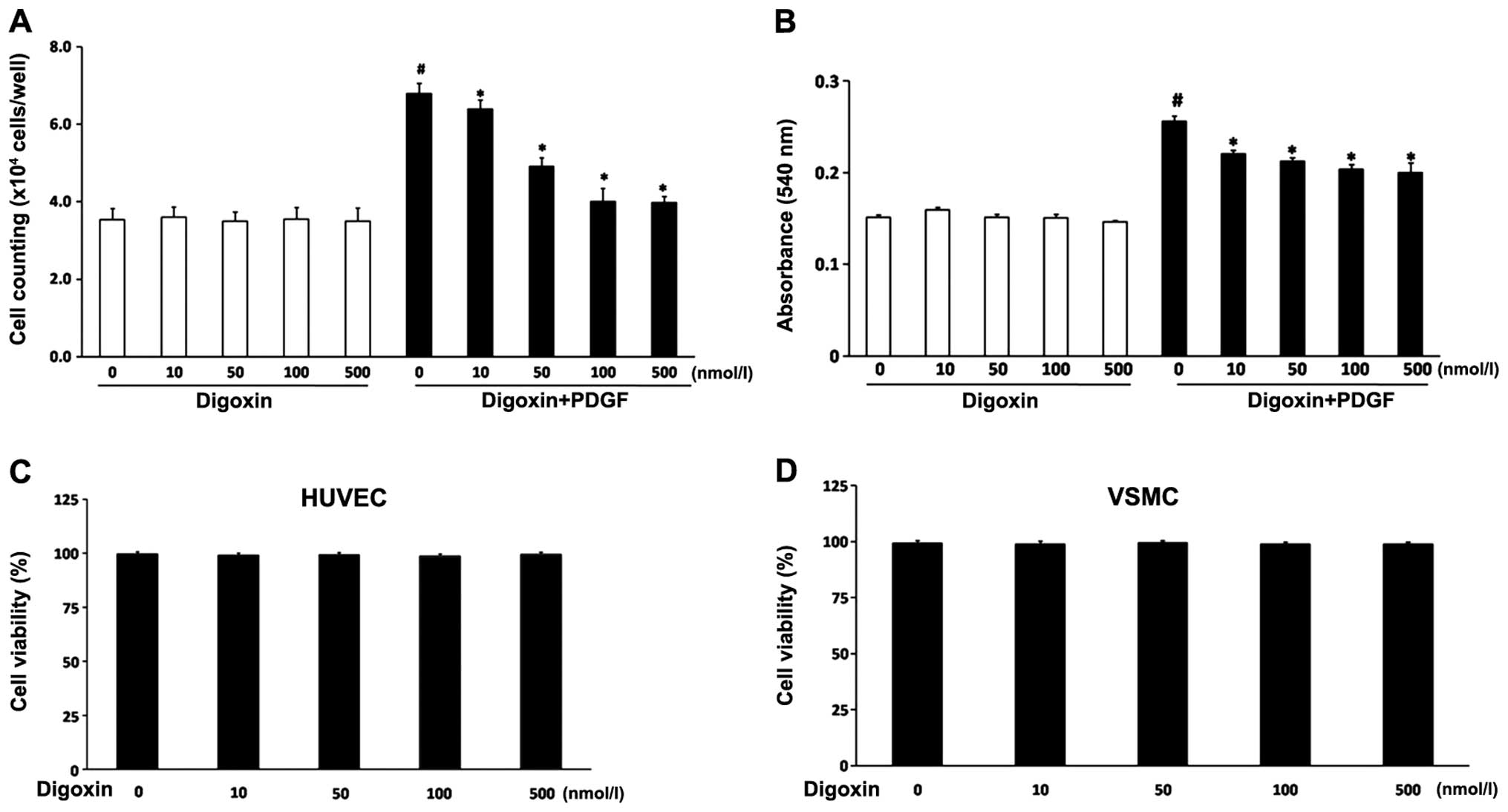
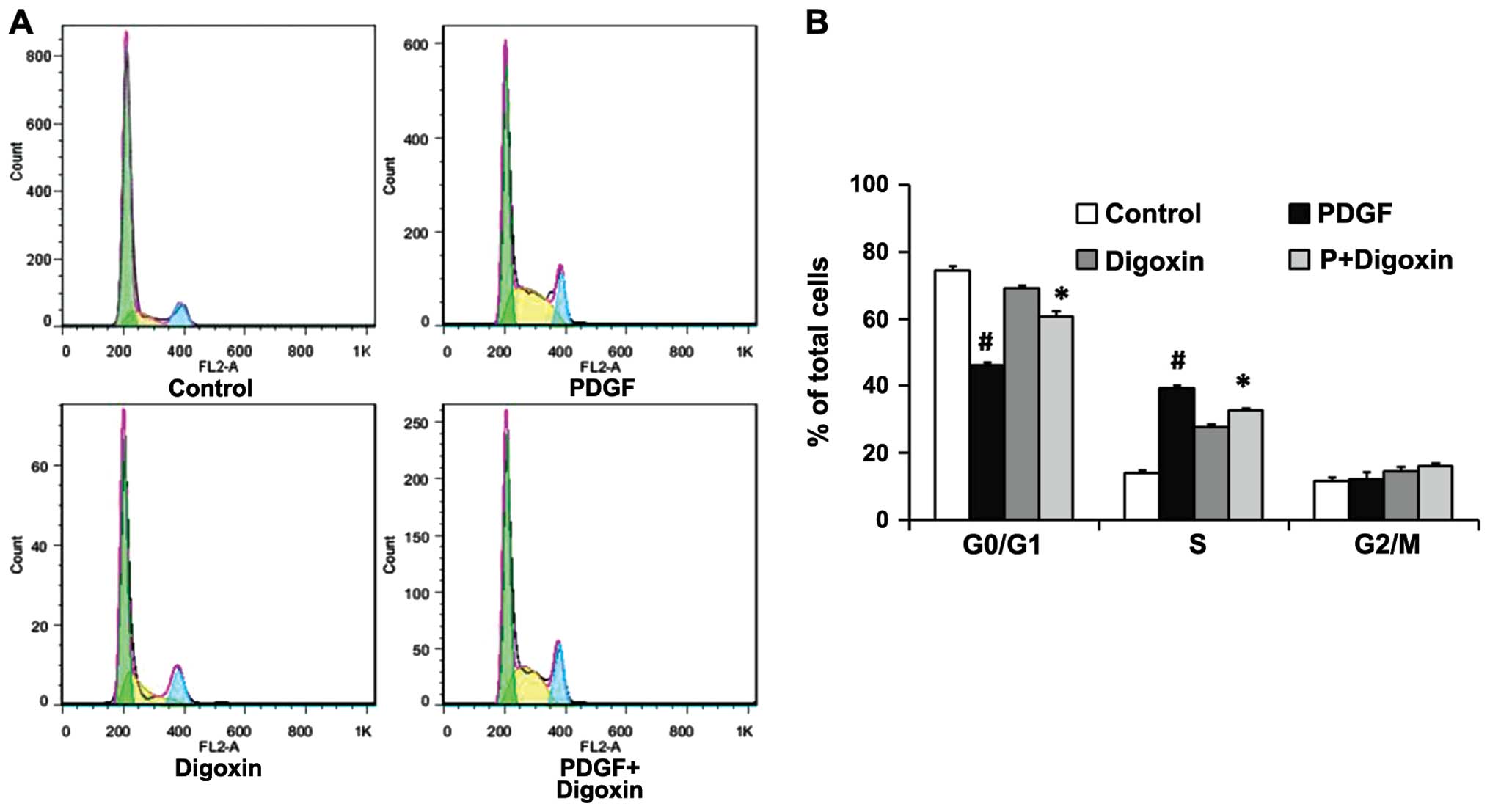
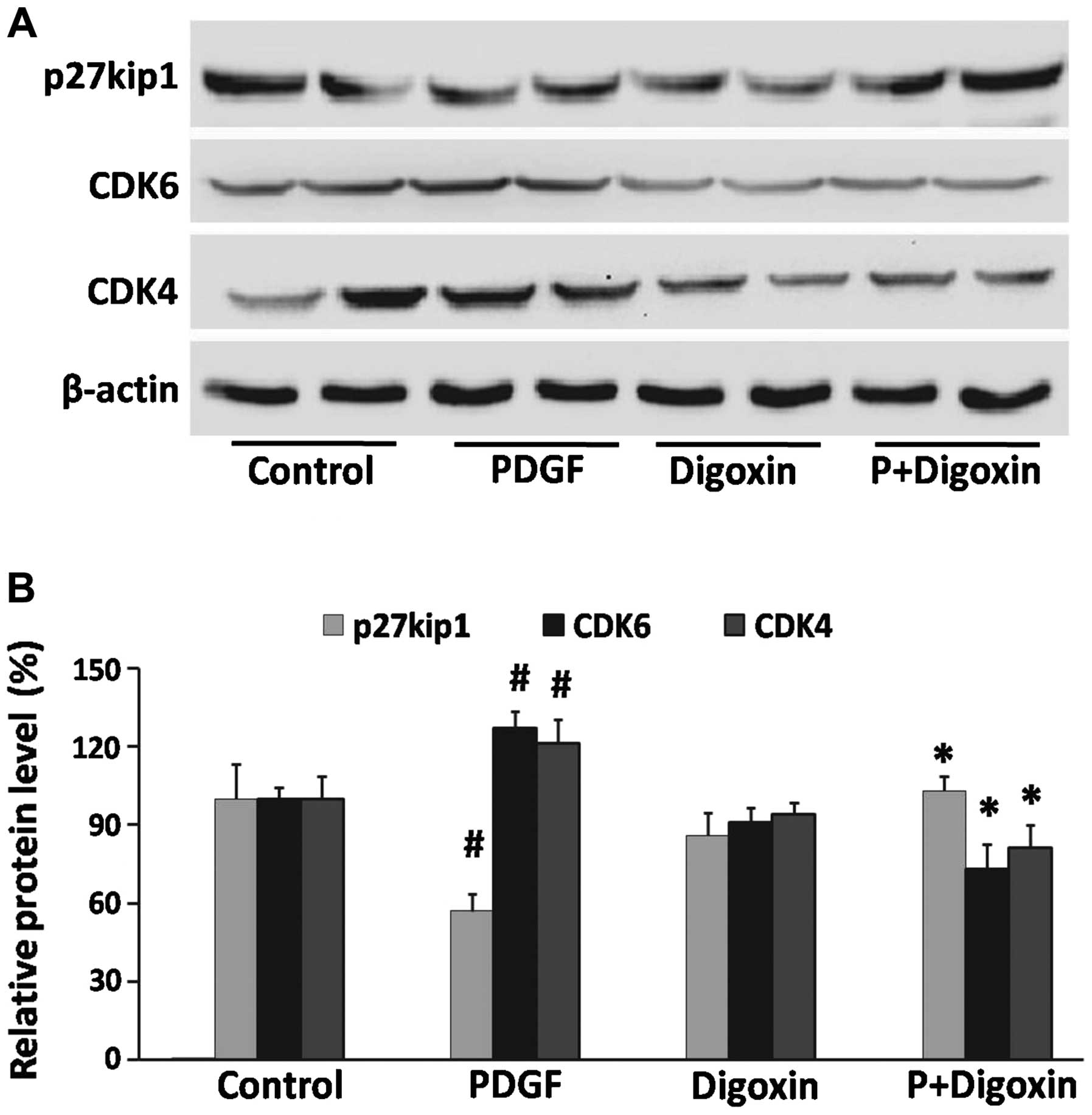
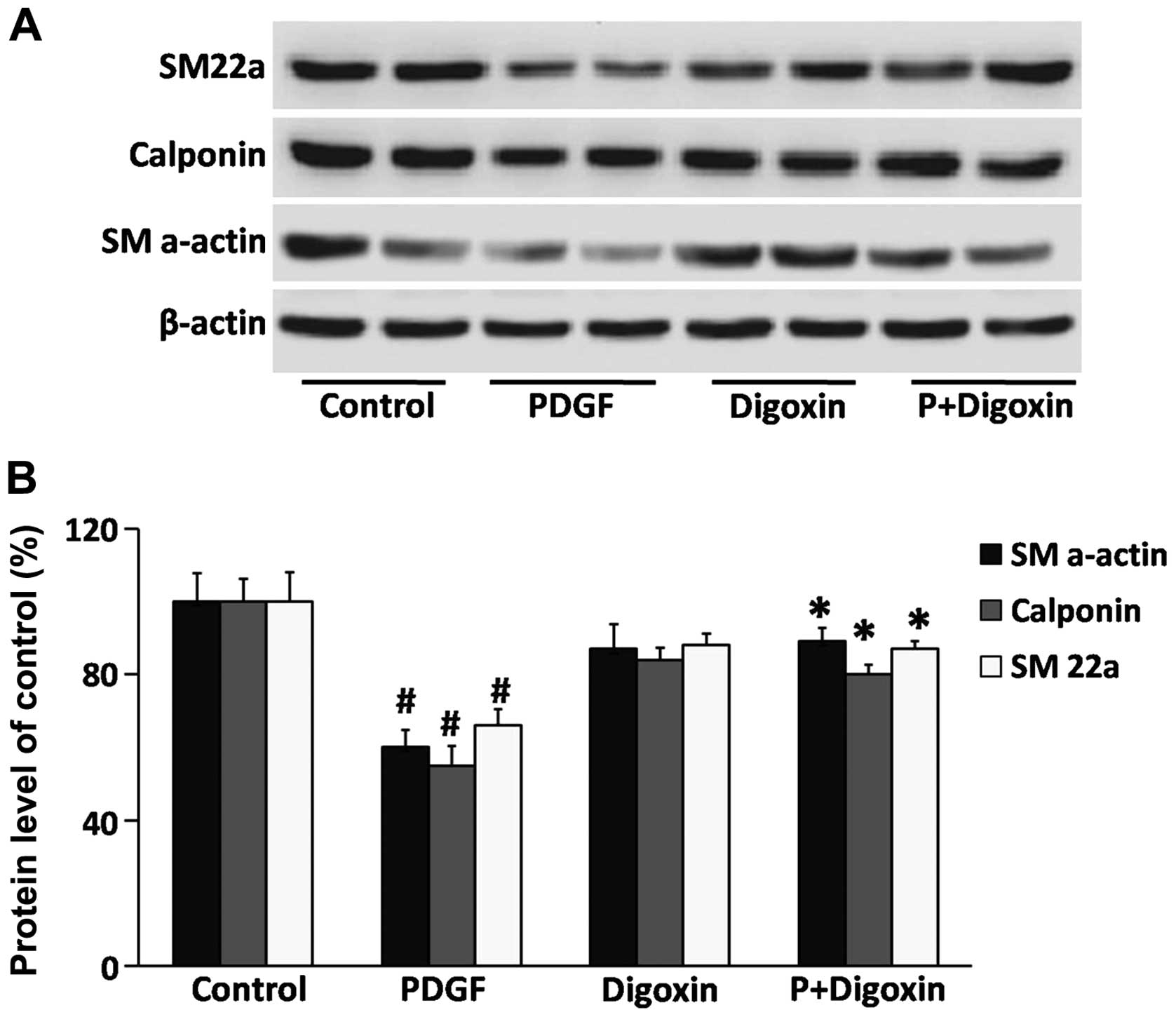
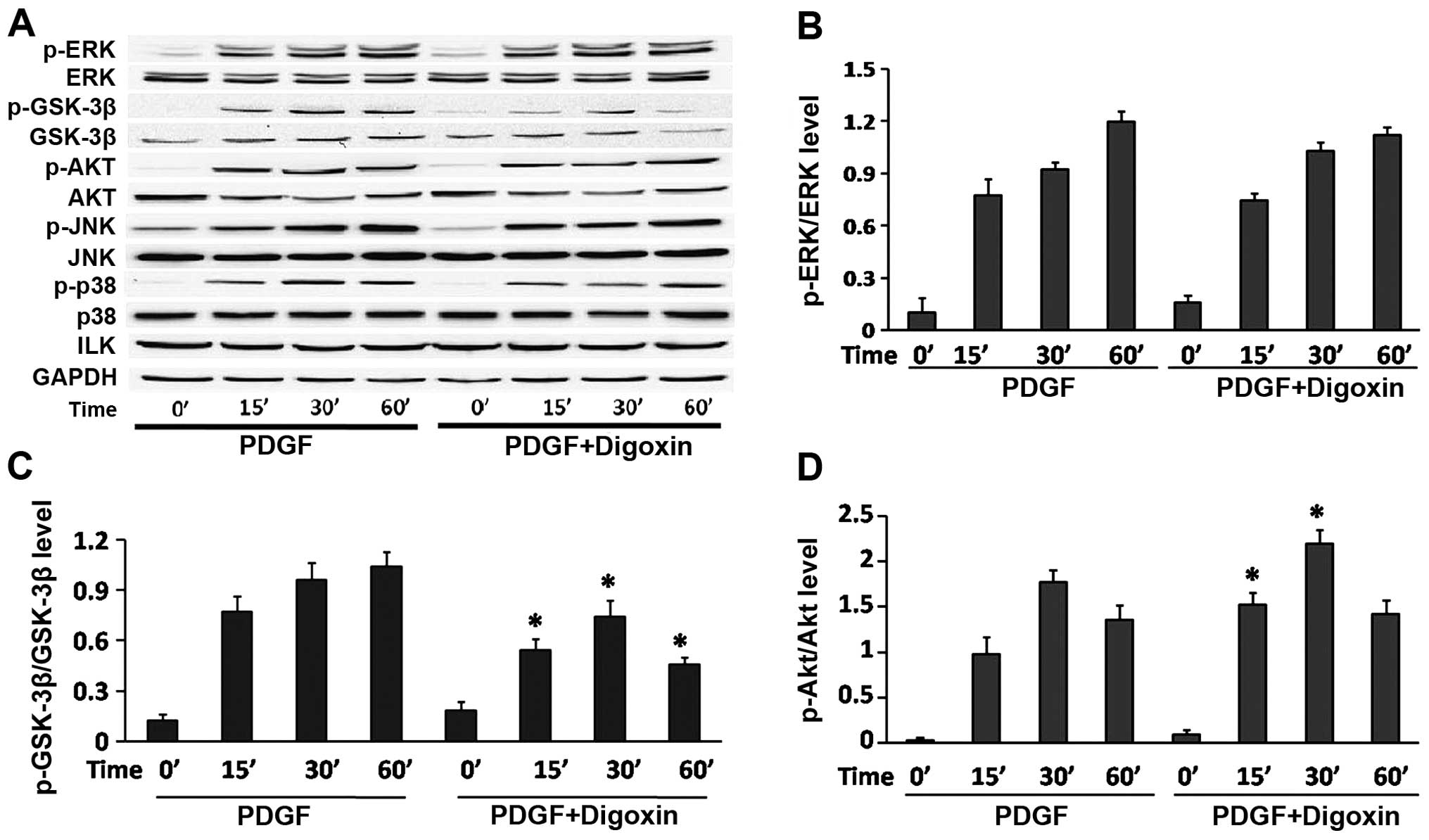
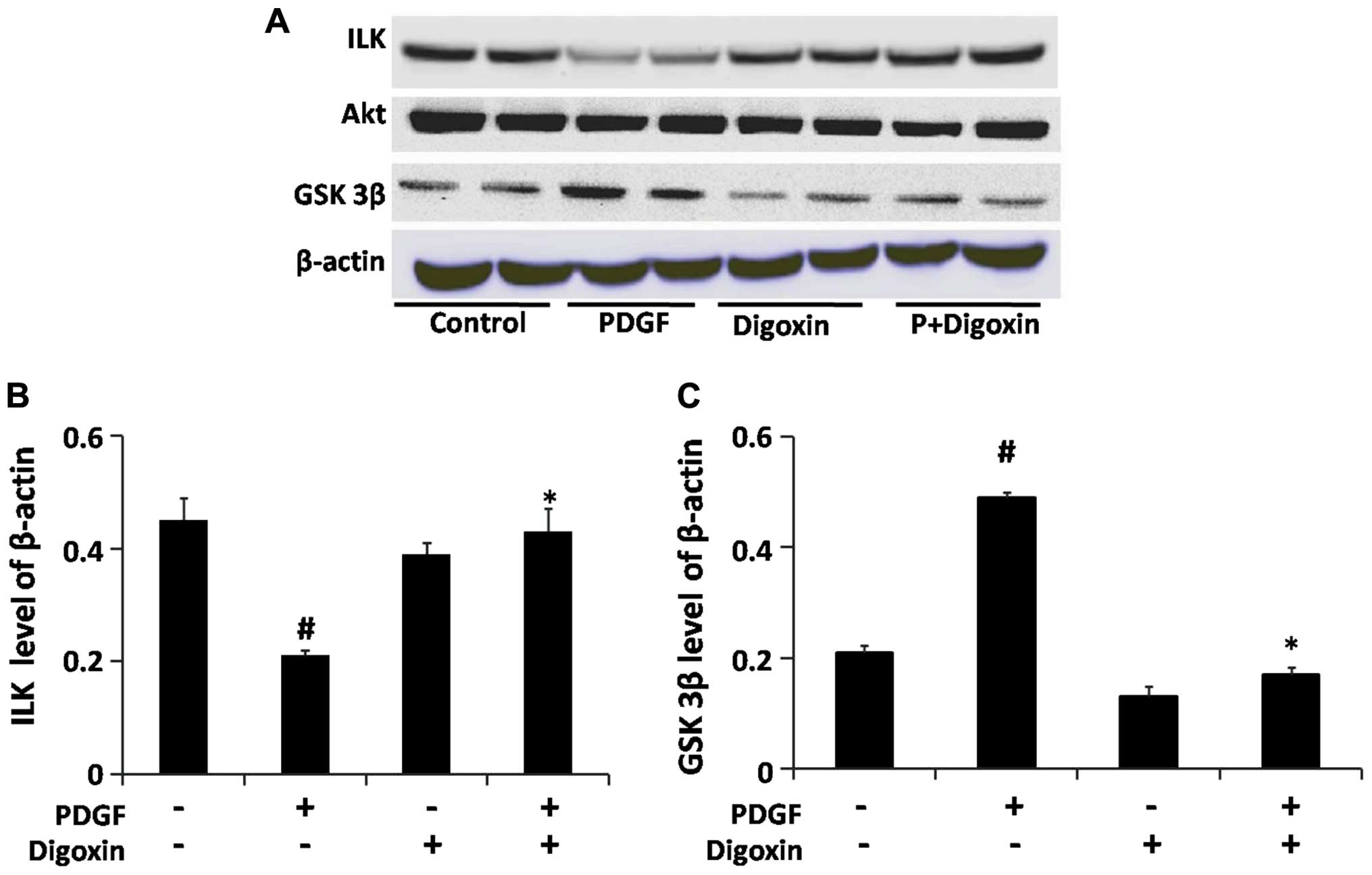
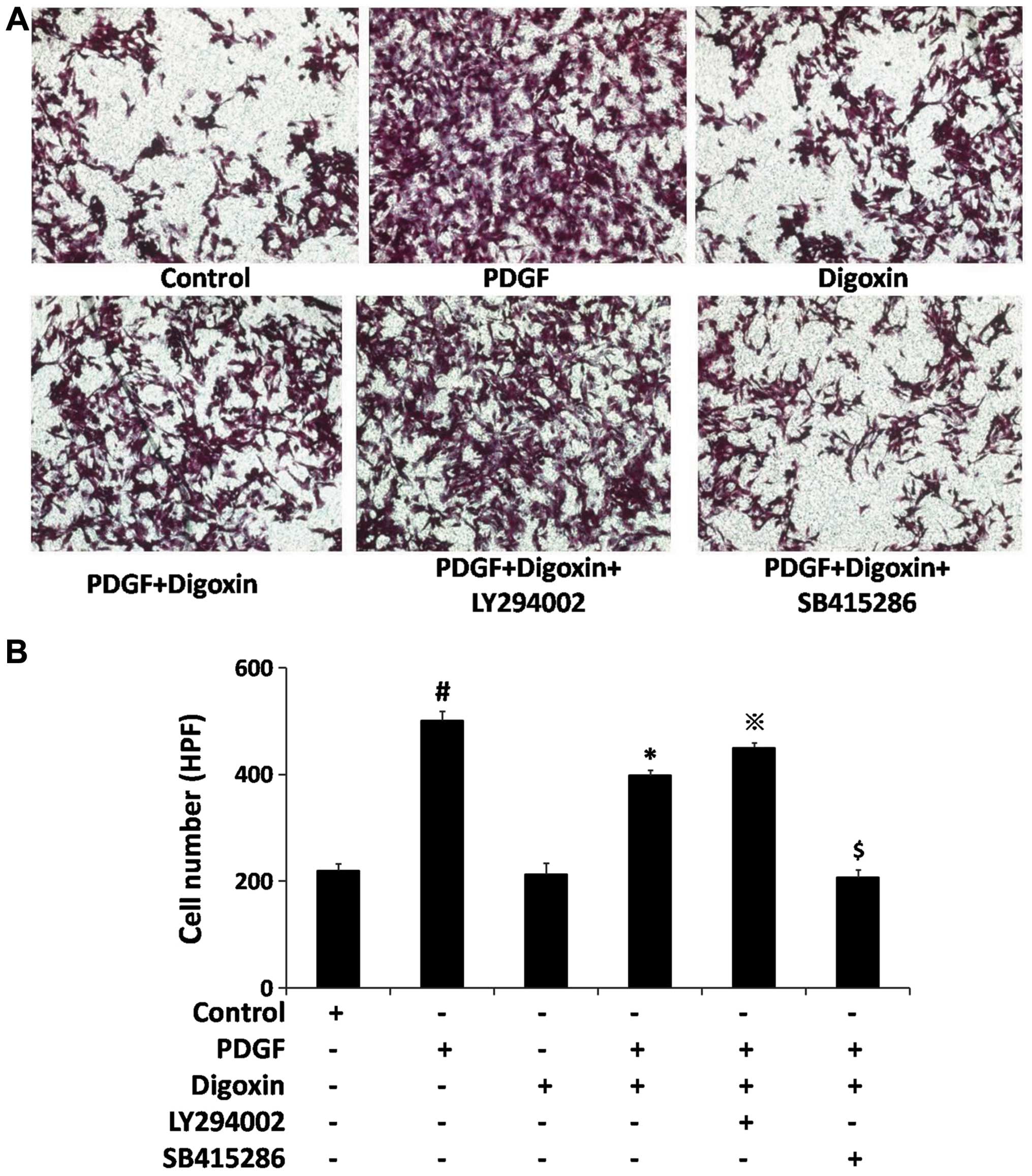
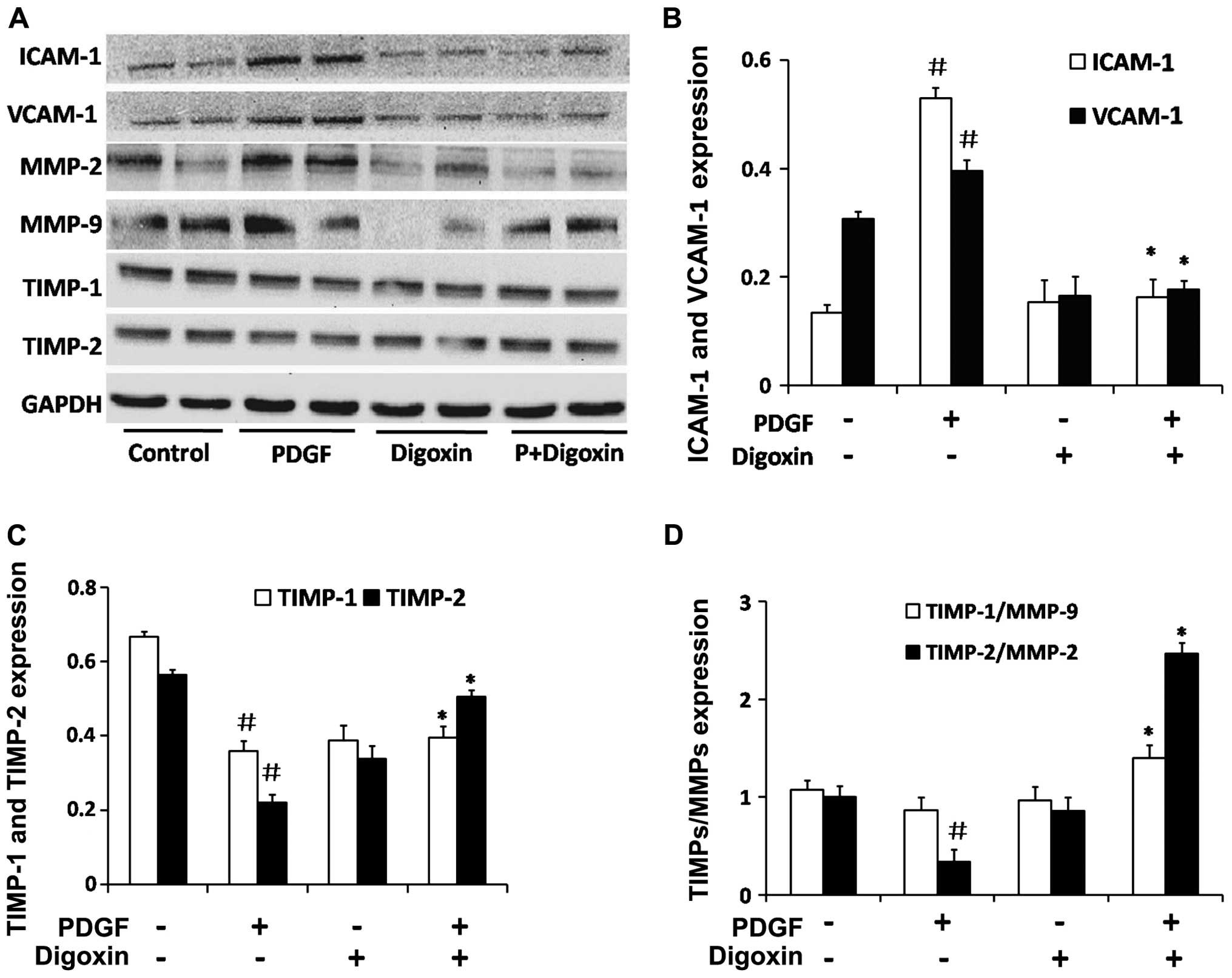
|
1
|
Davis-Dusenbery BN, Wu C, Hata A and Sessa
WC: Micromanaging vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and
phenotypic modulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2370–2377.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goel SA, Guo LW, Liu B and Kent KC:
Mechanisms of post-intervention arterial remodelling. Cardiovasc
Res. 96:363–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weintraub WS: The pathophysiology and
burden of restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 100:3K–9K. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dzau VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC and Sedding DG:
Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: New perspectives and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 8:1249–1256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raines EW: PDGF and cardiovascular
disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:237–254. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahmed A, Pitt B, Rahimtoola SH, Waagstein
F, White M, Love TE and Braunwald E: Effects of digoxin at low
serum concentrations on mortality and hospitalization in heart
failure: A propensity-matched study of the DIG trial. Int J
Cardiol. 123:138–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pervaiz MH, Dickinson MG and Yamani M: Is
digoxin a drug of the past? Cleve Clin J Med. 73:821–824.
826829–832, passim. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Newman RA, Yang P, Pawlus AD and Block KI:
Cardiac glycosides as novel cancer therapeutic agents. Mol Interv.
8:36–49. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prassas I and Diamandis EP: Novel
therapeutic applications of cardiac glycosides. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 7:926–935. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takara K, Takagi K, Tsujimoto M, Ohnishi N
and Yokoyama T: Digoxin up-regulates multidrug resistance
transporter (MDR1) mRNA and simultaneously down-regulates steroid
xenobiotic receptor mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 306:116–120.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schoner W: Endogenous cardiac glycosides,
a new class of steroid hormones. Eur J Biochem. 269:2440–2448.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schoner W and Scheiner-Bobis G: Endogenous
and exogenous cardiac glycosides and their mechanisms of action. Am
J Cardiovasc Drugs. 7:173–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schoner W and Scheiner-Bobis G: Endogenous
and exogenous cardiac glycosides: Their roles in hypertension, salt
metabolism, and cell growth. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
293:C509–C536. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
López-Lázaro M: Digitoxin as an anticancer
agent with selectivity for cancer cells: Possible mechanisms
involved. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:1043–1053. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mijatovic T, Van Quaquebeke E, Delest B,
Debeir O, Darro F and Kiss R: Cardiotonic steroids on the road to
anti-cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1776:32–57.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Winnicka K, Bielawski K and Bielawska A:
Cardiac glycosides in cancer research and cancer therapy. Acta Pol
Pharm. 63:109–115. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Svensson A, Azarbayjani F, Bäckman U,
Matsumoto T and Christofferson R: Digoxin inhibits neuroblastoma
tumor growth in mice. Anticancer Res. 25(1A): 207–212.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshida T, Zhang H, Iwase T, Shen J,
Semenza GL and Campochiaro PA: Digoxin inhibits retinal
ischemia-induced HIF-1alpha expression and ocular
neovascularization. FASEB J. 24:1759–1767. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abud EM, Maylor J, Undem C, Punjabi A,
Zaiman AL, Myers AC, Sylvester JT, Semenza GL and Shimoda LA:
Digoxin inhibits development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in
mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:1239–1244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Zheng J, Du Y, Huang Y, Li J, Liu
B, Liu CJ, Zhu Y, Gao Y, Xu Q, et al: Cartilage oligomeric matrix
protein maintains the contractile phenotype of vascular smooth
muscle cells by interacting with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin. Circ
Res. 106:514–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Norbury C and Nurse P: Animal cell cycles
and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 61:441–470. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: To cycle or
not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
1:222–231. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Qin J and Wu C: ILK: A pseudokinase in the
center stage of cell-matrix adhesion and signaling. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 24:607–613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ross R: The pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 362:801–809.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ferns GA, Raines EW, Sprugel KH, Motani
AS, Reidy MA and Ross R: Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle
accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science.
253:1129–1132. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glass CK and Witztum JL: Atherosclerosis.
the road ahead. Cell. 104:503–516. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Contreras RG, Shoshani L, Flores-Maldonado
C, Lázaro A and Cereijido M: Relationship between Na(+),K(+)-ATPase
and cell attachment. J Cell Sci. 112:4223–4232. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rajasekaran SA, Palmer LG, Moon SY,
Peralta Soler A, Apodaca GL, Harper JF, Zheng Y and Rajasekaran AK:
Na,K-ATPase activity is required for formation of tight junctions,
desmosomes, and induction of polarity in epithelial cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 12:3717–3732. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Wible BA, Wan X and Ficker E:
Cardiac glycosides as novel inhibitors of human
ether-a-go-go-related gene channel trafficking. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 320:525–534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saunders R and Scheiner-Bobis G: Ouabain
stimulates endothelin release and expression in human endothelial
cells without inhibiting the sodium pump. Eur J Biochem.
271:1054–1062. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abramowitz J, Dai C, Hirschi KK, Dmitrieva
RI, Doris PA, Liu L and Allen JC: Ouabain- and
marinobufagenin-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein
smooth muscle cells and a rat vascular smooth muscle cell line,
A7r5. Circulation. 108:3048–3053. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bielawski K, Winnicka K and Bielawska A:
Inhibition of DNA topoisomerases I and II, and growth inhibition of
breast cancer MCF-7 cells by ouabain, digoxin and proscillaridin A.
Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1493–1497. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McConkey DJ, Lin Y, Nutt LK, Ozel HZ and
Newman RA: Cardiac glycosides stimulate Ca2+ increases
and apoptosis in androgen-independent, metastatic human prostate
adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 60:3807–3812. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newman RA, Yang P, Hittelman WN, Lu T, Ho
DH, Ni D, Chan D, Vijjeswarapu M, Cartwright C, Dixon S, et al:
Oleandrin-mediated oxidative stress in human melanoma cells. J Exp
Ther Oncol. 5:167–181. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Newman RA, Kondo Y, Yokoyama T, Dixon S,
Cartwright C, Chan D, Johansen M and Yang P: Autophagic cell death
of human pancreatic tumor cells mediated by oleandrin, a
lipid-soluble cardiac glycoside. Integr Cancer Ther. 6:354–364.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Frese S, Frese-Schaper M, Andres AC,
Miescher D, Zumkehr B and Schmid RA: Cardiac glycosides initiate
Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells
by up-regulation of death receptors 4 and 5. Cancer Res.
66:5867–5874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hallböök H, Felth J, Eriksson A, Fryknäs
M, Bohlin L, Larsson R and Gullbo J: Ex vivo activity of cardiac
glycosides in acute leukaemia. PloS one. 6:e157182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kulikov A, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A and
Scheiner-Bobis G: Ouabain activates signaling pathways associated
with cell death in human neuroblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1768:1691–1702. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
López-Lázaro M, Pastor N, Azrak SS, Ayuso
MJ, Austin CA and Cortés F: Digitoxin inhibits the growth of cancer
cell lines at concentrations commonly found in cardiac patients. J
Nat Prod. 68:1642–1645. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gallo R, Padurean A, Jayaraman T, Marx S,
Roque M, Adelman S, Chesebro J, Fallon J, Fuster V, Marks A, et al:
Inhibition of intimal thickening after balloon angioplasty in
porcine coronary arteries by targeting regulators of the cell
cycle. Circulation. 99:2164–2170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang SH, Liang CJ, Weng YW, Chen YH, Hsu
HY, Chien HF, Tsai JS, Tseng YC, Li CY and Chen YL: Ganoderma
lucidum polysaccharides prevent platelet-derived growth
factor-stimulated smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and
neointimal hyperplasia in the endothelial-denuded artery in vivo. J
Cell Physiol. 227:3063–3071. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Guan H, Gao L, Zhu L, Yan L, Fu M, Chen C,
Dong X, Wang L, Huang K and Jiang H: Apigenin attenuates neointima
formation via suppression of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic
transformation. J Cell Biochem. 113:1198–1207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gomez D and Owens GK: Smooth muscle cell
phenotypic switching in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res.
95:156–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Z, Wang DZ, Hockemeyer D, McAnally J,
Nordheim A and Olson EN: Myocardin and ternary complex factors
compete for SRF to control smooth muscle gene expression. Nature.
428:185–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Mawji N, Deng
JT, Leung D, Yan J, Sanghera J, Walsh MP and Dedhar S: Regulation
of protein kinase B/Akt-serine 473 phosphorylation by
integrin-linked kinase: Critical roles for kinase activity and
amino acids arginine 211 and serine 343. J Biol Chem.
276:27462–27469. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yudowski GA, Efendiev R, Pedemonte CH,
Katz AI, Berggren PO and Bertorello AM: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase
binds to a proline-rich motif in the Na+,
K+-ATPase alpha subunit and regulates its trafficking.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:6556–6561. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Eva A, Kirch U and Scheiner-Bobis G:
Signaling pathways involving the sodium pump stimulate NO
production in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1758:1809–1814. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jagielska J, Salguero G, Schieffer B and
Bavendiek U: Digitoxin elicits anti-inflammatory and vasoprotective
properties in endothelial cells: Therapeutic implications for the
treatment of atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis. 206:390–396. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chase AJ and Newby AC: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase (matrixin) genes in blood vessels: A
multi-step recruitment model for pathological remodelling. J Vasc
Res. 40:329–343. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Johnson JL, Dwivedi A, Somerville M,
George SJ and Newby AC: Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 activates
MMP-9 mediated vascular smooth muscle cell migration and neointima
formation in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:e35–e44. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|