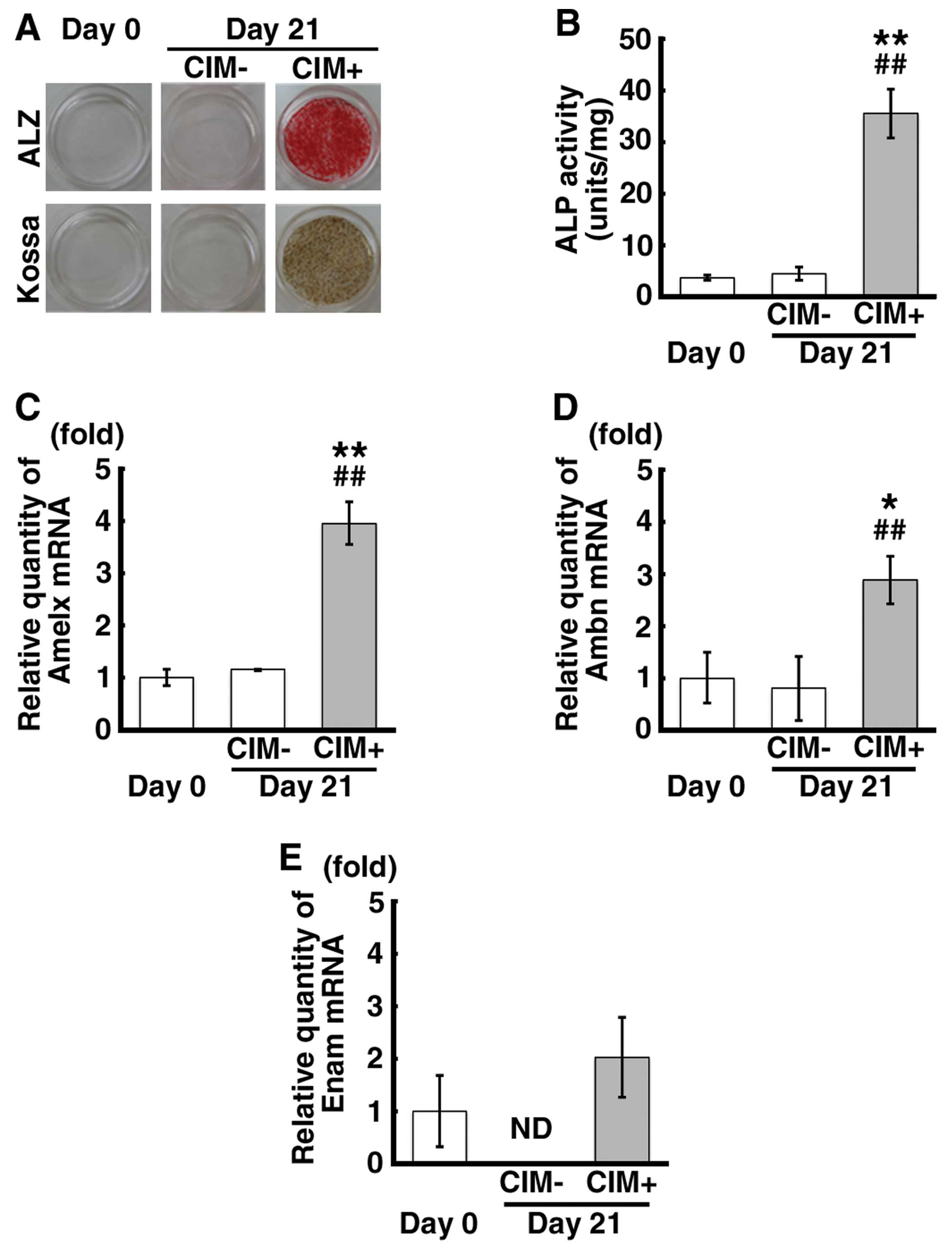
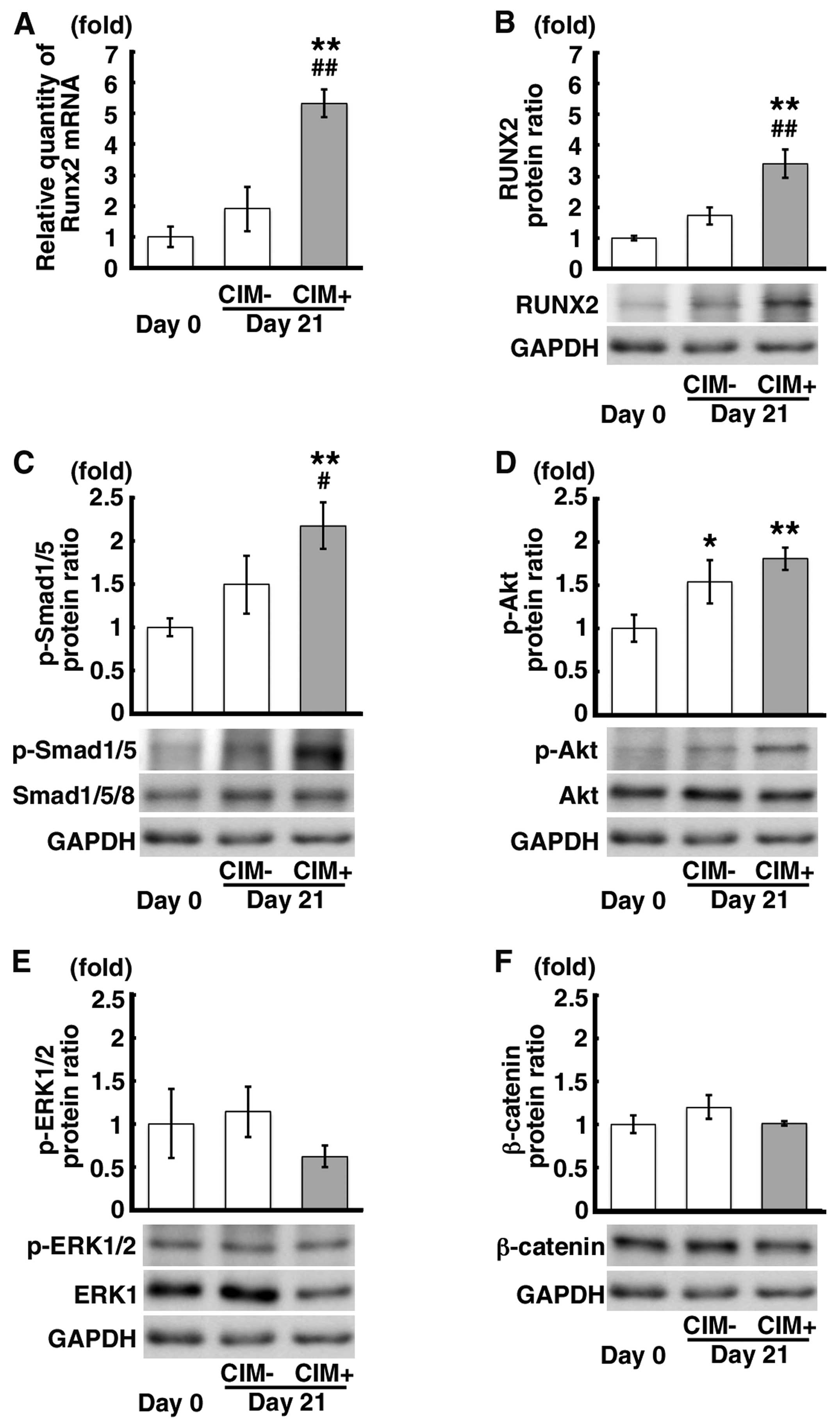
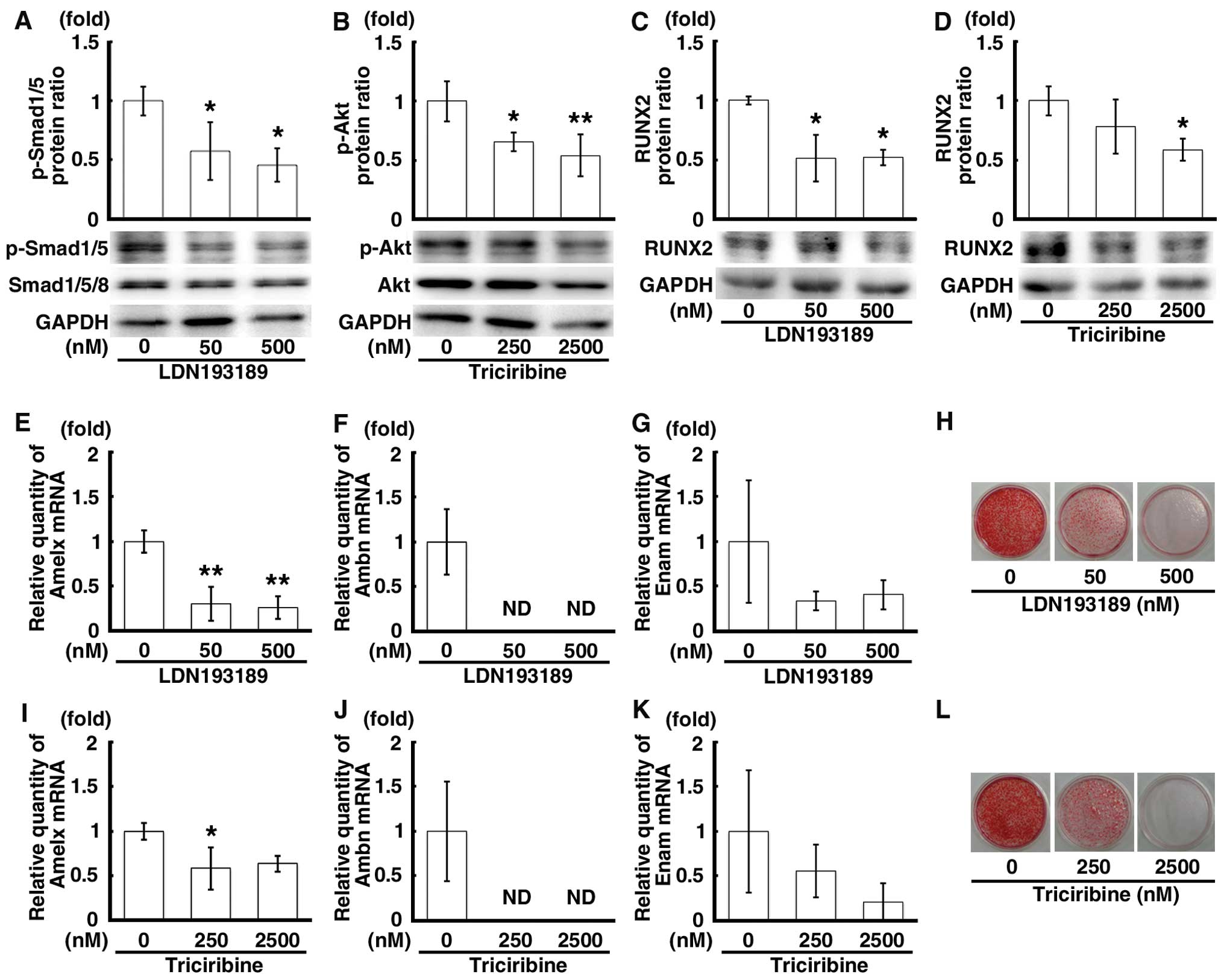
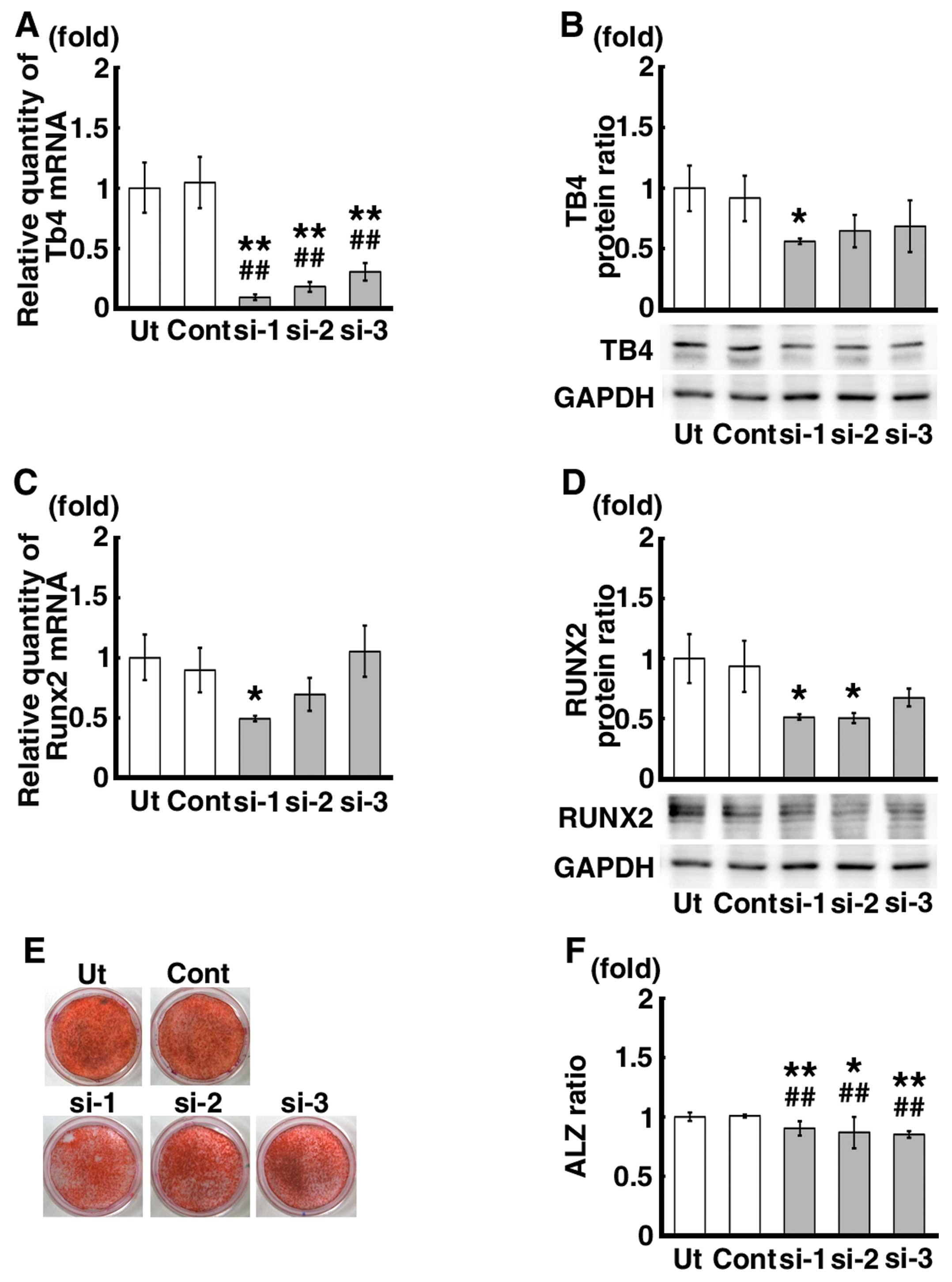
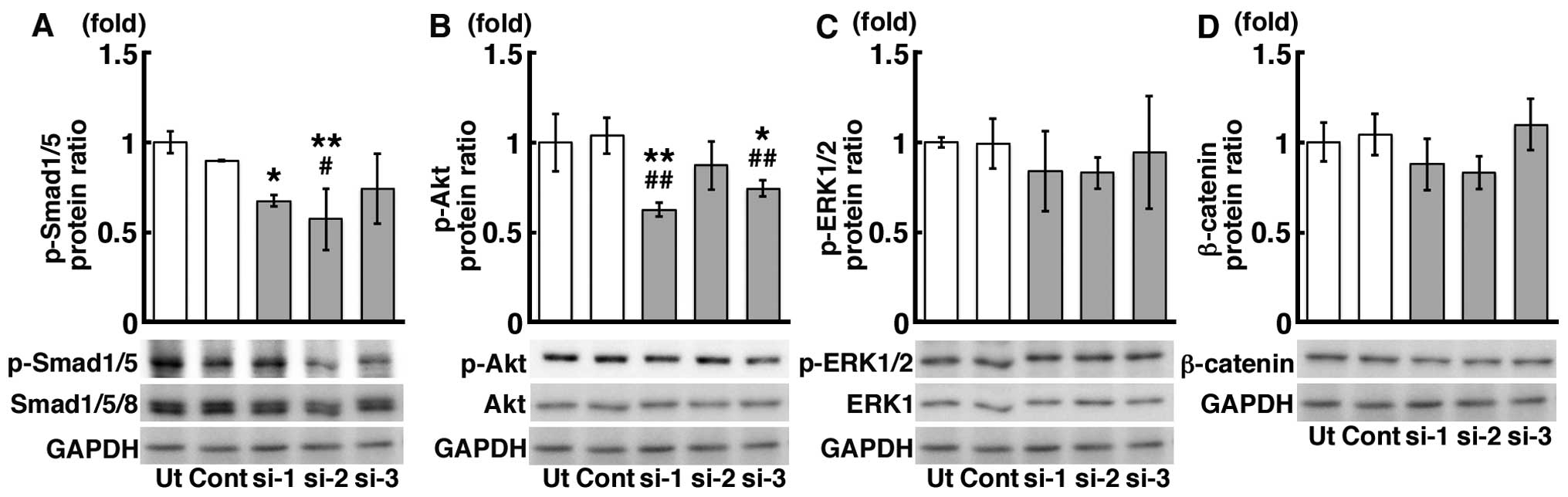
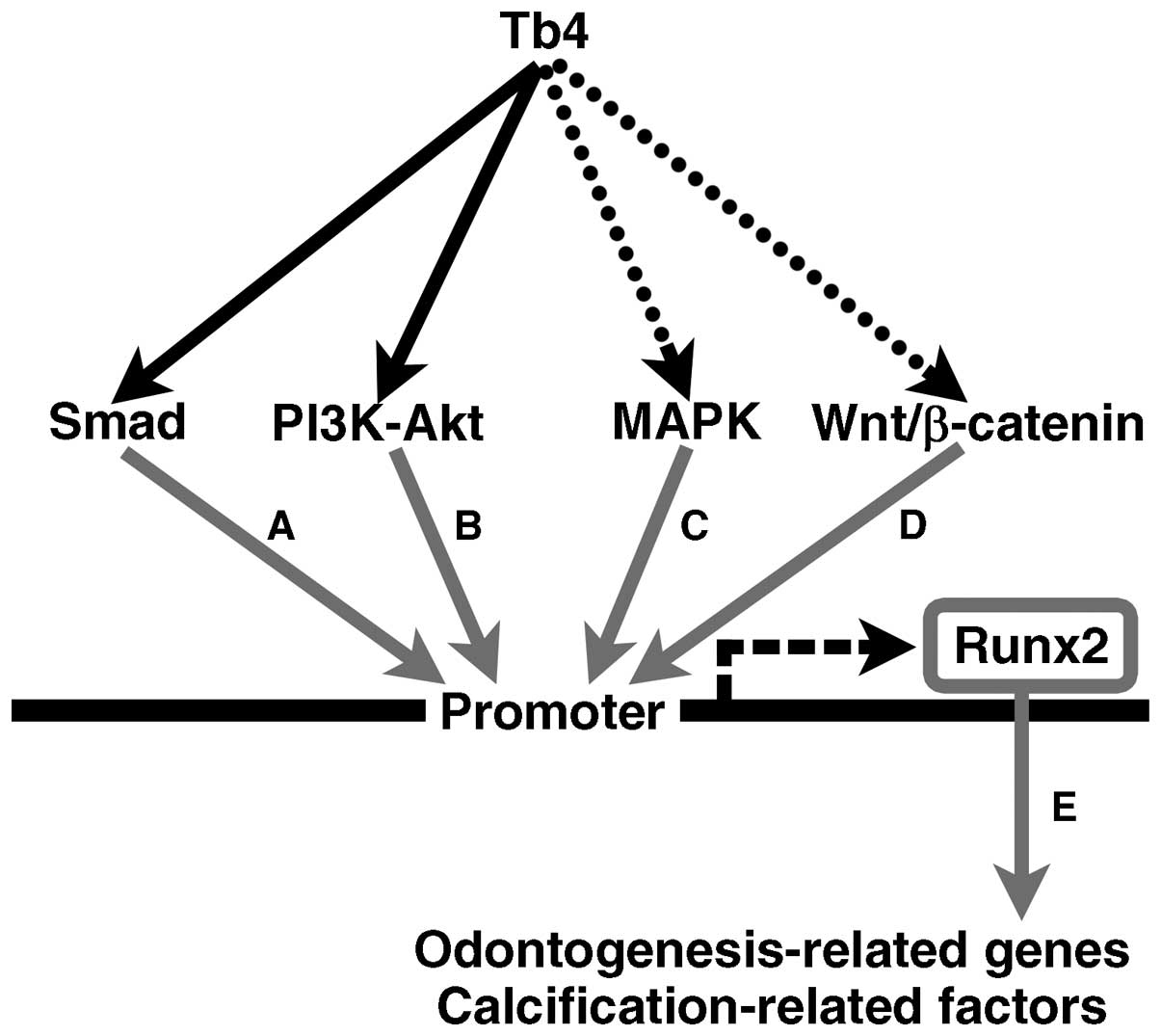
|
1
|
Maas R and Bei M: The genetic control of
early tooth development. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 8:4–39. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thesleff I and Aberg T: Molecular
regulation of tooth development. Bone. 25:123–125. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jernvall J and Thesleff I: Reiterative
signaling and patterning during mammalian tooth morphogenesis. Mech
Dev. 92:19–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pispa J and Thesleff I: Mechanisms of
ectodermal organogenesis. Dev Biol. 262:195–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thesleff I: Epithelial-mesenchymal
signalling regulating tooth morphogenesis. J Cell Sci.
116:1647–1648. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamaza H, Matsuo K, Kiyoshima T, Shigemura
N, Kobayashi I, Wada H, Akamime A and Sakai H: Detection of
differentially expressed genes in the early developmental stage of
the mouse mandible. Int J Dev Biol. 45:675–680. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wada H, Kobayashi I, Yamaza H, Matsuo K,
Kiyoshima T, Akhtar M, Sakai T, Koyano K and Sakai H: In situ
expression of heat shock proteins, Hsc73, Hsj2 and Hsp86 in the
developing tooth germ of mouse lower first molar. Histochem J.
34:105–109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Akhter M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Matsuo
K, Yamaza H, Wada H, Honda JY, Ming X and Sakai H: Possible
functional involvement of thymosin beta 4 in developing tooth germ
of mouse lower first molar. Histochem Cell Biol. 124:207–213. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Wada H, Matsuo
K, Nonaka K, Honda JY, Koyano K and Sakai H: Type II/III
Runx2/Cbfa1 is required for tooth germ development. Bone.
38:836–844. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xie M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Yamaza H,
Honda JY, Takahashi K, Enoki N, Akamine A and Sakai H: Functional
implication of nucleolin in the mouse first molar development. J
Biol Chem. 282:23275–23283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Honda JY, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Yamaza
H, Xie M, Takahashi K, Enoki N, Nagata K, Nakashima A and Sakai H:
Glycolytic enzyme Pgk1 is strongly expressed in the developing
tooth germ of the mouse lower first molar. Histol Histopathol.
23:423–432. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Nagata K,
Ookuma Y, Fujiwara H and Sakai H: In situ expression of ribosomal
protein L21 in developing tooth germ of the mouse lower first
molar. J Mol Histol. 40:361–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Akhter M, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Nagata
K, Wada H, Ookuma Y, Fujiwara H, Honda JY and Sakai H: In situ
expression of 15 kDa interferon alpha responsive gene in the
developing tooth germ of the mouse lower first molar. J Mol Histol.
41:185–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takahashi KF, Kiyoshima T, Kobayashi I,
Xie M, Yamaza H, Fujiwara H, Ookuma Y, Nagata K, Wada H, Sakai T,
et al: Protogenin, a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily,
is implicated in the development of the mouse lower first molar.
BMC Dev Biol. 10:115–130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Honda JY, Kobayashi I, Kiyoshima T, Nagata
K, Wada H, Ookuma Y, Fujiwara H, Shiotsuka M, Takahashi I and Sakai
H: In situ expression of the mitochondrial ATPase6 gene in the
developing tooth germ of the mouse lower first molar. J Mol Histol.
42:83–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shiotsuka M, Wada H, Kiyoshima T, Nagata
K, Fujiwara H, Kihara M, Hasegawa K, Someya H, Takahashi I and
Sakai H: The expression and function of thymosin beta 10 in tooth
germ development. Int J Dev Biol. 57:873–883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ookuma YF, Kiyoshima T, Kobayashi I,
Nagata K, Wada H, Fujiwara H, Yamaza H, Nonaka K and Sakai H:
Multiple functional involvement of thymosin beta-4 in tooth germ
development. Histochem Cell Biol. 139:355–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kihara M, Kiyoshima T, Nagata K, Wada H,
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa K, Someya H, Takahashi I and Sakai H: Itm2a
expression in the developing mouse first lower molar, and the
subcellular localization of Itm2a in mouse dental epithelial cells.
PLoS One. 9:e1039282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kiyoshima T, Fujiwara H, Nagata K, Wada H,
Ookuma YF, Shiotsuka M, Kihara M, Hasegawa K, Someya H and Sakai H:
Induction of dental epithelial cell differentiation marker gene
expression in non-odontogenic human keratinocytes by transfection
with thymosin beta 4. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 12:309–322. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cha HJ, Philp D, Lee SH, Moon HS, Kleinman
HK and Nakamura T: Over-expression of thymosin beta 4 promotes
abnormal tooth development and stimulation of hair growth. Int J
Dev Biol. 54:135–140. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee SI, Kim DS, Lee HJ, Cha HJ and Kim EC:
The role of thymosin beta 4 on odontogenic differentiation in human
dental pulp cells. PLoS One. 8:e619602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hannappel E and Huff T: The thymosins.
Prothymosin alpha, parathymosin, and beta-thymosins: Structure and
function. Vitam Horm. 66:257–296. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Safer D, Elzinga M and Nachmias VT:
Thymosin beta 4 and Fx, an actin-sequestering peptide, are
indistinguishable. J Biol Chem. 266:4029–4032. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smart N, Bollini S, Dubé KN, Vieira JM,
Zhou B, Davidson S, Yellon D, Riegler J, Price AN, Lythgoe MF, et
al: De novo cardiomyocytes from within the activated adult heart
after injury. Nature. 474:640–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao ZS, Hjelmeland AB and Quarles LD:
Selective deficiency of the ‘bone-related’ Runx2-II unexpectedly
preserves osteoblast-mediated skeletogenesis. J Biol Chem.
279:20307–20313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stock M and Otto F: Control of RUNX2
isoform expression: The role of promoters and enhancers. J Cell
Biochem. 95:506–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Camilleri S and McDonald F: Runx2 and
dental development. Eur J Oral Sci. 114:361–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen S, Gluhak-Heinrich J, Wang YH, Wu YM,
Chuang HH, Chen L, Yuan GH, Dong J, Gay I and MacDougall M: Runx2,
osx, and dspp in tooth development. J Dent Res. 88:904–909. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aberg T, Wang XP, Kim JH, Yamashiro T, Bei
M, Rice R, Ryoo HM and Thesleff I: Runx2 mediates FGF signaling
from epithelium to mesenchyme during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol.
270:76–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dhamija S and Krebsbach PH: Role of Cbfa1
in ameloblastin gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 276:35159–35164.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee HK, Lee DS, Ryoo HM, Park JT, Park SJ,
Bae HS, Cho MI and Park JC: The odontogenic ameloblast-associated
protein (ODAM) cooperates with RUNX2 and modulates enamel
mineralization via regulation of MMP-20. J Cell Biochem.
111:755–767. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
D'Souza RN, Aberg T, Gaikwad J, Cavender
A, Owen M, Karsenty G and Thesleff I: Cbfa1 is required for
epithelial-mesenchymal interactions regulating tooth development in
mice. Development. 126:2911–2920. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL and
Karsenty G: Osf2/Cbfa1: A transcriptional activator of osteoblast
differentiation. Cell. 89:747–754. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martin JW, Zielenska M, Stein GS, van
Wijnen AJ and Squire JA: The Role of RUNX2 in Osteosarcoma
Oncogenesis. Sarcoma. 2011:2827452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim EJ, Cho SW, Shin JO, Lee MJ, Kim KS
and Jung HS: Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate
early chondrogenesis: A mouse model. PLoS One. 8:e552962013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu F, Chu EY, Watt B, Zhang Y, Gallant
NM, Andl T, Yang SH, Lu MM, Piccolo S, Schmidt-Ullrich R, et al:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling directs multiple stages of tooth
morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 313:210–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hardcastle Z, Mo R, Hui CC and Sharpe PT:
The Shh signalling pathway in tooth development: Defects in Gli2
and Gli3 mutants. Development. 125:2803–2811. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Feurino LW, Zhai Q, Wang H,
Fisher WE, Chen C, Yao Q and Li M: Thymosin Beta 4 is overexpressed
in human pancreatic cancer cells and stimulates proinflammatory
cytokine secretion and JNK activation. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:419–423.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Oh SY, Song JH, Gil JE, Kim JH, Yeom YI
and Moon EY: ERK activation by thymosin-beta-4 (TB4) overexpression
induces paclitaxel-resistance. Exp Cell Res. 312:1651–1657. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sosne G, Qiu P, Goldstein AL and Wheater
M: Biological activities of thymosin beta4 defined by active sites
in short peptide sequences. FASEB J. 24:2144–2151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huff T, Rosorius O, Otto AM, Müller CS,
Ballweber E, Hannappel E and Mannherz HG: Nuclear localisation of
the G-actin sequestering peptide thymosin beta4. J Cell Sci.
117:5333–5341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu Y, Du Y, Jiang H and Jiang GS: Cerium
promotes bone marrow stromal cells migration and osteogenic
differentiation via Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:5369–5378. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma P, Gu B, Xiong W, Tan B, Geng W, Li J
and Liu H: Glimepiride promotes osteogenic differentiation in rat
osteoblasts via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in a high glucose
microenvironment. PLoS One. 9:e1122432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hou X, Shen Y, Zhang C, Zhang L, Qin Y, Yu
Y, Wang L and Sun X: A specific oligodeoxynucleotide promotes the
differentiation of osteoblasts via ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Int J
Mol Sci. 13:7902–7914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baron R and Rawadi G: Targeting the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to regulate bone formation in the adult
skeleton. Endocrinology. 148:2635–2643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cho KW, Cai J, Kim HY, Hosoya A, Ohshima
H, Choi KY and Jung HS: ERK activation is involved in tooth
development via FGF10 signaling. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol.
312:901–911. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kumamoto H and Ooya K: Immunohistochemical
detection of phosphorylated Akt, PI3K, and PTEN in ameloblastic
tumors. Oral Dis. 13:461–467. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang G, Yuan G, Ye W, Cho KW and Chen Y:
An atypical canonical bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling
pathway regulates Msh homeobox 1 (Msx1) expression during
odonto-genesis. J Biol Chem. 289:31492–31502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takayama T, Suzuki N, Narukawa M, Tokunaga
T, Otsuka K and Ito K: Enamel matrix derivative stimulates core
binding factor alpha1/Runt-related transcription factor-2
expression via activation of Smad1 in C2C12 cells. J Periodontol.
76:244–249. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu L, Takahashi R, Harada H and Taniguchi
A: Effect of BMP-2 on gene expression of enamel matrix proteins at
the dental epithelial cell line. Open Biotechnol J. 1:18–20. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bock-Marquette I, Saxena A, White MD,
Dimaio JM and Srivastava D: Thymosin beta4 activates
integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration,
survival and cardiac repair. Nature. 432:466–472. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|