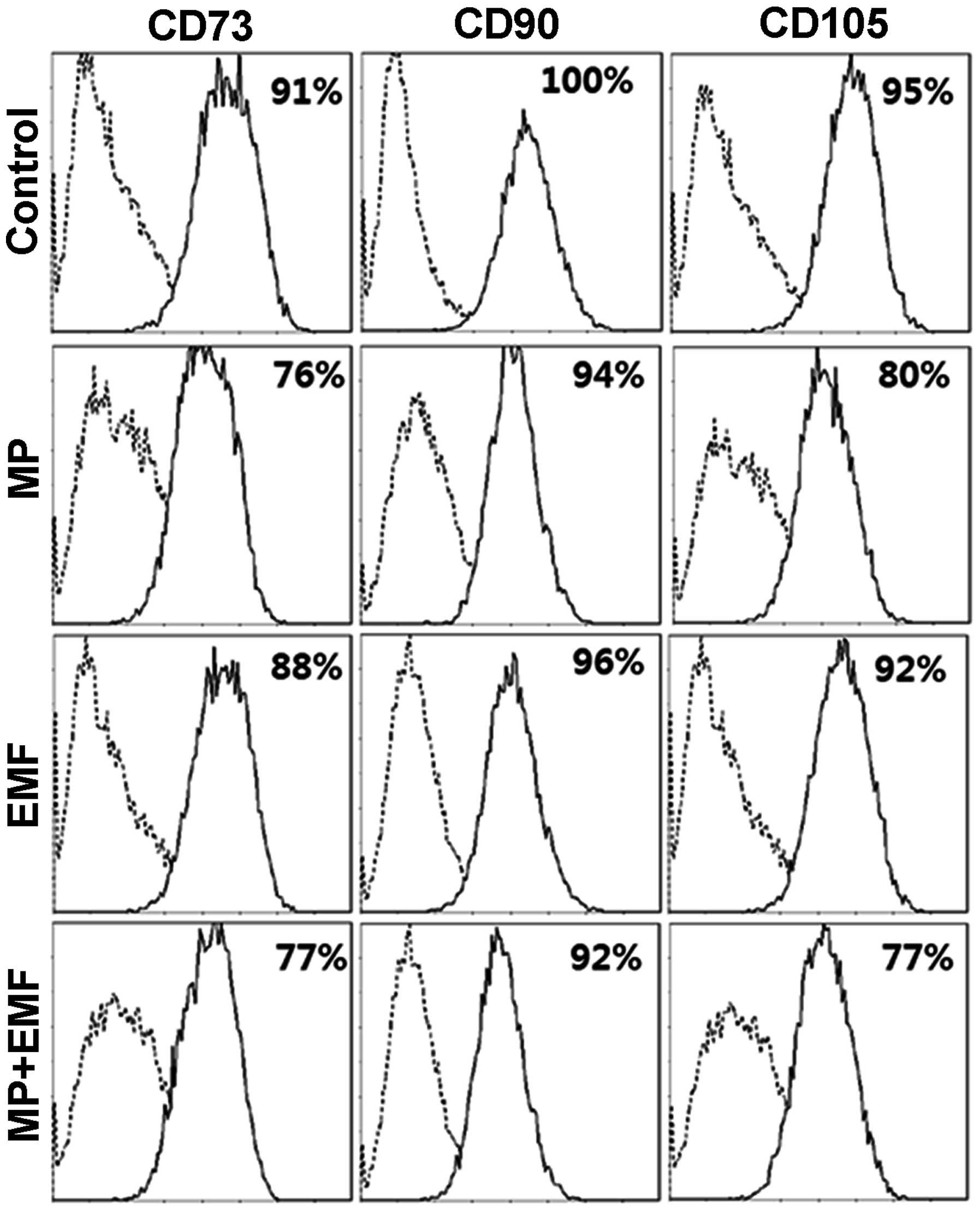
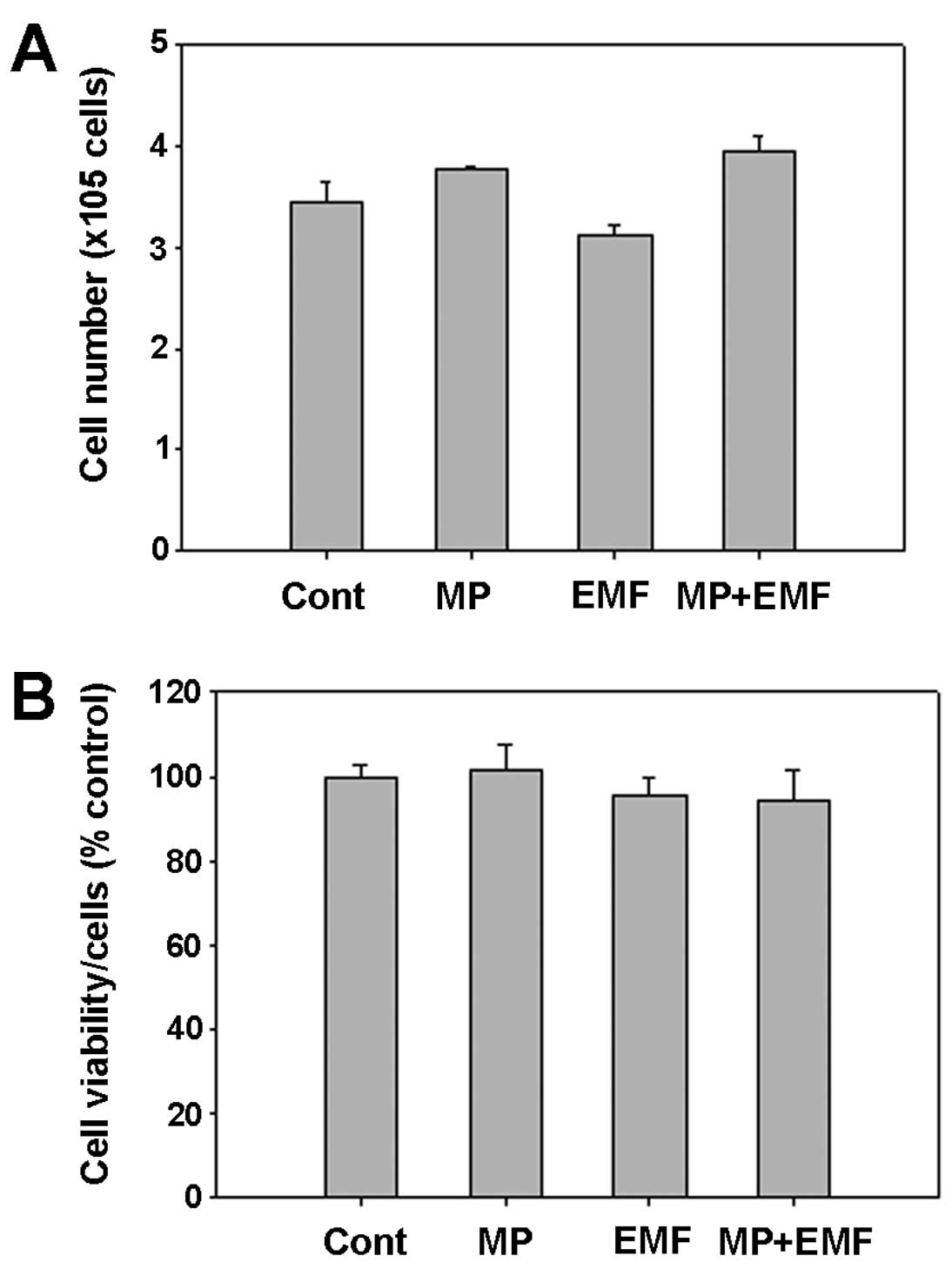
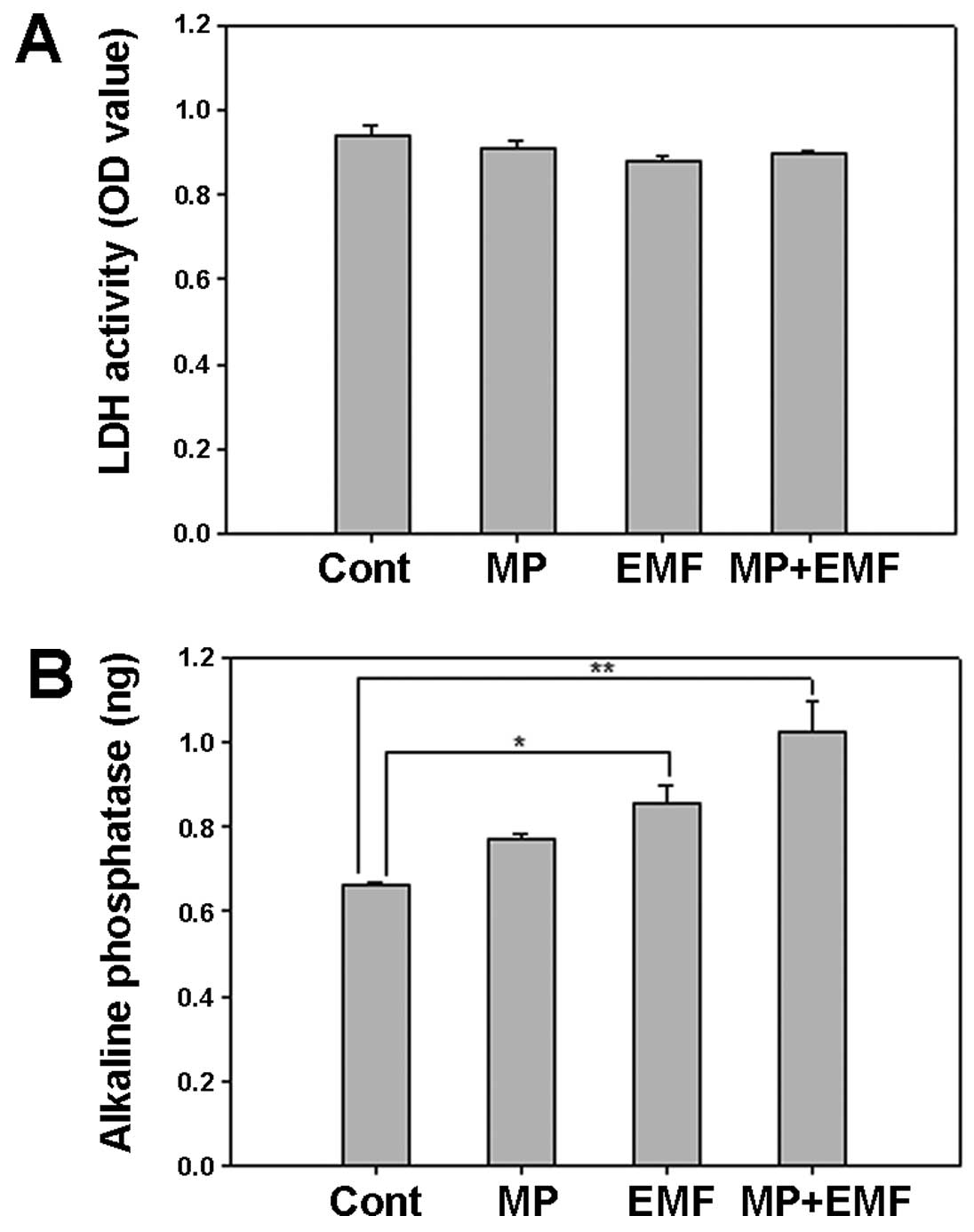
|
1
|
Sadan O, Melamed E and Offen D:
Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy for
neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:1487–1497.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,
Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund
T, Blackstad M, Du J, Aldrich S, Lisberg A, Low WC, Largaespada DA
and Verfaillie C: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived
from adult marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bielby R, Jones E and McGonagle D: The
role of mesenchymal stem cells in maintenance and repair of bone.
Injury. 38(Suppl 1): S26–S32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fukada E and Yasuda I: On the
piezoelectric effect of bone. J Phys Soc Japan. 12:1158–1162. 1957.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bassett CA and Pawluk RJ: Effects of
electric currents on bone in vivo. Nature. 204:652–654. 1964.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsai MT, Li WJ, Tuan RS and Chang WH:
Modulation of osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells by
specific pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation. J Orthop Res.
27:1169–1174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun LY, Hsieh DK, Lin PC, Chiu HT and
Chiou TW: Pulsed electromagnetic fields accelerate proliferation
and osteogenic gene expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells during osteogenic differentiation. Bioelectromagnetics.
31:209–219. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones S and
Dobson J: Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J
Phys D Appl Phys. 36:R167–R181. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cartmell SH, Dobson J, Verschueren SB and
El Haj AJ: Development of magnetic particle techniques for
long-term culture of bone cells with intermittent mechanical
activation. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 1:92–97. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cho H, Choi YK, Lee DH, Park HJ, Seo YK,
Jung H, Kim SC, Kim SM and Park JK: Effects of magnetic
nanoparticle-incorporated human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells exposed to pulsed electromagnetic fields on injured rat
spinal cord. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 60:596–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ducy P, Desbois C, Boyce B, Pinero G,
Story B, Dunstan C, Smith E, Bonadio J, Goldstein S, Gundberg C,
Bradley A and Karsenty G: Increased bone formation in
osteocalcin-deficient mice. Nature. 382:448–452. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kelm RJ Jr, Hair GA, Mann KG and Grant BW:
Characterization of human osteoblast and megakaryocyte-derived
osteonectin (SPARC). Blood. 80:3112–3119. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sodek J, Ganss B and McKee M: Osteopontin.
Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 11:279–303. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
von Kossa J: Über die im Organismus
künstlich erzeugbaren Verkalkungen. Beit Path Anat. 29:163–202.
1901.(In German).
|
|
15
|
Bills C, Eisenberg H and Pallante SL:
Complexes of organic acids with calcium phosphate: the von Kossa
stain as a clue to the composition of bone mineral. Johns Hopkins
Med J. 128:194–207. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Puchtler H and Meloan S: On the chemistry
of formaldehyde fixation and its effects on immunohistochemical
reactions. Histochemistry. 82:201–204. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meloan SN and Puchtler H: Chemical
mechanisms of staining methods: von Kossa’s technique: what von
Kossa really wrote and a modified reaction for selective
demonstration of inorganic phosphates. J Histotechnol. 8:11–13.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schwartz Z, Simon B, Duran M, Barabino G,
Chaudhri R and Boyan B: Pulsed electromagnetic fields enhance BMP-2
dependent osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells. J Orthop Res. 26:1250–1255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schwartz Z, Lohmann C, Oefinger J,
Bonewald L, Dean D and Boyan B: Implant surface characteristics
modulate differentiation behavior of cells in the osteoblastic
lineage. Adv Dent Res. 13:38–48. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ogawa E, Inuzuka M, Maruyama M, Satake M,
Naito-Fujimoto M, Ito Y and Shigesada K: Molecular cloning and
characterization of PEBP2β, the heterodimeric partner of a novel
Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2α. Virology.
194:314–331. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyoshi H, Shimizu K, Kozu T, Maseki N,
Kaneko Y and Ohki M: t (8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute
myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single
gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:10431–10434. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A,
Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson R, Gao YH, Inada M, Sato M,
Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S and Kishimoto T: Targeted
disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation
owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 89:755–764.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL and
Karsenty G: Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast
differentiation. Cell. 89:747–754. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A,
Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen
BR, Selby PB and Owen MJ: Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial
dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and
bone development. Cell. 89:765–771. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Komori T: Regulation of bone development
and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. Cell Tissue Res.
339:189–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Klar RM, Duarte R, Dix-Peek T, Dickens C,
Ferretti C and Ripamonti U: Calcium ions and osteoclastogenesis
initiate the induction of bone formation by coral-derived
macroporous constructs. J Cell Mol Med. 17:1444–1457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wen L, Wang Y, Wang H, Kong L, Zhang L,
Chen X and Ding Y: L-type calcium channels play a crucial role in
the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:439–445.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lai CF, Chaudhary L, Fausto A, Halstead
LR, Ory DS, Avioli LV and Cheng SL: Erk is essential for growth,
differentiation, integrin expression, and cell function in human
osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 276:14443–14450. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Azuma N, Duzgun SA, Ikeda M, Kito H,
Akasaka N, Sasajima T and Sumpio BE: Endothelial cell response to
different mechanical forces. J Vasc Surg. 32:789–794. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oldenhof AD, Shynlova OP, Liu M, Langille
BL and Lye SJ: Mitogen-activated protein kinases mediate
stretch-induced c-fos mRNA expression in myometrial smooth muscle
cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 283:C1530–C1539. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferraro JT, Daneshmand M, Bizios R and
Rizzo V: Depletion of plasma membrane cholesterol dampens
hydrostatic pressure and shear stress-induced mechanotransduction
pathways in osteoblast cultures. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
286:C831–C839. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kapur S, Baylink DJ and Lau KH: Fluid flow
shear stress stimulates human osteoblast proliferation and
differentiation through multiple interacting and competing signal
transduction pathways. Bone. 32:241–251. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schieker M, Pautke C, Haasters F, Schieker
J, Docheva D, Böcker W, Guelkan H, Neth P, Jochum M and Mutschler
W: Human mesenchymal stem cells at the single-cell level:
simultaneous seven-colour immunofluorescence. J Anat. 210:592–599.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Barry FP and Murphy JM: Mesenchymal stem
cells: clinical applications and biological characterization. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 36:568–584. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bobis S, Jarocha D and Majka M:
Mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics and clinical applications.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 44:215–214. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mitchell DB, Santone KS and Acosta D:
Evaluation of cytotoxicity in cultured cells by enzyme leakage. J
Tissue Cult Methods. 6:113–116. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gundberg C, Looker A, Nieman S and Calvo
M: Patterns of osteocalcin and bone specific alkaline phosphatase
by age, gender, and race or ethnicity. Bone. 31:703–708. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|