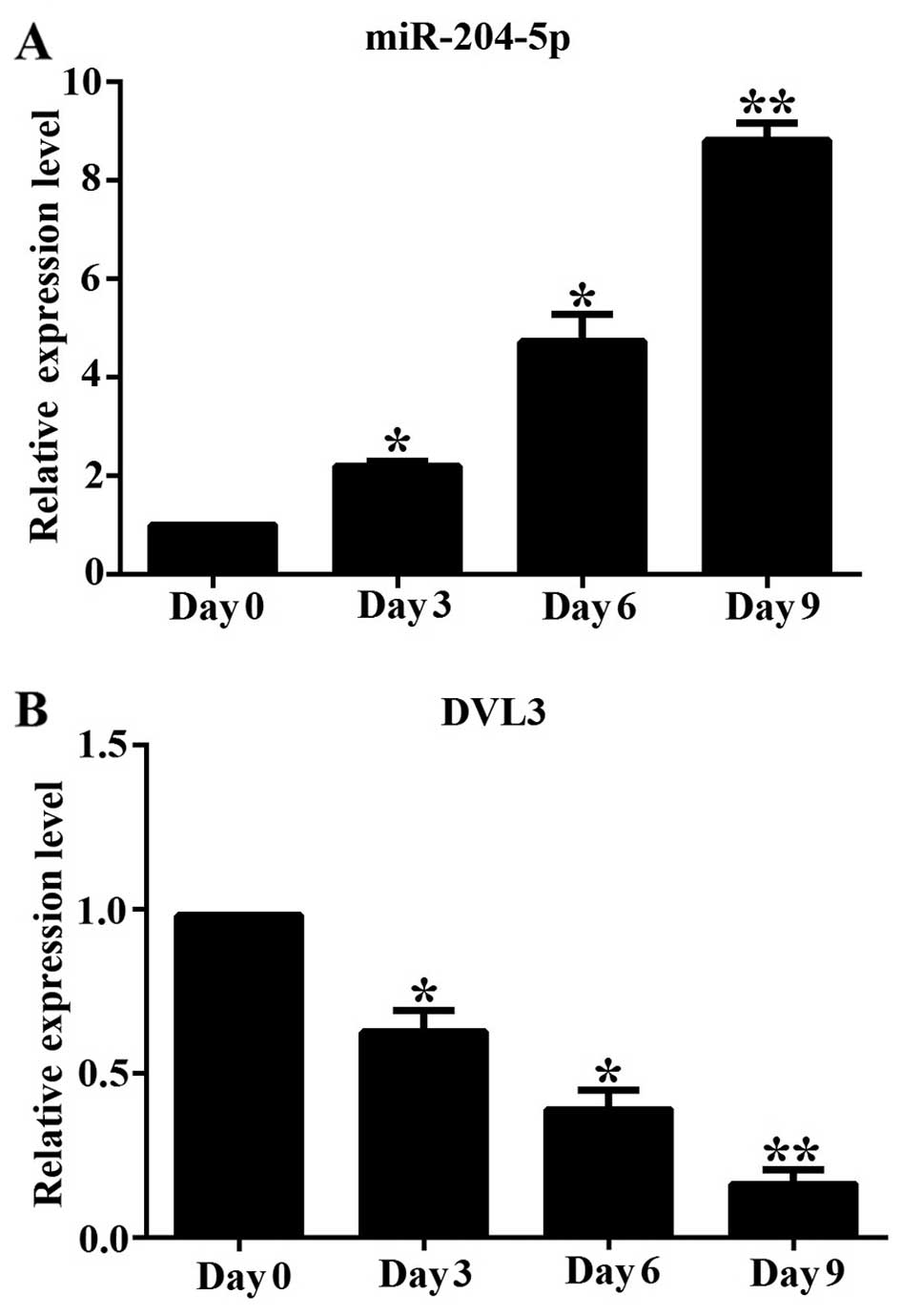
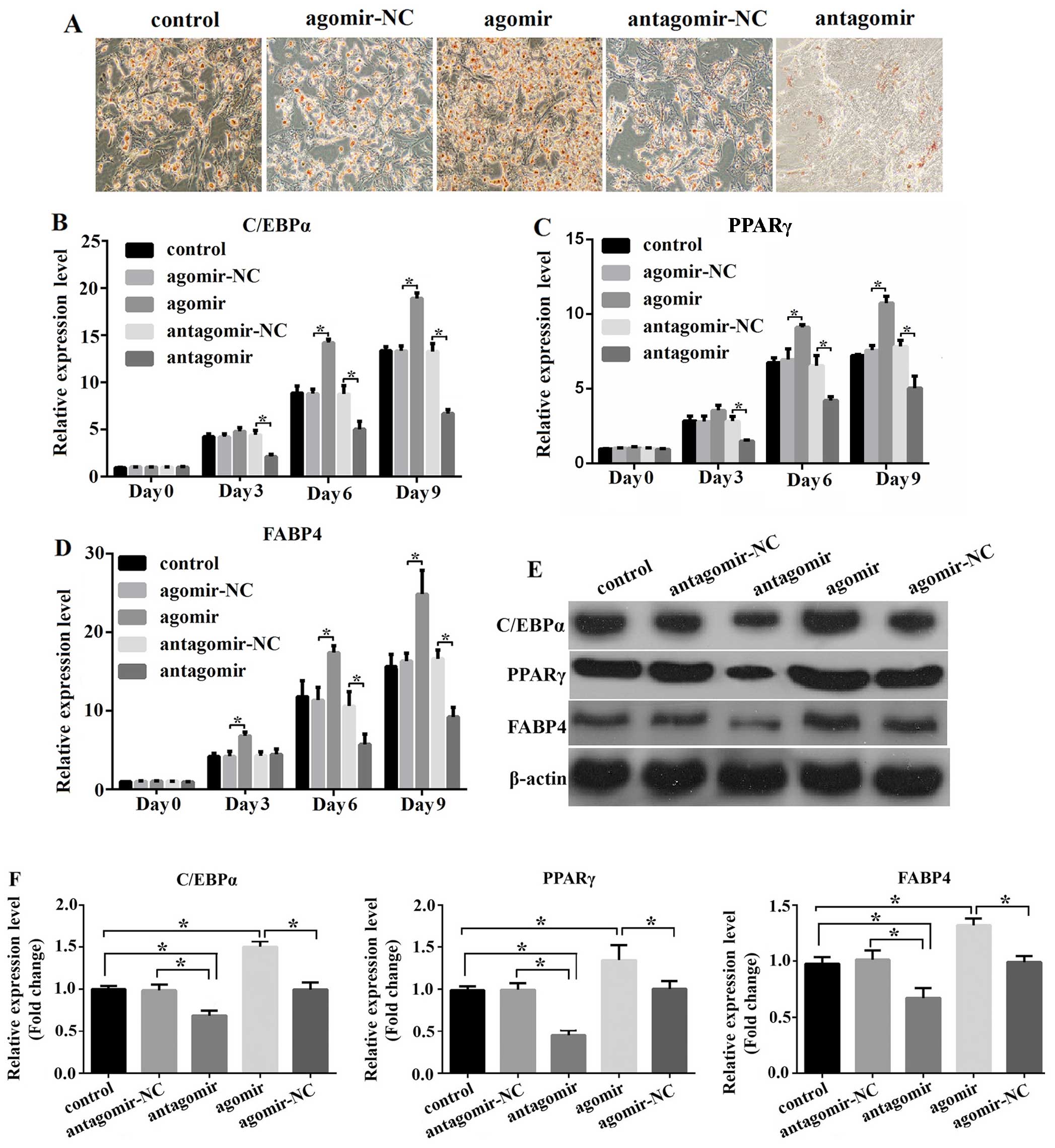
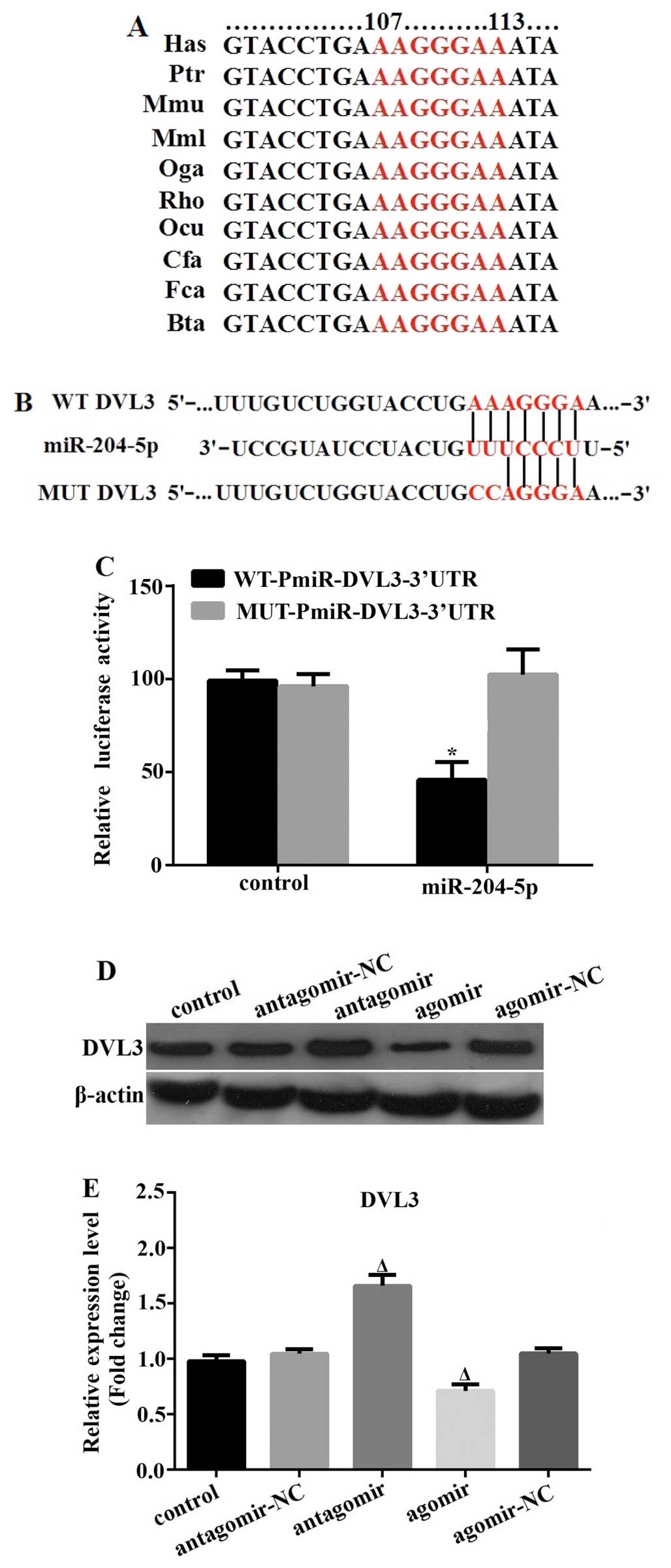
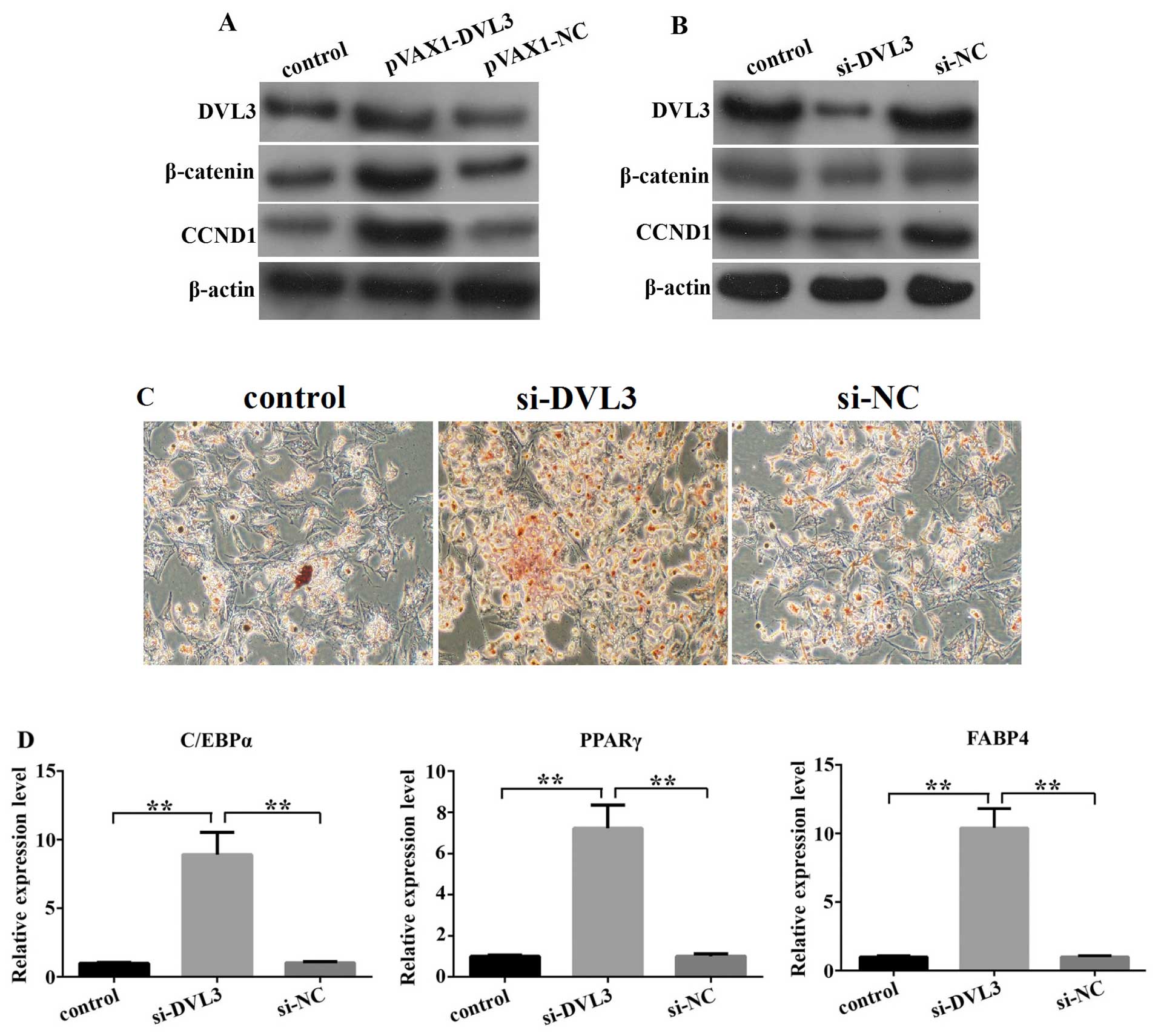
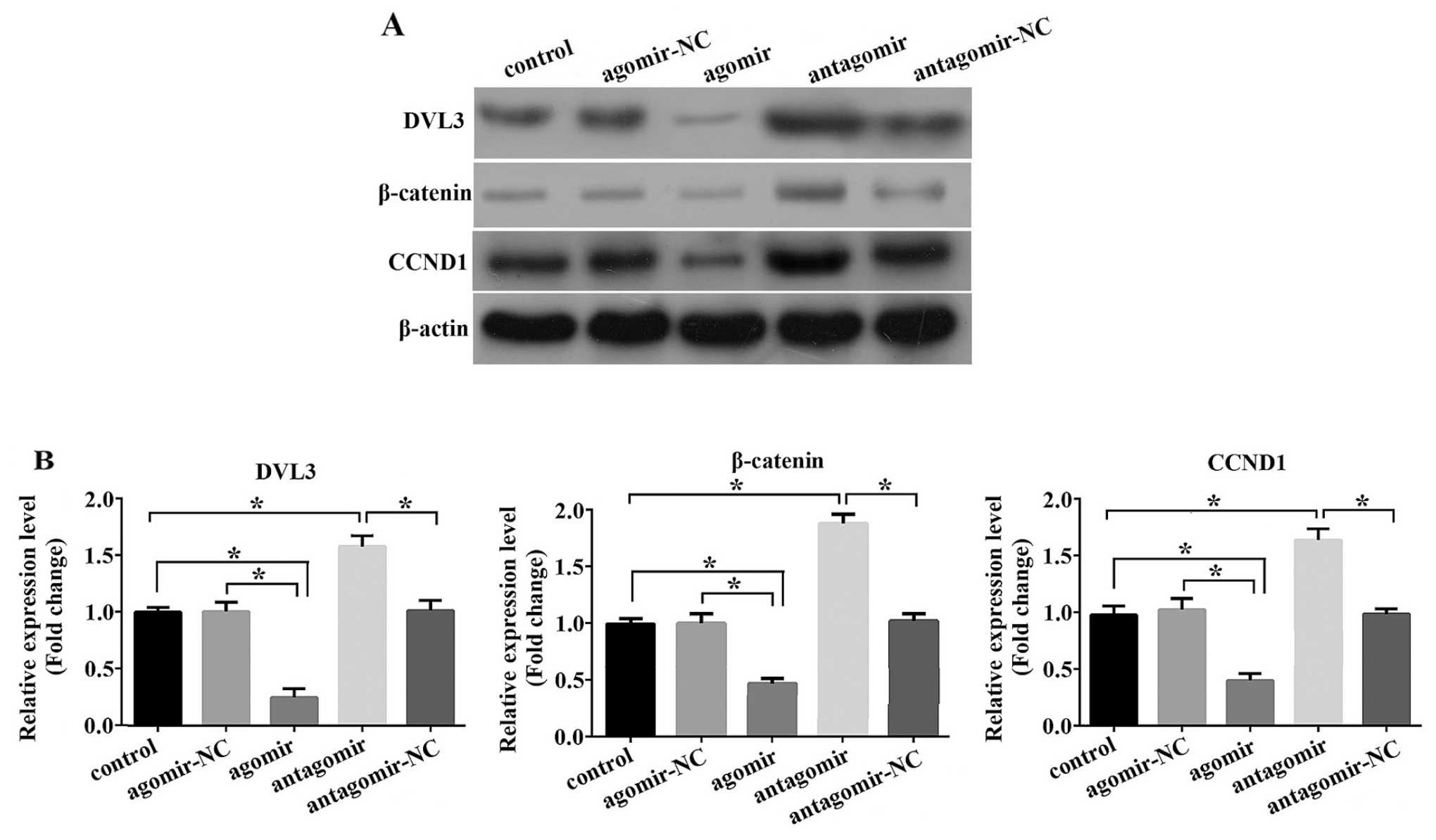
|
1
|
Kanuri G and Bergheim I: In vitro and in
vivo models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Int J Mol
Sci. 14:11963–11980. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung YY, Yoon T, Yang WK, Moon BC and Kim
HK: Anti-obesity effects of Actinidia polygama extract in mice with
high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol Med Rep. 7:396–400. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Ma J, Jiang Z, He S, Liu Y, Chen L, Long
K, Jin L, Jiang A, Zhu L, Wang J, Li M and Li X: Intrinsic features
in microRNA transcriptomes link porcine visceral rather than
subcutaneous adipose tissues tometabolic risk. PLoS One.
8:e800412013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Song G, Xu G, Ji C, Shi C, Shen Y, Chen L,
Zhu L, Yang L, Zhao Y and Guo X: The role of microRNA-26b in human
adipocyte differentiation and proliferation. Gene. 10:481–487.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen L, Song J, Cui J, Hou J, Zheng X, Li
C and Liu L: microRNAs regulate adipocyte differentiation. Cell
Biol Int. 37:533–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karbiener M, Neuhold C, Oprriessnig P,
Prokesch A, Bogner- Strauss JG and Scheideler M: MicroRNA-30c
promotes human adipocyte differentiation and co-represses PAI-1 and
ALK2. RNA Biol. 8:850–860. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Q, Li YC, Wang J, Kong J, Qi Y, Quigg
RJ and Li X: miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte
differentiation by negatively regulating tumor-suppressor Rb2/p130.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 26:2889–2894. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee EK, Lee MJ, Abdelmohsen K, Kim W, Kim
MM, Srikantan S, Martindale JL, Hutchison ER, Kim HH, Marasa BS,
Selimyan R, Egan JM, Smith SR, Fried SK and Gorospe M: miR-130
suppresses adipogenesis by inhibiting peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression. Mol Cell Biol.
31:626–638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee HW, Son YH, Lee GY,
Lee JW, Lee YS and Kim JB: miR-27a is a negative regulator of
adipocyte differentiation via suppressing PPARgamma expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:323–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, Sousa KM,
Krishnan V and MacDougald OA: Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte
gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
299:E198–E206. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martinelli R, Nardelli C, Pilone V,
Buonomo T, Liguori R, Castanò I, Buono P, Masone S, Persico G,
Forestieri P, Pastore L and Sacchetti L: miR-519d overexpression is
associated with human obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring).
18:2170–2176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC and Jung JS:
MiR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation
of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stemcells derived from human
adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 27:3093–3102. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kennell JA, Gerin I, MacDougald OA and
Cadigan KM: The microRNA miR-8 is a conserved negative regulator of
Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15417–1522. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen H, Wang S, Chen L, Chen Y, Wu M,
Zhang Y, Yu K, Huang Z, Qin L and Mo D: MicroRNA-344 inhibits
3T3-L1 cell differentiation via targeting GSK3β of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 588:429–435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Qin L, Chen Y, Niu Y, Chen W, Wang Q, Xiao
S, Li A, Xie Y, Li J, Zhao X, He Z and Mo D: A deep investigation
into the adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating
adipogenesis by modulating the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. BMC Genomics. 11:3202010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Christodoulides C, Lagathu C, Sethi JK and
Vidal-Puig A: Adipogenesis and WNT signaling. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 20:16–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang J, Zhao L, Xing L and Chen D:
MicroRNA-204 regulates Runx2 protein expression and mesenchymal
progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 28:357–364. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Yang X, Shang H, Katz A and Li X: A
modified aggregate culture for chondrogenesis of human
adipose-derived stem cells genetically modified with growth and
differentiation factor 5. Biores Open Access. 2:258–265. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hausman GJ, Dodson MV, Ajuwon K, Azain M,
Barnes KM, Guan LL, Jiang Z, Poulors SP, Srainz RD, Smith S,
Spurlock M, Novakofski J, Fernyhough ME and Bergen WG:
Board-invited review: the biology and regulation of preadipocytes
and adipocytes in meat animals. J Anim Sci. 87:1218–1246. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chartoumpekis DV, Zaravinos A, Ziros PG,
Iskrenova RP, Psyrogiannis AI, Kyriazopoulou VE and Habeos IG:
Differential expression of microRNAs in adipose tissue after
long-term high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. PLoS One.
7:e348722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fei J, Tamski H, Cook C and Santanam N:
MicroRNA regulation of adipose derived stem cells in aging rats.
PLoS One. 8:e592382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Gordon J, LeBlanc K,
Stein JL, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: Control of
mesenchymal lineage progression by microRNAs targeting skeletal
gene regulators Trps1 and Runx2. J Biol Chem. 22:21926–21935. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu J and Farmer SR: Regulating the
balance between peroxi-some proliferator-activated receptor gamma
andbeta-catenin signaling during adipogenesis. A glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta phosphorylation-defective mutant of beta-catenin
inhibits expression of a subset of adipogenic genes. J Biol Chem.
22:45020–45027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN,
Lucas PC, Erickson RL and MacDougald OA: Inhibition of adipogenesis
by Wnt signaling. Science. 11:950–953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lee H, Kang R, Bae S and Yoon Y: AICAR, an
activator of AMPK, inhibits adipogenesis via the WNT/β-catenin
pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Med. 28:65–71.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chan CY, Wei L, Castro-Muñozledo F and Koo
WL: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks 3T3-L1 adipose conversion
by inhibition of cell proliferation and suppression of adipose
phenotype expression. Life Sci. 21:779–785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee H, Bae S and Yoon Y: The
anti-adipogenic effects of (−)epigallocatechin gallate are
dependent on the WNT/β-catenin pathway. J Nutr Biochem.
24:1232–1240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee H, Bae S, Kim YS and Yoon Y:
WNT/β-catenin pathway mediates the anti-adipogenic effect of
platycodin D, a natural compound found in Platycodon grandiflorum.
Life Sci. 12:388–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee H, Bae S and Yoon Y: Anti-adipogenic
effects of 1,25-dihy-droxyvitamin D3 are mediated by the
maintenance of the wingless-type MMTV integration site/β-catenin
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 30:1219–1224. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lagathu C, Christodoulides C, Virtue S,
Cawthorn WP, Franzin C, Kimber WA, Nora ED, Campbell M, Medina-
Gomez G, Cheyette BN, Vidal-Puig AJ and Sethi JK: Dact1, a
nutritionally regulated preadipocyte gene, controls adipogen-esis
by coordinating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling network. Diabetes.
58:609–619. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Lee H, Kang R, Hahn Y, Yang Y, Kim SS, Cho
SH, Chung SI and Yoon Y: Anti obesity effect of baicalin involves
the modulations of proadipogenic and antiadipogenic regulators of
the adipogenesis pathway. Phytother Res. 23:1615–1623. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|