|
1
|
Motamedolshariati M, Memar B, Aliakbaian
M, Shakeri MT, Samadi M and Jangjoo A: Accuracy of prognostic and
predictive markers in core needle breast biopsies compared with
excisional specimens. Breast Care Basel. 9:107–110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Dunn NA, Muller JM,
Pyke CM and Baade PD: The descriptive epidemiology of female breast
cancer: An international comparison of screening, incidence,
survival and mortality. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:237–248. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
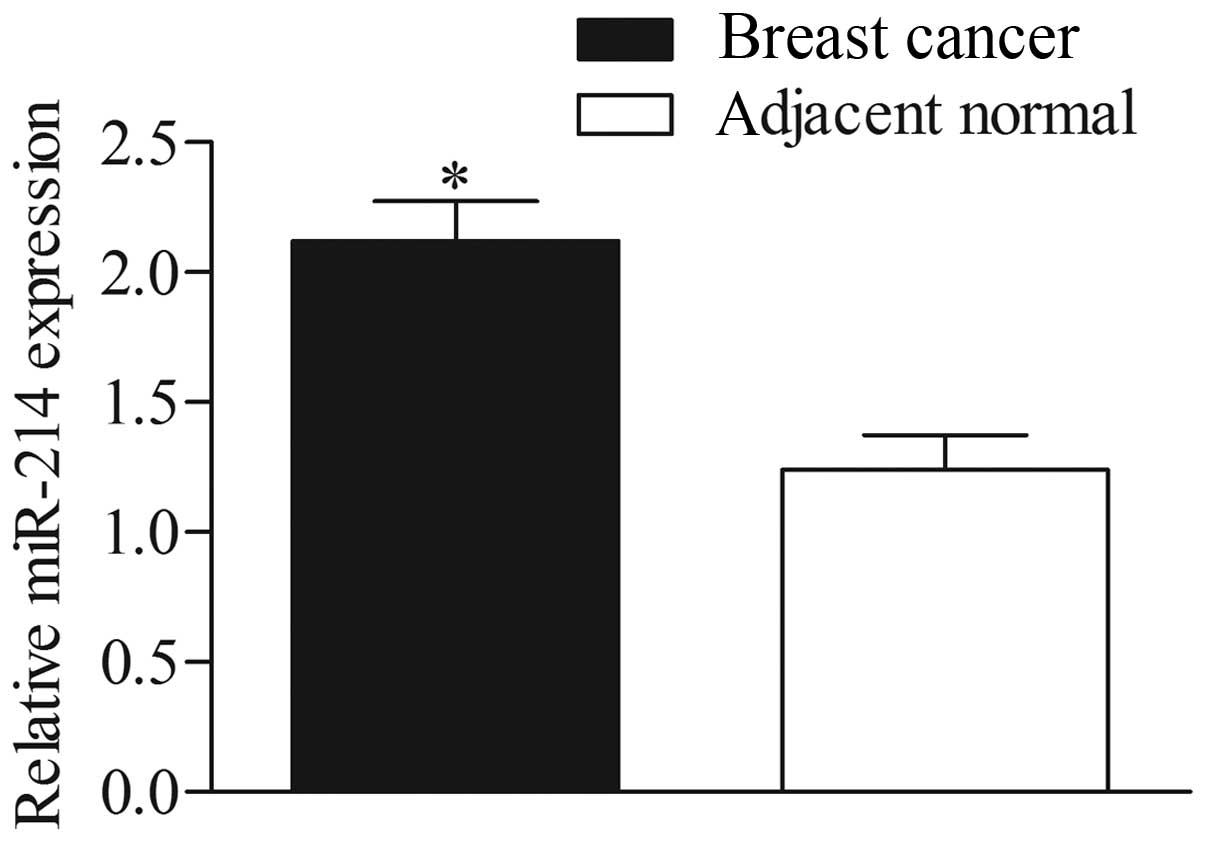
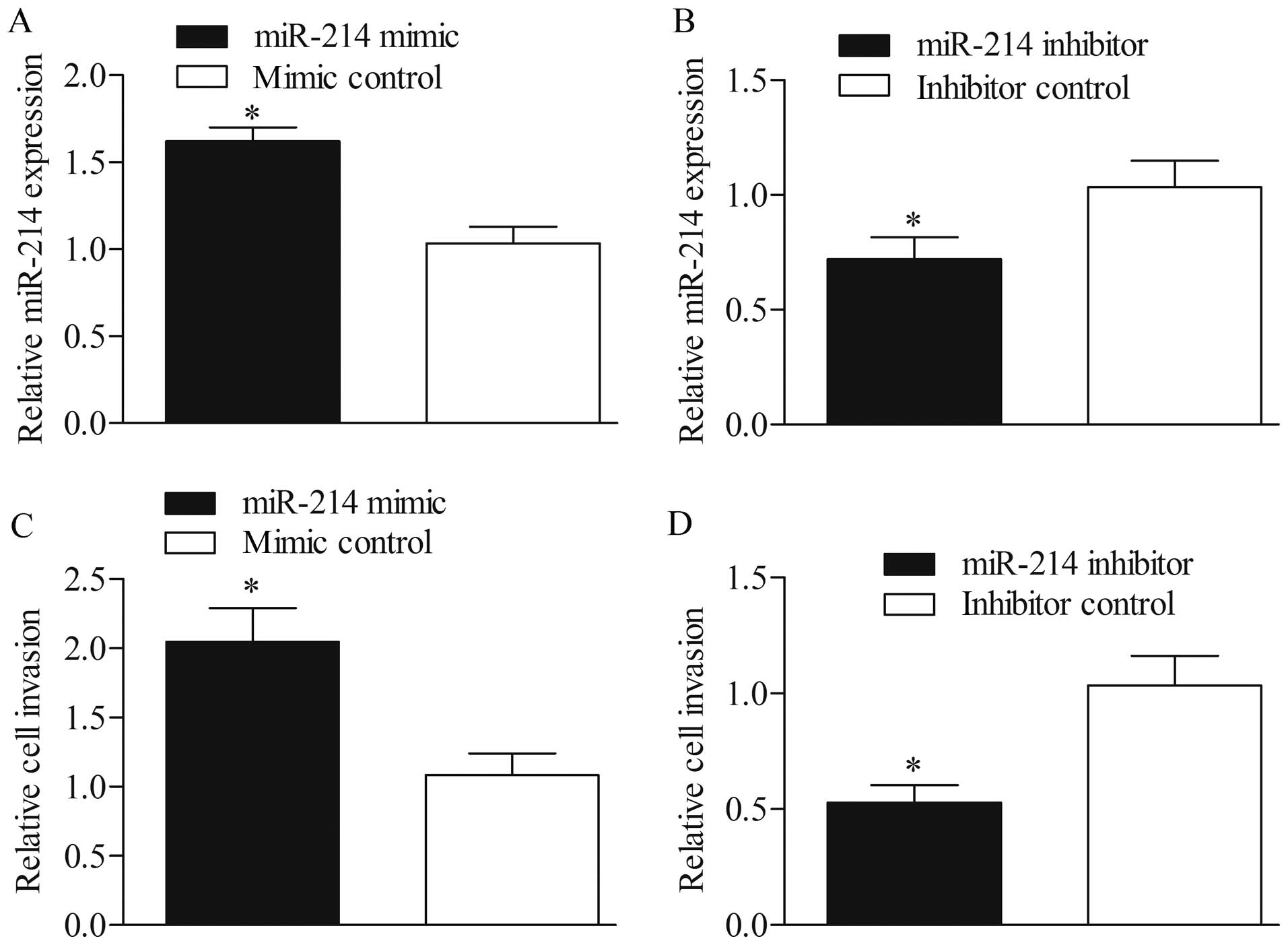
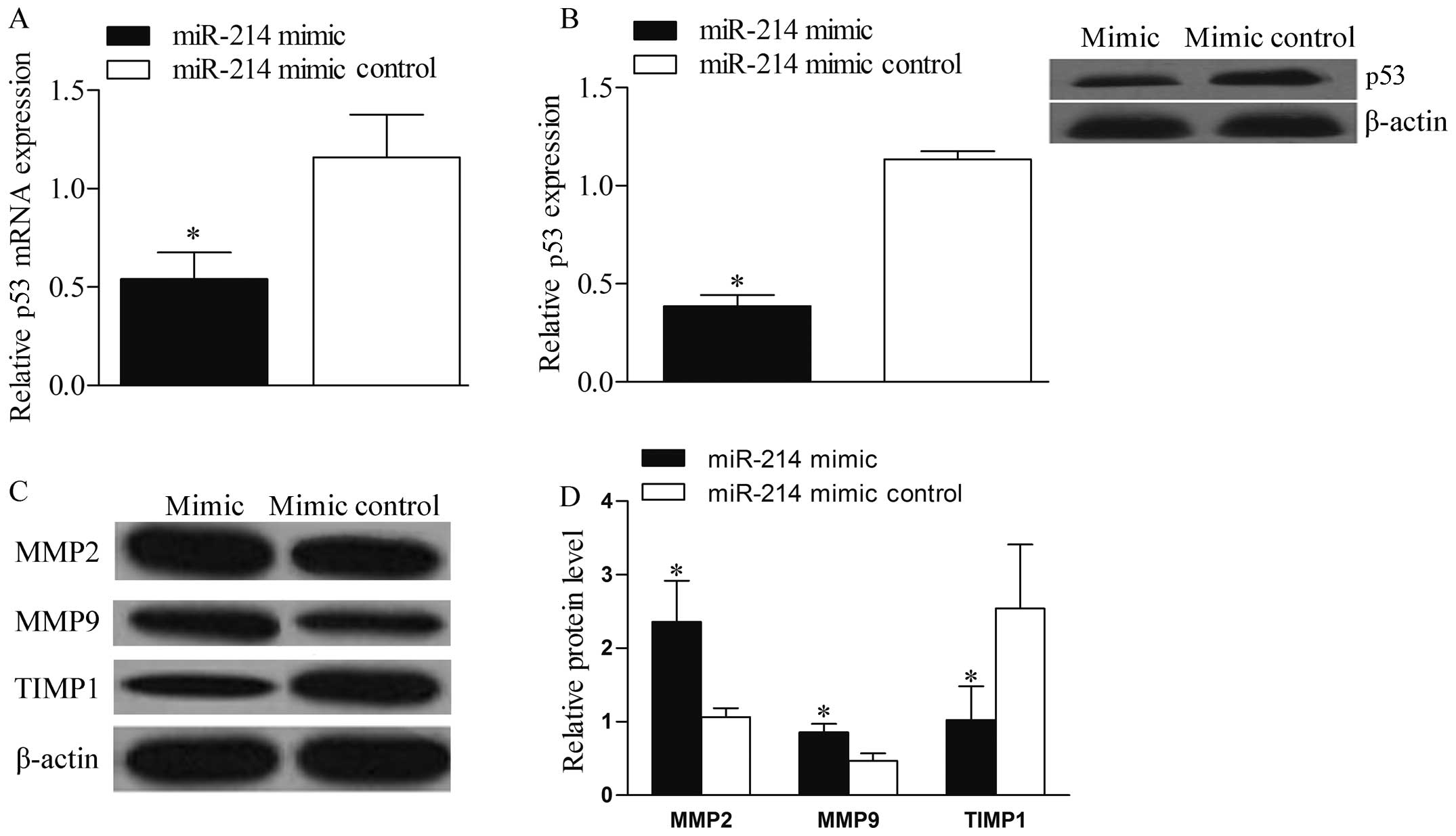
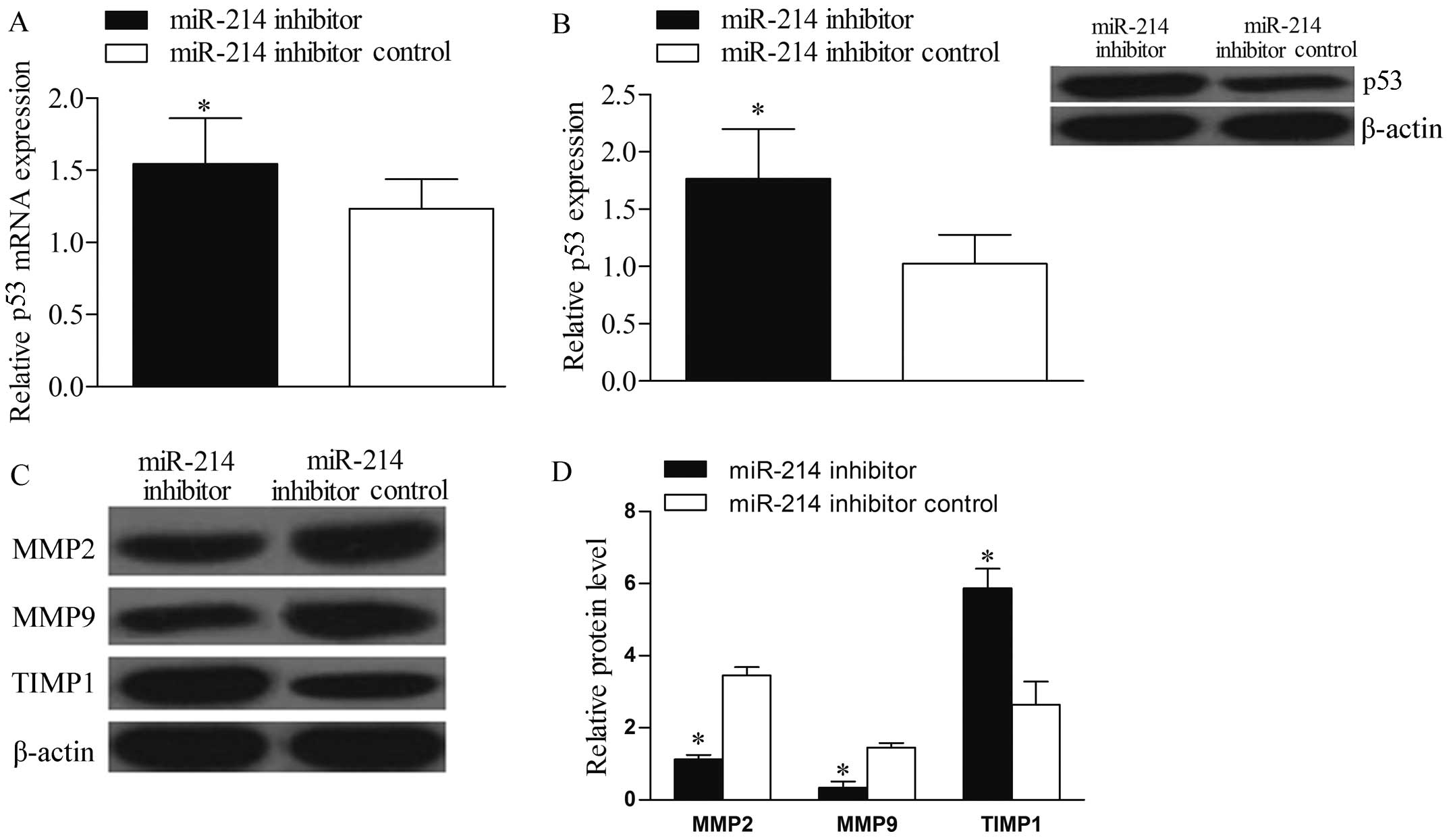
4
|
Thorn SR, Regnault TR, Brown LD, Rozance
PJ, Keng J, Roper M, Wilkening RB, Hay WW Jr and Friedman JE:
Intrauterine growth restriction increases fetal hepatic
gluconeogenic capacity and reduces messenger ribonucleic acid
translation initiation and nutrient sensing in fetal liver and
skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 150:3021–3030. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H,
Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR and Zhang W:
Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic
colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 6:e177452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fornari F, Milazzo M, Chieco P, et al: In
hepatocellular carcinoma miR-519d is up-regulated by p53 and DNA
hypomethylation and targets CDKN1A/p21, PTEN, AKT3 and TIMP2. J
Pathol. 227:275–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. MicroRNA Cancer Regulation. Springer;
pp. 1–20. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Volinia S, Galasso M, Sana ME, Wise TF,
Palatini J, Huebner K and Croce CM: Breast cancer signatures for
invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:3024–3029. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q and
Yin Y: Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show
significantly different biological patterns: From functions to
targets. PLoS One. 5:52010.
|
|
10
|
Tang J, Ahmad A and Sarkar FH: The role of
microRNAs in breast cancer migration, invasion and metastasis. Int
J Mol Sci. 13:13414–13437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He ML, Luo MX, Lin MC and Kung HF:
MicroRNAs: Potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for
EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1825:1–10. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Fei B, Wang Q, et al:
MicroRNA-638 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and regulates
cell cycle by targeting tetraspanin 1 in human colorectal
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:12083–12096. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Gao W, Hu F, Xu Z and Wang F:
MicroRNA-874 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human breast cancer by targeting CDK9. FEBS Lett. 588:4527–4535.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou SW, Su BB, Zhou Y, Feng YQ, Guo Y,
Wang YX, Qi P and Xu S: Aberrant miR-215 expression is associated
with clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. Med Oncol.
31:2592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Penna E, Orso F, Cimino D, et al:
microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour progression through
suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 30:1990–2007. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shih TC, Tien YJ, Wen CJ, Yeh TS, Yu MC,
Huang CH, Lee YS, Yen TC and Hsieh SY: MicroRNA-214 downregulation
contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the
hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J Hepatol.
57:584–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z and Cai H, Lin L, Tang M and Cai H:
Upregulated expression of microRNA-214 is linked to tumor
progression and adverse prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:206–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yin G, Chen R, Alvero AB, Fu HH, Holmberg
J, Glackin C, Rutherford T and Mor G: TWISTing stemness,
inflammation and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells
through MIR199A2/214. Oncogene. 29:3545–3553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Narducci MG, Arcelli D, Picchio MC, et al:
MicroRNA profiling reveals that miR-21, miR486 and miR-214 are
upregulated and involved in cell survival in Sézary syndrome. Cell
Death Dis. 2:e1512011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang Z, Chen S, Luan X, Li Y, Liu M, Li X,
Liu T and Tang H: MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical
cancers and inhibits the growth of HeLa cells. IUBMB Life.
61:1075–1082. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang XJ, Ye H, Zeng CW, He B, Zhang H and
Chen YQ: Dysregulation of miR-15a and miR-214 in human pancreatic
cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 3:462010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duan Q, Wang X, Gong W, Ni L, Chen C, He
X, Chen F, Yang L, Wang P and Wang DW: ER stress negatively
modulates the expression of the miR-199a/214 cluster to regulates
tumor survival and progression in human hepatocellular cancer. PLoS
One. 7:e315182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schwarzenbach H, Milde-Langosch K,
Steinbach B, Müller V and Pantel K: Diagnostic potential of
PTEN-targeting miR-214 in the blood of breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:933–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu M, Yao J, Carroll DK, et al: Regulation
of in situ to invasive breast carcinoma transition. Cancer Cell.
13:394–406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Furlan A, Vercamer C, Bouali F, Damour I,
Chotteau-Lelievre A, Wernert N, Desbiens X and Pourtier A: Ets-1
controls breast cancer cell balance between invasion and growth.
Int J Cancer. 135:2317–2328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jaafar H, Sharif SE and Murtey MD: Pattern
of collagen fibers and localization of matrix metalloproteinase 2
and 9 during breast cancer invasion. Tumori. 100:e204–e211.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye ZB, Ma G, Zhao YH, et al: miR-429
inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro.
Int J Oncol. 46:531–538. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Meng Y, Zou Q, Liu T, Cai X, Huang Y and
Pan J: microRNA-335 inhibits proliferation, cell-cycle progression,
colony formation, and invasion via targeting PAX6 in breast cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:379–385. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Hidaka H, Yoshino H, Enokida H, et al:
Tumor-suppressive miR-135a inhibits cancer cell proliferation by
targeting the c-MYC oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
189:e1902013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Baumjohann D, Kageyama R, Clingan JM, et
al: 16: MIR-17~92 promotes T follicular helper cell differentiation
and represses subset-inappropriate gene expression. Cytokine.
63:246–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou Y, Xiong M, Niu J, Sun Q, Su W, Zen
K, Dai C and Yang J: Secreted fibroblast-derived miR-34a induces
tubular cell apoptosis in fibrotic kidney. J Cell Sci.
127:4494–4506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao M, Huang J, Gui K, Xiong M, Cai G, Xu
J, Wang K, Liu D, Zhang X and Yin W: The downregulation of miR-144
is associated with the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma cells
through the regulation of TAGLN expression. Int J Mol Med.
34:1565–1572. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Misiewicz-Krzeminska I, Sarasquete ME,
Quwaider D, et al: Restoration of microRNA-214 expression reduces
growth of myeloma cells through positive regulation of P53 and
inhibition of DNA replication. Haematologica. 98:640–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Walerych D, Napoli M, Collavin L and Del
Sal G: The rebel angel: Mutant p53 as the driving oncogene in
breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:2007–2017. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Olivier M, Hollstein M and Hainaut P: TP53
mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical
use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0010082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lane D and Levine A: p53 Research: The
past thirty years and the next thirty years. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 2:a0008932010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lam S, Wiercinska E, Teunisse AF, Lodder
K, ten Dijke P and Jochemsen AG: Wild-type p53 inhibits
pro-invasive properties of TGF-β3 in breast cancer, in part through
regulation of EPHB2, a new TGF-β target gene. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 148:7–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Noh S, Jung JJ, Jung M, Kim KH, Lee HY,
Wang B, Cho J, Kim TS, Jeung HC and Rha SY: Body fluid MMP-2 as a
putative biomarker in metastatic breast cancer. Oncol Lett.
3:699–703. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Gao Y, Ma M, Li M, Zou D, Yang J,
Zhu Z and Zhao X: Effect of miR-21 on renal fibrosis by regulating
MMP-9 and TIMP1 in kk-ay diabetic nephropathy mice. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 67:537–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Piva R, Spandidos DA and Gambari R: From
microRNA functions to microRNA therapeutics: Novel targets and
novel drugs in breast cancer research and treatment (Review). Int J
Oncol. 43:985–994. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|