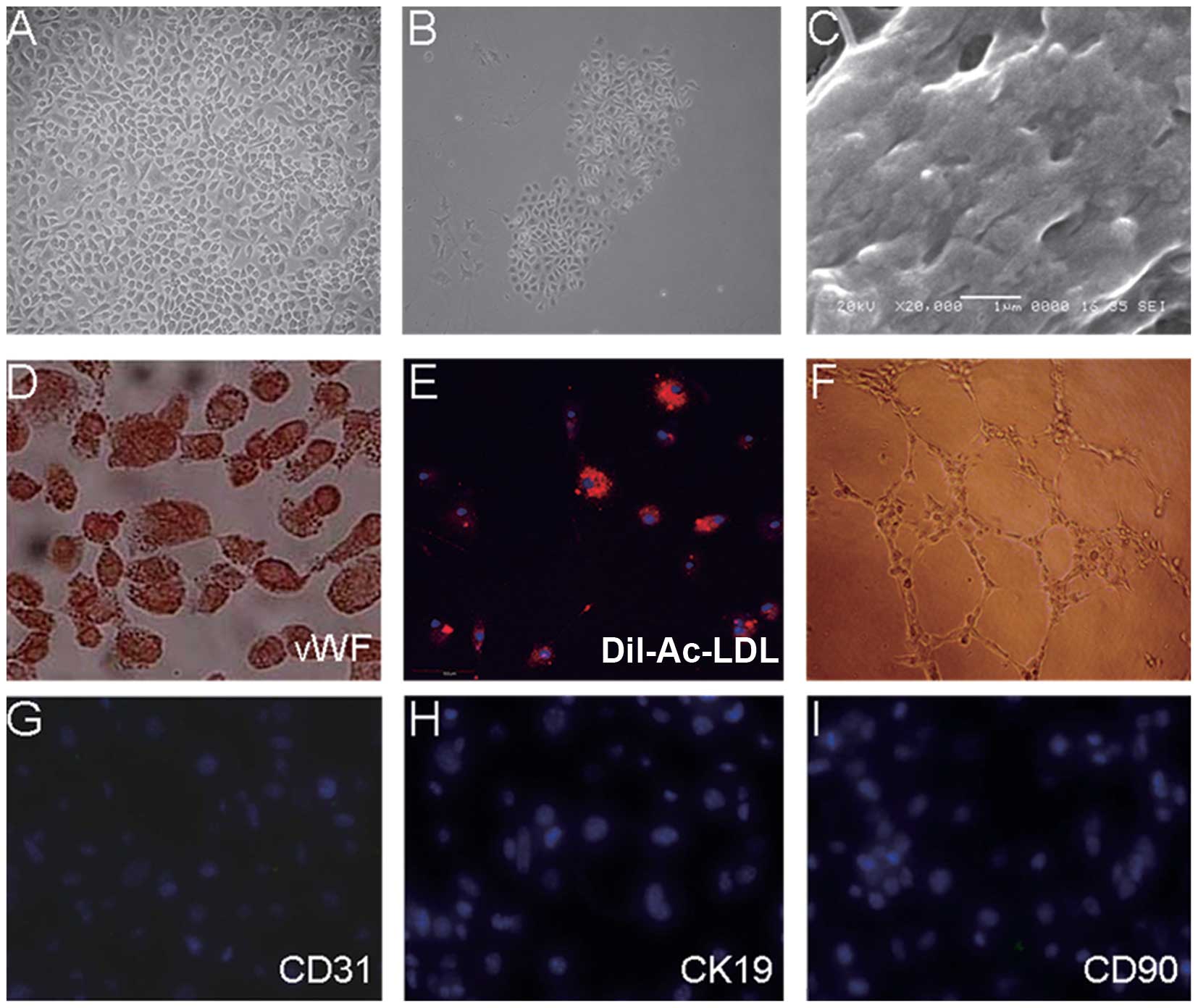
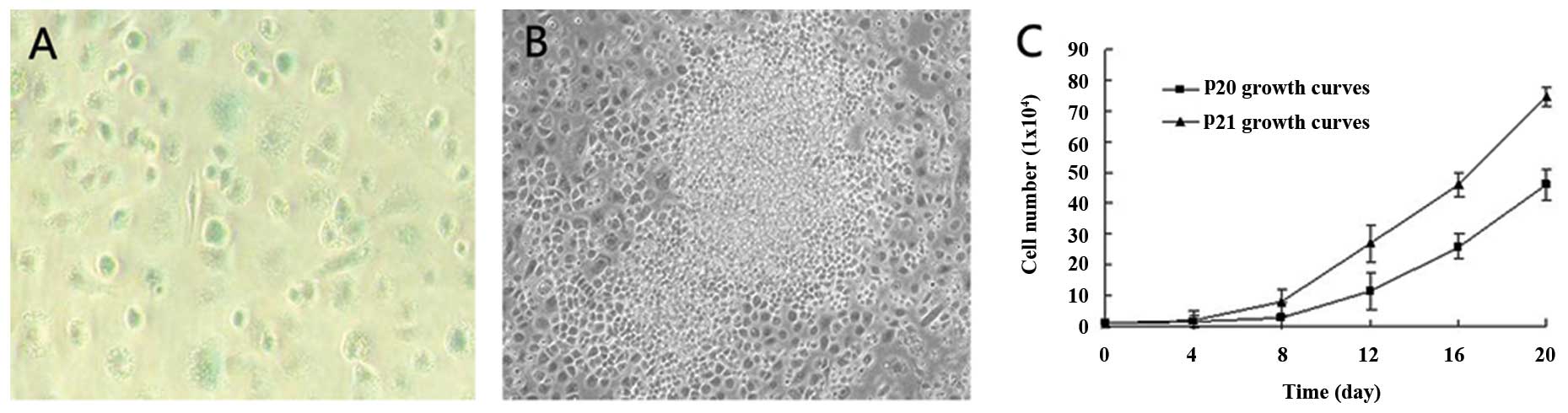
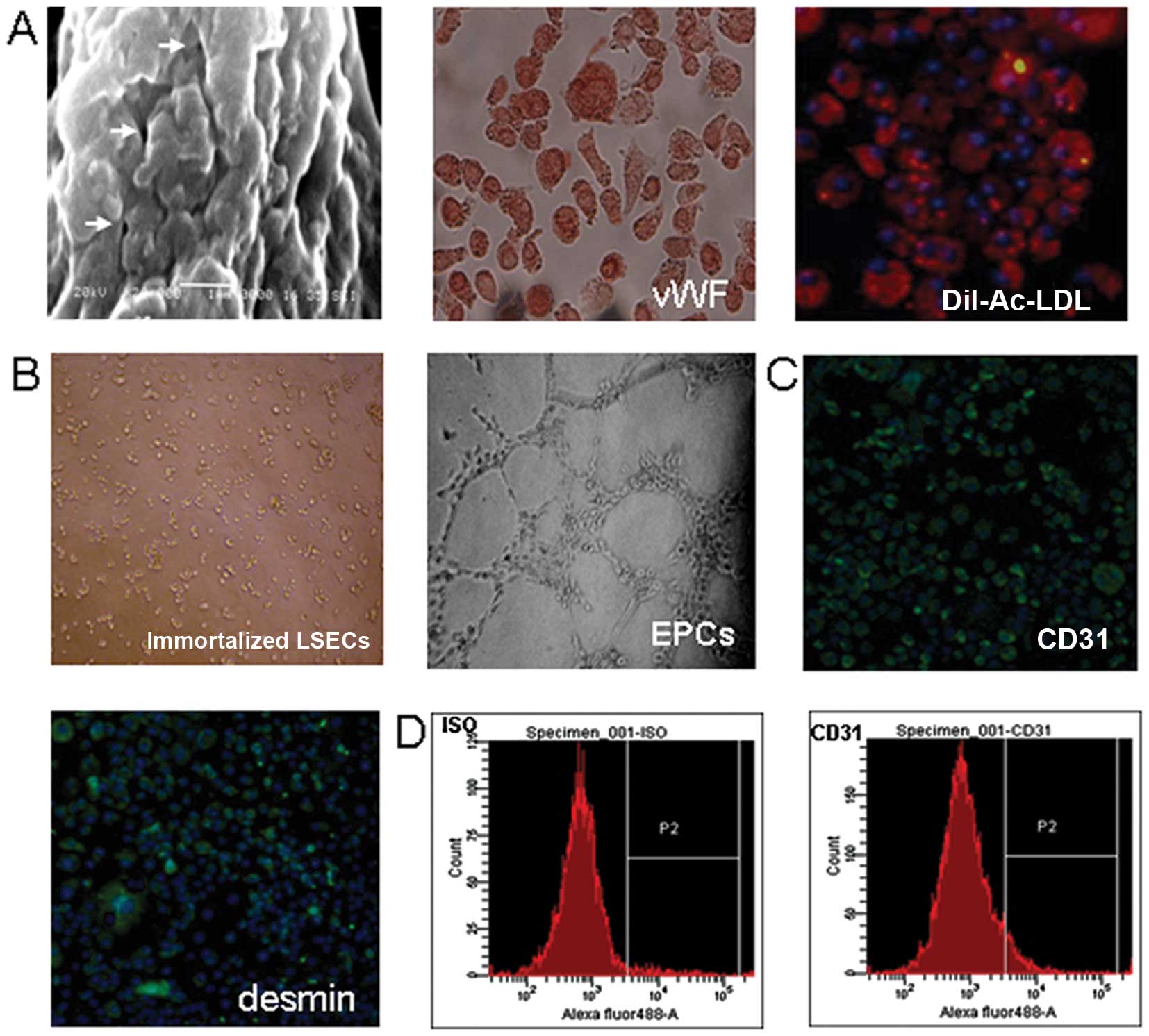
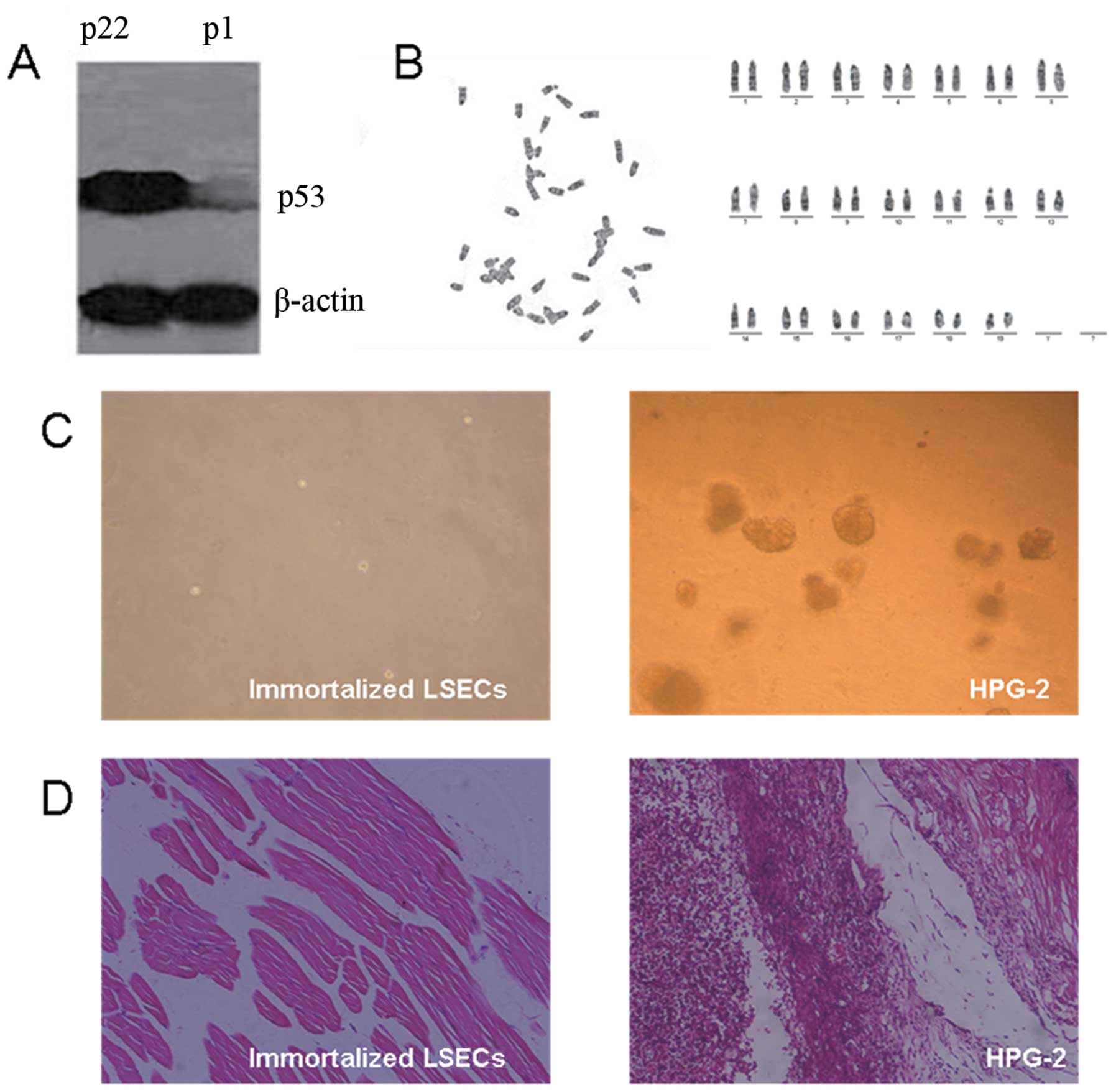
|
1
|
Wisse E: An electron microscopic study of
the fenestrated endothelial lining of rat liver sinusoids. J
Ultrastruct Res. 31:125–150. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Braet F, Riches J, Geerts W, Jahn KA,
Wisse E and Frederik P: Three-dimensional organization of fenestrae
labyrinths in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int.
29:603–613. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Elvevold K, Smedsrod B and Martinez I: The
liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: a cell type of controversial and
confusing identity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
294:G391–G400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wisse E, De Zanger RB, Charels K, Van Der
Smissen P and McCuskey RS: The liver sieve: considerations
concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the
sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology. 5:683–692.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
LeCouter J, Moritz DR, Li B, et al:
Angiogenesis-independent endothelial protection of liver: role of
VEGFR-1. Science. 299:890–893. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ratsch SB, Gao Q, Srinivasan S, Wazer DE
and Band V: Multiple genetic changes are required for efficient
immortalization of different subtypes of normal human mammary
epithelial cells. Radiat Res. 155:143–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yaswen P and Stampfer MR: Molecular
changes accompanying senescence and immortalization of cultured
human mammary epithelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
34:1382–1394. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsutsui T, Fujino T, Kodama S, Tainsky MA,
Boyd J and Barrett JC: Aflatoxin B1-induced immortalization of
cultured skin fibroblasts from a patient with Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Carcinogenesis. 16:25–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Todaro GJ and Green H: Quantitative
studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their
development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 17:299–313. 1963.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuspa SH, Poirier MC, Harness JR, Olsom DR
and Steinert PM: Specific quantification of mouse and human keratin
proteins by radioimmunoassay. Biochem J. 187:281–284.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heimann R and Rice RH: Rat esophageal and
epidermal keratinocytes: intrinsic differences in culture and
derivation of continuous lines. J Cell Physiol. 117:362–367. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Phillips MA and Rice RH: Convergent
differentiation in cultured rat cells from nonkeratinized
epithelia: keratinocyte character and intrinsic differences. J Cell
Biol. 97:686–691. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davis T and Kipling D: Telomeres and
telomerase biology in vertebrates: progress towards a non-human
model for replicative senescence and ageing. Biogerontology.
6:371–385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Christman SA, Kong BW, Landry MM, Kim H
and Foster DN: Contributions of differential p53 expression in the
spontaneous immortalization of a chicken embryo fibroblast cell
line. BMC Cell Biol. 7(27): 2006
|
|
15
|
Dimri G, Band H and Band V: Mammary
epithelial cell transformation: insights from cell culture and
mouse models. Breast Cancer Res. 7:171–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oh HY, Jin X, Kim JG, et al:
Characteristics of primary and immortalized fibroblast cells
derived from the miniature and domestic pigs. BMC Cell Biol. 8(20):
2007
|
|
17
|
Itahana K, Campisi J and Dimri GP: Methods
to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: the
senescence-associated beta-galactosidase assay. Methods Mol Biol.
371:21–31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gustashaw KM: Chromosome stains. The AGT
Cytogenetics Laboratory Manual. Barch MJ, Knutsen T and Spurbeck
JL: Lippincott-Raven Press; Philadelphia, New York: pp. 269–280.
1997
|
|
19
|
Daneker GW, Lund SA, Caughman SW, et al:
Culture and characterization of sinusoidal endothelial cells
isolated from human liver. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 34:370–377.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karrar A, Broome U, Uzunel M, Qureshi AR
and Sumitran-Holgersson S: Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
induce apoptosis in activated T cells: a role in tolerance
induction. Gut. 56:243–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Knolle PA and Limmer A: Neighborhood
politics: the immunoregulatory function of organ-resident liver
endothelial cells. Trends Immunol. 22:432–437. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
DeLeve LD, Wang X, McCuskey MK and
McCuskey RS: Rat liver endothelial cells isolated by anti-CD31
immunomagnetic separation lack fenestrae and sieve plates. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 291:G1187–G1189. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karaa A, Kamoun WS and Clemens MG:
Oxidative stress disrupts nitric oxide synthase activation in liver
endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:1320–1331. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Knolle PA, Germann T, Treichel U, et al:
Endotoxin down-regulates T cell activation by antigen-presenting
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Immunol. 162:1401–1407.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang WQ and Wang QR: Bone marrow
endothelial cells secrete thymosin beta4 and AcSDKP. Exp Hematol.
29:12–18. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang QR, Wang BH, Huang YH, Dai G, Li WM
and Yan Q: Purification and growth of endothelial progenitor cells
from murine bone marrow mononuclear cells. J Cell Biochem.
103:21–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK and
McCuskey RS: Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is
maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G757–G763. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Braet F and Wisse E: Structural and
functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae:
a review. Comp Hepatol. 1(1): 2002
|
|
29
|
Namba M, Nishitani K, Fukushima F, Kimoto
T and Yuasa Y: Multi-step neoplastic transformation of normal human
fibroblasts by Co-60 gamma rays and Ha-ras oncogenes. Mutat Res.
199:415–423. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chapman S, Liu X, Meyers C, Schlegel R and
McBride AA: Human keratinocytes are efficiently immortalized by a
Rho kinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 120:2619–2626. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Katakura Y, Alam S and Shirahata S:
Immortalization by gene transfection. Methods Cell Biol. 57:69–91.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Masamune A, Satoh M, Kikuta K, Suzuki N
and Shimosegawa T: Establishment and characterization of a rat
pancreatic stellate cell line by spontaneous immortalization. World
J Gastroenterol. 9:2751–2758. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shay JW, Tomlinson G, Piatyszek MA and
Gollahon LS: Spontaneous in vitro immortalization of breast
epithelial cells from a patient with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Mol Cell
Biol. 15:425–432. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Elmore LW, Turner KC, Gollahon LS, Landon
MR, Jackson-Cook CK and Holt SE: Telomerase protects cancer-prone
human cells from chromosomal instability and spontaneous
immortalization. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:391–397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao C, Meng L, Hu H, et al: Spontaneously
immortalised bovine mammary epithelial cells exhibit a distinct
gene expression pattern from the breast cancer cells. BMC Cell
Biol. 11(82): 2010
|
|
36
|
Nowak JA, Malowitz J, Girgenrath M, et al:
Immortalization of mouse myogenic cells can occur without loss of
p16INK4a, p19ARF, or p53 and is accelerated
by inactivation of Bax. BMC Cell Biol. 5(1): 2004
|
|
37
|
Gillio-Meina C, Swan CL, Crellin NK,
Stocco DM and Chedrese PJ: Generation of stable cell lines by
spontaneous immortalization of primary cultures of porcine
granulosa cells. Mol Reprod Dev. 57:366–374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Denhardt DT, Edwards DR, McLeod M, Norton
G, Parfett CL and Zimmer M: Spontaneous immortalization of mouse
embryo cells: strain differences and changes in gene expression
with particular reference to retroviral gag-pol genes. Exp Cell
Res. 192:128–136. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li WM, Huang YH, Jiang DZ and Wang QR: The
effects of cytokines produced by bone marrow endothelial cells on
the regulation of hematopoiesis. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 52:45–49.
2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Duan HX, Cheng LM, Wang J, Hu LS and Lu
GX: Angiogenic potential difference between two types of
endothelial progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood. Cell
Biol Int. 30:1018–1027. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|