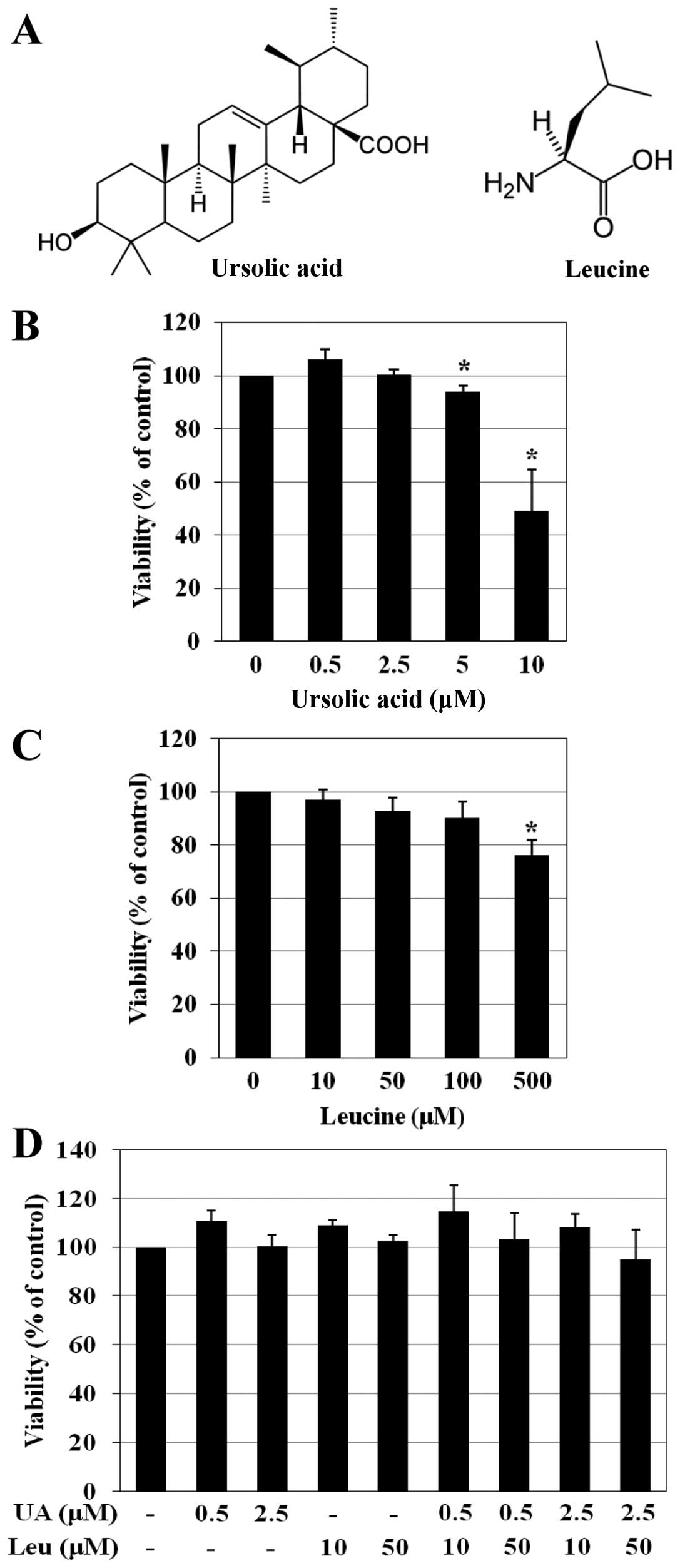
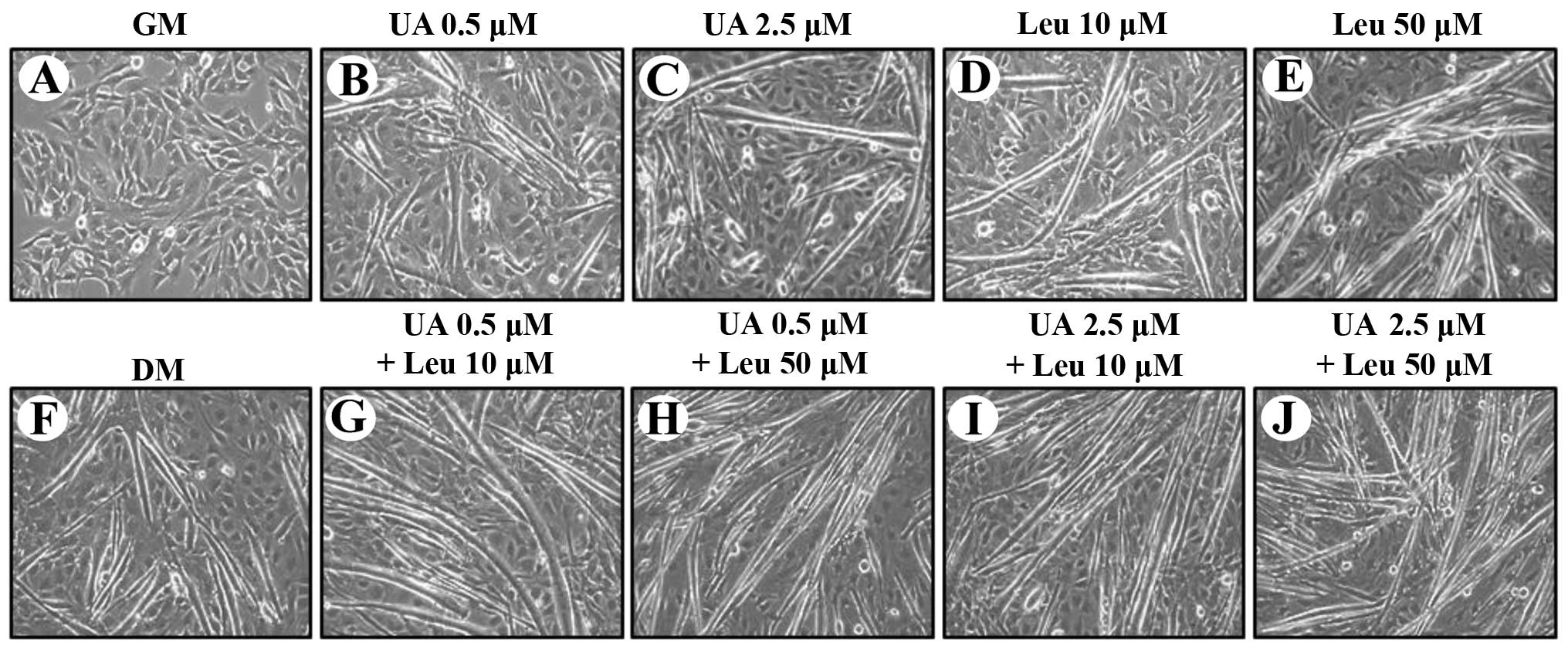
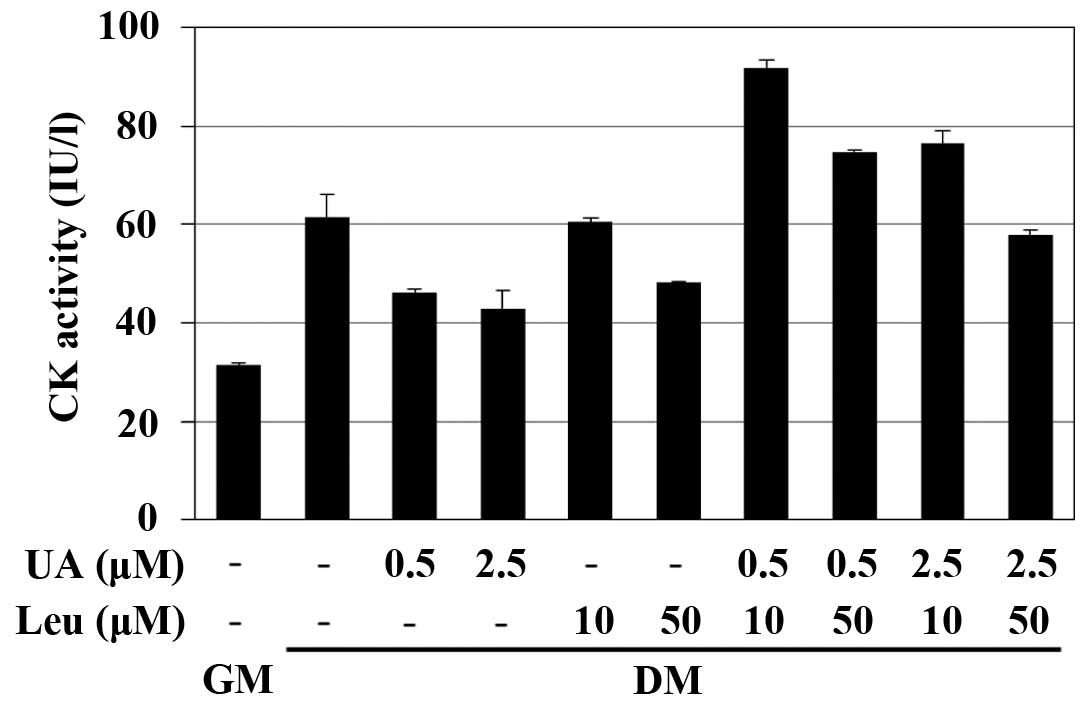
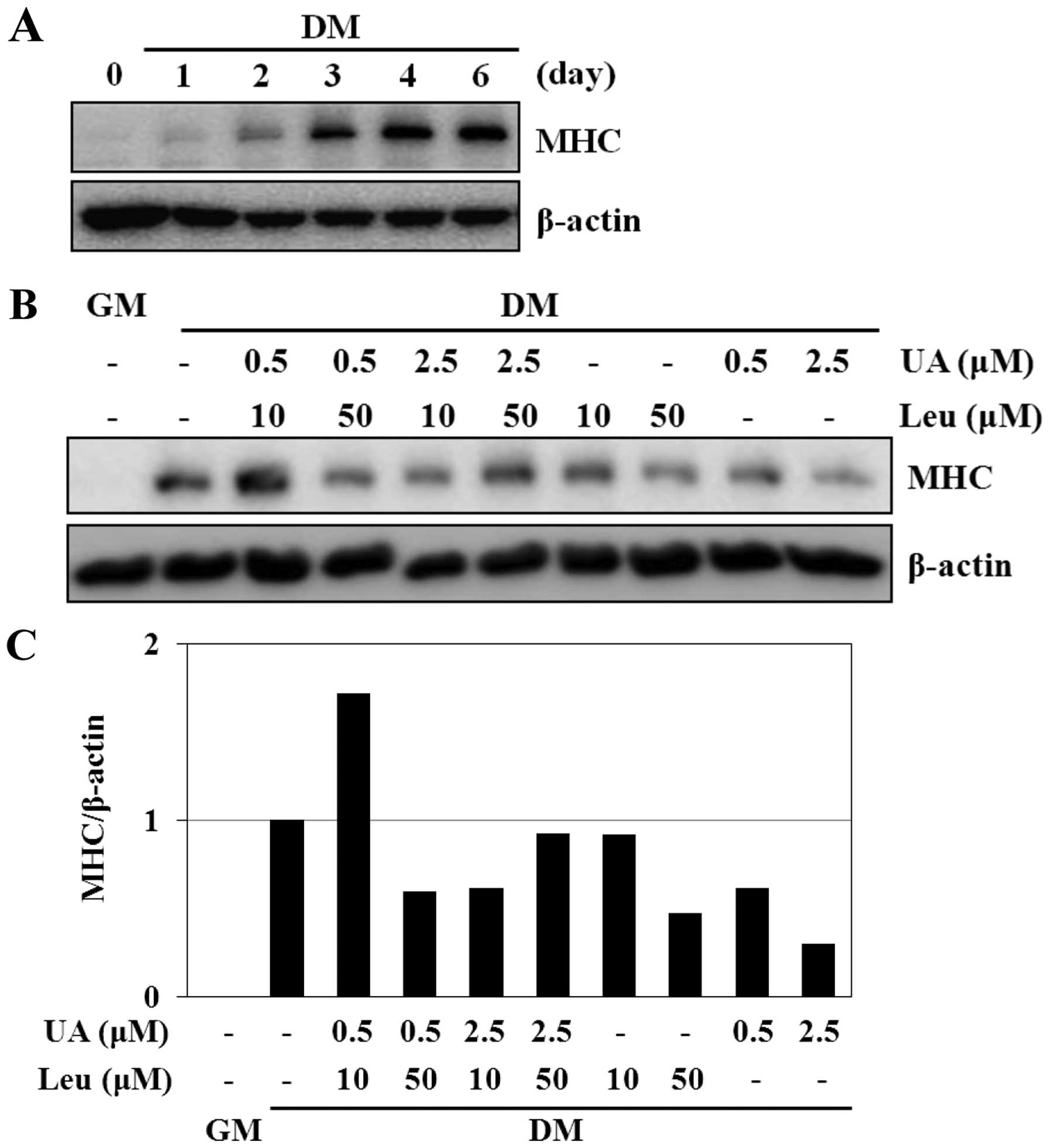
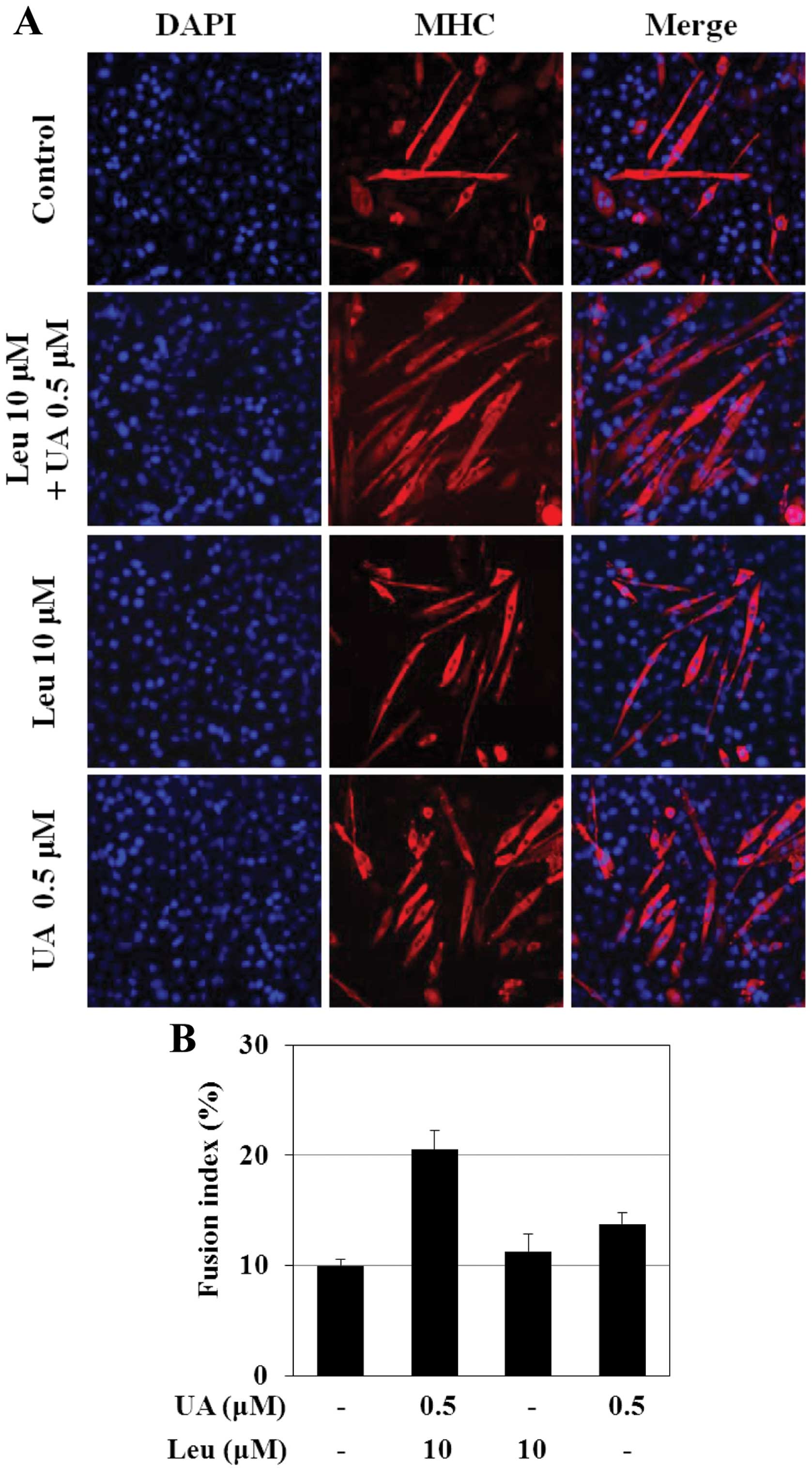
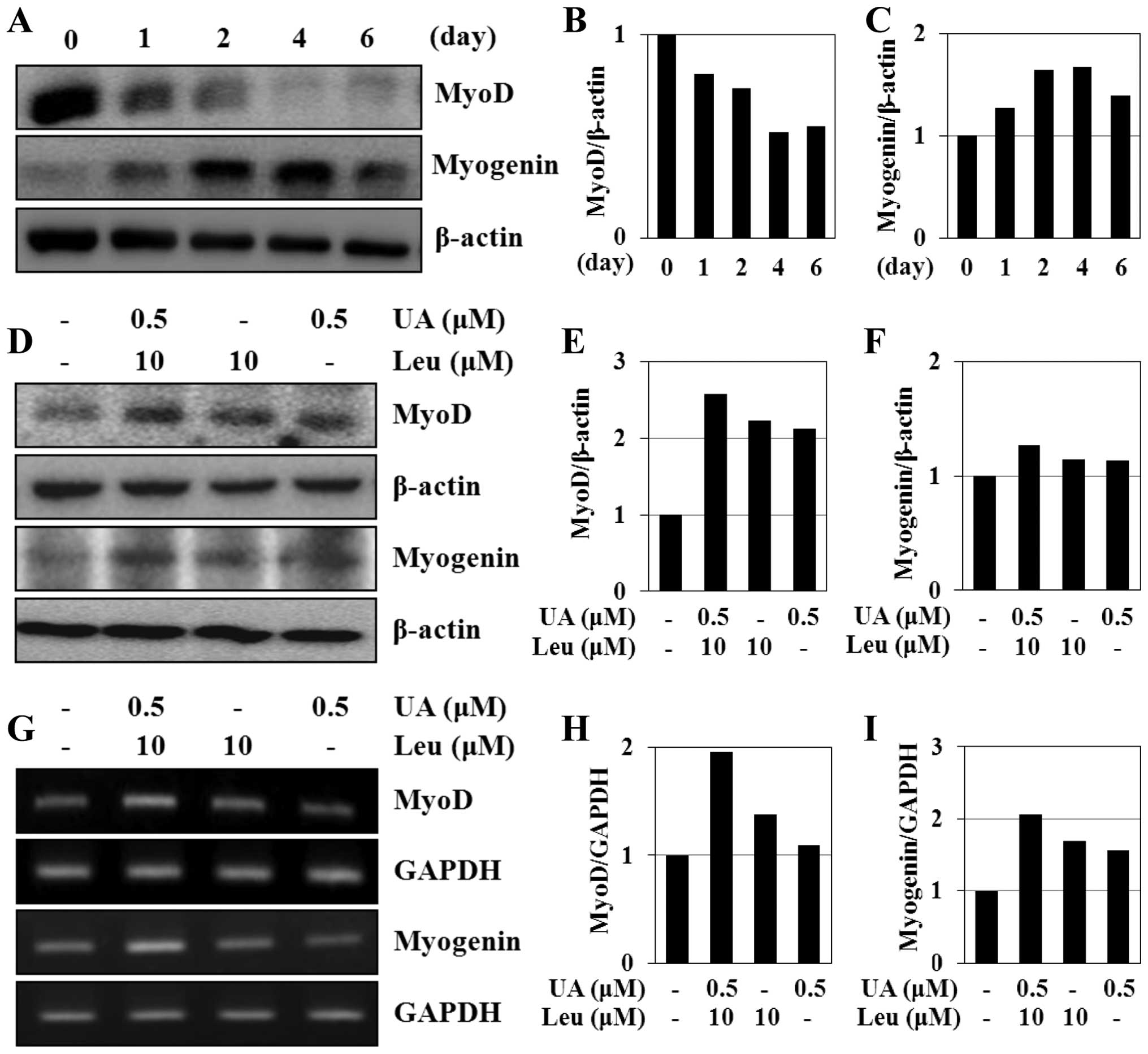
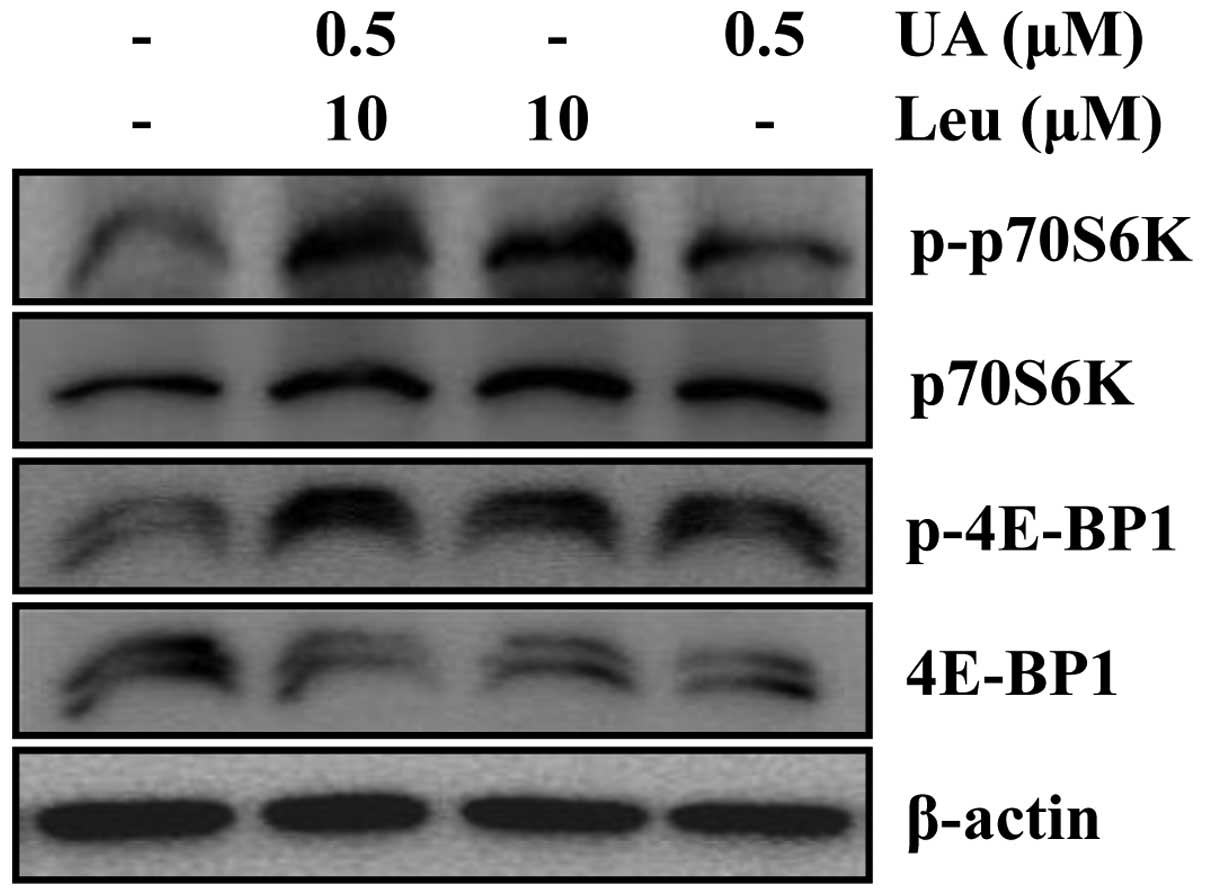
|
1
|
Dedieu S, Mazeres G, Cottin P and Brustis
JJ: Involvement of myogenic regulator factors during fusion in the
cell line C2C12. Int J Dev Biol. 46:235–241. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doherty JT, Lenhart KC, Cameron MV, Mack
CP, Conlon FL and Taylor JM: Skeletal muscle differentiation and
fusion are regulated by the BAR-containing Rho-GTPase-activating
protein (Rho-GAP), GRAF1. J Biol Chem. 286:25903–25921. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rudnicki MA, Schnegelsberg PN, Stead RH,
Braun T, Arnold HH and Jaenisch R: MyoD or Myf-5 is required for
the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 75:1351–1359. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kablar B, Krastel K, Ying C, Asakura A,
Tapscott SJ and Rudnicki MA: MyoD and Myf-5 differentially regulate
the development of limb versus trunk skeletal muscle. Development.
124:4729–4738. 1997.
|
|
5
|
Ishibashi J, Perry RL, Asakura A and
Rudnicki MA: MyoD induces myogenic differentiation through
cooperation of its NH2-and COOH-terminal regions. J Cell Biol.
171:471–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Naidu PS, Ludolph DC, To RQ, Hinterberger
TJ and Konieczny SF: Myogenin and MEF2 function synergistically to
activate the MRF4 promoter during myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol.
15:2707–2718. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J: Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and
ursolic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 49:57–68. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jager S, Trojan H, Kopp T, Laszczyk MN and
Scheffler A: Pentacyclic triterpene distribution in various plants
- rich sources for a new group of multi-potent plant extracts.
Molecules. 14:2016–2031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leng S, Hao Y, Du D, et al: Ursolic acid
promotes cancer cell death by inducing Atg5-dependent autophagy.
Int J Cancer. 133:2781–2790. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang W, Hong D, Zhou Y, et al: Ursolic
acid and its derivative inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B,
enhancing insulin receptor phosphorylation and stimulating glucose
uptake. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1760:1505–1512. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilkinson K, Boyd JD, Glicksman M, Moore
KJ and El Khoury J: A high content drug screen identifies ursolic
acid as an inhibitor of amyloid beta protein interactions with its
receptor CD36. J Biol Chem. 286:34914–34922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He Y, Li Y, Zhao T, Wang Y and Sun C:
Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through
LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e701352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung SH, Ha YJ, Shim EK, et al:
Insulin-mimetic and insulin-sensitizing activities of a pentacyclic
triterpenoid insulin receptor activator. Biochem J. 403:243–250.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kunkel SD, Suneja M, Ebert SM, et al: mRNA
expression signatures of human skeletal muscle atrophy identify a
natural compound that increases muscle mass. Cell Metab.
13:627–638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kunkel SD, Elmore CJ, Bongers KS, et al:
Ursolic acid increases skeletal muscle and brown fat and decreases
diet-induced obesity, glucose intolerance and fatty liver disease.
PLoS One. 7:e393322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
She P, Olson KC, Kadota Y, et al: Leucine
and protein metabolism in obese Zucker rats. PLoS One.
8:e594432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haegens A, Schols AM, van Essen AL, van
Loon LJ and Langen RC: Leucine induces myofibrillar protein
accretion in cultured skeletal muscle through mTOR dependent and
-independent control of myosin heavy chain mRNA levels. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 56:741–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fitschen PJ, Wilson GJ, Wilson JM and
Wilund KR: Efficacy of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate
supplementation in elderly and clinical populations. Nutrition.
29:29–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nissen S, Sharp RL, Panton L, Vukovich M,
Trappe S and Fuller JC Jr: beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB)
supplementation in humans is safe and may decrease cardiovascular
risk factors. J Nutr. 130:1937–1945. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Salles J, Chanet A, Giraudet C, et al:
1,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 enhances the stimulating effect of
leucine and insulin on protein synthesis rate through Akt/PKB and
mTOR mediated pathways in murine C2C12 skeletal myotubes. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 57:2137–2146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alway SE, Pereira SL, Edens NK, Hao Y and
Bennett BT: beta-Hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) enhances the
proliferation of satellite cells in fast muscles of aged rats
during recovery from disuse atrophy. Exp Gerontol. 48:973–984.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pereira MG, Baptista IL, Carlassara EO,
Moriscot AS, Aoki MS and Miyabara EH: Leucine supplementation
improves skeletal muscle regeneration after cryolesion in rats.
PLoS One. 9:e852832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou H and Huang S: The complexes of
mammalian target of rapamycin. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 11:409–424.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Teleman AA, Chen YW and Cohen SM: 4E-BP
functions as a metabolic brake used under stress conditions but not
during normal growth. Genes Dev. 19:1844–1848. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miron M, Verdú J, Lachance PE, Birnbaum
MJ, Lasko PF and Sonenberg N: The translational inhibitor 4E-BP is
an effector of PI(3)K/Akt signalling and cell growth in Drosophila.
Nat Cell Biol. 3:596–601. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding M, Xie Y, Wagner RJ, et al:
Adiponectin induces vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation via
repression of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 and FoxO4.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1403–1410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hara K, Yonezawa K, Weng QP, Kozlowski MT,
Belham C and Avruch J: Amino acid sufficiency and mTOR regulate p70
S6 kinase and eIF-4E BP1 through a common effector mechanism. J
Biol Chem. 273:14484–14494. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Proud CG: mTOR-mediated regulation of
translation factors by amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:429–436. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lian J, Yan XH, Peng J and Jiang SW: The
mammalian target of rapamycin pathway and its role in molecular
nutrition regulation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:393–399. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH
and Sabatini DM: RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational
regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:1432–1437. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vinciguerra M, Musaro A and Rosenthal N:
Regulation of muscle atrophy in aging and disease. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 694:211–233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Averous J, Gabillard JC, Seiliez I and
Dardevet D: Leucine limitation regulates myf5 and myoD expression
and inhibits myoblast differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 318:217–227.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ogasawara R, Sato K, Higashida K, Nakazato
K and Fujita S: Ursolic acid stimulates mTORC1 signaling after
resistance exercise in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 305:E760–E765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kablar B, Krastel K, Tajbakhsh S and
Rudnicki MA: Myf5 and MyoD activation define independent myogenic
compartments during embryonic development. Dev Biol. 258:307–318.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Myer A, Olson EN and Klein WH: MyoD cannot
compensate for the absence of myogenin during skeletal muscle
differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells. Dev Biol.
229:340–350. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meadows E, Cho JH, Flynn JM and Klein WH:
Myogenin regulates a distinct genetic program in adult muscle stem
cells. Dev Biol. 322:406–414. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Breitschopf K, Bengal E, Ziv T, Admon A
and Ciechanover A: A novel site for ubiquitination: the N-terminal
residue, and not internal lysines of MyoD, is essential for
conjugation and degradation of the protein. EMBO J. 17:5964–5973.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sartorelli V, Puri PL, Hamamori Y, et al:
Acetylation of MyoD directed by PCAF is necessary for the execution
of the muscle program. Mol Cell. 4:725–734. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jo C, Cho SJ and Jo SA: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) stabilizes MyoD through direct
phosphorylation at tyrosine 156 during myogenic differentiation. J
Biol Chem. 286:18903–18913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ling BM, Bharathy N, Chung TK, et al:
Lysine methyltransferase G9a methylates the transcription factor
MyoD and regulates skeletal muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:841–846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu W, Schneider JW, Condorelli G, Kaushal
S, Mahdavi V and Nadal-Ginard B: Interaction of myogenic factors
and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and
differentiation. Cell. 72:309–324. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang JM, Wei Q, Zhao X and Paterson BM:
Coupling of the cell cycle and myogenesis through the cyclin
D1-dependent interaction of MyoD with cdk4. EMBO J. 18:926–933.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang H, Li F, Kong X, et al: Chemerin
regulates proliferation and differentiation of myoblast cells via
ERK1/2 and mTOR signaling pathways. Cytokine. 60:646–652. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|