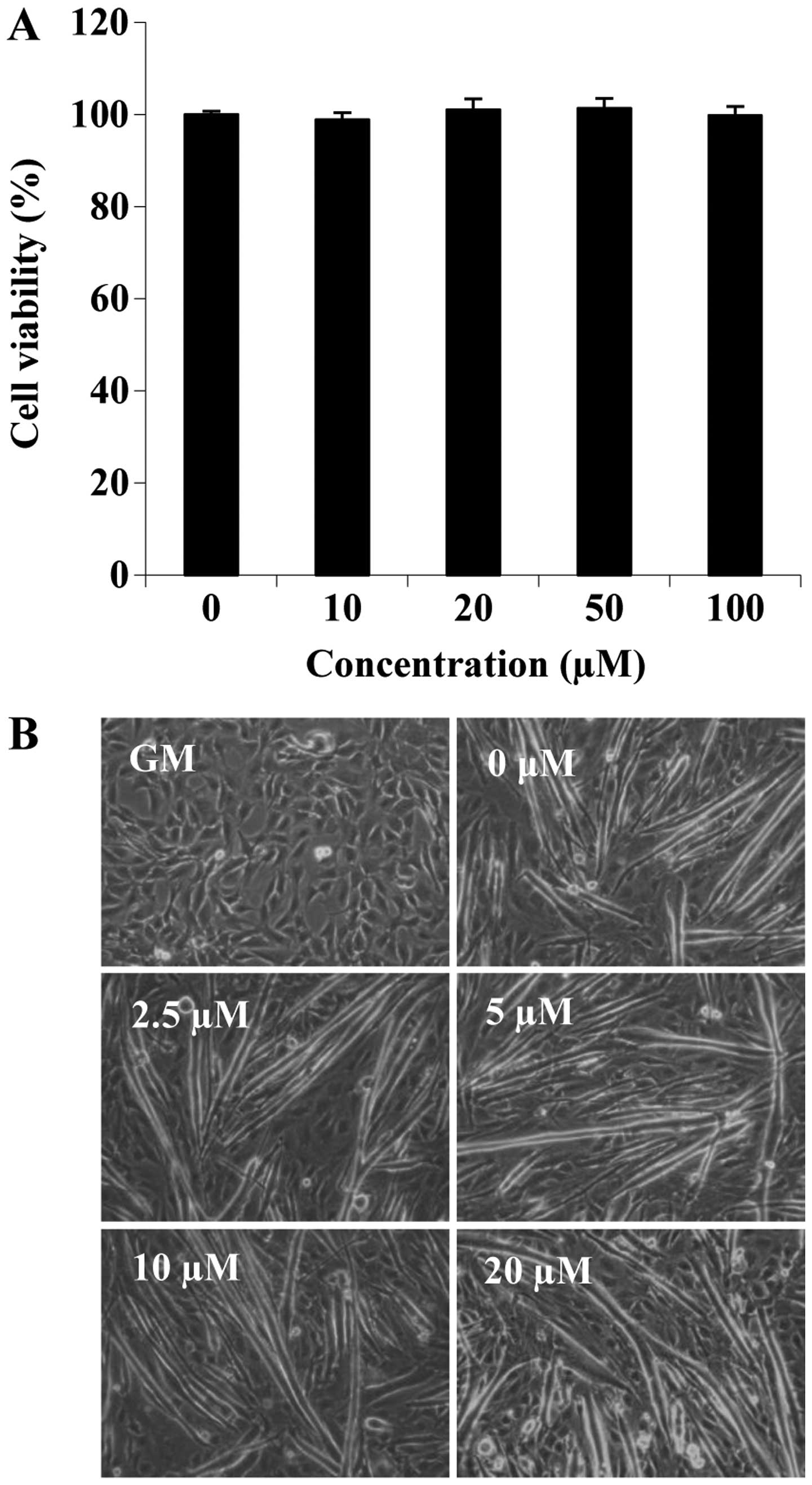
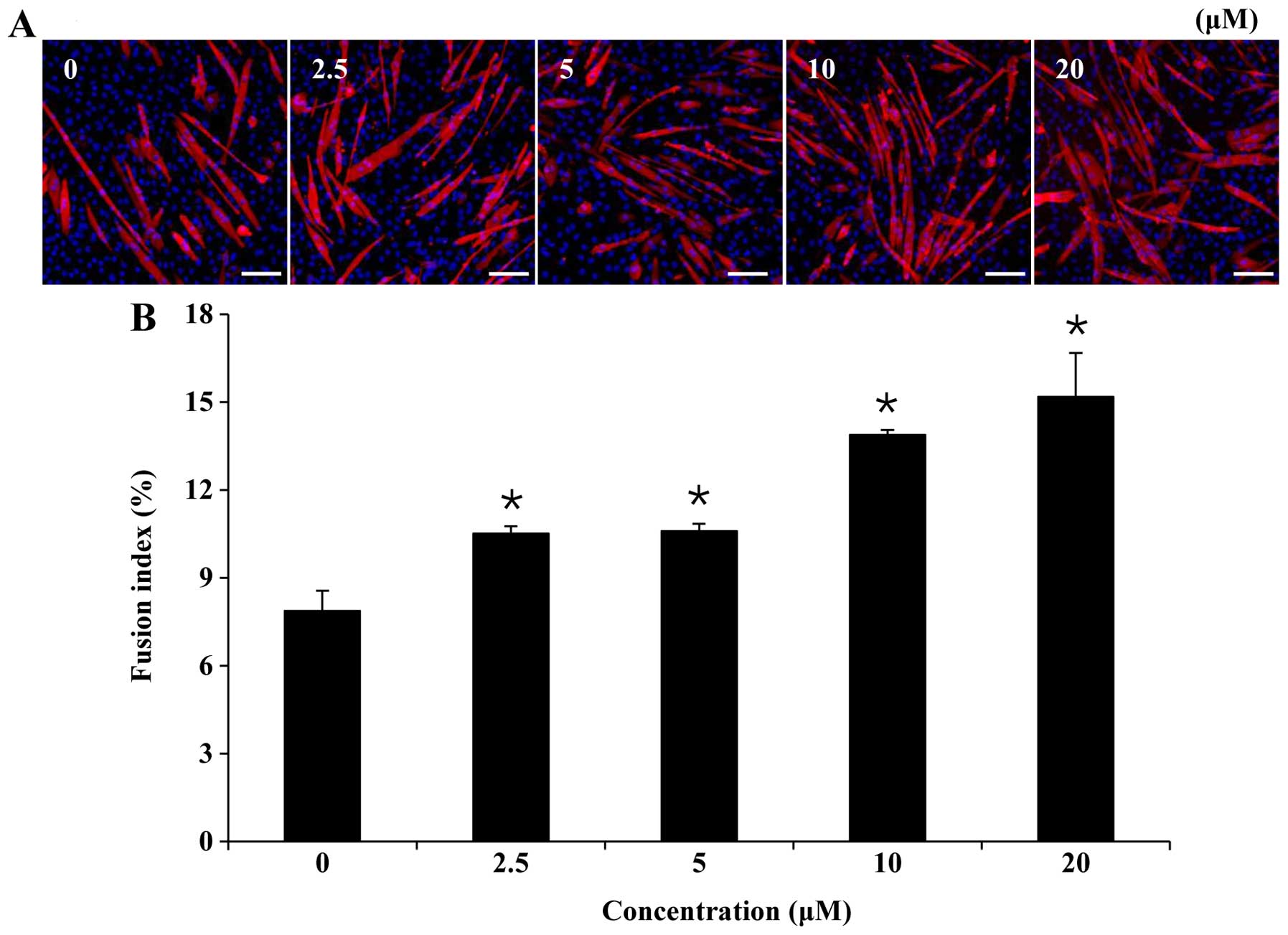
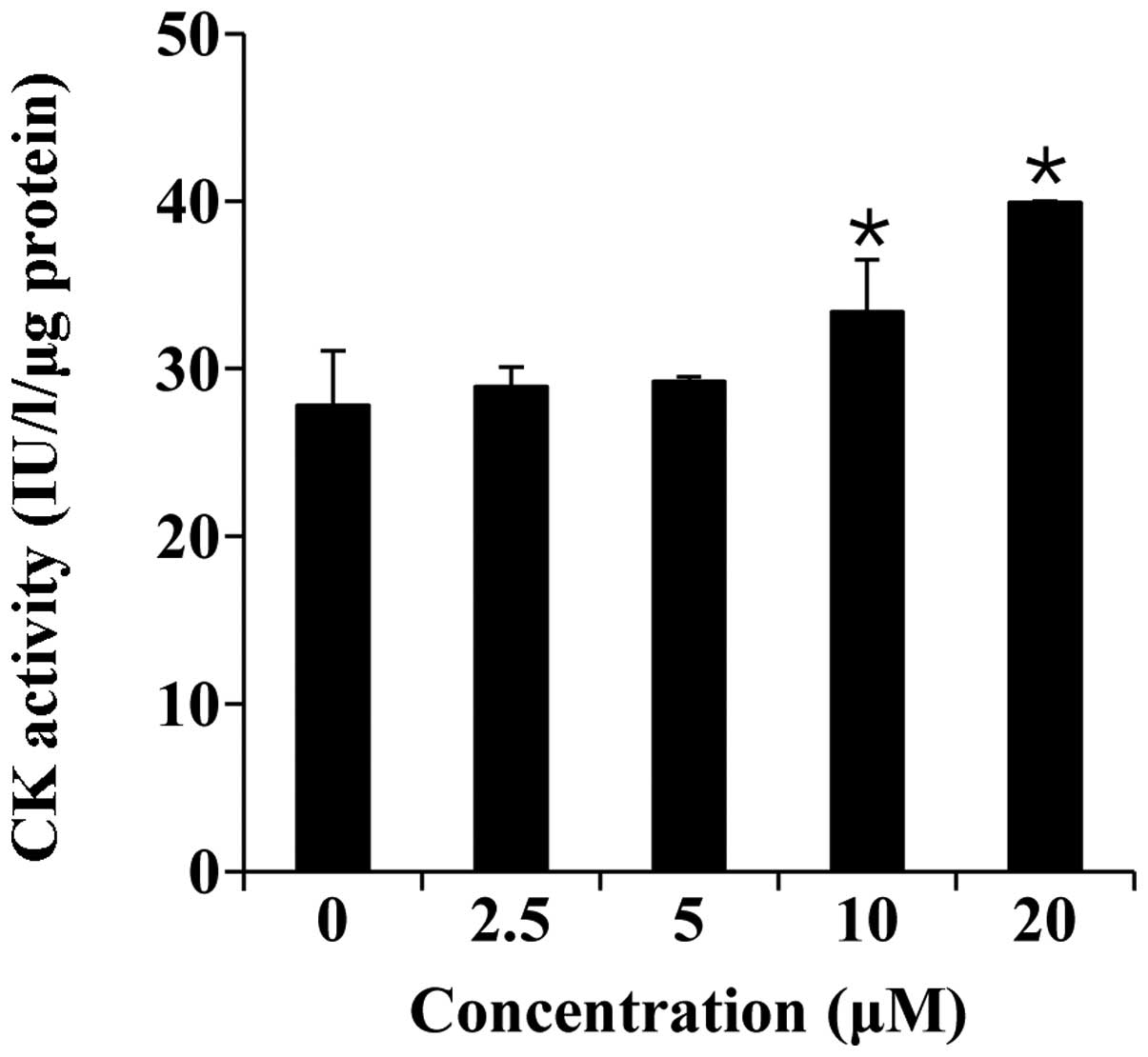
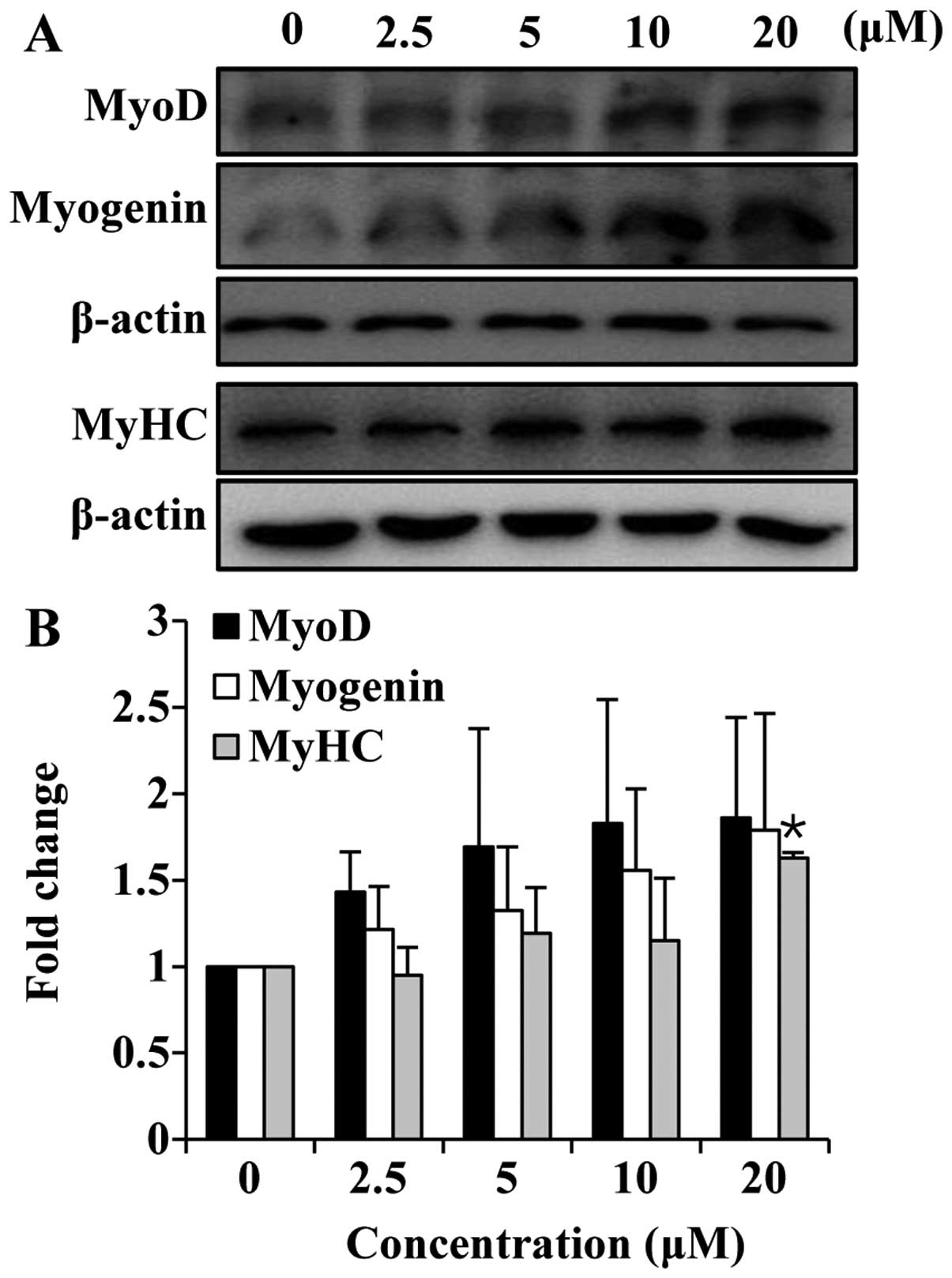
|
1
|
Iyer R and Tomar SK: Folate: a functional
food constituent. J Food Sci. 74:R114–R122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lucock M: Is folic acid the ultimate
functional food component for disease prevention? BMJ. 328:211–214.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Czeizel AE, Dudás I, Vereczkey A and
Bánhidy F: Folate deficiency and folic acid supplementation: the
prevention of neural-tube defects and congenital heart defects.
Nutrients. 5:4760–4775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hou TC, Lin JJ, Wen HC, Chen LC, Hsu SP
and Lee WS: Folic acid inhibits endothelial cell migration through
inhibiting the RhoA activity mediated by activating the folic acid
receptor/cSrc/p190RhoGAP-signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
85:376–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim YI: Will mandatory folic acid
fortification prevent or promote cancer? Am J Clin Nutr.
80:1123–1128. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Zhang X, Sun Y, Feng Q, Li G, Wang
M, Cui X, Kang L and Jiang Y: Folate deficiency during early-mid
pregnancy affects the skeletal muscle transcriptome of piglets from
a reciprocal cross. PLoS One. 8:e826162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Swart KM, Enneman AW, van Wijngaarden JP,
van Dijk SC, Brouwer-Brolsma EM, Ham AC, Dhonukshe-Rutten RA, van
der Velde N, Brug J, van Meurs JB, et al: Homocysteine and the
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase 677C–>T polymorphism in
relation to muscle mass and strength, physical performance and
postural sway. Eur J Clin Nutr. 67:743–748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Olthof MR and Verhoef P: Effects of
betaine intake on plasma homocysteine concentrations and
consequences for health. Curr Drug Metab. 6:15–22. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Senesi P, Luzi L, Montesano A, Mazzocchi N
and Terruzzi I: Betaine supplement enhances skeletal muscle
differentiation in murine myoblasts via IGF-1 signaling activation.
J Transl Med. 11:1742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Meurs JB, Dhonukshe-Rutten RA, Pluijm
SM, van der Klift M, de Jonge R, Lindemans J, de Groot LC, Hofman
A, Witteman JC, van Leeuwen JP, et al: Homocysteine levels and the
risk of osteoporotic fracture. N Engl J Med. 350:2033–2041. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sato Y, Honda Y, Iwamoto J, Kanoko T and
Satoh K: Effect of folate and mecobalamin on hip fractures in
patients with stroke: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA.
293:1082–1088. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P,
Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D and Relaix F: The
formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb. J Anat.
202:59–68. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Parker MH, Seale P and Rudnicki MA:
Looking back to the embryo: defining transcriptional networks in
adult myogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 4:497–507. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weintraub H: The MyoD family and
myogenesis: redundancy, networks, and thresholds. Cell.
75:1241–1244. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lassar AB, Skapek SX and Novitch B:
Regulatory mechanisms that coordinate skeletal muscle
differentiation and cell cycle withdrawal. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
6:788–794. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olson EN, Perry M and Schulz RA:
Regulation of muscle differentiation by the MEF2 family of MADS box
transcription factors. Dev Biol. 172:2–14. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rudnicki MA, Braun T, Hinuma S and
Jaenisch R: Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of
the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle
development. Cell. 71:383–390. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rudnicki MA, Schnegelsberg PN, Stead RH,
Braun T, Arnold HH and Jaenisch R: MyoD or Myf-5 is required for
the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 75:1351–1359. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perry RL and Rudnick MA: Molecular
mechanisms regulating myogenic determination and differentiation.
Front Biosci. 5:D750–D767. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moncaut N, Rigby PW, Carvajal JJ and Dial
M: Dial M(RF) for myogenesis. FEBS J. 280:3980–3990. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ceci M, Ross J Jr and Condorelli G:
Molecular determinants of the physiological adaptation to stress in
the cardiomyocyte: a focus on AKT. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:905–912.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guttridge DC: Signaling pathways weigh in
on decisions to make or break skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Clin Nutr
Metab Care. 7:443–450. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim M, Sung B, Kang YJ, Kim DH, Lee Y,
Hwang SY, Yoon JH, Yoo MA, Kim CM, Chung HY and Kim ND: The
combination of ursolic acid and leucine potentiates the
differentiation of C2C12 murine myoblasts through the mTOR
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 35:755–762. 2015.
|
|
25
|
Erbay E and Chen J: The mammalian target
of rapamycin regulates C2C12 myogenesis via a kinase-independent
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 276:36079–36082. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gingras AC, Raught B and Sonenberg N:
Regulation of translation initiation by FRAP/mTOR. Genes Dev.
15:807–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohanna M, Sobering AK, Lapointe T, Lorenzo
L, Praud C, Petroulakis E, Sonenberg N, Kelly PA, Sotiropoulos A
and Pende M: Atrophy of S6K1(−/−) skeletal muscle cells reveals
distinct mTOR effectors for cell cycle and size control. Nat Cell
Biol. 7:286–294. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lawson MA and Purslow PP: Differentiation
of myoblasts in serum-free media: effects of modified media are
cell line-specific. Cells Tissues Organs. 167:130–137. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nabeshima Y, Hanaoka K, Hayasaka M, Esumi
E, Li S, Nonaka I and Nabeshima Y: Myogenin gene disruption results
in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature.
364:532–535. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hasty P, Bradley A, Morris JH, Edmondson
DG, Venuti JM, Olson EN and Klein WH: Muscle deficiency and
neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin
gene. Nature. 364:501–506. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tidball JG and Villalta SA: Regulatory
interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle
regeneration. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
298:R1173–R1187. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yaffe D and Saxel O: Serial passaging and
differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse
muscle. Nature. 270:725–727. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tapscott SJ: The circuitry of a master
switch: Myod and the regulation of skeletal muscle gene
transcription. Development. 132:2685–2695. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hawke TJ and Garry DJ: Myogenic satellite
cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol (1985).
91:534–551. 2001.
|
|
35
|
Yoshida N, Yoshida S, Koishi K, Masuda K
and Nabeshima Y: Cell heterogeneity upon myogenic differentiation:
down-regulation of MyoD and Myf-5 generates 'reserve cells'. J Cell
Sci. 111:769–779. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ferri P, Barbieri E, Burattini S, Guescini
M, D'Emilio A, Biagiotti L, Del Grande P, De Luca A, Stocchi V and
Falcieri E: Expression and subcellular localization of myogenic
regulatory factors during the differentiation of skeletal muscle
C2C12 myoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 108:1302–1317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kitzmann M, Carnac G, Vandromme M, Primig
M, Lamb NJ and Fernandez A: The muscle regulatory factors MyoD and
myf-5 undergo distinct cell cycle-specific expression in muscle
cells. J Cell Biol. 142:1447–1459. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Molkentin JD, Black BL, Martin JF and
Olson EN: Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2
and myogenic bHLH proteins. Cell. 83:1125–1136. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Park SY, Yun Y, Kim MJ and Kim IS:
Myogenin is a positive regulator of MEGF10 expression in skeletal
muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:1631–1637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ludolph DC and Konieczny SF: Transcription
factor families: muscling in on the myogenic program. FASEB J.
9:1595–1604. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cornelison DD, Olwin BB, Rudnicki MA and
Wold BJ: MyoD(−/−) satellite cells in single-fiber culture are
differentiation defective and MRF4 deficient. Dev Biol.
224:122–137. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jiang BH, Aoki M, Zheng JZ, Li J and Vogt
PK: Myogenic signaling of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase requires
the serine-threonine kinase Akt/protein kinase B. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:2077–2081. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sumitani S, Goya K, Testa JR, Kouhara H
and Kasayama S: Akt1 and Akt2 differently regulate muscle creatine
kinase and myogenin gene transcription in insulin-induced
differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Endocrinology. 143:820–828.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Peter AK and Crosbie RH: Hypertrophic
response of Duchenne and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies is
associated with activation of Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res.
312:2580–2591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Izumiya Y, Hopkins T, Morris C, Sato K,
Zeng L, Viereck J, Hamilton JA, Ouchi N, LeBrasseur NK and Walsh K:
Fast/Glycolytic muscle fiber growth reduces fat mass and improves
metabolic parameters in obese mice. Cell Metab. 7:159–172. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Florini JR, Ewton DZ and Roof SL:
Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates terminal myogenic
differentiation by induction of myogenin gene expression. Mol
Endocrinol. 5:718–724. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu Q and Wu Z: The insulin-like growth
factor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway
regulates myogenin expression in normal myogenic cells but not in
rhabdomyo-sarcoma-derived RD cells. J Biol Chem. 275:36750–36757.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jagoe RT and Goldberg AL: What do we
really know about the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle
atrophy? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 4:183–190. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Glass DJ: Signalling pathways that mediate
skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Nat Cell Biol. 5:87–90.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
No authors listed. Epidemiologic and
methodologic problems in determining nutritional status of older
persons. Proceedings of a conference Albuquerque, New Mexico,
October 19–21, 1988. Am J Clin Nutr. 50(Suppl): 1121–1235.
1989.
|
|
51
|
Solini A, Santini E and Ferrannini E:
Effect of short-term folic acid supplementation on insulin
sensitivity and inflammatory markers in overweight subjects. Int J
Obes. 30:1197–1202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Feng D, Zhou Y, Xia M and Ma J: Folic acid
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in
RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing MAPKs and NF-κB activation.
Inflamm Res. 60:817–822. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Veeranki S, Winchester LJ and Tyagi SC:
Hyperhomocysteinemia associated skeletal muscle weakness involves
mitochondrial dysfunction and epigenetic modifications. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:732–741. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Moat SJ, Doshi SN, Lang D, McDowell IF,
Lewis MJ and Goodfellow J: Treatment of coronary heart disease with
folic acid: is there a future? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H1–H7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|