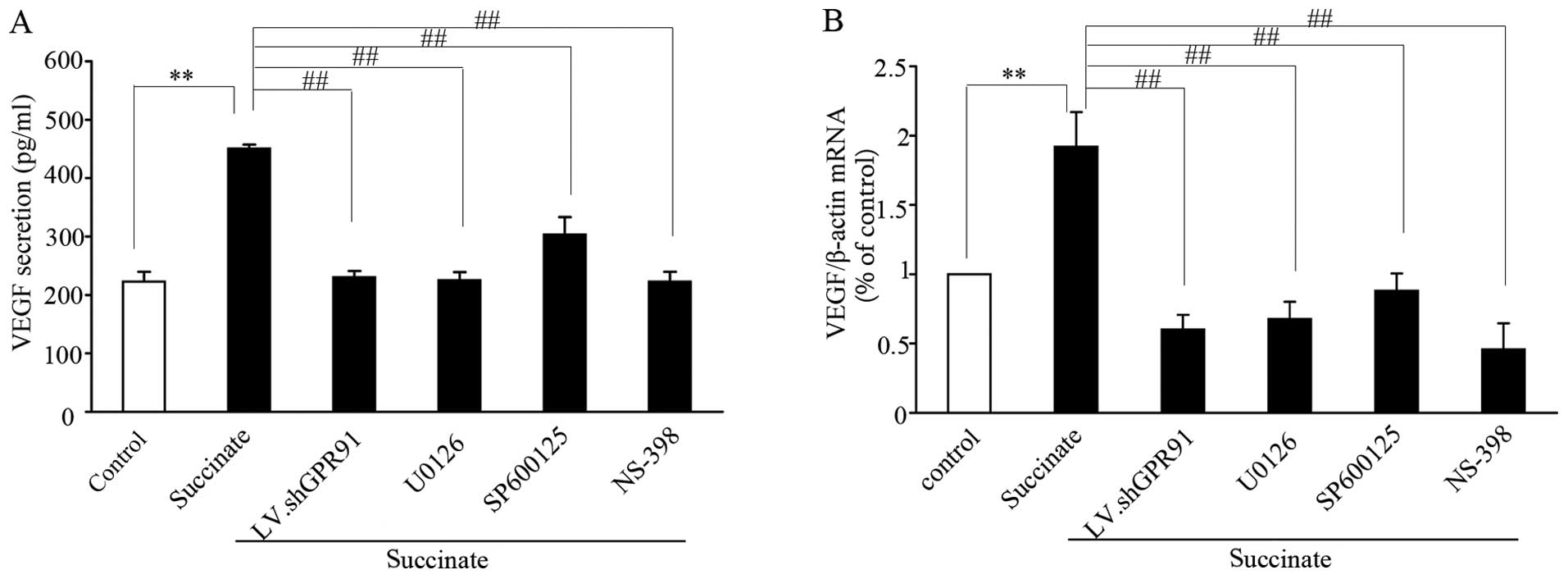
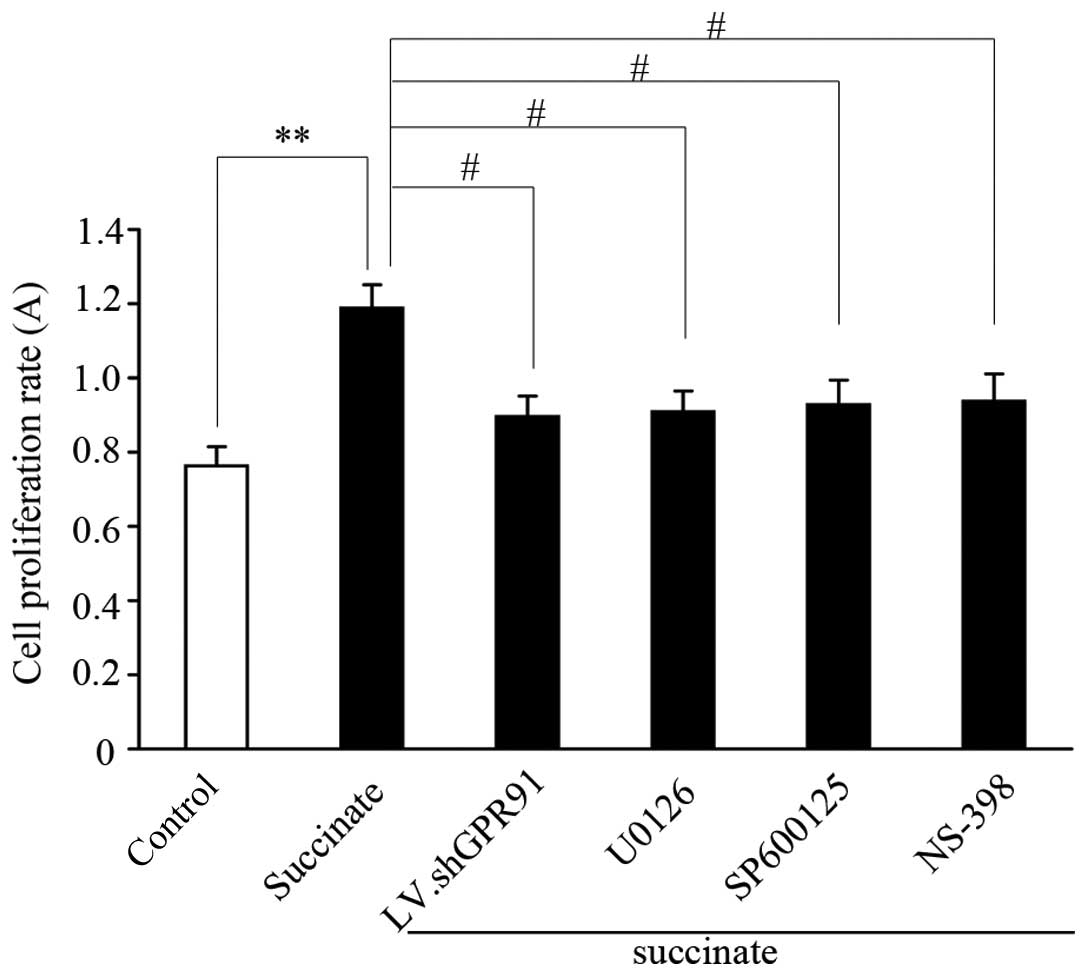
|
1
|
Nolan CJ, Damm P and Prentki M: Type 2
diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and
management. Lancet. 378:169–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Witmer AN, Blaauwgeers HG, Weich HA,
Alitalo K, Vrensen GF and Schlingemann RO: Altered expression
patterns of VEGF receptors in human diabetic retina and in
experimental VEGF-induced retinopathy in monkey. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 43:849–857. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng Z, Chen H, Wang H, et al:
Improvement of retinal vascular injury in diabetic rats by Statins
is associated with the inhibition of mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species pathway mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor coactivator 1. Diabetes. 59:2315–2325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S and
Poltorak Z: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its
receptors. FASEB J. 13:9–22. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Duh E and Aiello LP: Vascular endothelial
growth factor and diabetes: the agonist versus antagonist paradox.
Diabetes. 48:1899–1906. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dahrouj M, Alsarraf O, McMillin JC, Liu Y,
Crosson CE and Ablonczy Z: Vascular endothelial growth factor
modulates the function of the retinal pigment epithelium in vivo.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:2269–2275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krizova D, Vokrojova M, Liehneova K and
Studeny P: Treatment of corneal neovascularization using anti-VEGF
Bevacizumab. J Ophthalmol. 2014:1781322014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sapieha P, Sirinyan M, Hamel D, et al: The
succinate receptor GPR91 in neurons has a major role in retinal
angiogenesis. Nat Med. 14:1067–1076. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He W, Miao FJ, Lin DC, et al: Citric acid
cycle intermediates as ligands for orphan G-protein-coupled
receptors. Nature. 429:188–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li T, Hu J, Du S, Chen Y, Wang S and Wu Q:
ERK1/2/COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway mediates GPR91-dependent VEGF
release in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Mol Vis. 20:1109–1121.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Correa PR, Kruglov EA, Thompson M, Leite
MF, Dranoff JA and Nathanson MH: Succinate is a paracrine signal
for liver damage. J Hepatol. 47:262–269. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aguiar CJ, Andrade VL, Gomes ER, et al:
Succinate modulates Ca2+ transient and cardiomyocyte
viability through PKA-dependent pathway. Cell Calcium. 47:37–46.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rubic T, Lametschwandtner G, Jost S, et
al: Triggering the succinate receptor GPR91 on dendritic cells
enhances immunity. Nat Immunol. 9:1261–1269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Robben JH, Fenton RA, Vargas SL, Schweer
H, Peti-Peterdi J, Deen PM and Milligan G: Localization of the
succinate receptor in the distal nephron and its signaling in
polarized MDCK cells. Kidney Int. 76:1258–1267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsumoto M, Suzuma K, Maki T, Kinoshita
H, Tsuiki E, Fujikawa A and Kitaoka T: Succinate increases in the
vitreous fluid of patients with active proliferative diabetic
retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 153:896–902.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu J, Wu Q, Li T, Chen Y and Wang S:
Inhibition of high glucose-induced VEGF release in retinal ganglion
cells by RNA interference targeting G protein-coupled receptor 91.
Exp Eye Res. 109:31–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Toma I, Kang JJ, Sipos A, et al: Succinate
receptor GPR91 provides a direct link between high glucose levels
and renin release in murine and rabbit kidney. J Clin Invest.
118:2526–2534. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vargas SL, Toma I, Kang JJ, Meer EJ and
Peti-Peterdi J: Activation of the succinate receptor GPR91 in
macula densa cells causes renin release. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:1002–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schulte G and Fredholm BB: Human adenosine
A1, A2A, A2B, and A3
receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells all mediate the
phosphorylation of extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol
Pharmacol. 58:477–482. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoon S and Seger R: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse
cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24:21–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raman M, Chen W and Cobb MH: Differential
regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 26:3100–3112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JJ, Hsiao CC, Yang IH, et al:
High-mobility group box 1 protein is implicated in advanced
glycation end products-induced vascular endothelial growth factor A
production in the rat retinal ganglion cell line RGC-5. Mol Vis.
18:838–850. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adachi T, Teramachi M, Yasuda H, Kamiya T
and Hara H: Contribution of p38 MAPK, NF-kappaB and glucocorticoid
signaling pathways to ER stress-induced increase in retinal
endothelial permeability. Arch Biochem Biophys. 520:30–35. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Du Y, Tang J, Li G, et al: Effects of p38
MAPK inhibition on early stages of diabetic retinopathy and sensory
nerve function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:2158–2164. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ayalasomayajula SP, Amrite AC and Kompella
UB: Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2, but not cyclooxygenase-1,
reduces prostaglandin E2 secretion from diabetic rat retinas. Eur J
Pharmacol. 498:275–278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xin X, Majumder M, Girish GV, Mohindra V,
Maruyama T and Lala PK: Targeting COX-2 and EP4 to control tumor
growth, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to the lungs
and lymph nodes in a breast cancer model. Lab Invest. 92:1115–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou LH, Hu Q, Sui H, et al: Tanshinone
II-a inhibits angiogenesis through down regulation of COX-2 in
human colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4453–4458.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Amrite AC, Ayalasomayajula SP, Cheruvu NP
and Kompella UB: Single periocular injection of celecoxib-PLGA
microparticles inhibits diabetes-induced elevations in retinal
PGE2, VEGF, and vascular leakage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 47:1149–1160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan Y, Ichikawa T, Li J, et al: Diabetic
downregulation of Nrf2 activity via ERK contributes to oxidative
stress-induced insulin resistance in cardiac cells in vitro and in
vivo. Diabetes. 60:625–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakabayashi H and Shimizu K: HA1077, a Rho
kinase inhibitor, suppresses glioma-induced angiogenesis by
targeting the Rho-ROCK and the mitogen-activated protein kinase
kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK/ERK) signal
pathways. Cancer Sci. 102:393–399. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Reddy EP: JNK
signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:6245–6251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Campo GM, Avenoso A, D’Ascola A, et al:
4-mer hyaluronan oligosaccharides stimulate inflammation response
in synovial fibroblasts in part via TAK-1 and in part via p38-MAPK.
Curr Med Chem. 20:1162–1172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Michler T, Storr M, Kramer J, et al:
Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 reduces inflammation in acute
experimental pancreatitis via intra-acinar activation of p38 and
MK2-dependent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
304:G181–G192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pollard PJ, Wortham NC and Tomlinson IP:
The TCA cycle and tumorigenesis: the examples of fumarate hydratase
and succinate dehydrogenase. Ann Med. 35:632–639. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Buzzi N, Bilbao PS, Boland R and de Boland
AR: Extracellular ATP activates MAP kinase cascades through a P2Y
purinergic receptor in the human intestinal Caco-2 cell line.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1790:1651–1659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kern TS: Contributions of inflammatory
processes to the development of the early stages of diabetic
retinopathy. Exp Diabetes Res. 2007:951032007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Neroev VV, Zueva MV and Kalamkarov GR:
Molecular mechanisms of retinal ischemia. Vestn Oftalmol.
126:59–64. 2010.In Russian. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Patel N: Targeting leukostasis for the
treatment of early diabetic retinopathy. Cardiovasc. Hematol Disord
Drug Targets. 9:222–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nagoya H, Futagami S, Shimpuku M, et al:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1 is associated with
angiogenesis and VEGF production via upregulation of COX-2
expression in esophageal cancer tissues. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 306:G183–G190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yanni SE, Barnett JM, Clark ML and Penn
JS: The role of PGE2 receptor EP4 in pathologic ocular
angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:5479–5486. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Inoue H, Takamori M, Nagata N, Nishikawa
T, Oda H, Yamamoto S and Koshihara Y: An investigation of cell
proliferation and soluble mediators induced by interleukin 1beta in
human synovial fibroblasts: comparative response in osteoarthritis
and rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res. 50:65–72. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Höper MM, Voelkel NF, Bates TO, Allard JD,
Horan M, Shepherd D and Tuder RM: Prostaglandins induce vascular
endothelial growth factor in a human monocytic cell line and rat
lungs via cAMP. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 17:748–756. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheng T, Cao W, Wen R, Steinberg RH and
LaVail MM: Prostaglandin E2 induces vascular endothelial
growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor mRNA expression in
cultured rat Muller cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 39:581–591.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhong X, Wang H and Jian X: Insulin
augments mechanical strain-induced ERK activation and
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in MG63 cells through integrins. Exp
Ther Med. 7:295–299. 2014.
|
|
47
|
Chuang YF, Yang HY, Ko TL, Hsu YF, Sheu
JR, Ou G and Hsu MJ: Valproic acid suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression via MKP-1 in
murine brain micro-vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
88:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Amrite A, Pugazhenthi V, Cheruvu N and
Kompella U: Delivery of celecoxib for treating diseases of the eye:
influence of pigment and diabetes. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
7:631–645. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ferrara N and Davis-Smyth T: The biology
of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 18:4–25. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li F, Xu H, Zeng Y and Yin ZQ:
Overexpression offibulin-5 in retinal pigment epithelial cells
inhibits cell proliferation and migration and downregulates VEGF,
CXCR4, and TGFB1 expression in cocultured choroidal endothelial
cells. Cur Eye Res. 37:540–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|