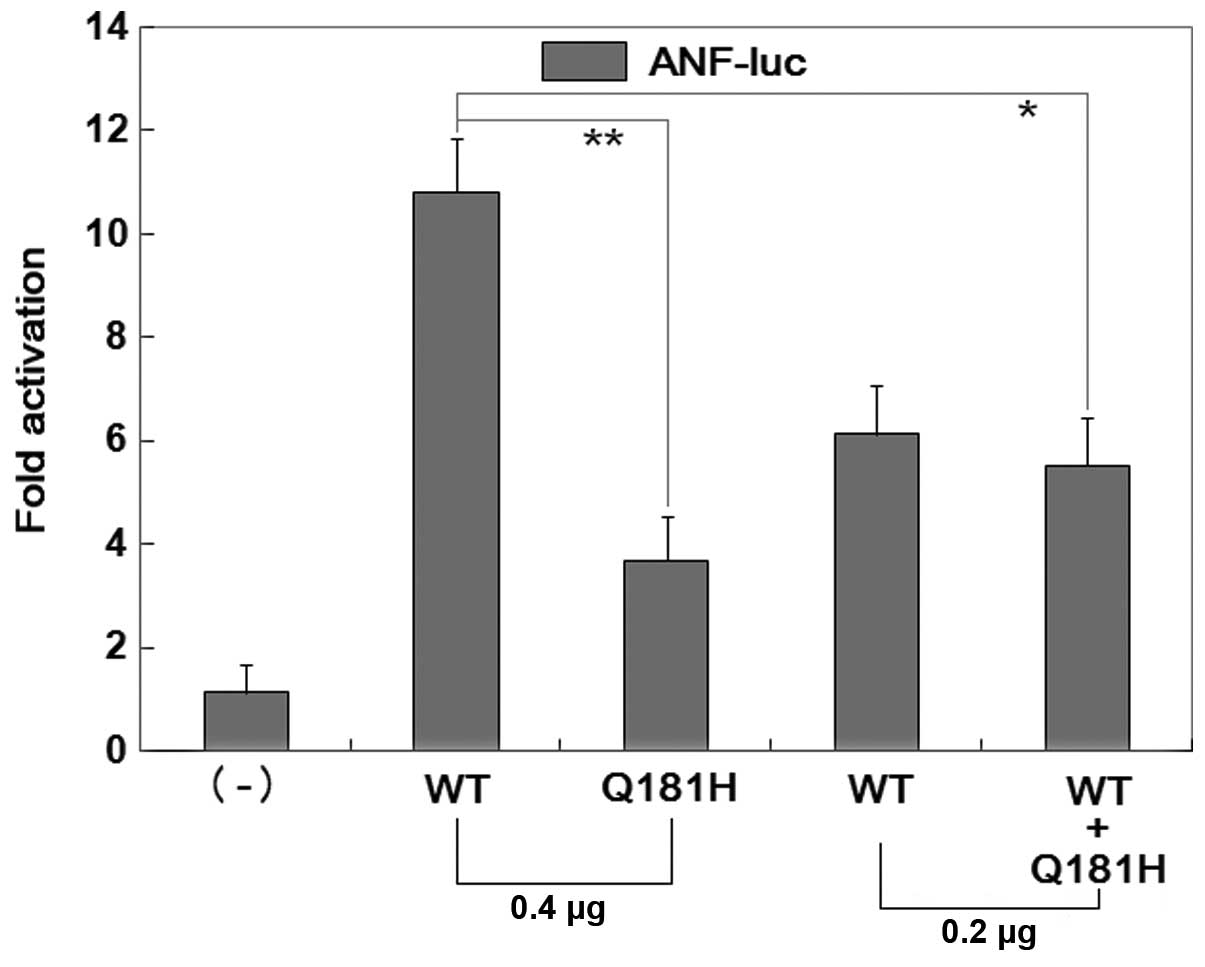
|
1
|
Fuster V, Rydén LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ,
Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, Halperin JL, Kay GN, Le Huezey JY, Lowe
JE, Olsson SB, Prystowsky EN, Tamargo JL, Wann LS, Smith SC Jr,
Priori SG, Estes NA III, Ezekowitz MD, Jackman WM, January CT, Lowe
JE, Page RL, Slotwiner DJ, Stevenson WG, Tracy CM, Jacobs AK,
Anderson JL, Albert N, Buller CE, Creager MA, Ettinger SM, Guyton
RA, Halperin JL, Hochman JS, Kushner FG, Ohman EM, Stevenson WG,
Tarkington LG and Yancy CW: American College of Cardiology
Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force: 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS
focused updates incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines
for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report
of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart
Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation.
123:e269–e367. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y,
Henault LE, Selby JV and Singer DE: Prevalence of diagnosed atrial
fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management
and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in
Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 285:2370–2375. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, Larson
MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, D’Agostino RB, Massaro JM, Beiser A, Wolf PA
and Benjamin EJ: Lifetime risk for development of atrial
fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation.
110:1042–1046. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS,
Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB and Tsang TS: Secular trends
in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota,
1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future
prevalence. Circulation. 114:119–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB,
Silbershatz H, Kannel WB and Levy D: Impact of atrial fibrillation
on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation.
98:946–952. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wolf PA, Abbott RD and Kannel WB: Atrial
fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the
Framingham Study. Stroke. 22:983–988. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh SN, Tang XC, Singh BN, Dorian P,
Reda DJ, Harris CL, Fletcher RD, Sharma SC, Atwood JE, Jacobson AK,
Lewis HD Jr, Lopez B, Raisch DW and Ezekowitz MD: SAFE-T
Investigators: Quality of life and exercise performance in patients
in sinus rhythm versus persistent atrial fibrillation: a Veterans
Affairs Cooperative Studies Program Substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol.
48:721–730. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Bai R, Mohanty
S, Pump A, Cereceda Brantes M, Horton R, Burkhardt JD, Lakkireddy
D, Reddy YM, Casella M, Dello Russo A, Tondo C and Natale A: Atrial
fibrillation and the risk of incident dementia: a meta-analysis.
Heart Rhythm. 9:1761–1768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chao TF, Tsao HM, Ambrose K, Lin YJ, Lin
WS, Chang SL, Lo LW, Hu YF, Tuan TC, Suenari K, Li CH, Hartono B,
Chang HY, Chung FP, Hanafy DA, Lin WY and Chen SA: Renal
dysfunction and the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with
atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation - the potential role
beyond the CHA2DS2-VASc score. Heart Rhythm. 9:1755–1760. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calvo N, Bisbal F, Guiu E, Ramos P, Nadal
M, Tolosana JM, Arbelo E, Berruezo A, Sitges M, Brugada J and Mont
L: Impact of atrial fibrillation-induced tachycardiomyopathy in
patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation. Int J Cardiol.
168:4093–4097. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Naji F, Pagliaruzzi M, Penko M, Kanic V
and Vokac D: Changes in left ventricular filling in patients with
persistent atrial fibrilation. Int J Med Sci. 10:1876–1879. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tayebjee MH, Gilbert K, Macdonald W,
Hogarth AJ, Lewis NT and Tan LB: Atrial fibrillation reduces the
functional REServe of the heart by a fifth: a pilot FRESH-AF study.
Int J Cardiol. 168:4369–4370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weijs B, Pisters R, Haest RJ, Kragten JA,
Joosen IA, Versteylen M, Timmermans CC, Pison L, Blaauw Y, Hofstra
L, Nieuwlaat R, Wildberger J and Crijns HJ: Patients originally
diagnosed with idiopathic atrial fibrillation more often suffer
from insidious coronary artery disease compared to healthy sinus
rhythm controls. Heart Rhythm. 9:1923–1929. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Soliman EZ, Safford MM, Muntner P,
Khodneva Y, Dawood FZ, Zakai NA, Thacker EL, Judd S, Howard VJ,
Howard G, Herrington DM and Cushman M: Atrial fibrillation and the
risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA Intern Med. 174:107–114. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marijon E, Le Heuzey JY, Connolly S, Yang
S, Pogue J, Brueckmann M, Eikelboom J, Themeles E, Ezekowitz M,
Wallentin L and Yusuf S: RE-LY Investigators: Causes of death and
influencing factors in patients with atrial fibrillation: a
competing-risk analysis from the randomized evaluation of long-term
anticoagulant therapy study. Circulation. 128:2192–2201. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton
HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd
SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD,
Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK,
Mohler ER III, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey
DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan
TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D and Turner MB: American Heart
Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics
Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2014 update: a
report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
129:e28–e292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ball J, Carrington MJ, McMurray JJ and
Stewart S: Atrial fibrilation: profile and burden of an evolving
epidemic in the 21st century. Int J Cardiol. 67:1807–1824. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coyne KS, Paramore C, Grandy S, Mercader
M, Reynolds M and Zimetbaum P: Assessing the direct costs of
treating nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the United States.
Value Health. 9:348–356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nattel S: New ideas about atrial
fibrillation 50 years on. Nature. 415:219–226. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abed HS, Samuel CS, Lau DH, Kelly DJ,
Royce SG, Alasady M, Mahajan R, Kuklik P, Zhang Y, Brooks AG,
Nelson AJ, Worthley SG, Abhayaratna WP, Kalman JM, Wittert GA and
Sanders P: Obesity results in progressive atrial structural and
electrical remodeling: implications for atrial fibrillation. Heart
Rhythm. 10:90–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Naruse Y, Tada H, Satoh M, Yanagihara M,
Tsuneoka H, Hirata Y, Ito Y, Kuroki K, Machino T, Yamasaki H,
Igarashi M, Sekiguchi Y, Sato A and Aonuma K: Concomitant
obstructive sleep apnea increases the recurrence of atrial
fibrillation following radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial
fibrillation: clinical impact of continuous positive airway
pressure therapy. Heart Rhythm. 10:331–337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chao TF, Hung CL, Chen SJ, Wang KL, Chen
TJ, Lin YJ, Chang SL, Lo LW, Hu YF, Tuan TC and Chen SA: The
association between hyperuricemia, left atrial size and new-onset
atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 168:4027–4032. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D and Nattel
S: The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation:
relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and
mechanisms. Circ Res. 114:1453–1468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fox CS, Parise H, D’Agostino RB Sr,
Lloyd-Jones DM, Vasan RS, Wang TJ, Levy D, Wolf P and Benjamin EJ:
Parental atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for atrial
fibrillation in offspring. JAMA. 291:2851–2855. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ellinor PT, Yoerger DM, Ruskin JN and
MacRae CA: Familial aggregation in lone atrial fibrillation. Hum
Genet. 118:179–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Arnar DO, Thorvaldsson S, Manolio TA,
Thorgeirsson G, Kristjansson K, Hakonarson H and Stefansson K:
Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur Heart
J. 27:708–712. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Christophersen IE, Ravn LS,
Budtz-Joergensen E, Skytthe A, Haunsoe S, Svendsen JH and
Christensen K: Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation: a study
in Danish twins. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2:378–383. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang YQ, Zhang XL, Wang XH, Tan HW, Shi
HF, Fang WY and Liu X: Familial aggregation of lone atrial
fibrillation in Chinese population. Intern Med. 49:2385–2391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lubitz SA, Yin X, Fontes JD, Magnani JW,
Rienstra M, Pai M, Villalon ML, Vasan RS, Pencina MJ, Levy D,
Larson MG, Ellinor PT and Benjamin EJ: Association between familial
atrial fibrillation and risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation.
JAMA. 304:2263–2269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zöller B, Ohlsson H, Sundquist J and
Sundquist K: High familial risk of atrial fibrillation/atrial
flutter in multiplex families: a nationwide family study in Sweden.
J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0033842012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oyen N, Ranthe MF, Carstensen L, Boyd HA,
Olesen MS, Olesen SP, Wohlfahrt J and Melbye M: Familial
aggregation of lone atrial fibrillation in young persons. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 60:917–921. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brugada R, Tapscott T, Czernuszewicz GZ,
Marian AJ, Iglesias A, Mont L, Brugada J, Girona J, Domingo A,
Bachinski LL and Roberts R: Identification of a genetic locus for
familial atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 336:905–911. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen YH, Xu SJ, Bendahhou S, Wang XL, Wang
Y, Xu WY, Jin HW, Sun H, Su XY, Zhuang QN, Yang YQ, Li YB, Liu Y,
Xu HJ, Li XF, Ma N, Mou CP, Chen Z, Barhanin J and Huang W: KCNQ1
gain-of-function mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. Science.
299:251–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ellinor PT, Shin JT, Moore RK, Yoerger DM
and MacRae CA: Locus for atrial fibrillation maps to chromosome
6q14-16. Circulation. 107:2880–2883. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oberti C, Wang L, Li L, Dong J, Rao S, Du
W and Wang Q: Genome-wide linkage scan identifies a novel genetic
locus on chromosome 5p13 for neonatal atrial fibrillation
associated with sudden death and variable cardiomyopathy.
Circulation. 110:3753–3759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Volders PG, Zhu Q, Timmermans C, Eurlings
PM, Su X, Arens YH, Li L, Jongbloed RJ, Xia M, Rodriguez LM and
Chen YH: Mapping a novel locus for familial atrial fibrillation on
chromosome 10p11-q21. Heart Rhythm. 4:469–475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Darbar D, Hardy A, Haines JL and Roden DM:
Prolonged signal-averaged P-wave duration as an intermediate
phenotype for familial atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol.
51:1083–1089. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Olesen MS, Bentzen BH, Nielsen JB,
Steffensen AB, David JP, Jabbari J, Jensen HK, Haunsø S, Svendsen
JH and Schmitt N: Mutations in the potassium channel subunit KCNE1
are associated with early-onset familial atrial fibrillation. BMC
Med Genet. 13:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Xia M, Jin Q, Bendahhou S, Shi J
and Chen Y, Liang B, Lin J, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhou Q, Zhang D, Wang R,
Ma N, Su X, Niu K, Pei Y, Xu W, Chen Z, Wan H, Cui J, Barhanin J
and Chen Y: Identification of a KCNE2 gain-of-function mutation in
patients with familial atrial fibrillation. Am J Hum Genet.
75:899–905. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nielsen JB, Bentzen BH, Olesen MS, David
JP, Olesen SP, Haunsø S, Svendsen JH and Schmitt N:
Gain-of-function mutations in potassium channel subunit KCNE2
associated with early-onset lone atrial fibrillation. Biomark Med.
8:557–570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lundby A, Ravn LS, Svendsen JH, Hauns S,
Olesen SP and Schmitt N: KCNE3 mutation V17M identified in a
patient with lone atrial fibrillation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
21:47–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zeng Z, Tan C, Teng S, Chen J, Su S, Zhou
X, Wang F, Zhang S, Gu D, Makielski JC and Pu J: The single
nucleotide polymorphisms of I(Ks) potassium channel genes and their
association with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese population.
Cardiology. 108:97–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ravn LS, Aizawa Y, Pollevick GD,
Hofman-Bang J, Cordeiro JM, Dixen U, Jensen G, Wu Y, Burashnikov E,
Haunso S, Guerchicoff A, Hu D, Svendsen JH, Christiansen M and
Antzelevitch C: Gain of function in IKs secondary to a mutation in
KCNE5 associated with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 5:427–435.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hong K, Bjerregaard P, Gussak I and
Brugada R: Short QT syndrome and atrial fibrillation caused by
mutation in KCNH2. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 16:394–396. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sinner MF, Pfeufer A, Akyol M, Beckmann
BM, Hinterseer M, Wacker A, Perz S, Sauter W, Illig T, Näbauer M,
Schmitt C, Wichmann HE, Schömig A, Steinbeck G, Meitinger T and
Kääb S: The non-synonymous coding IKr-channel variant KCNH2-K897T
is associated with atrial fibrillation: results from a systematic
candidate gene-based analysis of KCNH2 (HERG). Eur Heart J.
29:907–914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Olson TM, Alekseev AE, Liu XK, Park S,
Zingman LV, Bienengraeber M, Sattiraju S, Ballew JD, Jahangir A and
Terzic A: Kv1.5 channelopathy due to KCNA5 loss-of-function
mutation causes human atrial fibrillation. Hum Mol Genet.
15:2185–2191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang Y, Li J, Lin X, Yang Y, Hong K, Wang
L, Liu J, Li L, Yan D, Liang D, Xiao J, Jin H, Wu J, Zhang Y and
Chen YH: Novel KCNA5 loss-of-function mutations responsible for
atrial fibrillation. J Hum Genet. 54:277–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Christophersen IE, Olesen MS, Liang B,
Andersen MN, Larsen AP, Nielsen JB, Haunsø S, Olesen SP, Tveit A,
Svendsen JH and Schmitt N: Genetic variation in KCNA5: impact on
the atrial-specific potassium current IKur in patients with lone
atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 34:1517–1525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Olesen MS, Refsgaard L, Holst AG, Larsen
AP, Grubb S, Haunsø S, Svendsen JH, Olesen SP, Schmitt N and Calloe
K: A novel KCND3 gain-of-function mutation associated with
early-onset of persistent lone atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res.
98:488–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xia M, Jin Q, Bendahhou S, He Y, Larroque
MM and Chen Y, Zhou Q, Yang Y, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhu Q, Zhou Y, Lin J,
Liang B, Li L, Dong X, Pan Z, Wang R, Wan H, Qiu W, Xu W, Eurlings
P, Barhanin J and Chen Y: A Kir2.1 gain-of-function mutation
underlies familial atrial fibrillation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
332:1012–1019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Delaney JT, Muhammad R, Blair MA, Kor K,
Fish FA, Roden DM and Darbar D: A KCNJ8 mutation associated with
early repolarization and atrial fibrillation. Europace.
14:1428–1432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gollob MH, Jones DL, Krahn AD, Danis L,
Gong XQ, Shao Q, Liu X, Veinot JP, Tang AS, Stewart AF, Tesson F,
Klein GJ, Yee R, Skanes AC, Guiraudon GM, Ebihara L and Bai D:
Somatic mutations in the connexin 40 gene (GJA5) in atrial
fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 354:2677–2688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun Y, Yang YQ, Gong XQ, Wang XH, Li RG,
Tan HW, Liu X, Fang WY and Bai D: Novel germline GJA5/connexin40
mutations associated with lone atrial fibrillation impair gap
junctional intercellular communication. Hum Mutat. 34:603–609.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shi HF, Yang JF, Wang Q, Li RG, Xu YJ, Qu
XK, Fang WY, Liu X and Yang YQ: Prevalence and spectrum of GJA5
mutations associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Mol Med Rep.
7:767–774. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Thibodeau IL, Xu J, Li Q, Liu G, Lam K,
Veinot JP, Birnie DH, Jones DL, Krahn AD, Lemery R, Nicholson BJ
and Gollob MH: Paradigm of genetic mosaicism and lone atrial
fibrillation: physiological characterization of a connexin
43-deletion mutant identified from atrial tissue. Circulation.
122:236–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Hodgson-Zingman DM, Karst ML, Zingman LV,
Heublein DM, Darbar D, Herron KJ, Ballew JD, de Andrade M, Burnett
JC Jr and Olson TM: Atrial natriuretic peptide frameshift mutation
in familial atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 359:158–165. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Darbar D, Kannankeril PJ, Donahue BS,
Kucera G, Stubblefield T, Haines JL, George AL Jr and Roden DM:
Cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) variants associated with atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 117:1927–1935. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Watanabe H, Darbar D, Kaiser DW,
Jiramongkolchai K, Chopra S, Donahue BS, Kannankeril PJ and Roden
DM: Mutations in sodium channel β1- and β2-subunits associated with
atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2:268–275.
2009.
|
|
59
|
Olesen MS, Holst AG, Svendsen JH, Haunsø S
and Tfelt-Hansen J: SCN1Bb R214Q found in 3 patients: 1 with
Brugada syndrome and 2 with lone atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm.
9:770–773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang P, Yang Q, Wu X, Yang Y, Shi L, Wang
C, Wu G, Xia Y, Yang B, Zhang R, Xu C, Cheng X, Li S, Zhao Y, Fu F,
Liao Y, Fang F, Chen Q, Tu X and Wang QK: Functional
dominant-negative mutation of sodium channel subunit gene SCN3B
associated with atrial fibrillation in a Chinese GeneID population.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:98–104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li RG, Wang Q, Xu YJ, Zhang M, Qu XK, Liu
X, Fang WY and Yang YQ: Mutations of the SCN4B-encoded sodium
channel β4 subunit in familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med.
32:144–150. 2013.
|
|
62
|
Olesen MS, Andreasen L, Jabbari J,
Refsgaard L, Haunsø S, Olesen SP, Nielsen JB, Schmitt N and
Svendsen JH: Very early-onset lone atrial fibrillation patients
have a high prevalence of rare variants in genes previously
associated with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 11:246–251.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Weeke P, Parvez B, Blair M, Short L,
Ingram C, Kucera G, Stubblefield T, Roden DM and Darbar D:
Candidate gene approach to identifying rare genetic variants
associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 11:46–52.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mommersteeg MT, Christoffels VM, Anderson
RH and Moorman AF: Atrial fibrillation: a developmental point of
view. Heart Rhythm. 6:1818–1824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mahida S: Transcription factors and atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 101:194–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Schott JJ, Benson DW, Basson CT, Pease W,
Silberbach GM, Moak JP, Maron BJ, Seidman CE and Seidman JG:
Congenital heart disease caused by mutations in the transcription
factor NKX2-5. Science. 281:108–111. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reamon-Buettner SM and Borlak J: NKX2-5:
an update on this hypermutable homeodomain protein and its role in
human congenital heart disease (CHD). Hum Mutat. 31:1185–1194.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Costa MW, Guo G, Wolstein O, Vale M,
Castro ML, Wang L, Otway R, Riek P, Cochrane N, Furtado M,
Semsarian C, Weintraub RG, Yeoh T, Hayward C, Keogh A, Macdonald P,
Feneley M, Graham RM, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Rosenthal N, Fatkin D
and Harvey RP: Functional characterization of a novel mutation in
NKX2-5 associated with congenital heart disease and adult-onset
cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 6:238–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R,
Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS,
Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, Matsuoka R, Cohen JC and Srivastava D:
GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an
interaction with TBX5. Nature. 424:443–447. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhou P, He A and Pu WT: Regulation of
GATA4 transcriptional activity in cardiovascular development and
disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 100:143–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang YQ, Wang J, Liu XY, Chen XZ, Zhang W,
Wang XZ, Liu X and Fang WY: Novel GATA4 mutations in patients with
congenital ventricular septal defects. Med Sci Monit.
18:CR344–CR350. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang YQ, Wang J, Liu XY, Chen XZ, Zhang W
and Wang XZ: Mutation spectrum of GATA4 associated with congenital
atrial septal defects. Arch Med Sci. 9:976–983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang YQ, Gharibeh L, Li RG, Xin YF, Wang
J, Liu ZM, Qiu XB, Xu YJ, Xu L, Qu XK, Liu X, Fang WY, Huang RT,
Xue S and Nemer G: GATA4 loss-of-function mutations underlie
familial tetralogy of fallot. Hum Mutat. 34:1662–1671. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li RG, Li L, Qiu XB, Yuan F, Xu L, Li X,
Xu YJ, Jiang WF, Jiang JQ, Liu X, Fang WY, Zhang M, Peng LY, Qu XK
and Yang YQ: GATA4 loss-of-function mutation underlies familial
dilated cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 439:591–596.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhao L, Xu JH, Xu WJ, Yu H, Wang Q, Zheng
HZ, Jiang WF, Jiang JF and Yang YQ: A novel GATA4 loss-of-function
mutation responsible for familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol
Med. 33:654–660. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jiang JQ, Li RG, Wang J, Liu XY, Xu YJ,
Fang WY, Chen XZ, Zhang W, Wang XZ and Yang YQ: Prevalence and
spectrum of GATA5 mutations associated with congenital heart
disease. Int J Cardiol. 165:570–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wei D, Bao H, Zhou N, Zheng GF, Liu XY and
Yang YQ: GATA5 loss-of-function mutation responsible for the
congenital ventriculoseptal defect. Pediatr Cardiol. 34:504–511.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wei D, Bao H, Liu XY, Zhou N, Wang Q, Li
RG, Xu YJ and Yang YQ: GATA5 loss-of-function mutations underlie
tetralogy of fallot. Int J Med Sci. 10:34–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ, Zhou M and Yang
YQ: Somatic GATA5 mutations in sporadic tetralogy of Fallot. Int J
Mol Med. 33:1227–1235. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shi LM, Tao JW, Qiu XB, Wang J, Yuan F, Xu
L, Liu H, Li RG, Xu YJ, Wang Q, Zheng HZ, Li X, Wang XZ, Zhang M,
Qu XK and Yang YQ: GATA5 loss-of-function mutations associated with
congenital bicuspid aortic valve. Int J Mol Med. 33:1219–1226.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kodo K, Nishizawa T, Furutani M, Arai S,
Yamamura E, Joo K, Takahashi T, Matsuoka R and Yamagishi H: GATA6
mutations cause human cardiac outflow tract defects by disrupting
semaphorin-plexin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:13933–13938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zheng GF, Wei D, Zhao H, Zhou N, Yang YQ
and Liu XY: A novel GATA6 mutation associated with congenital
ventricular septal defect. Int J Mol Med. 29:1065–1071.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang J, Luo XJ, Xin YF, Liu Y, Liu ZM,
Wang Q, Li RG, Fang WY, Wang XZ and Yang YQ: Novel GATA6 mutations
associated with congenital ventricular septal defect or tetralogy
of fallot. DNA Cell Biol. 31:1610–1617. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ and Yang YQ:
Somatic mutations in the GATA6 gene underlie sporadic tetralogy of
Fallot. Int J Mol Med. 31:51–58. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yuan F, Zhao L, Wang J, Zhang W, Li X, Qiu
XB, Li RG, Xu YJ, Xu L, Qu XK, Fang WY and Yang YQ: PITX2c
loss-of-function mutations responsible for congenital atrial septal
defects. Int J Med Sci. 10:1422–1429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang J, Xin YF, Xu WJ, Liu ZM, Qiu XB, Qu
XK, Xu L, Li X and Yang YQ: Prevalence and spectrum of PITX2c
mutations associated with congenital heart disease. DNA Cell Biol.
32:708–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wei D, Gong XH, Qiu G, Wang J and Yang YQ:
Novel PITX2c loss-of-function mutations associated with complex
congenital heart disease. Int J Mol Med. 33:1201–1208.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ, Zhou M and Yang
YQ: A novel NKX2.5 loss-of-function mutation responsible for
familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 31:1119–1126.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xie WH, Chang C, Xu YJ, Li RG, Qu XK, Fang
WY, Liu X and Yang YQ: Prevalence and spectrum of Nkx2.5 mutations
associated with idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 68:777–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yu H, Xu JH, Song HM, Zhao L, Xu WJ, Wang
J, Li RG, Xu L, Jiang WF, Qiu XB, Jiang JQ, Qu XK, Liu X, Fang WY,
Jiang JF and Yang YQ: Mutational spectrum of the NKX2-5 gene in
patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Med Sci. 11:554–563.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang J, Sun YM and Yang YQ: Mutation
spectrum of the GATA4 gene in patients with idiopathic atrial
fibrillation. Mol Biol Rep. 39:8127–8135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yang YQ, Wang J, Wang XH, Wang Q, Tan HW,
Zhang M, Shen FF, Jiang JQ, Fang WY and Liu X: Mutational spectrum
of the GATA5 gene associated with familial atrial fibrillation. Int
J Cardiol. 157:305–307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang XH, Huang CX, Wang Q, Li RG, Xu YJ,
Liu X, Fang WY and Yang YQ: A novel GATA5 loss-of-function mutation
underlies lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 31:43–50.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Gu JY, Xu JH, Yu H and Yang YQ: Novel
GATA5 loss-of-function mutations underlie familial atrial
fibrillation. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 67:1393–1399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yang YQ, Wang XH, Tan HW, Jiang WF, Fang
WY and Liu X: Prevalence and spectrum of GATA6 mutations associated
with familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 155:494–496.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yang YQ, Li L, Wang J, Zhang XL, Li RG, Xu
YJ, Tan HW, Wang XH, Jiang JQ, Fang WY and Liu X: GATA6
loss-of-function mutation in atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet.
55:520–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Li J, Liu WD, Yang ZL and Yang YQ: Novel
GATA6 loss-of-function mutation responsible for familial atrial
fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 30:783–790. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Yang YQ, Xu YJ, Li RG, Qu XK, Fang WY and
Liu X: Prevalence and spectrum of PITX2c mutations associated with
familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 168:2873–2876. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhou YM, Zheng PX, Yang YQ, Ge ZM and Kang
WQ: A novel PITX2c loss-of-function mutation underlies lone atrial
fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 32:827–834. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang J, Zhang DF, Sun YM and Yang YQ: A
novel PITX2c loss-of-function mutation associated with familial
atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet. 57:25–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Qiu XB, Xu YJ, Li RG, Xu L, Liu X, Fang
WY, Yang YQ and Qu XK: PITX2C loss-of-function mutations
responsible for idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 69:15–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Biben C, Hatzistavrou T and Harvey RP:
Expression of NK-2 class homeobox gene Nkx2-6 in foregut endoderm
and heart. Mech Dev. 73:125–127. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Tanaka M, Schinke M, Liao HS, Yamasaki N
and Izumo S: Nkx2.5 and Nkx2.6, homologs of Drosophila
tinman, are required for development of the pharynx. Mol Cell Biol.
21:4391–4398. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Heathcote K, Braybrook C, Abushaban L, Guy
M, Khetyar ME, Patton MA, Carter ND, Scambler PJ and Syrris P:
Common arterial trunk associated with a homeodomain mutation of
NKX2.6. Hum Mol Genet. 14:585–593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ta-Shma A, El-lahham N, Edvardson S,
Stepensky P, Nir A, Perles Z, Gavri S, Golender J,
Yaakobi-Simhayoff N, Shaag A, Rein AJ and Elpeleg O: Conotruncal
malformations and absent thymus due to a deleterious NKX2-6
mutation. J Med Genet. 51:268–270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Pradhan L, Genis C, Scone P, Weinberg EO,
Kasahara H and Nam HJ: Crystal structure of the human NKX2.5
homeodomain in complex with DNA target. Biochemistry. 51:6312–6319.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|