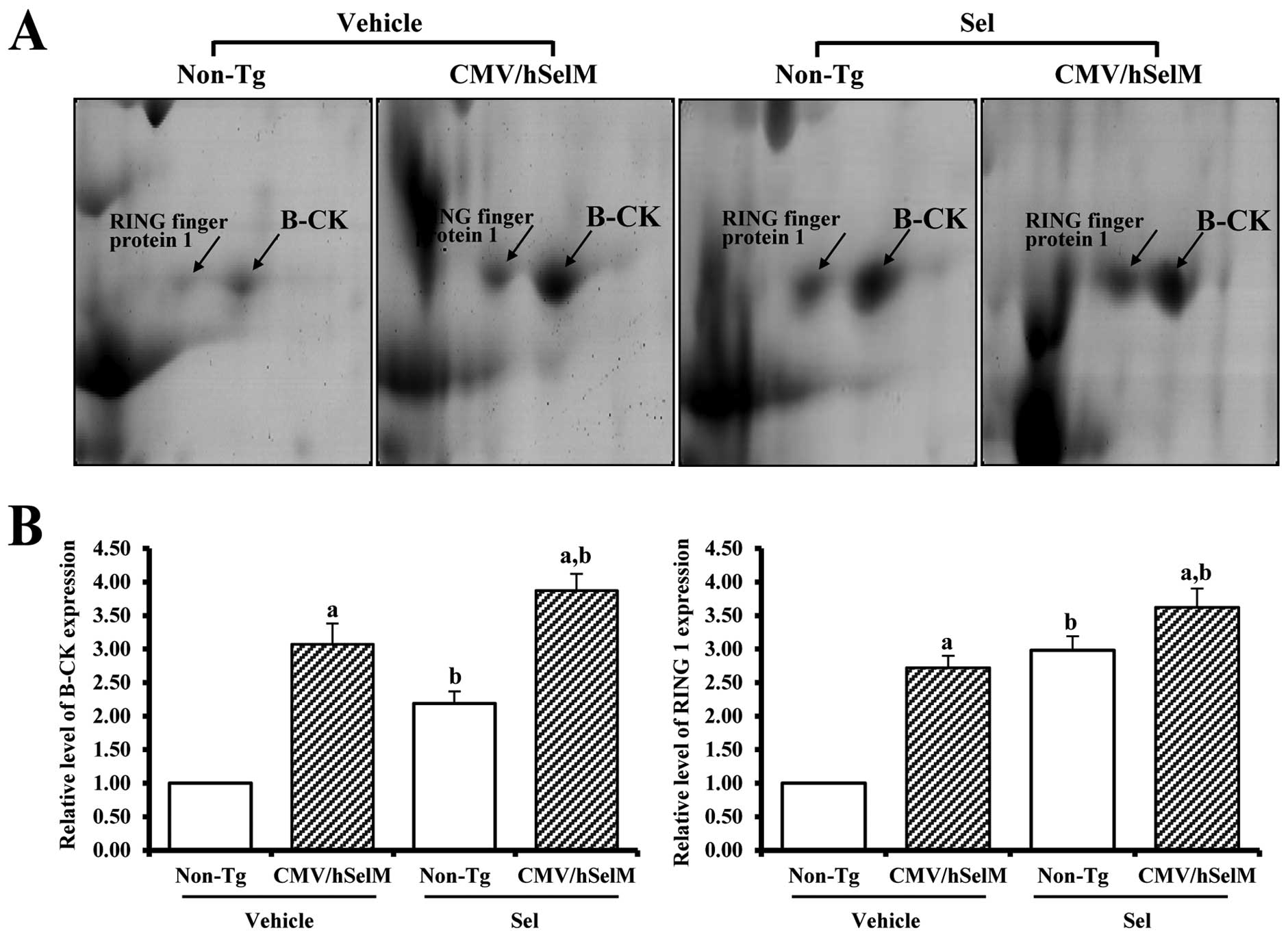
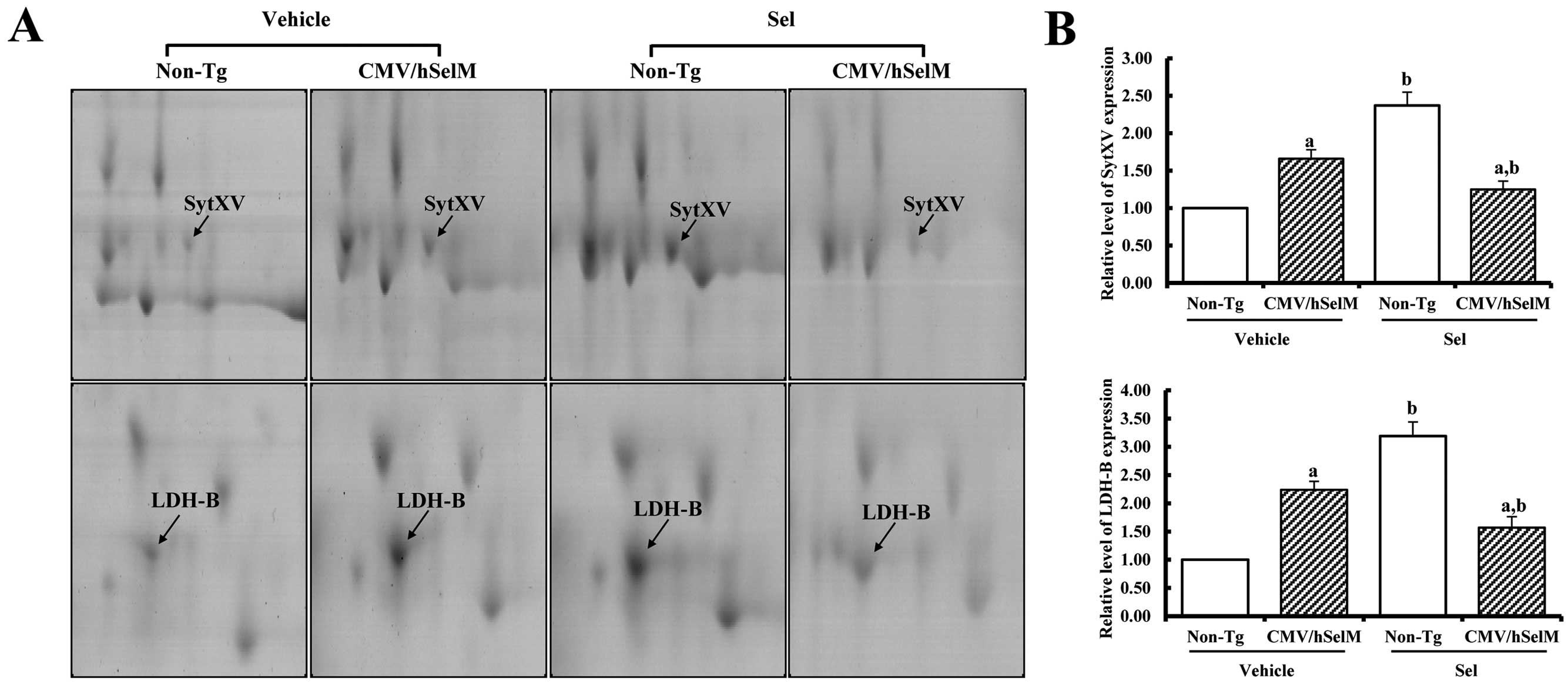
Goo JS, Kim YN, Choi KM, et al: Proteomic
analysis of kidneys from selenoprotein M transgenic rats in
response to increased bioability of selenium. Clin Proteomics.
10:102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park JY, Seong JK and Paik YK: Proteomic
analysis of diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice. Proteomics.
4:514–523. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim BH, Park EY, Yoo KH, Choi KM, Kim Y,
Seong Jk and Park JH: N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 is involved
in the regulation of cystogenesis in transgenic mice overexpressing
human PKD2 gene. Proteomics. 13:134–141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Selkoe DJ: Alzheimer’s disease: genes,
proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 81:741–766. 2001.
|
|
29
|
Savaskan NE, Bräuer AU, Kühbacher M, et
al: Selenium deficiency increases susceptibility to
glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. FASEB J. 17:112–114. 2003.
|
|
30
|
Hu H, Jiang C, Li G and Lü J: PKB/AKT and
ERK regulation of caspase-mediated apoptosis by methylseleninic
acid in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:1374–1381.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jaaro H, Rubinfeld H, Hanoch T and Seger
R: Nuclear translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
(MEK1) in response to mitogenic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:3742–3747. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seger R, Seger D, Reszka AA, et al:
Overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK)
and its mutants in NIH 3T3 cells. Evidence that MAPKK involvement
in cellular proliferation is regulated by phosphorylation of serine
residues in its kinase subdomains VII and VIII. J Biol Chem.
269:25699–25709. 1994.
|
|
33
|
Kim SK, Park HJ, Hong HS, Baik EJ, Jung MW
and Mook-Jung I: ERK1/2 is an endogenous negative regulator of the
gamma-secretase activity. FASEB J. 20:157–159. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwatsubo T: The gamma-secretase complex:
machinery for intramembrane proteolysis. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
14:379–383. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen F, Hasegawa H, Schmitt-Ulms G, et al:
TMP21 is a presenilin complex component that modulates
gamma-secretase but not epsilon-secretase activity. Nature.
440:1208–1212. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bessman SP and Carpenter CL: The
creatine-creatine phosphate energy shuttle. Annu Rev Biochem.
54:831–862. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schnyder T, Winkler H, Gross H,
Eppenberger HM and Wallimann T: Crystallization of mitochondrial
creatine kinase. Growing of large protein crystals and electron
microscopic investigation of microcrystals consisting of octamers.
J Biol Chem. 266:5318–5322. 1991.
|
|
38
|
David S, Shoemaker M and Haley BE:
Abnormal properties of creatine kinase in Alzheimer’s disease
brain: correlation of reduced enzyme activity and active site
photolabeling with aberrant cytosol-membrane partitioning. Brain
Res Mol Brain Res. 54:276–287. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tomimoto H, Yamamoto K, Homburger HA and
Yanagihara T: Immunoelectron microscopic investigation of creatine
kinase BB-isoenzyme after cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Acta
Neuropathol. 86:447–455. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gross WL, Bak MI, Ingwall JS, Arstall MA,
Smith TW, Balligand JL and Kelly RA: Nitric oxide inhibits creatine
kinase and regulates rat heart contractile reserve. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:5604–5609. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hamman BL, Bittl JA, Jacobus WE, Allen PD,
Spencer RS, Tian R and Ingwall JS: Inhibition of the creatine
kinase reaction decreases the contractile reserve of isolated rat
hearts. Am J Physiol. 269:H1030–H1036. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rech VC, Feksa LR, Fleck RM, Athaydes GA,
Dornelles PK, Rodrigues-Junior V and Wannmacher CM: Cysteamine
prevents inhibition of thiol-containing enzymes caused by cystine
or cystine dimethylester loading in rat brain cortex. Metab Brain
Dis. 23:133–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Steece-Collier K, Maries E and Kordower
JH: Etiology of Parkinson’s disease: genetics and environment
revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:13972–13974. 2002.
|
|
44
|
Dawson TM: Parkin and defective
ubiquitination in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl.
70:209–213. 2006.
|
|
45
|
Fukuda M and Mikoshiba K:
Synaptotagmin-like protein 1–3: a novel family of C-terminal-type
tandem C2 proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 281:1226–1233.
2001.
|
|
46
|
Fukuda M, Saegusa C and Mikoshiba K: Novel
splicing isoforms of synaptotagmin-like proteins 2 and 3:
identification of the Slp homology domain. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 283:513–519. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sugita S, Shin OH, Han W, Lao Y and Südhof
TC: Synaptotagmins form a hierarchy of exocytotic Ca(2+) sensors
with distinct Ca(2+) affinities. EMBO J. 21:270–280. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fukuda M, Kanno E, Ogata Y, Saegusa C, Kim
T, Loh YP and Yamamoto A: Nerve growth factor-dependent sorting of
synaptotagmin IV protein to mature dense-core vesicles that undergo
calcium-dependent exocytosis in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem.
278:3220–3226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chapman ER: Synaptotagmin: a Ca(2+) sensor
that triggers exocytosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:498–508. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mikoshiba K, Fukuda M, Moreira JE, Lewis
FMT, Sugimori M, Niinobe M and Llinás R: Role of the C2A domain of
synaptotagmin in transmitter release as determined by specific
antibody injection into the squid giant synapse preterminal. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:10703–10707. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Detrait ER, Yoo S, Eddleman CS, Fukuda M,
Bittner GD and Fishman HM: Plasmalemmal repair of severed neurites
of PC12 cells requires Ca(2+) and synaptotagmin. J Neurosci Res.
62:566–573. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Reddy A, Caler EV and Andrews NW: Plasma
membrane repair is mediated by Ca(2+)-regulated exocytosis of
lysosomes. Cell. 106:157–169. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Michaut M, De Blas G, Tomes CN, Yunes R,
Fukuda M and Mayorga LS: Synaptotagmin VI participates in the
acrosome reaction of human spermatozoa. Dev Biol. 235:521–529.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schiavo G, Osborne SL and Sgouros JG:
Synaptotagmins: more isoforms than functions? Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 248:1–8. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fukuda M and Mikoshiba K: The function of
inositol high polyphosphate binding proteins. Bioessays.
19:593–603. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Philibert RA, Nelson JJ, Sandhu HK, Crowe
RR and Coryell WH: Association of an exonic LDHA polymorphism with
altered respiratory response in probands at high risk for panic
disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 117:11–17. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nazam Ansari M, Bhandari U, Islam F and
Tripathi CD: Evaluation of antioxidant and neuroprotective effect
of ethanolic extract of Embelia ribes Burm in focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rats. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 22:305–314. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kim HS, Choi Y, Shin KY, et al: Swedish
amyloid precursor protein mutation increases phosphorylation of
eIF2alpha in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci Res.
85:1528–1537. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Petrov T, Underwood BD, Braun B, Alousi SS
and Rafols JA: Upregulation of iNOS expression and phosphorylation
of eIF-2alpha are paralleled by suppression of protein synthesis in
rat hypothalamus in a closed head trauma model. J Neurotrauma.
18:799–812. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hayashi T, Saito A, Okuno S, et al:
Oxidative damage to the endoplasmic reticulum is implicated in
ischemic neuronal cell death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
23:1117–1128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Foltz DR, Jansen LE, Black BE, Bailey AO,
Yates JR 3rd and Cleveland DW: The human CENP-A centromeric
nucleosome-associated complex. Nat Cell Biol. 8:458–469. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang Z, Ottens AK, Sadasivan S, Kobeissy
FH, Fang T, Hayes RL and Wang KK: Calpain-mediated collapsin
response mediator protein-1, -2, and -4 proteolysis after
neurotoxic and traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 24:460–472.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chung MA, Lee JE, Lee JY, Ko MJ, Lee ST
and Kim HJ: Alteration of collapsin response mediator protein-2
expression in focal ischemic rat brain. Neuroreport. 16:1647–1653.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|