|
1
|
Sung YH, Shin MS, Ko IG, et al:
Ulinastatin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced prostaglandin E-2
synthesis and nitric oxide production through the downregulation of
nuclear factor-κB in BV2 mouse microglial cells. Int J Mol Med.
31:1030–1036. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Navascues J, Perez-Rontome C, Gay M, et
al: Leghemoglobin green derivatives with nitrated hemes evidence
production of highly reactive nitrogen species during aging of
legume nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2660–2665. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsui-Hirai H, Hayashi T, Yamamoto S, et
al: Dose-dependent modulatory effects of insulin on glucose-induced
endothelial senescence in vitro and in vivo: a relationship between
telomeres and nitric oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 337:591–599.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ransohoff JD and Wu JC: Imaging stem cell
therapy for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 10:361–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu J, Qian J, Xie X, et al: High density
lipoprotein cholesterol promotes the proliferation of bone-derived
mesenchymal stem cells via binding scavenger receptor-B type I and
activation of PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways. Mol Cell Biochem.
371:55–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou M, Liu J, Liu F, Liu K and Yu B: C1q
tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem
cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med.
33:97–104. 2014.
|
|
7
|
Severino V, Alessio N, Farina A, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 4 and 7 released by
senescent cells promote premature senescence in mesenchymal stem
cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e9112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Li Z, Liu T, et al: Impaired
cardioprotective function of transplantation of mesenchymal stem
cells from patients with diabetes mellitus to rats with
experimentally induced myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lauer T, Heiss C, Balzer J, et al:
Age-dependent endothelial dysfunction is associated with failure to
increase plasma nitrite in response to exercise. Basic Res Cardiol.
103:291–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ward MR, Connelly KA, Vijayaraghavan R, et
al: eNOS overexpressing bone marrow cells are safe and effective in
a porcine model of myocardial regeneration following acute
myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Ther. 31:e72–e78. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang MY, Lin PM, Liu YC, et al: Induction
of cellular senescence by doxorubicin is associated with
upregulated miR-375 and induction of autophagy in K562 cells. PLoS
One. 7:e372052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bonet C, Giuliano S, Ohanna M, et al:
Aurora B is regulated by the mitogen-activated protein
kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) signaling
pathway and is a valuable potential target in melanoma cells. J
Biol Chem. 287:29887–29898. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qu K, Xu X, Liu C, et al: Negative
regulation of transcription factor FoxM1 by p53 enhances
oxaliplatin-induced senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 331:105–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Kang MJ and
Gorospe M: Regulation of senescence by microRNA biogenesis factors.
Ageing Res Rev. 11:491–500. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu J, Qian J, Xie X, et al: High density
lipoprotein protects mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and
suppression of reactive oxygen species. Int J Mol Sci.
13:17104–17120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, et al: FoxM1
is a novel target of a natural agent in pancreatic cancer. Pharm
Res. 27:1159–1168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Popovic R, Riesbeck LE, Velu CS, et al:
Regulation of mir-196b by MLL and its overexpression by MLL fusions
contributes to immortalization. Blood. 113:3314–3322. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhong W, Zou G, Gu J and Zhang J:
L-arginine attenuates high glucose-accelerated senescence in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
89:38–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Z, Liu Y, Takahashi M, et al: N
terminus of ASPP2 binds to Ras and enhances Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK
activation to promote oncogene-induced senescence. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:312–317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Yokoi T, Fukuo K, Yasuda O, et al:
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 mediates cellular senescence
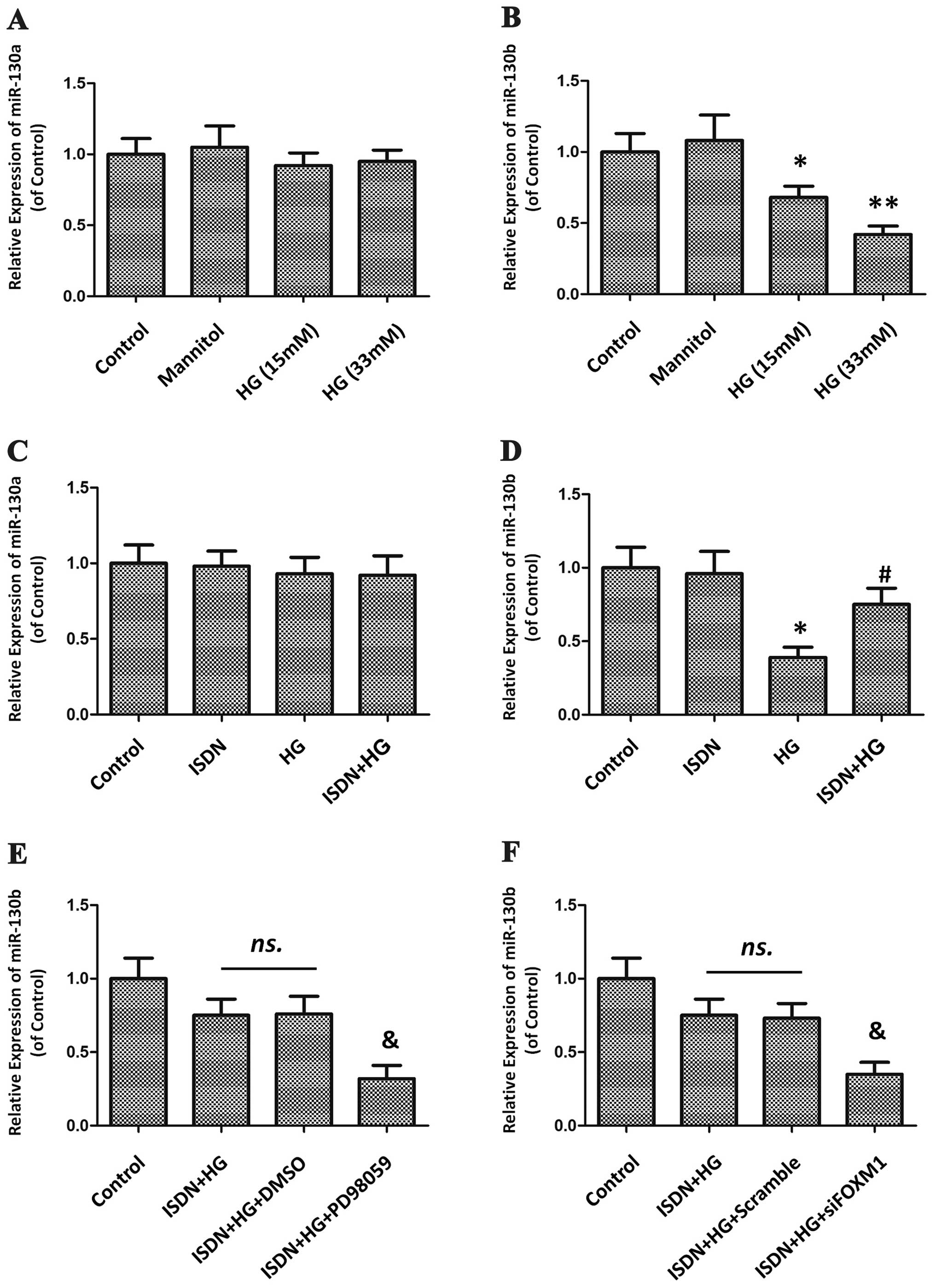
induced by high glucose in endothelial cells. Diabetes.
55:1660–1665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Munzel T: Recent studies on nitrates:
their action, bioactivation and development of tolerance. Dtsch Med
Wochenschr. 133:2277–2282. 2008.(In German).
|
|
22
|
Wang ZQ, Xu JF, Wang JP, Zhao WJ and Zeng
M: Involvement of guanylate cyclase and K+ channels in
relaxation evoked by ferulate nitrate in rat aorta artery. J
Pharmacol Sci. 118:521–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Thum T, Wiebking V, Ertl G and Bauersachs
J: Organic nitrates differentially modulate circulating endothelial
progenitor cells and endothelial function in patients with
symptomatic coronary artery disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:925–931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gori T and Daiber A: Non-hemodynamic
effects of organic nitrates and the distinctive characteristics of
pentaerithrityl tetranitrate. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 9:7–15. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Johnston PV, Sasano T, Mills K, et al:
Engraftment, differentiation, and functional benefits of autologous
cardiosphere-derived cells in porcine ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Circulation. 120:1075–1083. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Williams AR and Hare JM: Mesenchymal stem
cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and
therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res.
109:923–940. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Oelze M, Schuhmacher S and Daiber A:
Organic nitrates and nitrate resistance in diabetes: the role of
vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress with emphasis on
antioxidant properties of pentaerithrityl tetranitrate. Exp
Diabetes Res. 2010:2131762010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ling Q, Meng C, Chen Q and Xing D:
Activated ERK/FOXM1 pathway by low-power laser irradiation inhibits
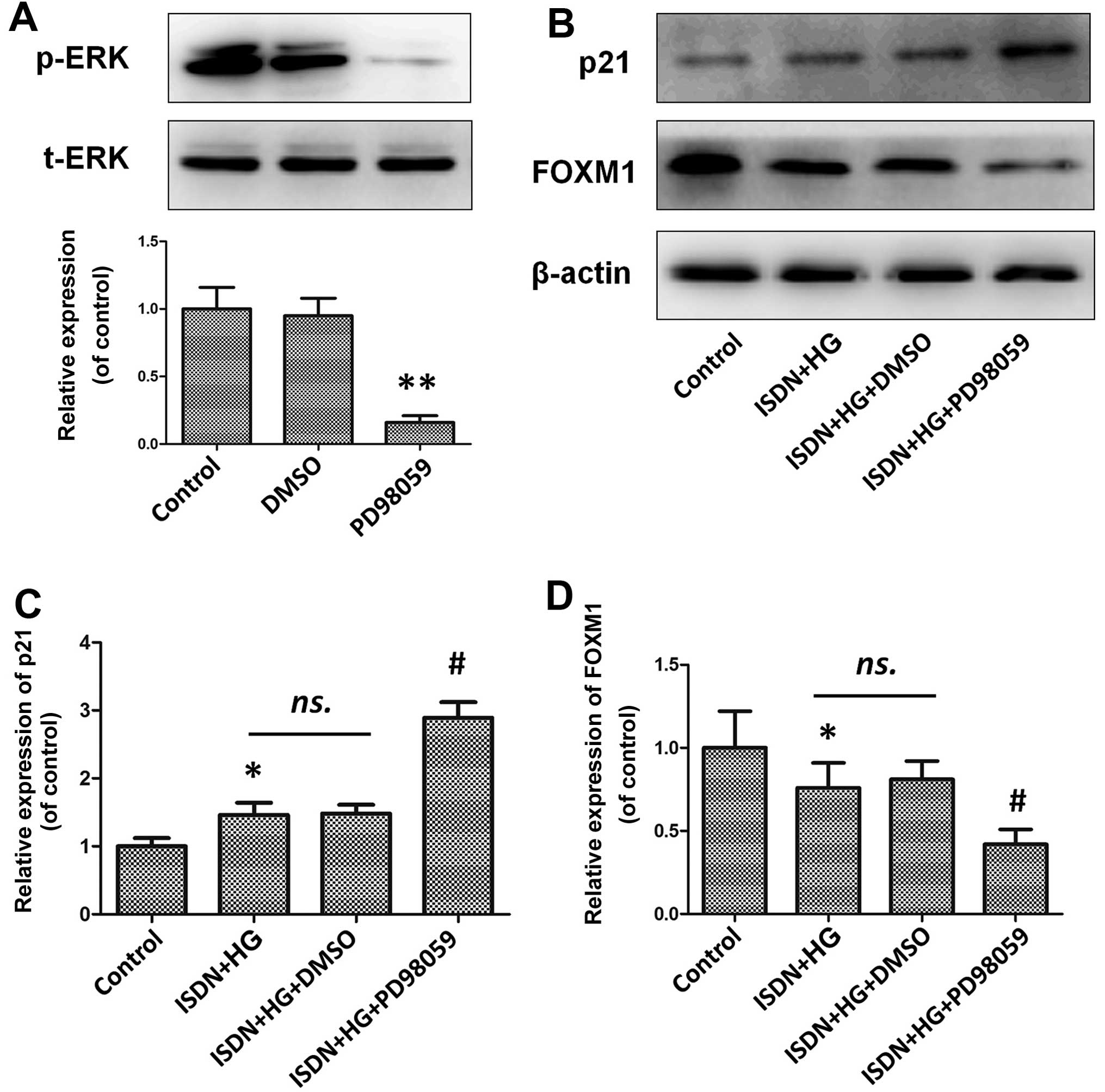
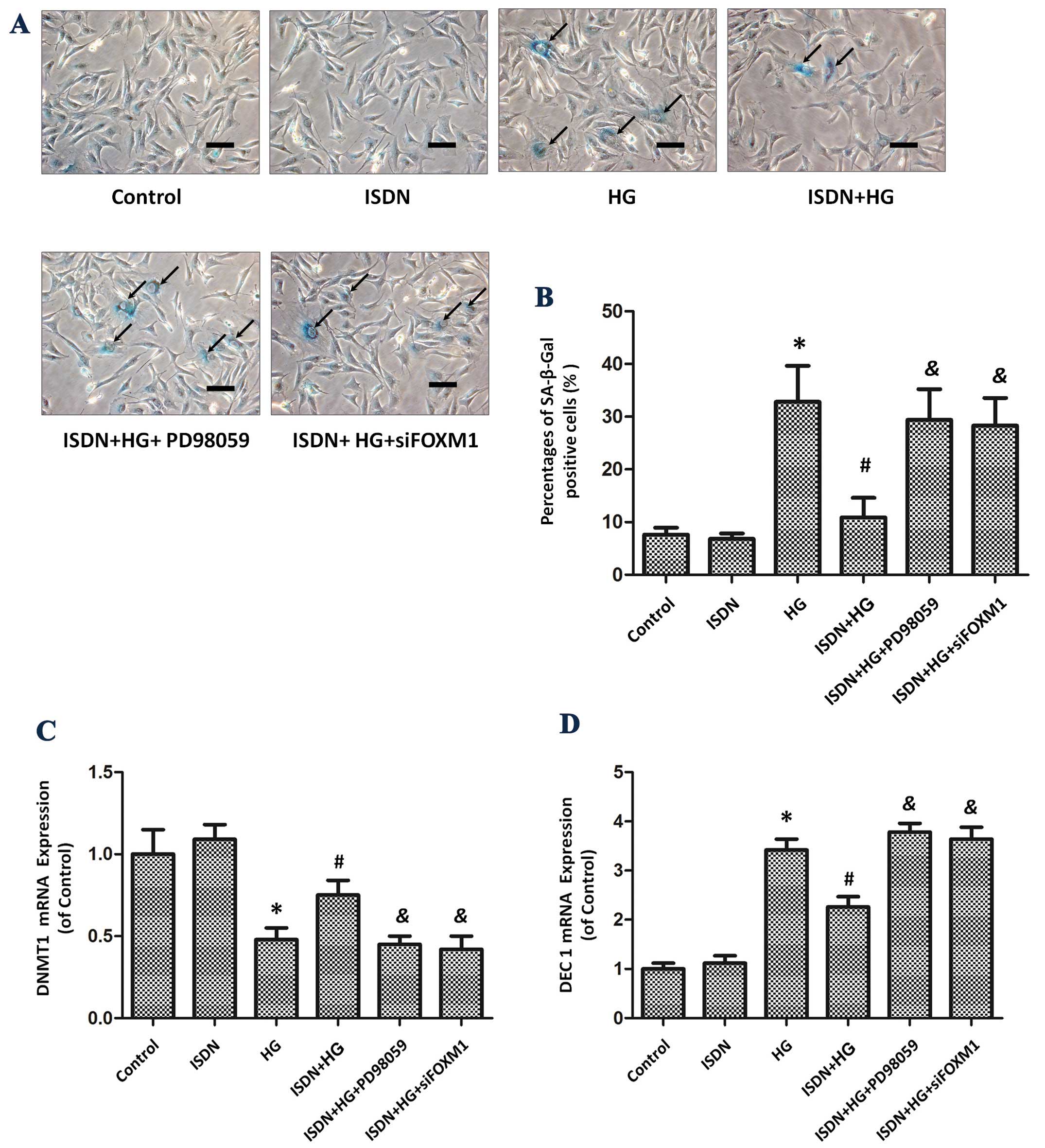
UVB-induced senescence through down-regulating p21 expression. J
Cell Physiol. 229:108–116. 2014.
|
|
29
|
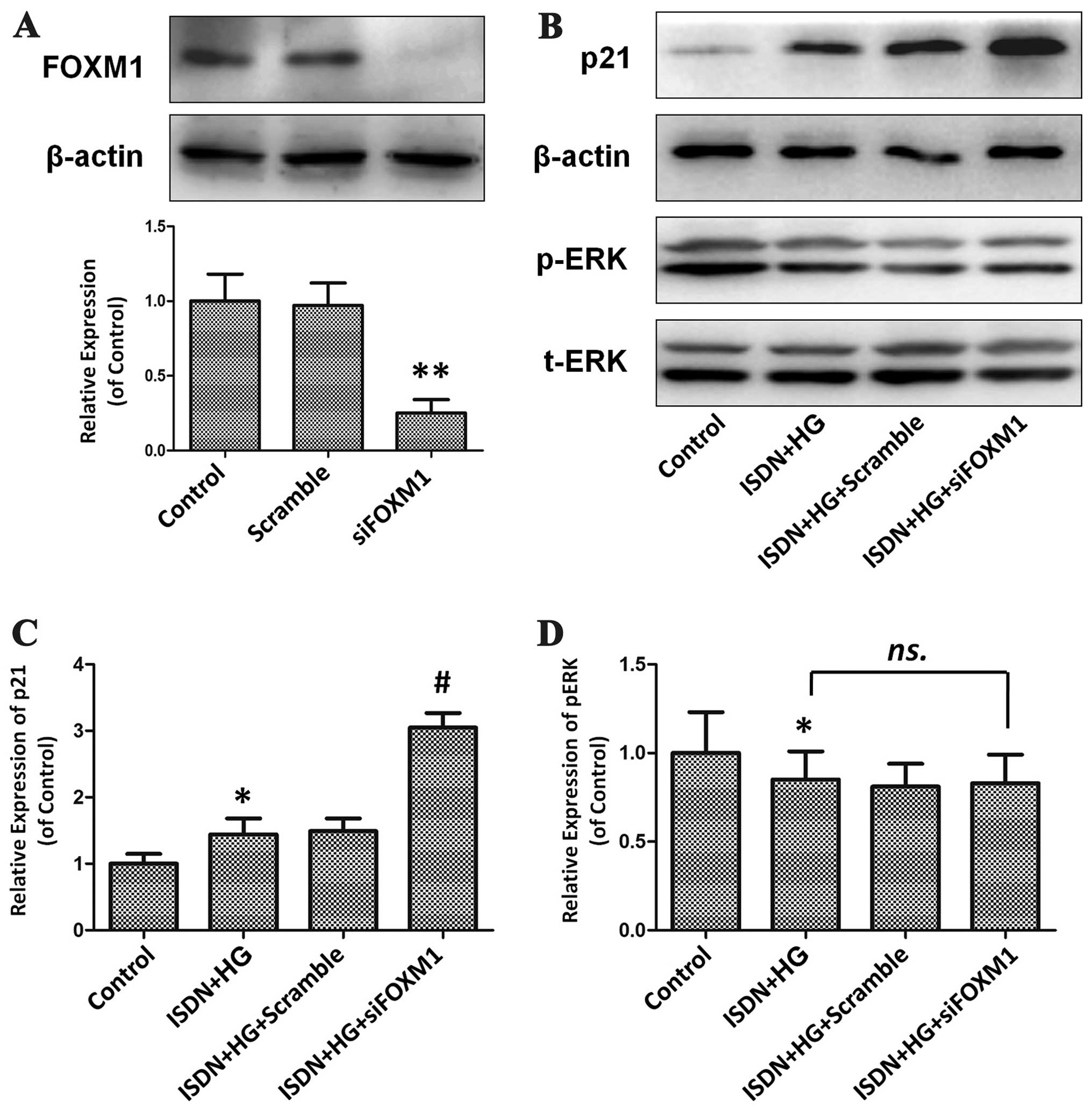
Zeng J, Wang L, Li Q, et al: FoxM1 is
up-regulated in gastric cancer and its inhibition leads to cellular
senescence, partially dependent on p27 kip1. J Pathol. 218:419–427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gorospe M and Abdelmohsen K:
MicroRegulators come of age in senescence. Trends Genet.
27:233–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Su X, Chakravarti D, Cho MS, et al: TAp63
suppresses metastasis through coordinate regulation of Dicer and
miRNAs. Nature. 467:986–990. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Borgdorff V, Lleonart ME, Bishop CL, et
al: Multiple microRNAs rescue from Ras-induced senescence by
inhibiting p21(Waf1/Cip1). Oncogene. 29:2262–2271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang L, Qiu N, Zhang C, et al:
Nitroglycerin enhances proliferation and osteoblastic
differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells via nitric oxide
pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:580–586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guiboileau A, Yoshimoto K, Soulay F,
Bataille MP, Avice JC and Masclaux-Daubresse C: Autophagy machinery
controls nitrogen remobilization at the whole-plant level under
both limiting and ample nitrate conditions in Arabidopsis. New
Phytol. 194:732–740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Desclos M, Etienne P, Coquet L, et al: A
combined N15 tracing/proteomics study in Brassica napus reveals the
chronology of proteomics events associated with N remobilisation
during leaf senescence induced by nitrate limitation or starvation.
Proteomics. 9:3580–3608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sykorova B, Kuresova G, Daskalova S, et
al: Senescence-induced ectopic expression of the A. tumefaciens ipt
gene in wheat delays leaf senescence, increases cytokinin content,
nitrate influx, and nitrate reductase activity, but does not affect
grain yield. J Exp Bot. 59:377–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Boe AE, Eren M, Murphy SB, et al:
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antagonist TM5441 attenuates
Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension and vascular
senescence. Circulation. 128:2318–2324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu DH, Chen YM, Liu Y, et al: Ginsenoside
Rb1 reverses H2O2-induced senescence in human
umbilical endothelial cells: involvement of eNOS pathway. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 59:222–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li N, Lu X, Zhao X, et al: Endothelial
nitric oxide synthase promotes bone marrow stromal cell migration
to the ischemic myocardium via upregulation of stromal cell-derived
factor-1alpha. Stem Cells. 27:961–970. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|