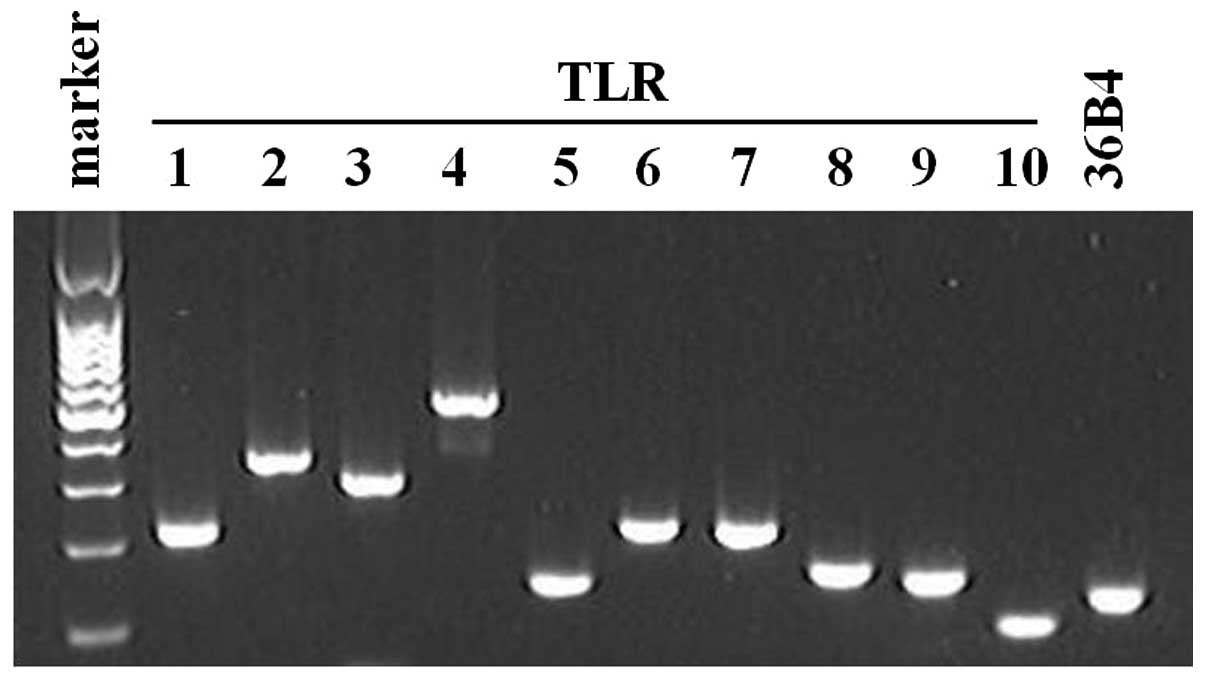
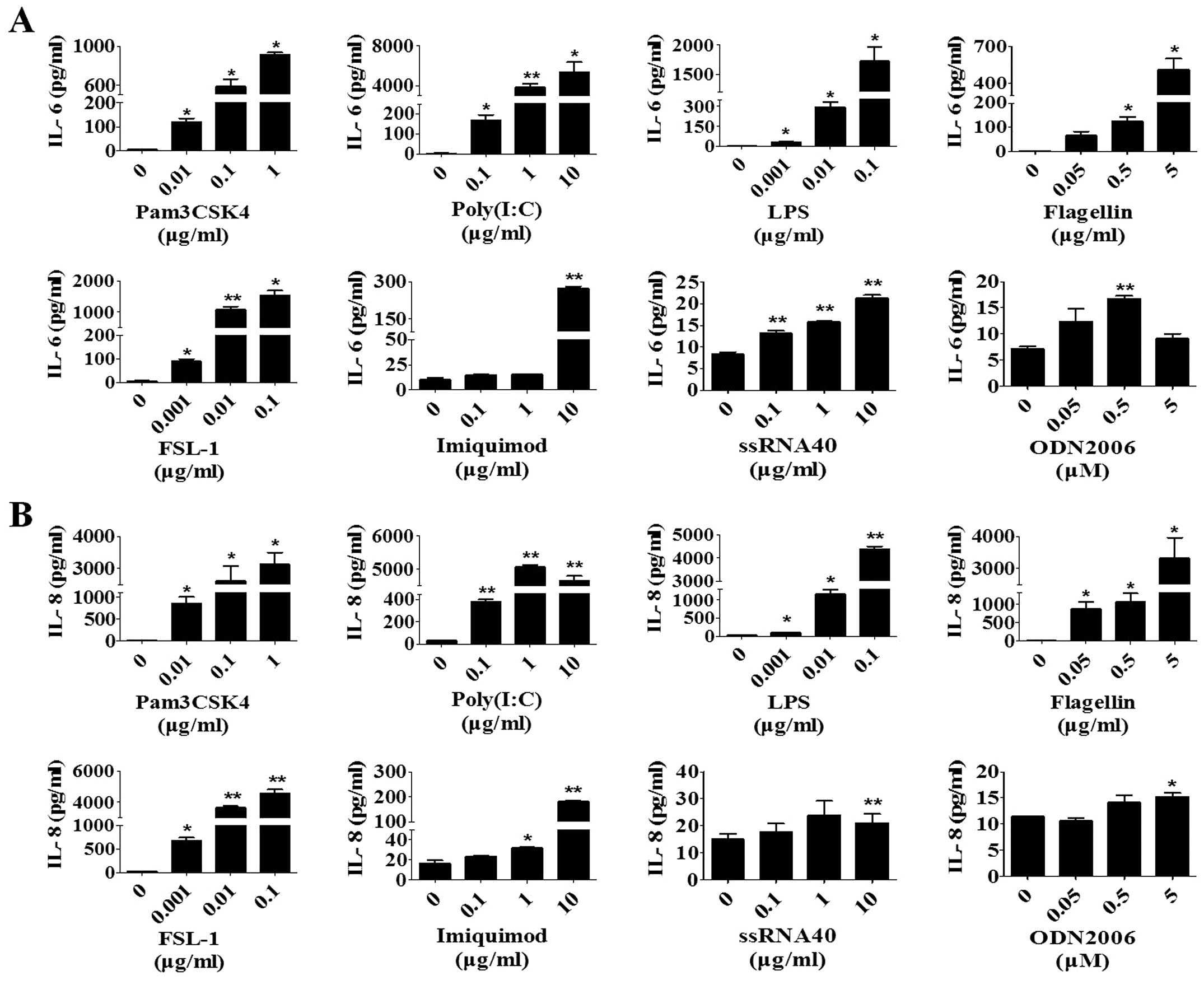
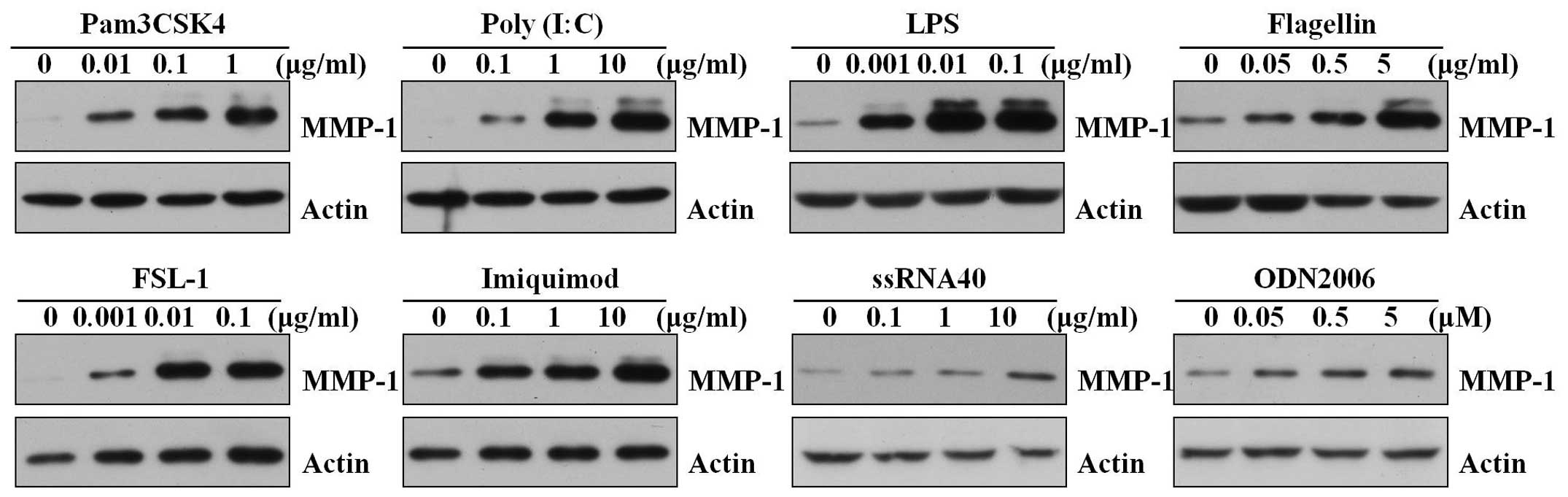
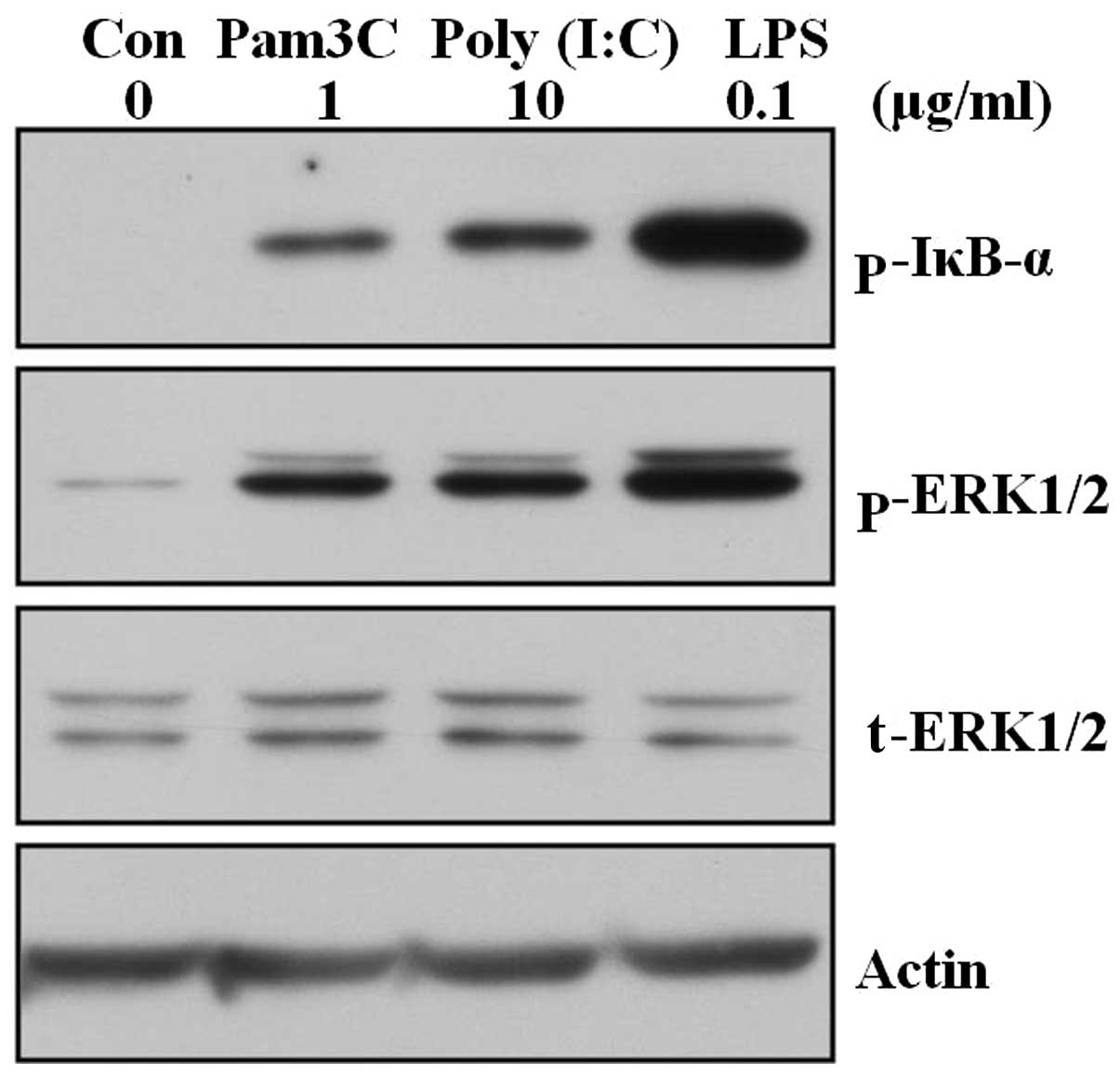
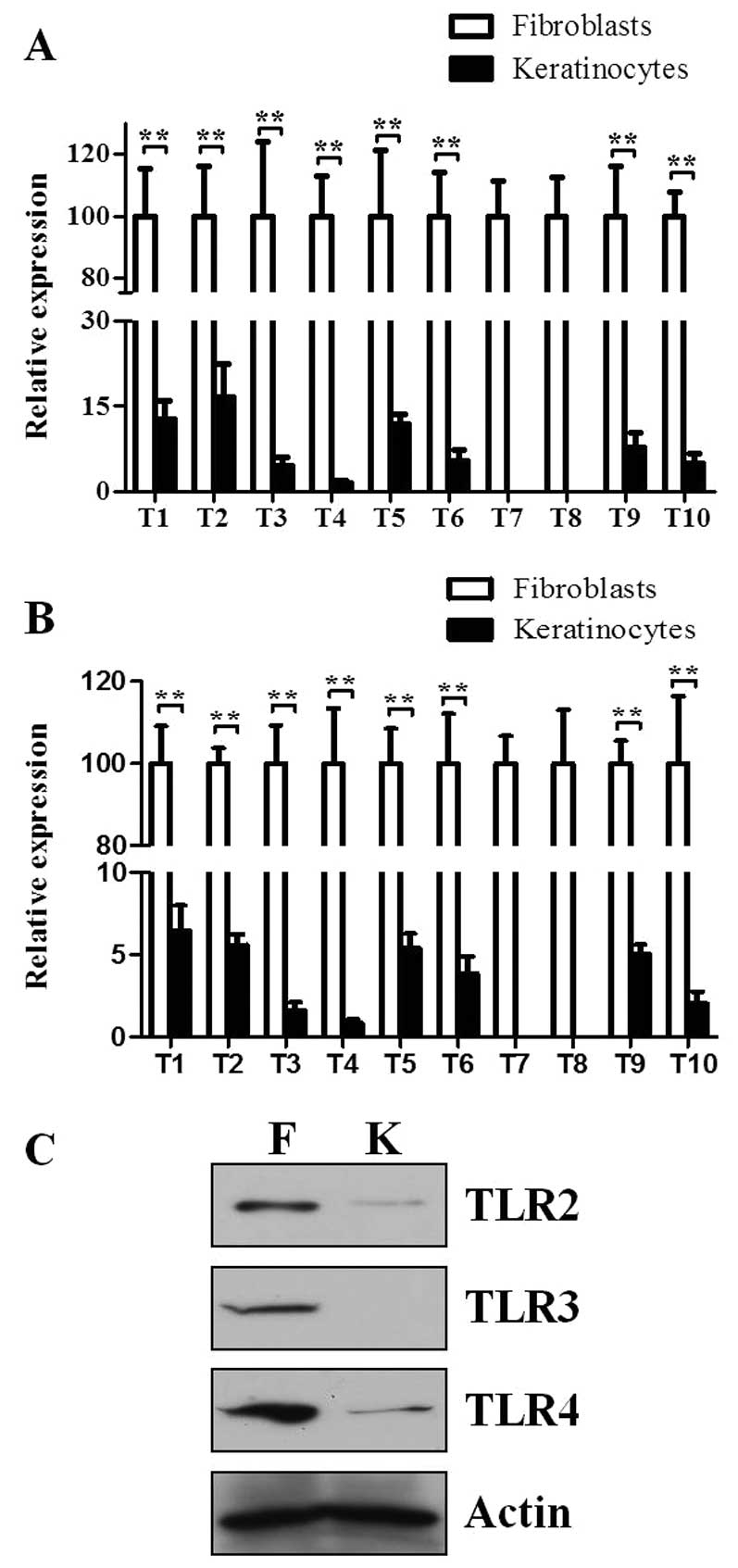
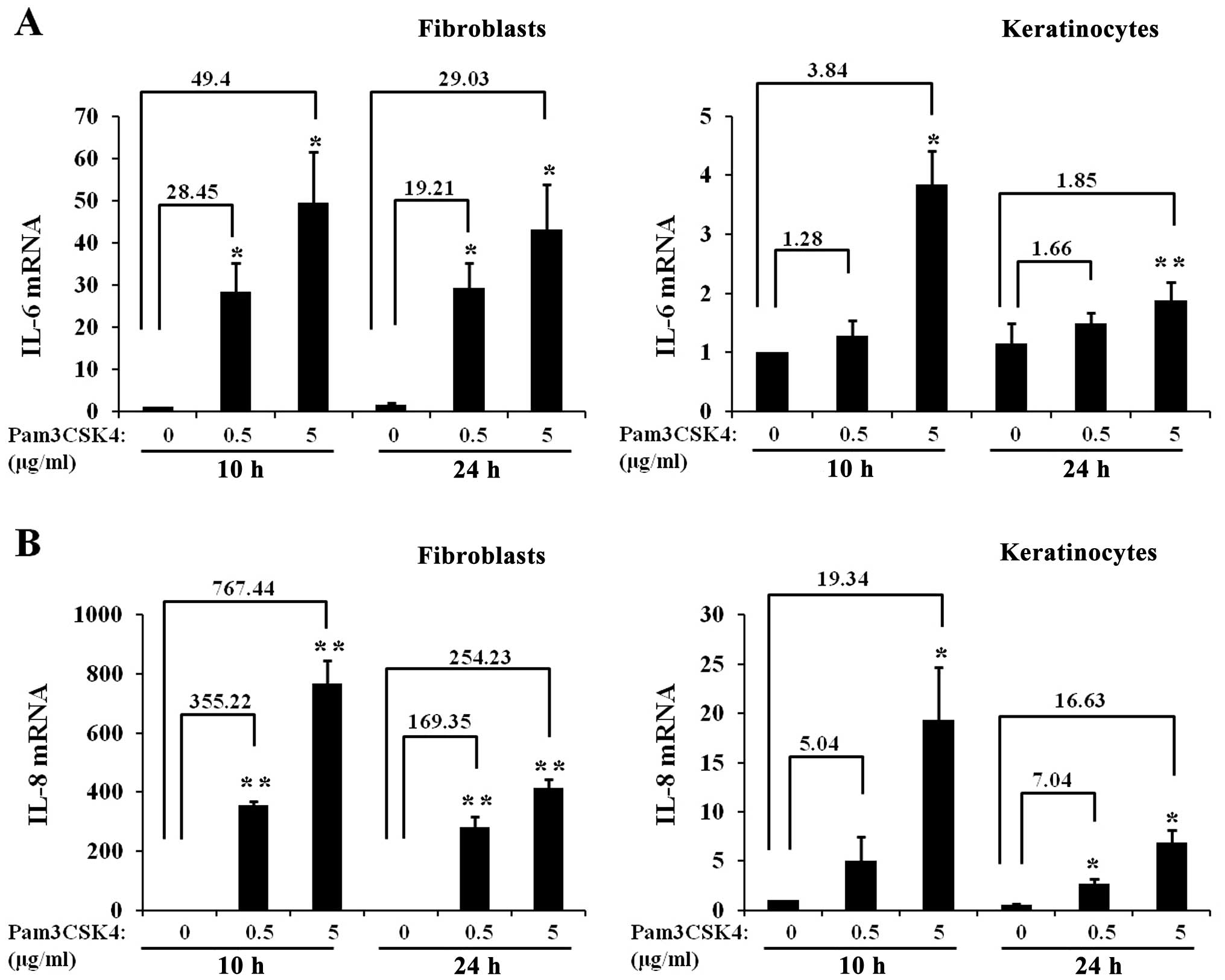
|
1
|
Akira S, Takeda K and Kaisho T: Toll-like
receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity.
Nat Immunol. 2:675–680. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 17:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Takeuchi O, Kaufmann A, Grote K, et al:
Cutting edge: preferentially the R-stereoisomer of the mycoplasmal
lipopeptide macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2 activates immune
cells through a toll-like receptor 2- and MyD88-dependent signaling
pathway. J Immunol. 164:554–557. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeuchi O, Sato S, Horiuchi T, et al:
Cutting edge: role of Toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune
response to microbial lipoproteins. J Immunol. 169:10–14. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Muhlradt PF, et al:
Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6.
Int Immunol. 13:933–940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R and
Flavell RA: Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of
NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 413:732–738. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tapping RI, Akashi S, Miyake K, Godowski
PJ and Tobias PS: Toll-like receptor 4, but not toll-like receptor
2, is a signaling receptor for Escherichia and Salmonella
lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 165:5780–5787. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, et al: The
innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by
Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 410:1099–1103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, et al:
Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like
receptor 7 and 8. Science. 303:1526–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, et al: A
Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 408:740–745.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sloane JA, Blitz D, Margolin Z and
Vartanian T: A clear and present danger: endogenous ligands of
Toll-like receptors. Neuromolecular Med. 12:149–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Calderwood SK, Mambula SS and Gray PJ Jr:
Extracellular heat shock proteins in cell signaling and immunity.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1113:28–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bernard JJ, Cowing–Zitron C, Nakatsuji T,
et al: Ultraviolet radiation damages self noncoding RNA and is
detected by TLR3. Nat Med. 18:1286–1290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sasai M and Yamamoto M: Pathogen
recognition receptors: ligands and signaling pathways by Toll-like
receptors. Int Rev Immunol. 32:116–133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Flacher V, Bouschbacher M, Verronese E, et
al: Human Langerhans cells express a specific TLR profile and
differentially respond to viruses and Gram-positive bacteria. J
Immunol. 177:7959–7967. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lebre MC, van der Aar AM, van Baarsen L,
et al: Human keratinocytes express functional Toll-like receptor 3,
4, 5, and 9. J Invest Dermatol. 127:331–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu N, Zhang S, Zuo F, Kang K, Guan M and
Xiang L: Cultured human melanocytes express functional toll-like
receptors 2–4, 7 and 9. J Dermatol Sci. 56:113–120. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jang S, Park JS, Won YH, Yun SJ and Kim
SJ: The expression of toll-like receptors (TLRs) in cultured human
skin fibroblast is modulated by histamine. Chonnam Med J. 48:7–14.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Hori K, Ding J, et al: Toll-like
receptors expressed by dermal fibroblasts contribute to
hypertrophic scarring. J Cell Physiol. 226:1265–1273. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee Y, Kim H, Kim S, Kim KH and Chung JH:
Activation of toll-like receptors 2, 3 or 5 induces matrix
metalloproteinase-1 and -9 expression with the involvement of MAPKs
and NF-kappaB in human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol.
19:e44–e49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
McMillan SJ, Kearley J, Campbell JD, et
al: Matrix metallopro-teinase-9 deficiency results in enhanced
allergen-induced airway inflammation. J Immunol. 172:2586–2594.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YM, Li WH, Kim YK, Kim KH and Chung
JH: Heat-induced MMP-1 expression is mediated by TRPV1 through
PKCalpha signaling in HaCaT cells. Exp Dermatol. 17:864–870. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kollisch G, Kalali BN, Voelcker V, et al:
Various members of the Toll-like receptor family contribute to the
innate immune response of human epidermal keratinocytes.
Immunology. 114:531–541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rittié L and Fisher GJ: UV-light-induced
signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res Rev. 1:705–720. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fisher GJ, Wang ZQ, Datta SC, Varani J,
Kang S and Voorhees JJ: Pathophysiology of premature skin aging
induced by ultraviolet light. N Engl J Med. 337:1419–1428. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang XY, Tao CJ, Wu QY and Yuan CD:
Protein extract of ultraviolet-irradiated human skin keratinocytes
promote the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinases,
nuclear factor-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor-3 in
Langerhans cells via Toll-like receptor 2 and 4. Photodermatol
Photoimmunol Photomed. 29:41–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vabulas RM, Ahmad-Nejad P, da Costa C, et
al: Endocytosed HSP60s use toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 to
activate the toll/interleukin-1 receptor signaling pathway in
innate immune cells. J Biol Chem. 276:31332–31339. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Libermann TA and Baltimore D: Activation
of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B
transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 10:2327–2334. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Elliott CL, Allport VC, Loudon JA, Wu GD
and Bennett PR: Nuclear factor-kappa B is essential for
up-regulation of interleukin-8 expression in human amnion and
cervical epithelial cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 7:787–790. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G and Brown K:
Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell
Biol. 10:405–455. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu-Bryan R, Scott P, Sydlaske A, Rose DM
and Terkeltaub R: Innate immunity conferred by Toll-like receptors
2 and 4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 expression is pivotal
to monosodium urate monohydrate crystal-induced inflammation.
Arthritis Rheum. 52:2936–2946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS,
et al: Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth
factor-beta responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and
amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol. 182:192–205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Niebuhr M, Baumert K and Werfel T:
TLR-2-mediated cytokine and chemokine secretion in human
keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 19:873–877. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Meisgen F, Xu Landen N, Wang A, et al:
MiR-146a negatively regulates TLR2-induced inflammatory responses
in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1931–1940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|