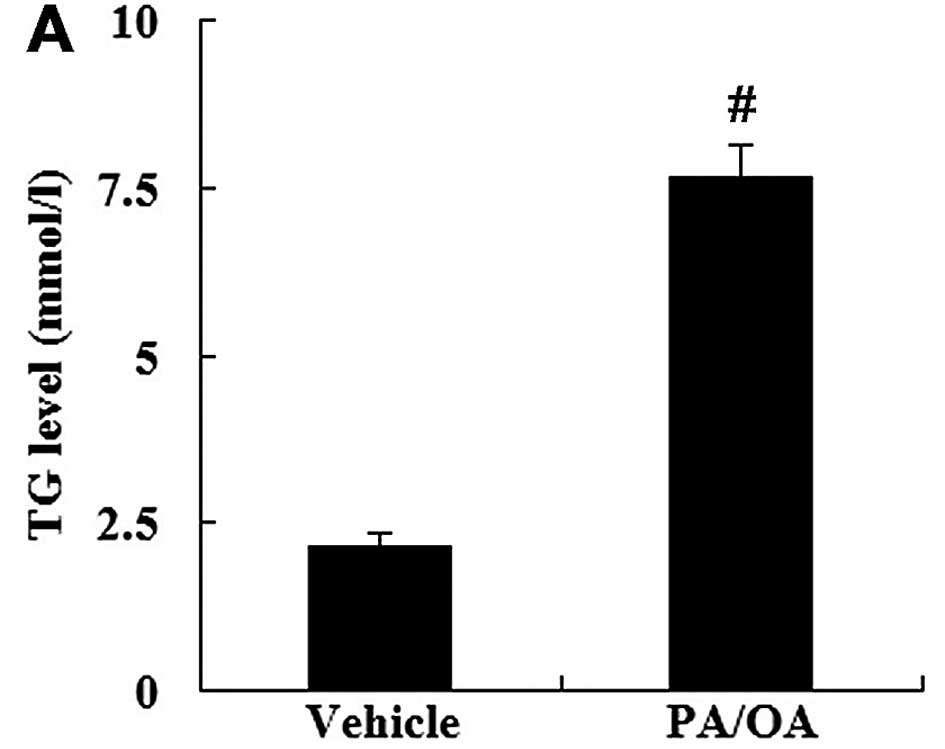
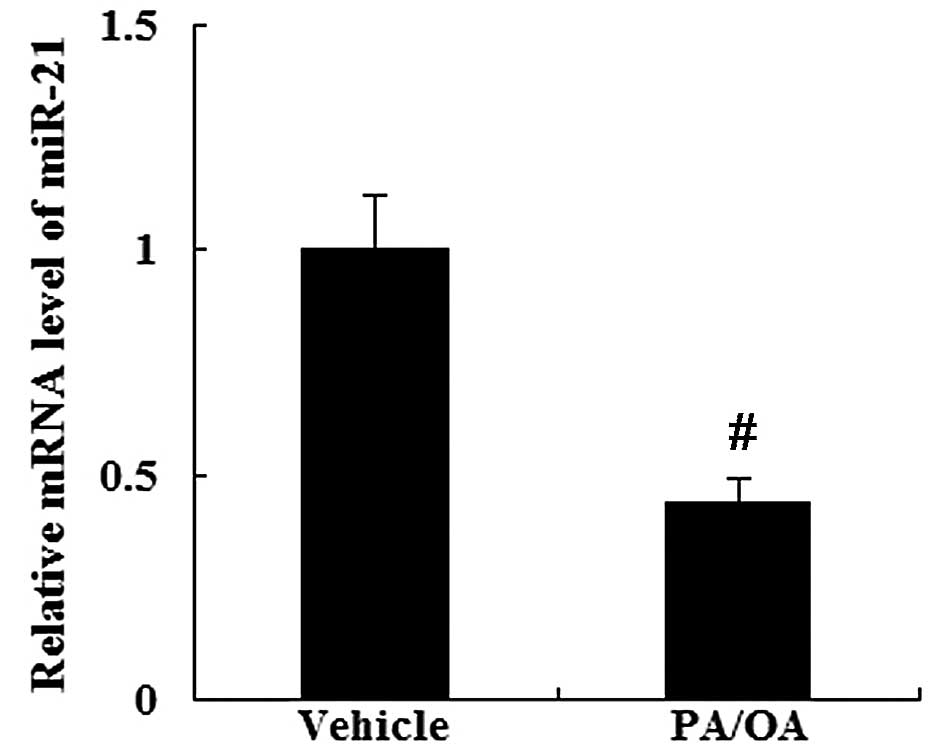
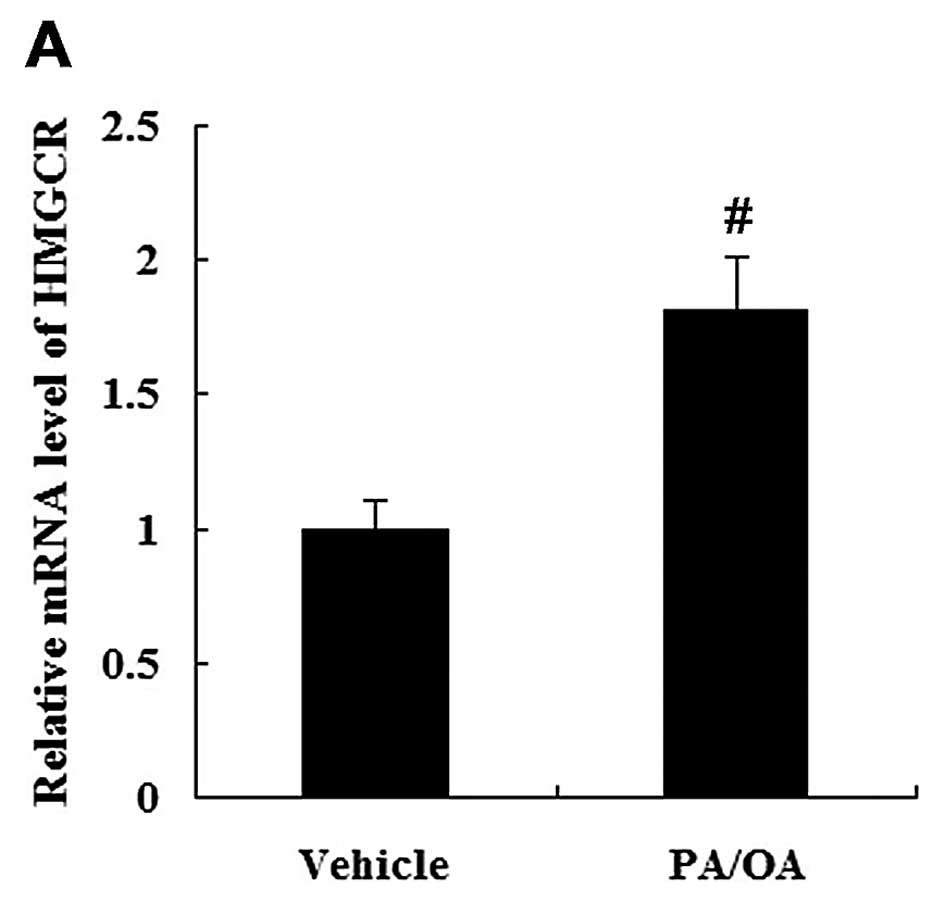
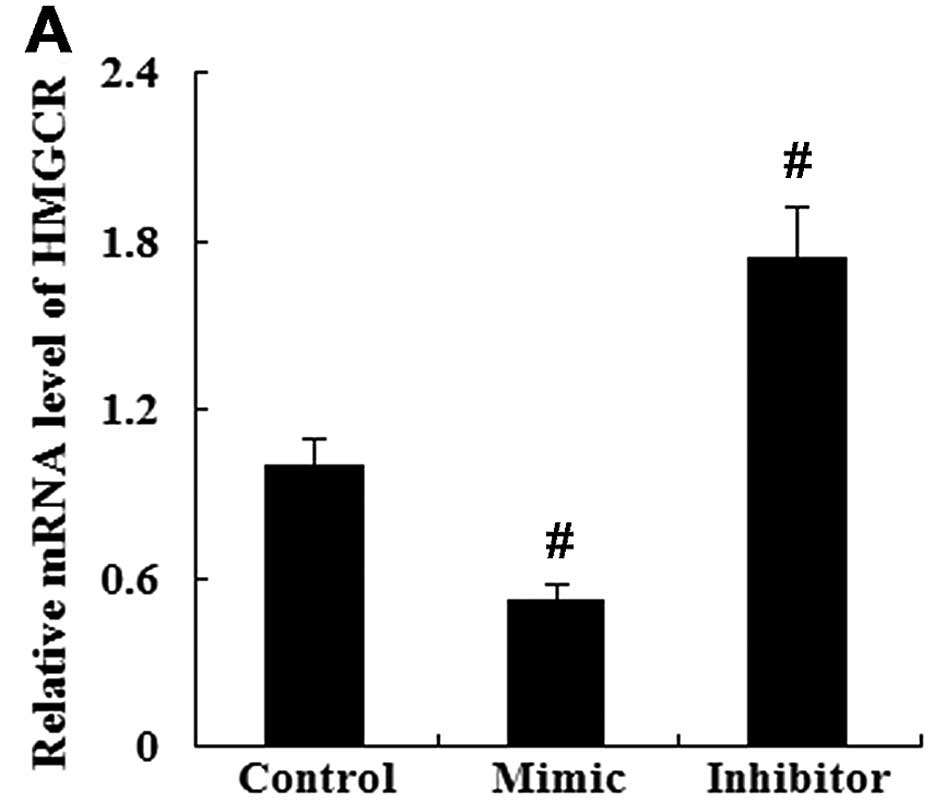
|
1
|
Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R, et al:
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association
with cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients.
Diabetes Care. 30:1212–1218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clark JM and Diehl AM: Hepatic steatosis
and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2:210–215. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F,
Tiribelli C, Marchesini G and Bellentani S: Prevalence of and risk
factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos
nutrition and liver study. Hepatology. 42:44–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et
al: Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the
United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 40:1387–1395. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vernon G, Baranova A and Younossi ZM:
Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan JG: An introduction of strategies for
the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
recommended by Asia Pacific Working Party on NAFLD. Zhonghua Gan
Zang Bing Za Zhi. 15:552–553. 2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ballestri S, Lonardo A, Bonapace S, Byrne
CD, Loria P and Targher G: Risk of cardiovascular, cardiac and
arrhythmic complications in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. World J Gastroenterol. 20:1724–1745. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oni ET, Agatston AS, Blaha MJ, et al: A
systematic review: burden and severity of subclinical
cardiovascular disease among those with nonalcoholic fatty liver;
should we care? Atherosclerosis. 230:258–267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nelson KM and Weiss GJ: MicroRNAs and
cancer: past, present, and potential future. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3655–3660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu P, Guo M and Hay BA: MicroRNAs and the
regulation of cell death. Trends Genet. 20:617–624. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karp X and Ambros V: Encountering
microRNAs in cell fate signaling. Science. 310:1288–1289. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li S, Chen X, Zhang H, et al: Differential
expression of microRNAs in mouse liver under aberrant energy
metabolic status. J Lipid Res. 50:1756–1765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheung O, Puri P, Eicken C, et al:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic
microRNA expression. Hepatology. 48:1810–1820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin X, Ye YF, Chen SH, Yu CH, Liu J and Li
YM: MicroRNA expression pattern in different stages of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 41:289–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pogribny IP, Starlard-Davenport A,
Tryndyak VP, Han T, Ross SA, Rusyn I and Beland FA: Difference in
expression of hepatic microRNAs miR-29c, miR-34a, miR-155, and
miR-200b is associated with strain-specific susceptibility to
dietary nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Lab Invest.
90:1437–1346. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cazanave SC, Mott JL, Elmi NA, et al:
JNK1-dependent PUMA expression contributes to hepatocyte
lipoapoptosis. J Biol Chem. 284:26591–26602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ahn J, Lee H, Jung CH and Ha T: Lycopene
inhibits hepatic steatosis via microRNA-21-induced downregulation
of fatty acid-binding protein 7 in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 56:1665–1674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nehra V, Angulo P, Buchman AL and Lindor
KD: Nutritional and metabolic considerations in the etiology of
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 46:2347–2352. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Richieri GV and Kleinfeld AM: Unbound free
fatty acid levels in human serum. J Lipid Res. 36:229–240.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sanyal AJ, Campbell-Sargent C, Mirshahi F,
et al: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: association of insulin
resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology.
120:1183–1192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, et al: A
placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 355:2297–2307. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yao HR, Liu J, Plumeri D, et al:
Lipotoxicity in HepG2 cells triggered by free fatty acids. Am J
Transl Res. 3:284–291. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beg ZH, Stonik JA and Brewer HB Jr:
Phosphorylation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A
reductase and modulation of its enzymic activity by
calcium-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol
Chem. 260:1682–1687. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beg ZH, Stonik JA and Brewer HB Jr:
Modulation of the enzymic activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl
coenzyme A reductase by multiple kinase systems involving
reversible phosphorylation: a review. Metabolism. 36:900–917. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caballero F, Fernández A, De Lacy AM,
Fernández-Checa JC, Caballería J and García-Ruiz C: Enhanced free
cholesterol, SREBP-2 and StAR expression in human NASH. J Hepatol.
50:789–796. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Min HK, Kapoor A, Fuchs M, et al:
Increased hepatic synthesis and dysregulation of cholesterol
metabolism is associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Cell Metab. 15:665–674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
DeBose-Boyd RA: Feedback regulation of
cholesterol synthesis: sterolaccelerated ubiquitination and
degradation of HMG CoA reductase. Cell Res. 18:609–621. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trapani L, Segatto M, Simeoni V, et al:
Short- and long-term regulation of 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl
coenzyme A reductase by a 4-methylcoumarin. Biochimie.
93:1165–1171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maron DJ, Fazio S and Linton MF: Current
perspectives on statins. Circulation. 101:207–213. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|