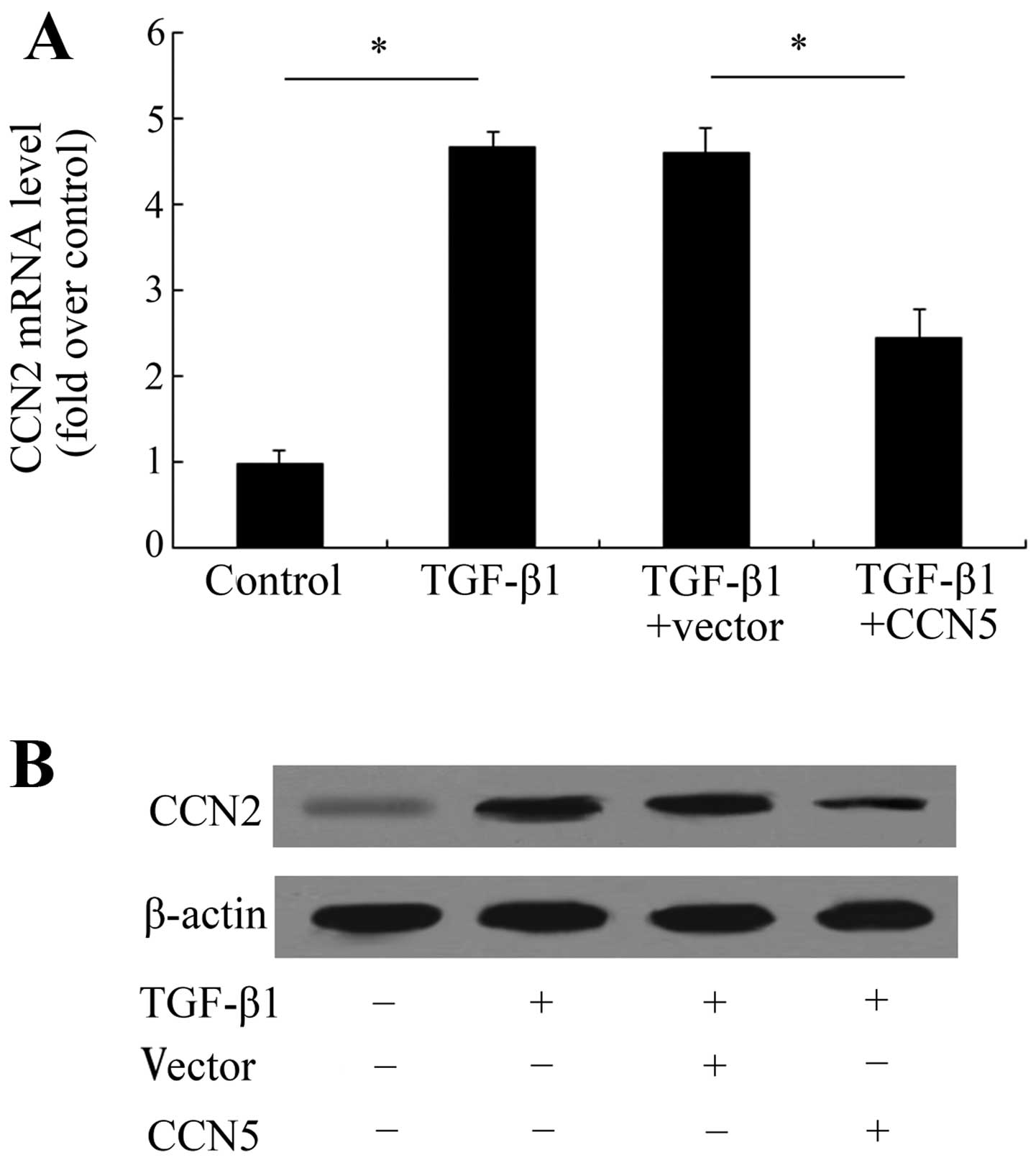
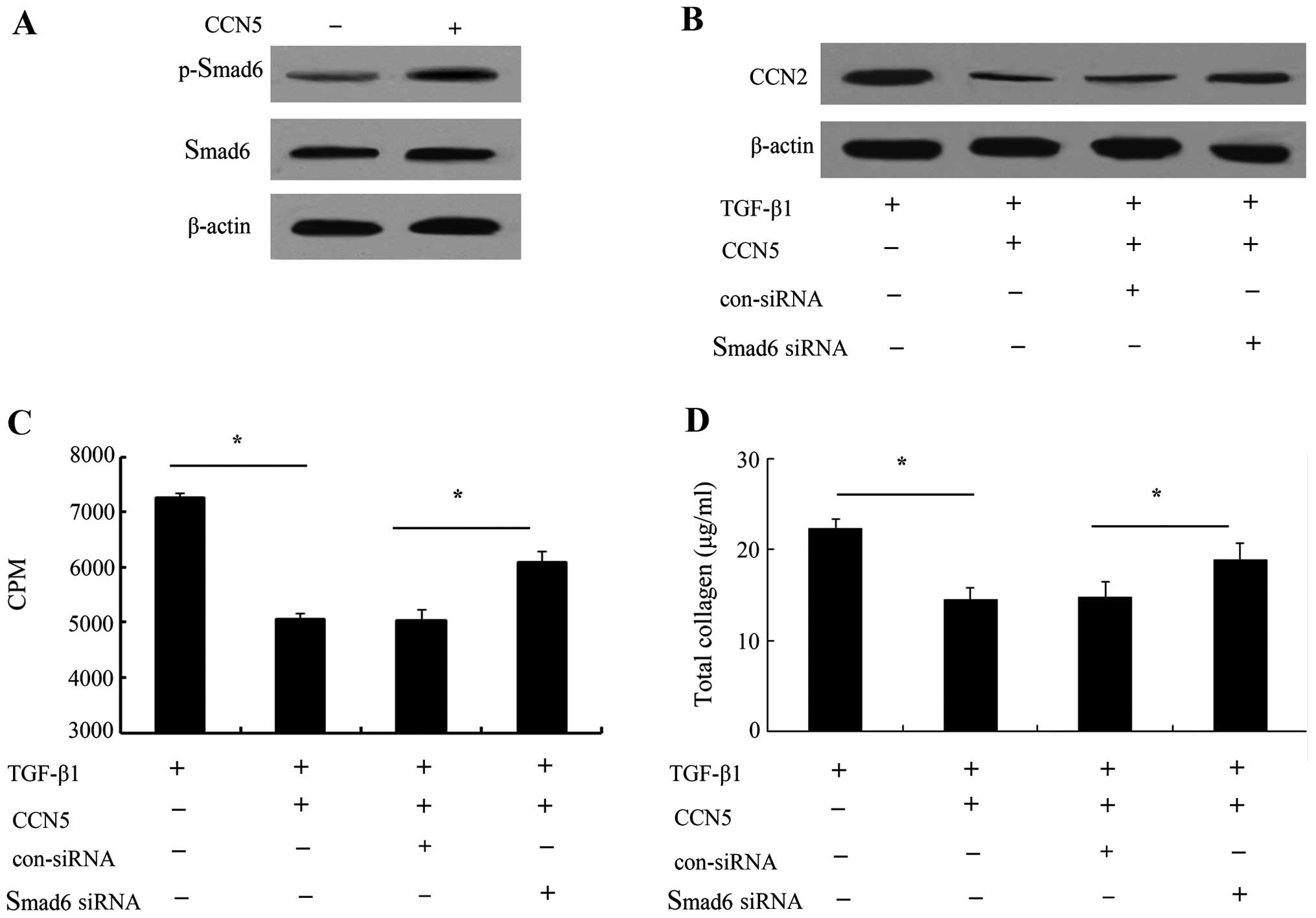
|
1
|
Bottegaro NB, Kos J, Pirkic B, et al:
Reduction of epidural fibrosis after laminectomy in rabbits by
omental free graft. Vet Med. 58:25–31. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Guo JD, Hou SX, Li L, et al: Laminectomy
and extraction of nucleus pulposus for treatment of lumbar disc
herniation: effect evaluation of over 10-year-followed-up. Zhongguo
Gu Shang. 26:24–28. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun Y, Wang L, Sun S, Liu B, Wu N and Cao
X: The effect of 10-hydroxycamptothecine in preventing fibroblast
proliferation and epidural scar adhesion after laminectomy in rats.
Eur J Pharmacol. 593:44–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang C, Kong X, Ning G, et al: All-trans
retinoic acid prevents epidural fibrosis through NF-κB signaling
pathway in post-laminectomy rats. Neuropharmacology. 79:275–281.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ray S, Ju X, Sun H, Finnerty CC, Herndon
DN and Brasier AR: The IL-6 trans-signaling-STAT3 pathway mediates
ECM and cellular proliferation in fibroblasts from hypertrophic
scar. J Invest Dermatol. 133:1212–1220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jun JI and Lau LF: The matricellular
protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis
in cutaneous wound healing. Nat Cell Biol. 12:676–685. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kular L, Pakradouni J, Kitabgi P, Laurent
M and Martinerie C: The CCN family: a new class of inflammation
modulators? Biochimie. 93:377–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen PC, Cheng HC, Yang SF, Lin CW and
Tang CH: The CCN family proteins: modulators of bone development
and novel targets in bone-associated tumors. Biomed Res Int.
2014:4370962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Minhas U, Martin TA, Ruge F, Harding KG
and Jiang WG: Pattern of expression of CCN family members Cyr61,
CTGF and NOV in human acute and chronic wounds. Exp Ther Med.
2:641–645. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sisco M, Kryger ZB, O’Shaughnessy KD, et
al: Antisense inhibition of connective tissue growth factor
(CTGF/CCN2) mRNA limits hypertrophic scarring without affecting
wound healing in vivo. Wound Repair Regen. 16:661–673. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shi-Wen X, Leask A and Abraham D:
Regulation and function of connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 in
tissue repair, scarring and fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
19:133–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lake AC, Bialik A, Walsh K and Castellot
JJ Jr: CCN5 is a growth arrest-specific gene that regulates smooth
muscle cell proliferation and motility. Am J Pathol. 162:219–231.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leask A: Yin and Yang Part Deux: CCN5
inhibits the pro-fibrotic effects of CCN2. J Cell Commun Signal.
4:155–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoon PO, Lee MA, Cha H, et al: The
opposing effects of CCN2 and CCN5 on the development of cardiac
hypertrophy and fibrosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:294–303. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang CY, Xie X, Gao DS and Zhang CX:
Effects of CCN5 overexpression on the expression of alpha-SMA and
collagen I in hepatic stellate cells and its mechanism. Zhongguo
Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 29:411–415. 2013.In Chinese.
|
|
16
|
Penn JW, Grobbelaar AO and Rolfe KJ: The
role of the TGF-β family in wound healing, burns and scarring: a
review. Int J Burns Trauma. 2:18–28. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Ichijo T, Voutetakis A, Cotrim AP, et al:
The Smad6-histone deacetylase 3 complex silences the
transcriptional activity of the glucocorticoid receptor: Potential
clinical implications. J Biol Chem. 280:42067–42077. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koźma EM, Wisowski G, Kusz D and Olczyk K:
The role of decorin and biglycan dermatan sulfate chain(s) in
fibrosis-affected fascia. Glycobiology. 21:1301–1316. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang Q, Usinger W, Nichols B, et al:
Cooperative interaction of CTGF and TGF-β in animal models of
fibrotic disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 4:42011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Imamura T, Takase M, Nishihara A, et al:
Smad6 inhibits signalling by the TGF-beta superfamily. Nature.
389:622–626. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amankwah EK, Thompson RC, Nabors LB, et
al: SWI/SNF gene variants and glioma risk and outcome. Cancer
Epidemiol. 37:162–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kasimcan MO, Bakar B, Aktaş S, Alhan A and
Yilmaz M: Effectiveness of the biophysical barriers on the
peridural fibrosis of a postlaminectomy rat model: an experimental
research. Injury. 42:778–781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karatay M, Celik H, Koktekir E, et al:
Role of tenoxicam in the prevention of postlaminectomy peridural
fibrosis in rats. J Neurol Sci. 30:559–565. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Zeinalizadeh M, Miri SM, Ardalan FA, et
al: Reduction of epidural fibrosis and dural adhesions after lamina
reconstruction by absorbable cement: an experimental study. Spine
J. 14:113–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bosscher HA and Heavner JE: Incidence and
severity of epidural fibrosis after back surgery: an endoscopic
study. Pain Practice. 10:18–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Massagué J: TGF-β signaling in development
and disease. FEBS Lett. 586:18332012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang C, Kong X, Zhou H, et al: An
experimental novel study: Angelica sinensis prevents epidural
fibrosis in laminectomy rats via downregulation of hydroxyproline,
IL-6, and TGF-β1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2918142013.
|
|
28
|
Kohta M, Kohmura E and Yamashita T:
Inhibition of TGF-beta1 promotes functional recovery after spinal
cord injury. Neurosci Res. 65:393–401. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast in wound
healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol. 200:500–503. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rujitanaroj PO, Jao B, Yang J, et al:
Controlling fibrous capsule formation through long-term
downregulation of collagen type I (COL1A1) expression by
nanofiber-mediated siRNA gene silencing. Acta Biomater.
9:4513–4524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ding N, Yu RT, Subramaniam N, et al: A
vitamin D receptor/SMAD genomic circuit gates hepatic fibrotic
response. Cell. 153:601–613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu X, Hu H and Yin JQ: Therapeutic
strategies against TGF-beta signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis.
Liver Int. 26:8–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lan HY: Diverse roles of TGF-β/Smads in
renal fibrosis and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. 7:1056–1067. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sabbah M, Prunier C, Ferrand N, et al:
CCN5, a novel transcriptional repressor of the transforming growth
factor β signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1459–1469. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|