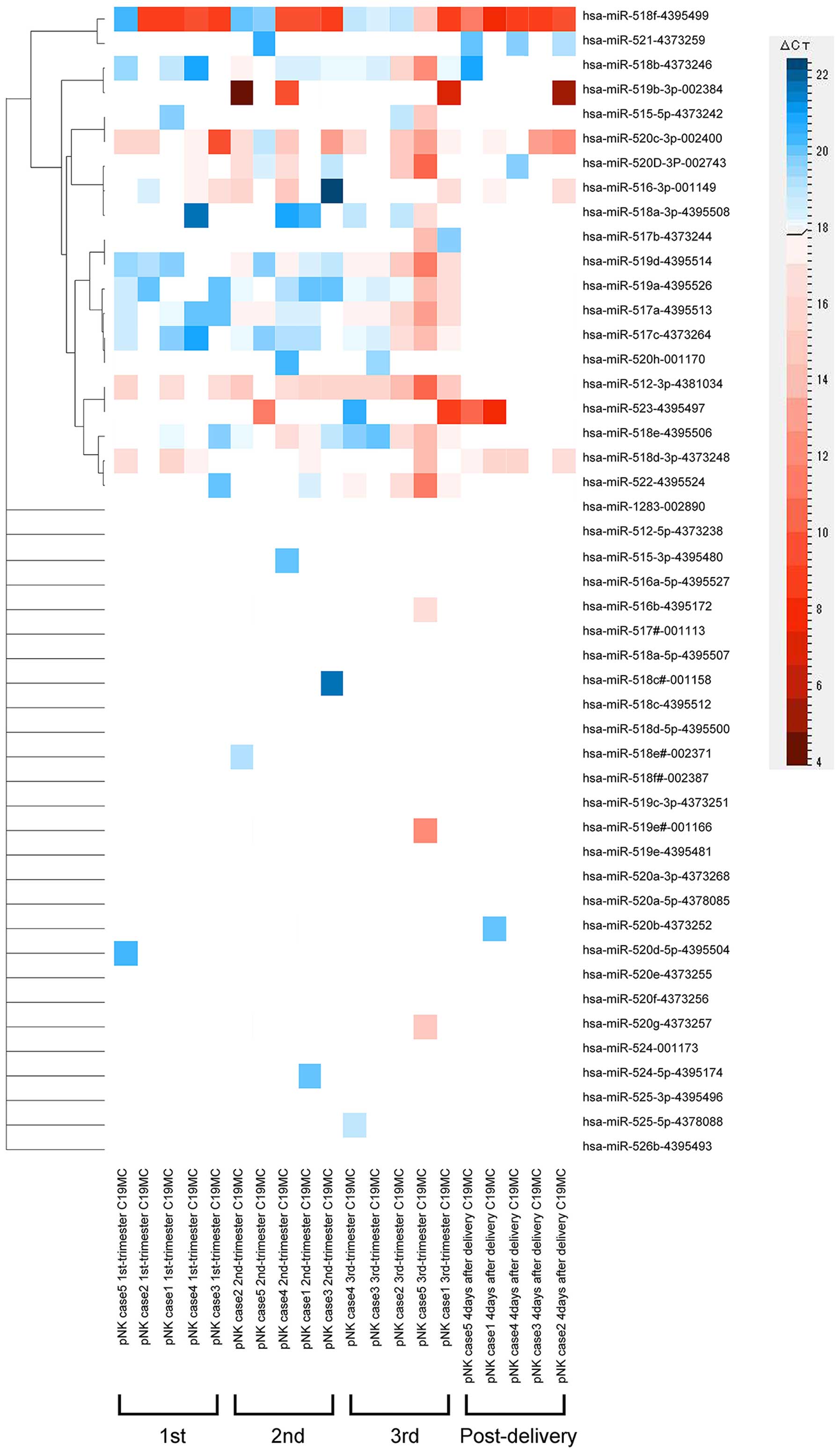
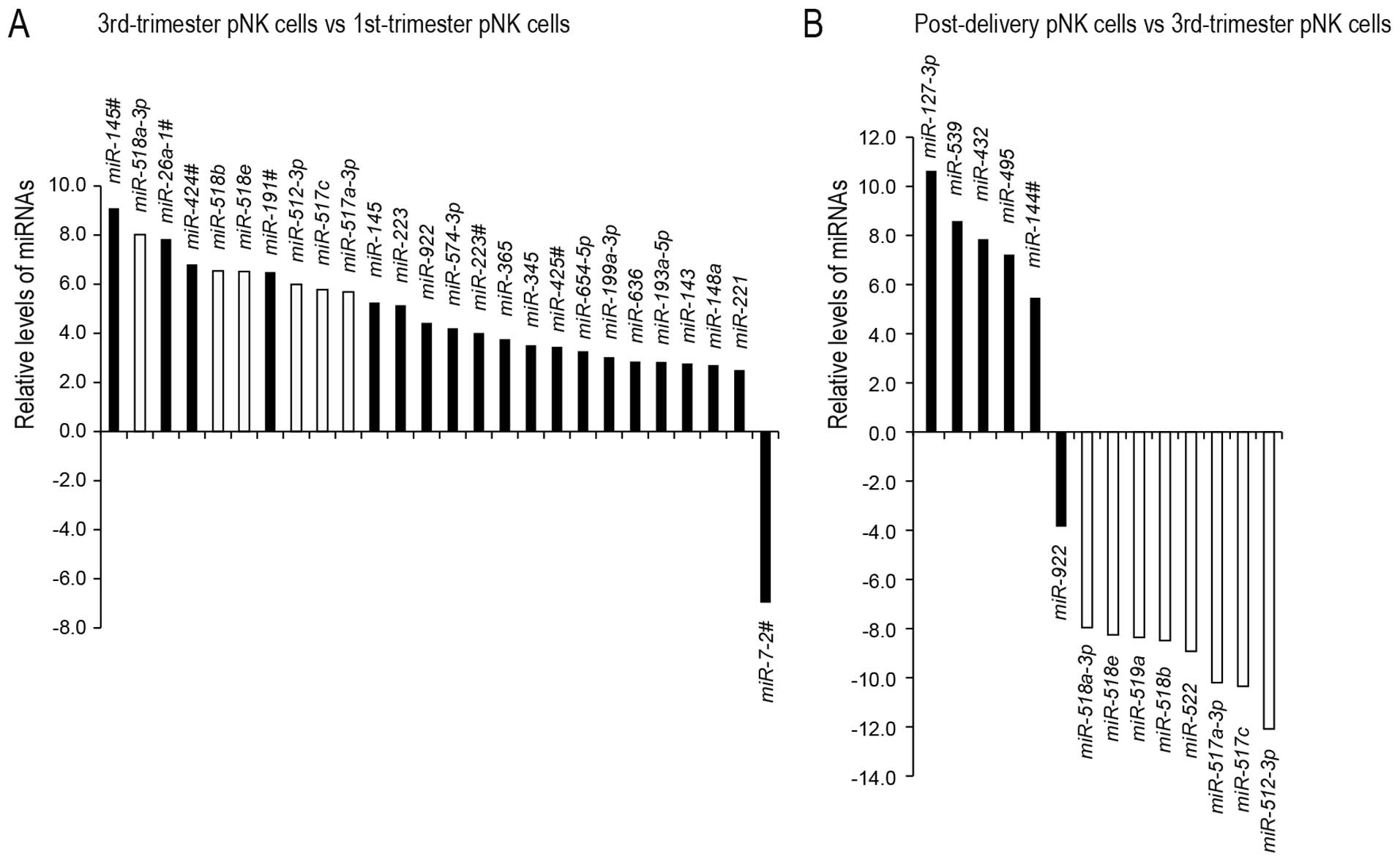
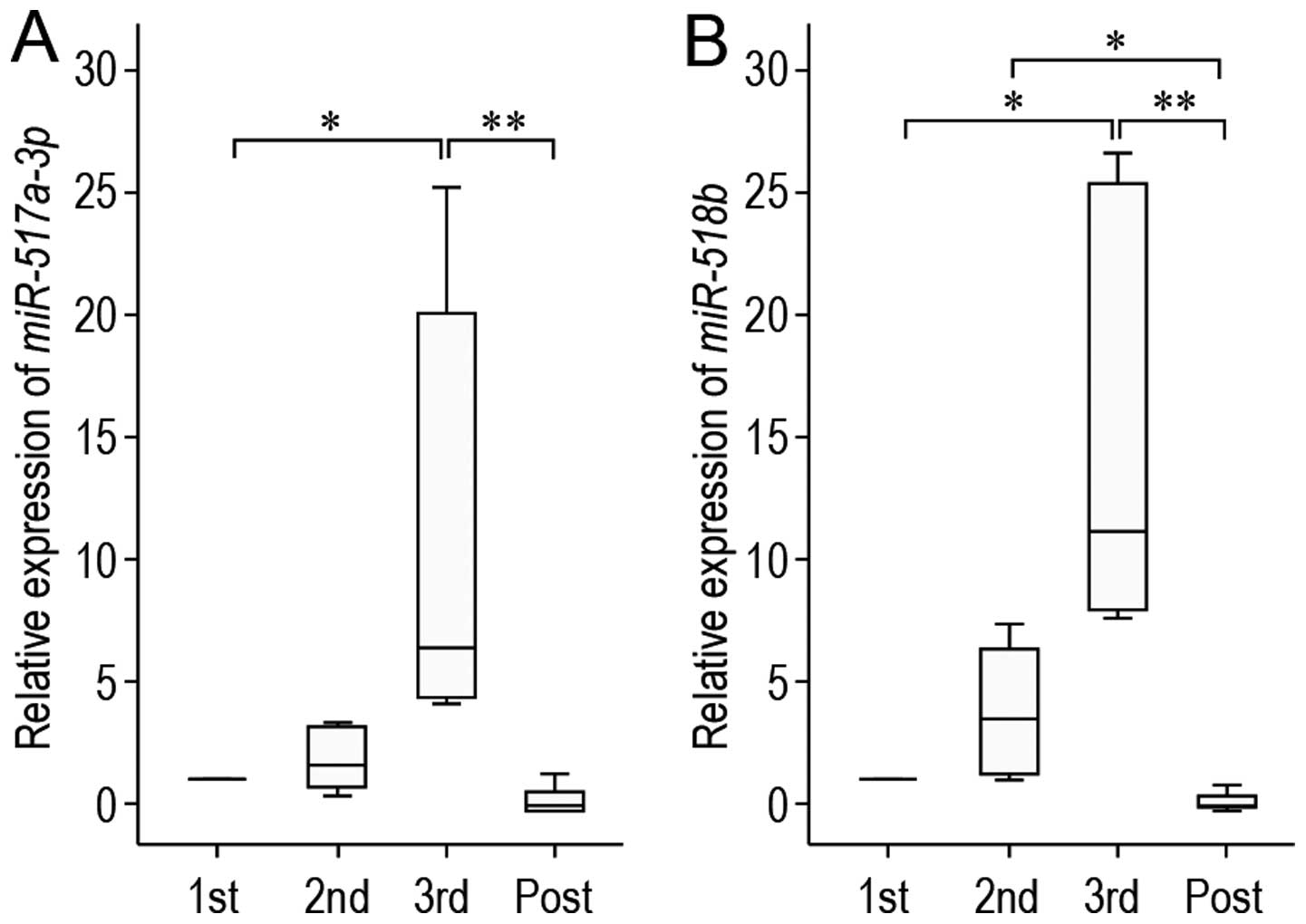
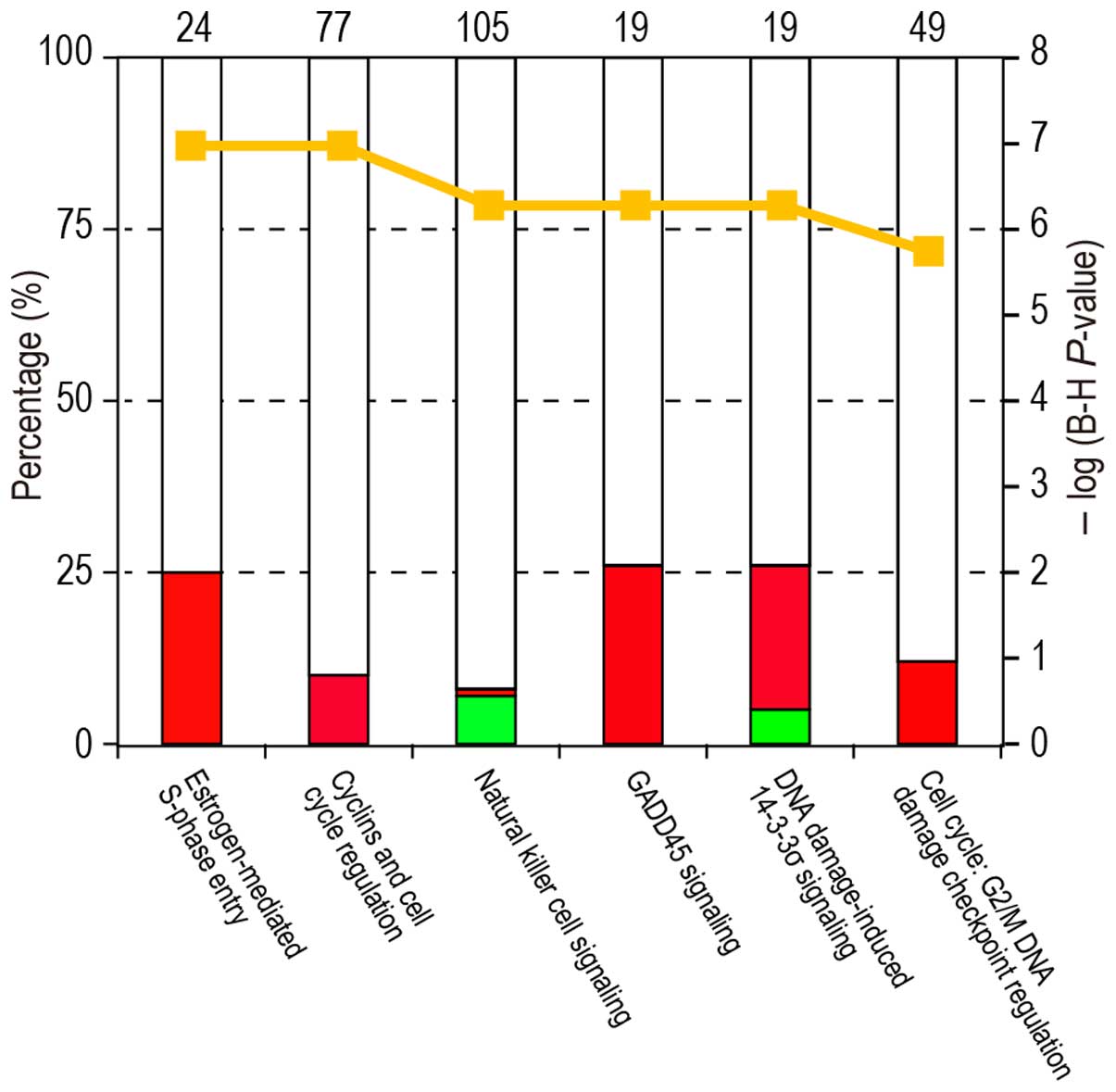
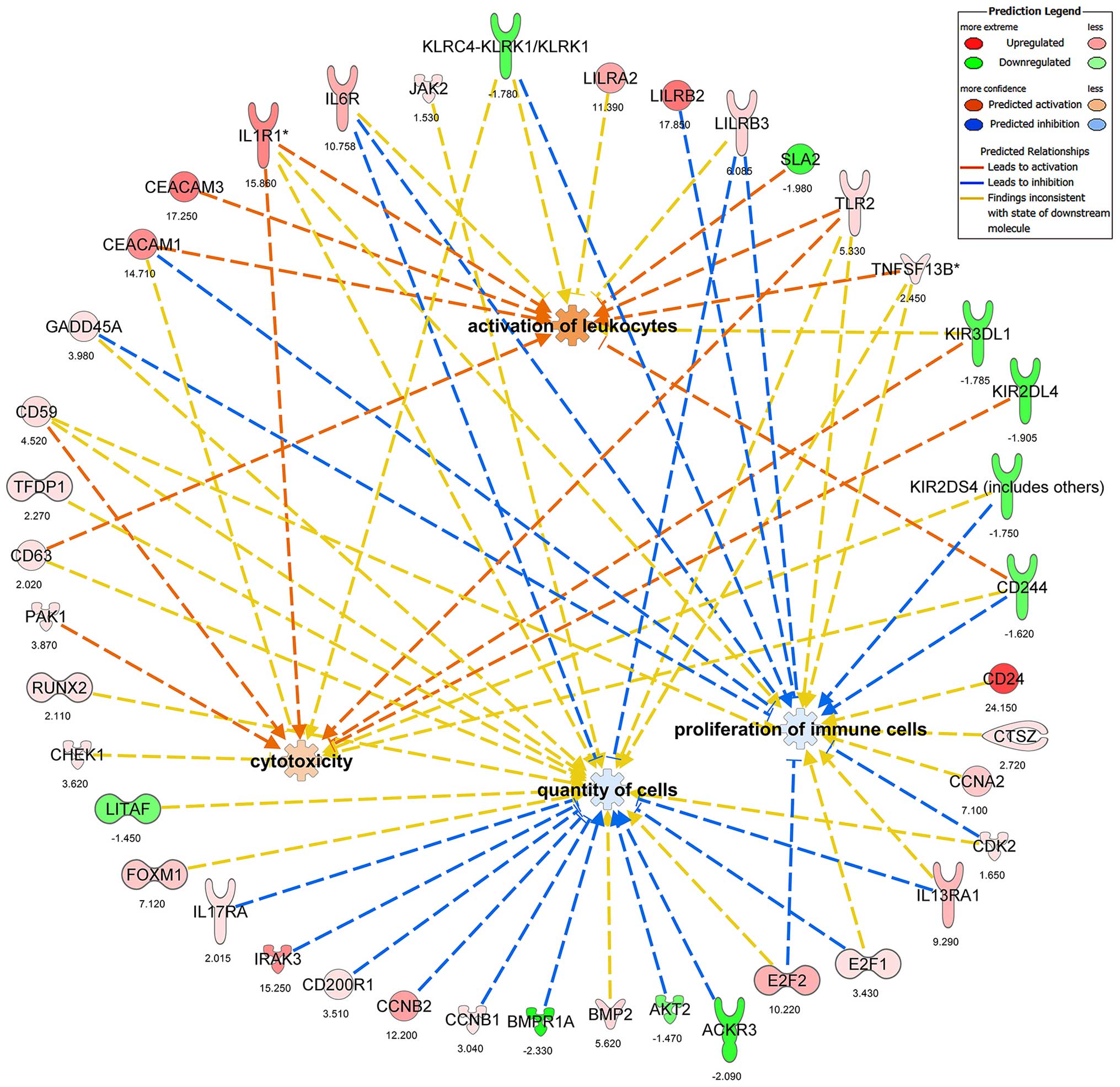
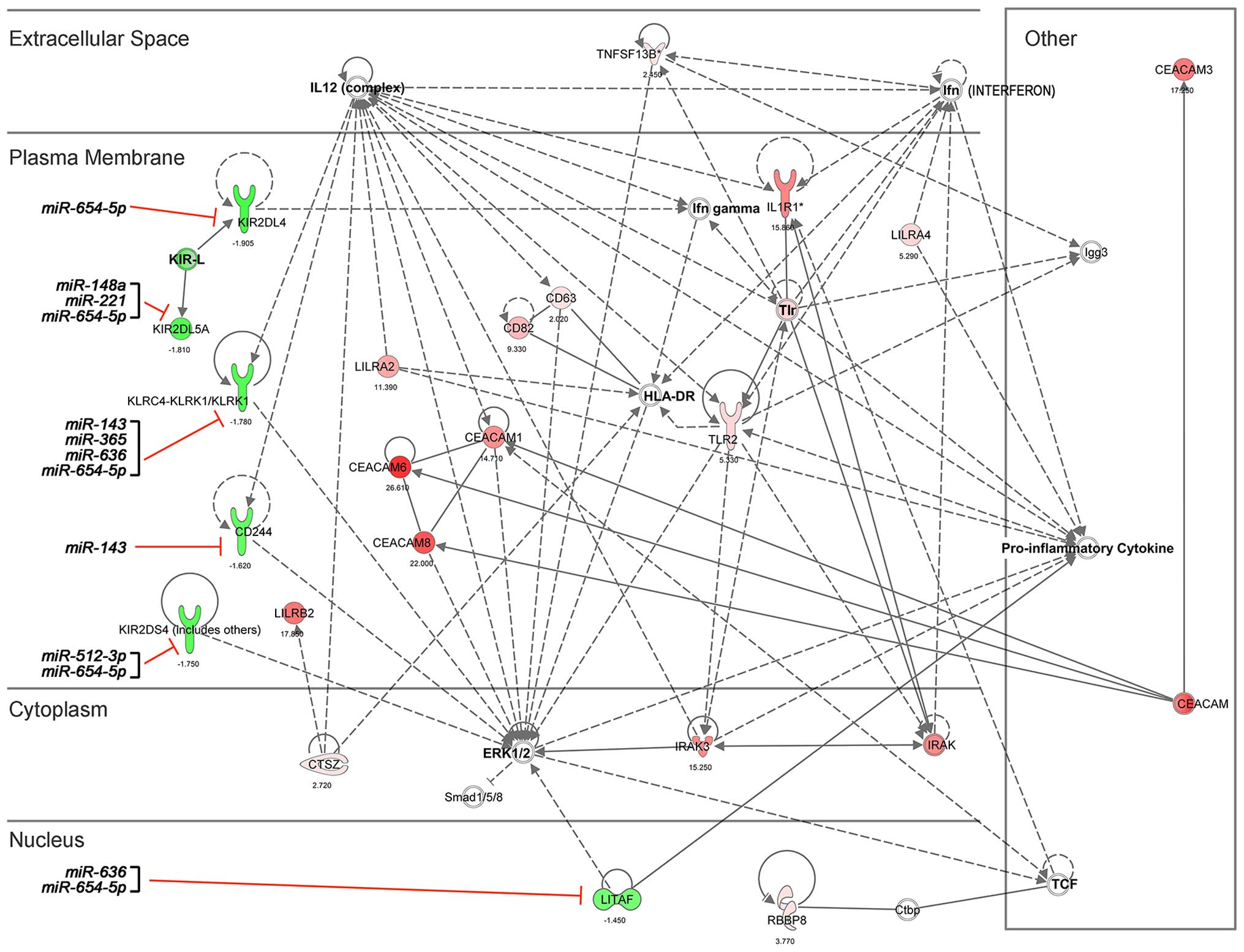
|
1
|
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T
and Ugolini S: Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol.
9:503–510. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vivier E, Raulet DH, Moretta A, Caligiuri
MA, Zitvogel L, Lanier LL, Yokoyama WM and Ugolini S: Innate or
adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science.
331:44–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carrega P and Ferlazzo G: Natural killer
cell distribution and trafficking in human tissues. Front Immunol.
3:3472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kalkunte S, Chichester CO, Gotsch F,
Sentman CL, Romero R and Sharma S: Evolution of non-cytotoxic
uterine natural killer cells. Am J Reprod Immunol. 59:425–432.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Santoni A, Carlino C, Stabile H and
Gismondi A: Mechanisms underlying recruitment and accumulation of
decidual NK cells in uterus during pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol.
59:417–424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moffett A and Colucci F: Uterine NK cells:
Active regulators at the maternal-fetal interface. J Clin Invest.
124:1872–1879. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hedlund M, Stenqvist AC, Nagaeva O,
Kjellberg L, Wulff M, Baranov V and Mincheva-Nilsson L: Human
placenta expresses and secretes NKG2D ligands via exosomes that
down-modulate the cognate receptor expression: Evidence for
immunosuppressive function. J Immunol. 183:340–351. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rossi RL, Rossetti G, Wenandy L, Curti S,
Ripamonti A, Bonnal RJ, Birolo RS, Moro M, Crosti MC, Gruarin P, et
al: Distinct microRNA signatures in human lymphocyte subsets and
enforcement of the naive state in CD4+ T cells by the
microRNA miR-125b. Nat Immunol. 12:796–803. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Allantaz F, Cheng DT, Bergauer T,
Ravindran P, Rossier MF, Ebeling M, Badi L, Reis B, Bitter H,
DAsaro M, et al: Expression profiling of human immune cell subsets
identifies miRNA-mRNA regulatory relationships correlated with cell
type specific expression. PLoS One. 7:e299792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Gu Y, Zhang Q, Han Y, Hou J, Lin
L, Wu C, Bao Y, Su X, Jiang M, et al: Identification of resting and
type I IFN-activated human NK cell miRNomes reveals microRNA-378
and microRNA-30e as negative regulators of NK cell cytotoxicity. J
Immunol. 189:211–221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Wang Y, Sun Q, Yan J, Huang J, Zhu
S and Yu J: Identification of microRNA transcriptome involved in
human natural killer cell activation. Immunol Lett. 143:208–217.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kambe S, Yoshitake H, Yuge K, Ishida Y,
Ali MM, Takizawa T, Kuwata T, Ohkuchi A, Matsubara S, Suzuki M, et
al: Human exosomal placenta-associated miR-517a-3p modulates the
expression of PRKG1 mRNA in Jurkat cells. Biol Reprod. 91:1292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dybkaer K, Iqbal J, Zhou G, Geng H, Xiao
L, Schmitz A, d’Amore F and Chan WC: Genome wide transcriptional
analysis of resting and IL2 activated human natural killer cells:
Gene expression signatures indicative of novel molecular signaling
pathways. BMC Genomics. 8:2302007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morales-Prieto DM, Ospina-Prieto S,
Schmidt A, Chaiwangyen W and Markert UR: Elsevier Trophoblast
Research Award Lecture: Origin, evolution and future of placenta
miRNAs. Placenta. 35(Suppl): pp. S39–S45. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noguer-Dance M, Abu-Amero S, Al-Khtib M,
Lefèvre A, Coullin P, Moore GE and Cavaillé J: The primate-specific
microRNA gene cluster (C19MC) is imprinted in the placenta. Hum Mol
Genet. 19:3566–3582. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo SS, Ishibashi O, Ishikawa G, Ishikawa
T, Katayama A, Mishima T, Takizawa T, Shigihara T, Goto T, Izumi A,
et al: Human villous trophoblasts express and secrete
placenta-specific microRNAs into maternal circulation via exosomes.
Biol Reprod. 81:717–729. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taylor DD, Akyol S and Gercel-Taylor C:
Pregnancy-associated exosomes and their modulation of T cell
signaling. J Immunol. 176:1534–1542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Doisneau-Sixou SF, Sergio CM, Carroll JS,
Hui R, Musgrove EA and Sutherland RL: Estrogen and antiestrogen
regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 10:179–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Curran EM, Berghaus LJ, Vernetti NJ,
Saporita AJ, Lubahn DB and Estes DM: Natural killer cells express
estrogen receptor-alpha and estrogen receptor-beta and can respond
to estrogen via a non-estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated pathway.
Cell Immunol. 214:12–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van den Heuvel MJ, Xie X, Tayade C,
Peralta C, Fang Y, Leonard S, Paffaro VA Jr, Sheikhi AK, Murrant C
and Croy BA: A review of trafficking and activation of uterine
natural killer cells. Am J Reprod Immunol. 54:322–331. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yusa S, Catina TL and Campbell KS: SHP-1-
and phosphotyrosine-independent inhibitory signaling by a killer
cell Ig-like receptor cytoplasmic domain in human NK cells. J
Immunol. 168:5047–5057. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu SX, Kappel LW, Charbonneau-Allard AM,
Atallah R, Holland AM, Turbide C, Hubbard VM, Rotolo JA, Smith M,
Suh D, et al: Ceacam1 separates graft-versus-host-disease from
graft-versus-tumor activity after experimental allogeneic bone
marrow transplantation. PLoS One. 6:e216112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Kaer L: Regulation of immune responses
by CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells. Immunol Res. 30:139–153.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ueda N, Kuki H, Kamimura D, Sawa S, Seino
K, Tashiro T, Fushuku K, Taniguchi M, Hirano T and Murakami M:
CD1d-restricted NKT cell activation enhanced homeostatic
proliferation of CD8+ T cells in a manner dependent on
IL-4. Int Immunol. 18:1397–1404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li D, Wang L, Yu L, Freundt EC, Jin B,
Screaton GR and Xu XN: Ig-like transcript 4 inhibits lipid antigen
presentation through direct CD1d interaction. J Immunol.
182:1033–1040. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ujike A, Takeda K, Nakamura A, Ebihara S,
Akiyama K and Takai T: Impaired dendritic cell maturation and
increased T(H)2 responses in PIR-B(−/−) mice. Nat Immunol.
3:542–548. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA:
The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol.
22:633–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jabrane-Ferrat N and Siewiera J: The up
side of decidual natural killer cells: New developments in
immunology of pregnancy. Immunology. 141:490–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Joncker NT, Shifrin N, Delebecque F and
Raulet DH: Mature natural killer cells reset their responsiveness
when exposed to an altered MHC environment. J Exp Med.
207:2065–2072. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Elliott JM, Wahle JA and Yokoyama WM: MHC
class I-deficient natural killer cells acquire a licensed phenotype
after transfer into an MHC class I-sufficient environment. J Exp
Med. 207:2073–2079. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Beaulieu AM, Bezman NA, Lee JE, Matloubian
M, Sun JC and Lanier LL: MicroRNA function in NK-cell biology.
Immunol Rev. 253:40–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leong JW, Sullivan RP and Fehniger TA:
microRNA management of NK developmental and functional programs.
Eur J Immunol. 44:2862–2868. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|