Introduction
Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury (MIRI)
causes irreversible damage to myocardial cells, decreases cell
viability and may have life-threatening consequences (1). Despite the significant negative
impact of MIRI on human health, alleviating I/R injury remains a
challenge for researchers and clinicians.
Previous studies have reported that ischemic
post-conditioning, including pharmacological post-conditioning
(2), may prevent I/R injury in
clinical practice. Ischemic post-conditioning has several clinical
advantages, including predictability, controllability and safety
(3). It has recently been
reported that inhalation anesthetics administered at the beginning
of reperfusion provides cardioprotection against I/R injury
(4). Sevoflurane is widely used
in cardiac surgery since it has the advantages of shorter
induction, reduced recovery time and higher safety when compared
with other anesthetics (5). It
has been demonstrated that sevoflurane reduces myocardial infarct
size and mortality in both animals (6,7)
and humans (8). It has been
suggested that a variety of molecular mechanisms may be responsible
for the protective effects of sevoflurane, including
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway activation
(4,9), reactive oxygen species (ROS)
regulation (10) and
mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) inhibition
(11). However, the exact
mechanisms through which sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces MIRI
remain unknown.
ROS play an important role in MIRI (12), and they have been reported to
modulate the activity of MPTPs (13). The MPTP is a multiprotein
megachannel, and its opening can cause permeability transition.
Massive MPTP opening can result in mitochondrial depolarization and
lead to apoptosis or autophagy (14). Recent studies have demonstrated
that nitric oxide (NO) inhibits sarcolemmal
Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) activity by
activating the soluble isoform of guanylyl cyclase (sGC) and
cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) (15). Both NO synthase (NOS) and NO have
been reported to exert anti-apoptotic effects (16) and play important roles in the
pathogenesis of MIRI (17).
NHE1 has been demonstrated to be a key factor
protecting against I/R injury in experimental animal models
(18). NHE1 is a major
Na+ influx pathway that couples H+ efflux to
Na+ influx in a 1:1 ratio under the driving force of a
Na+ gradient formed by the Na+ pump. NHE1
activation leads to elevated intracellular Na+
concentrations and cytoplasmic alkalinization (19). Villa-Abrille et al
(20) suggested that silencing
cardiac mitochondrial NHE1 prevents MPTP opening.
Even though a number of studies have demonstrated
the cardioprotective effects of NHE1 inhibitors against MIRI, it is
unknown whether NOS and/or phosphorylated (p-)NHE1 plays a role in
mediating the cardioprotective effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning. In the present study, we investigated the
underlying mechanisms through which sevoflurane post-conditioning
reduces myocardial infarct size and mortality following MIRI. Using
a rat heart model of I/R, we investigated new strategies for the
basic and clinical treatment of MIRI.
Materials and methods
Animals and reagents
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 270–350 g
(9–10 weeks old; n=144) were purchased from the Animal Center of
Soochow University (Suzhou, China). Male rats were used to avoid
any potentially confounding effects of female sex hormones (i.e.,
estrogen) on sevoflurane post-conditioning. All rats were kept
under a 12-h light-dark cycle in a temperature-controlled
environment, and were allowed free access to food and water for 1
week prior to euthanasia. All rats were randomly divided into the
experimental groups described below following euthanasia (all
animals were anaesthetized by single-dose intra-peritoneal
injection of pentobarbital, 50 mg/kg body weight). All experimental
protocols were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the policies of Soochow
University (protocol number: SZULL-20090309, approved on March 9,
2009).
Sevoflurane and 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride
(TTC) were purchased from Abbott Laboratories S.A. (Shanghai,
China). Sodium pentobarbital, p-NHE1 and total NHE1 were purchased
from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Antibodies against Bcl-2 (Cat. no.
2876), cleaved caspase-3 (Cat. no. 9665), Beclin-1 (Cat. no. 3495)
were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Danvers, MA,
USA), microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3-I/II; Cat.
no. ab62721-100) was purchased from Abcam, Inc. (Cambridge,
England), glyceralde-hyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; Cat.
no. AG019) and the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit were
purchased from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Nanjing,
China). NO and NOS detection assay kits were purchased from Nanjing
Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, Nanjing, China.
NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) was purchased from
Beyotime Biotechnology Corp. (Shanghai, China). TRIzol and AMV
First Strand cDNA Synthesis kits were obtained from Sangon Biotech
Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Langendorff heart preparation
The hearts were prepared according to the
Langendorff heart model, as described in a previous study (21). Briefly, the animals were
anesthetized with pentobarbital (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneal
injection) followed by heparinization (heparin, 1,000 U/kg). The
animals were then placed in a supine position, the chest cavity was
opened and the hearts were removed and immediately placed in
ice-cold Krebs-Henseleit (K-H) buffer (pH 7.4;
KH2PO4 1.2 mM, NaHCO3 25 mM, KCl
4.8 mM, MgSO4 1.2 mM, glucose 11 mM, NaCl 118 mM and
CaCl2 1.2 mM). The hearts were then perfused on the
Langendorff apparatus at 37°C under a constant pressure of 80 mmHg,
and continuously gassed with 95% O2 and 5%
CO2. A water-filled balloon was inserted into the left
ventricle via the left atrium, and the balloon catheter was then
linked to a pressure transducer that was connected to a
physiological signal acquisition system (U/4C501H Med Lab; Nanjing
Meiyi Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) to monitor
the initial left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). Left
ventricular developed presure (LVDP) was calculated as the
difference between left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP) and
LVEDP. The work index [rate pressure product (RPP)] was calculated
as the product of LVDP and heart rate (HR). All data acquisition
was performed and analyzed using Chart 5 software (ADInstruments,
Bella Vista, Australia).
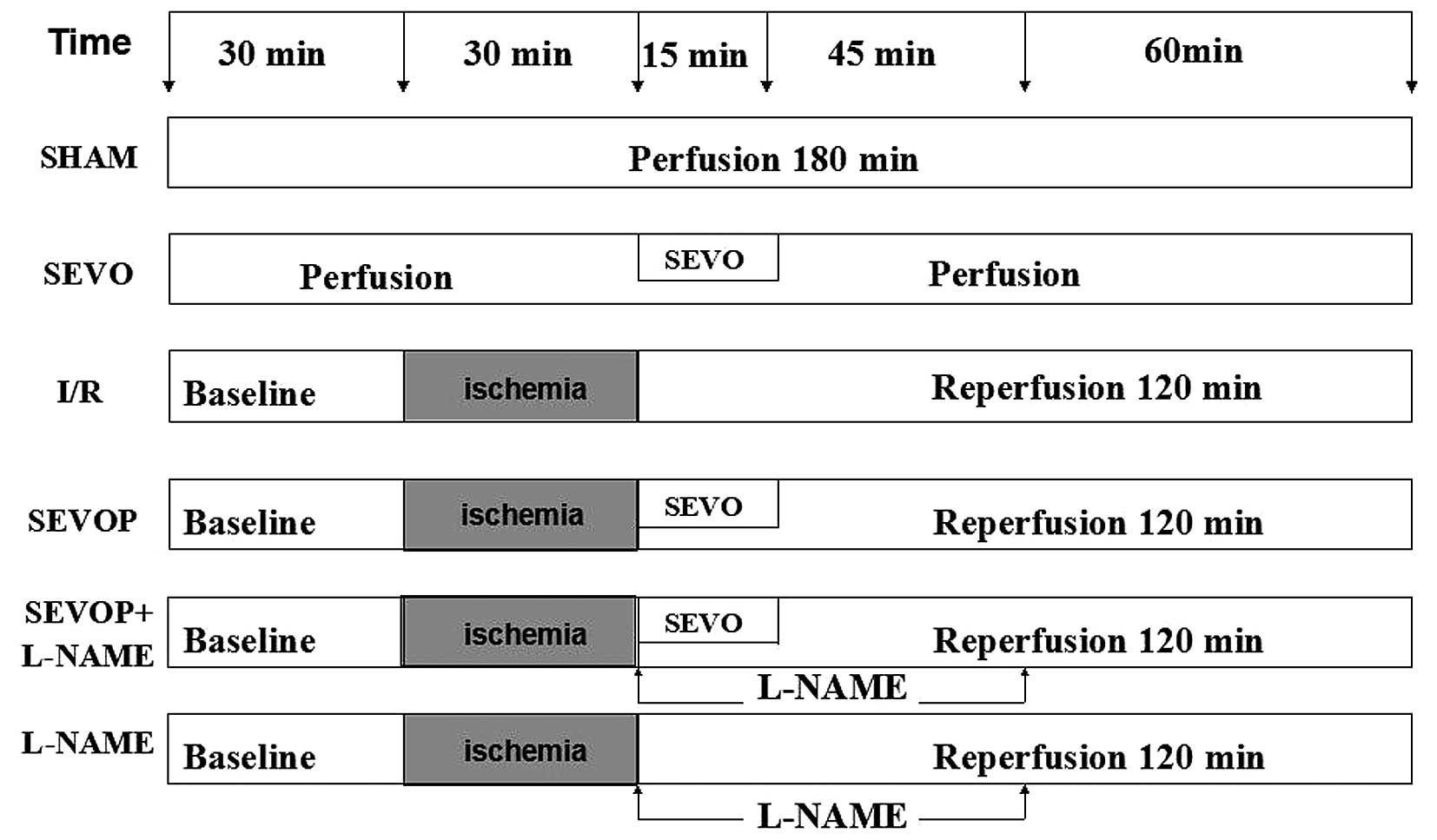
Experimental protocol
Following 30 min of equilibration, the isolated rat
hearts were randomly divided into the following 6 groups: i) the
sham-operated control group, continuously perfused with K-H buffer
for 180 min; ii) the sevoflurane group, exposed to 2.5% sevoflurane
for 15 min, as previously descrbied (22); iii) the I/R group, exposed to
global ischemia for 30 min followed by 120 min of reperfusion; iv)
the sevoflurane post-conditioning (SEVOP) group, exposed to I/R and
2.5% sevoflurane for 15 min; v) the sevoflurane post-conditioning +
L-NAME group (23), exposed to
I/R and 2.5% sevoflurane for 15 min, and 100 µmol/l L-NAME
for 60 min; vi) the L-NAME group, exposed to I/R and 100
µmol/l L-NAME for 60 min. The experimental protocol is
illustrated in Fig. 1.
Measurement of infarct size
Myocardial infarct size was determined by TTC
staining. Briefly, to visualize the unstained infarct area, the
isolated hearts were removed from the Langendorff device following
2 h of reperfusion, cut into 5 µm slices and incubated for
20 min in 0.1 mol/l sodium phosphate buffer containing 1% TTC at
37°C. The infarct and risk zone areas were calculated with digital
planimetry using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics Inc.,
Rockville, MD, USA), according to the methods described in previous
studies (24,25).
Determination of NOS and NO levels
Following reperfusion, the hearts were removed from
the Langendorff device and homogenized in ice-cold 0.9% saline
solution, and then centrifuged at 600 × g for 10 min. The NO and
NOS levels were measured using a diagnostic assay kit (Nanjing
Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute). The absorbance was
determined using a DU-640 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter Inc.,
Brea, CA, USA) at 530 nm and plotted as a percentage of the control
according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Detection of mitochondrial nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
The quantity of mitochondrial NAD+ in the
heart tissue was determined as previously described (26). Briefly, heart mitochondrial
proteins were treated with ice-cold perchloric acid (21%, v/v) for
30 min, centrifuged at 8,000 × g, and the supernatant was then
neutralized with KOH. The NAD+ content was determined by
fluorometrically measuring NAD+-dependent lactate
dehydrogenase activity in a reaction buffer containing 500 mM
glycine and 400 mM hydrazine at pH 9.0 and 25°C. Activity was
evaluated at a wavelength of 340 nm (DU-640; Beckman Coulter
Inc.).
Transmission electron microscopy
(TEM)
After teh other experiments, the isolated heart
tissues were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution for 2 h,
washed with 0.1 M cacodylate buffer and post-fixed with 1% osmium
tetroxide. Following dehydration with 50–100% (v/v) ethanol and
acetone, the sections were embedded in Epon 812 epoxy resin.
Ultrathin sections were obtained at 50–70 nm and stained with 1%
uranyl acetate and lead citrate. Apoptotic and autophagic cells
were examined under a transmission electron microscope (HT7700;
Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
Western blot analysis
Western blot analysis was performed as previously
described (27). Briefly, heart
tissue (40 mg) was homogenized in lysis buffer (0.13 M KCl; 20 mM
HEPES, pH 7.4; 1 mM EGTA; 1 µg/ml aprotinin; 1 µg/ml
leupeptin; and 1 mM PMSF). Protein concentrations were quantified
using a BCA protein assay kit. Protein samples (50 µg) were
resolved on a sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel and then
transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were
blocked for 2 h at room temperature with 5% milk in Tris-buffered
saline, followed by incubation with the following primary
antibodies at 4°C overnight: Bcl-2 (1:1,000 dilution), cleaved
caspase-3 (1:1,000 dilution), Beclin-1 (1:1,000 dilution), LC3-I
(1:1,000 dilution), LC3-II (1:1,000 dilution), NHE1 (1:1,000
dilution), p-NHE1 (1:1,000 dilution) and GAPDH (1:1,000 dilution).
After washing 3 times with 0.05% TBS and Tween-20, the membranes
were incubated with goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies
conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (A0216; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology), at a dilution of 1:2,000. Bands were detected
using the Pierce ECL detection system (Pierce Biotechnology, Thermo
Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Band intensity was
quantified using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health,
Bethesda, MD, USA). Protein expression was quantified relative to
GAPDH bands from the same sample.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
RT-qPCR was used to measure the NHE1 mRNA expression
levels. Briefly, the hearts were harvested following reperfusion,
total RNA was extracted from the left ventricular heart tissues
using TRIzol reagent and the RNA purity was quantified
spectrophotometrically at a ratio of 260 to 280 nm. cDNA was
obtained from 1 µg total RNA using the AMV First Strand cDNA
Synthesis kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (New
England Biolabs Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA). Quantitative (real-time)
PCR (qPCR) was performed using iQ SYBR-Green Supermix (Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). The NHE1 and GAPDH
(internal control) primer sequences were defined as follows: NHE1
forward, 5′-GCGGCGAGCAGATCAATAA-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACAGTGACGGCATCGTTGAG-3′; and GAPDH forward,
5′-CAAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CGCCAGTAGACTCCACGACA-3′. The reaction conditions were as
follows: 10 sec at 95°C, 40 sec at 60°C and 45 sec at 72°C for 40
cycles. Amplification of the products was followed by melting curve
analysis using Applied Biosystems 7500 system software, as
previously described (28) (Life
Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA). The value of NHE1 mRNA was
expressed relative to that of GAPDH from the same sample.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as the means ± standard
deviation (SD) and analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's
post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. A value of P<0.05
(two-tailed) was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference. All statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad
Prism 5.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA,
USA).
Results
Sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces the
myocardial infarct size
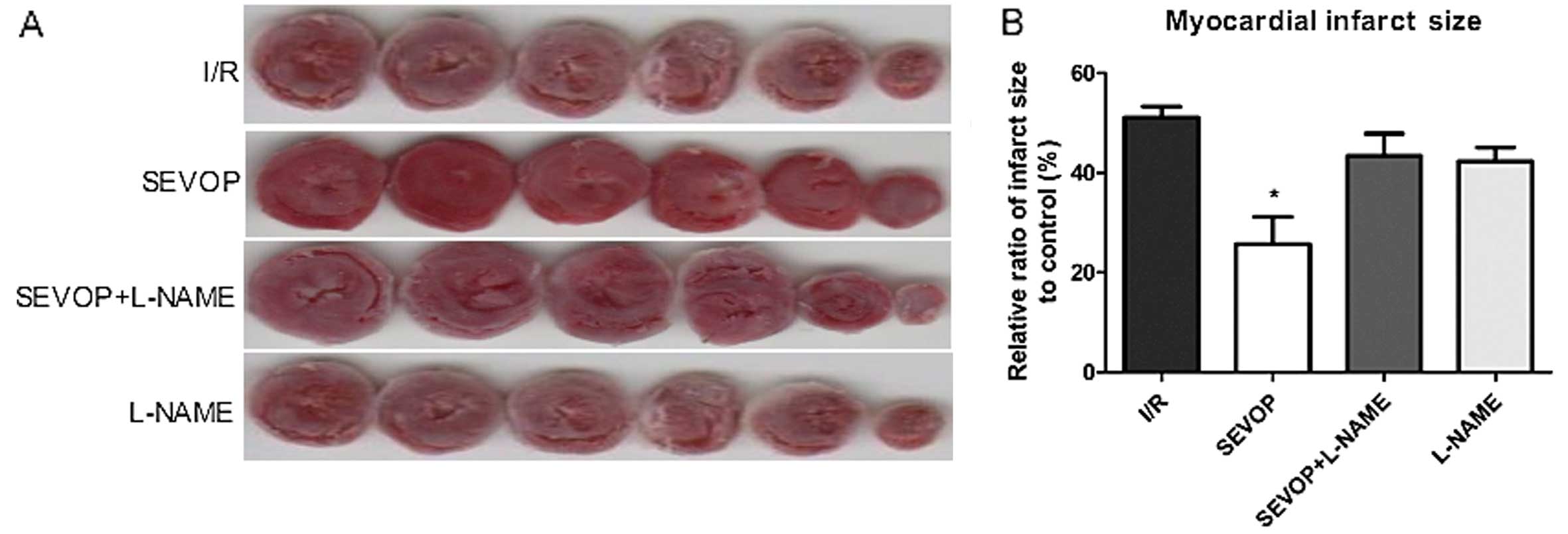
To evaluate the effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning on MIRI in vitro, we measured rat
myocardial infarct size using the TTC staining method, as
previously described (25).
Following 120 min of reperfusion, the infarct size in the
sevoflurane post-conditioning treatment group (SEVOP) decreased to
25.67±5.52% compared to that in the I/R group (I/R, no treatment,
51.07±2.27%; P<0.05). Treatment with L-NAME abolished the
reducing effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning on the infarct
size. Notably, without sevoflurane post-conditioning, treatment
with L-NAME alone did not affect the ratio of the infarct size when
compared with the untreated groups (P>0.05; Fig. 2).
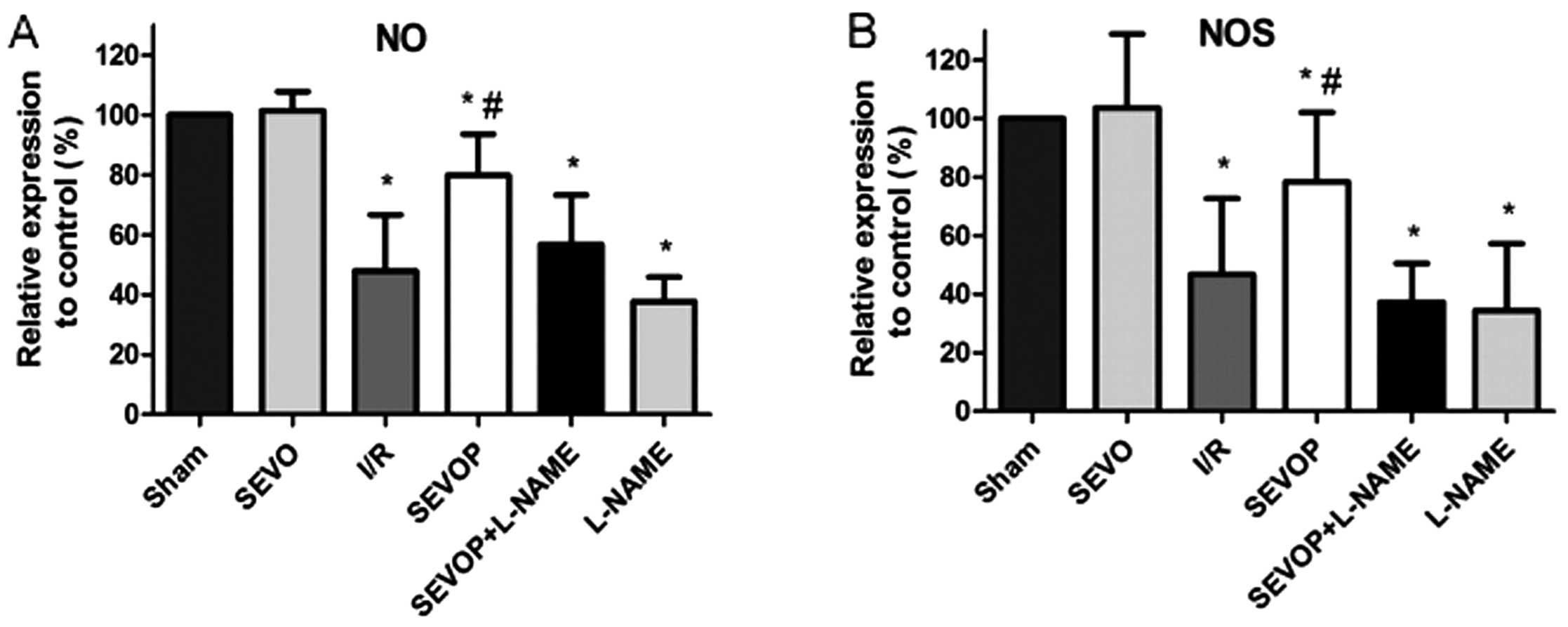
Sevoflurane post-conditioning upregulates
the NOS and NO levels
We measured the NO and NOS levels in the heart
tissues subjected to MIRI with or without sevoflurane
post-conditioning. We observed that the NO and NOS levels were
decreased in the heart tissues subjected to MIRI when compared with
the levels in the sham-operated group (P<0.05, n=6 experiments;
Fig. 3). However, sevoflurane
post-conditioning induced a significant increase in the NO and NOS
levels when compared with the I/R group (no treatment, P<0.05,
n=6 experiments; Fig. 3). The
increase in the levels of NO and NOS induced by sevoflurane
post-conditioning was markedly suppressed by treatment with L-NAME
(Fig. 3).
Sevoflurane post-conditioning inhibits
the I/R induced loss in NAD+ content
Mitochondrial NAD+ levels may be used as
a marker of MPTP opening in MIRI heart tissues and it has been
suggested that NAD+ levels are significantly decreased
in tissues subjected to MIRI (29). In this study, to confirm MPTP
opening in injured heart tissue during reperfusion, as well as the
protective effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning on this
process, we measured the NAD+ levels in the mitochondria
isolated from heart tissues. The NAD+ levels were
significantly decreased following exposure to I/R compared to the
group exposed to sevoflurane post-conditioning (181±40 to 91±27
nmol/g). The I/R-induced loss in the NAD+ content in the
heart tissues subjected to MIRI was reversed by sevoflurane
post-conditioning (from 91±27 to 122±30 nmol/g), and this effect
was largely blocked by treatment with L-NAME (Table I).
 | Table IDetermination of NAD+
content. |
Table I
Determination of NAD+
content.
| Groups | Sham | SEVO | I/R | SEVOP | SEVOP + L-NAME | L-NAME |
|---|
| NAD+
(nmol/g) | 178±37 | 181±40 | 91±27a |
122±30a,b | 95±26a | 88±24a |
Sevoflurane post-conditioning decreases
myocardial tissue apoptosis following MIRI
Western blot analysis and quantitative analysis
indicated that the Bcl-2 levels were significantly lower in the I/R
group (29.92±3.75) when compared with the sham-operated group
(61.54±7.89; P<0.05; Fig. 4A).
Sevoflurane post-conditioning increased Bcl-2 expression
(44.32±1.75); however, this effect was inhibited by treatment with
L-NAME (22.17±5.47), indicating that sevoflurane post-conditioning
inhibited I/R-induced apoptosis. The results obtained for the other
apoptotic marker, cleaved caspase-3 (Fig. 4B), also indicated that sevoflurane
post-conditioning inhibited apoptosis. I/R injury increased the
levels of cleaved caspase-3, and sevoflurane post-conditioning
decreased the cleaved caspase-3 levels. Once again, these effects
were reversed by treatment with L-NAME (Fig. 4B). We also used TEM to observe
apoptosome formation and confirmed reduced apoptosome formation
following sevoflurane post-conditioning. The ultrastructure of the
myocardial tissues exhibited a variety of characteristics
associated with apoptosis, including mild swelling of the nucleus,
chromatin edge set along the nuclear membrane, a loose cytoplasm,
moderate mitochondrial swelling and sparse cristae (Fig. 4C). However, sevoflurane
post-conditioning reversed these effects (Fig. 4D). These results confirm the
hypothesis that MIRI increases apoptosis in the heart and that
sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces MIRI-induced apoptosis in
myocardial tissue.
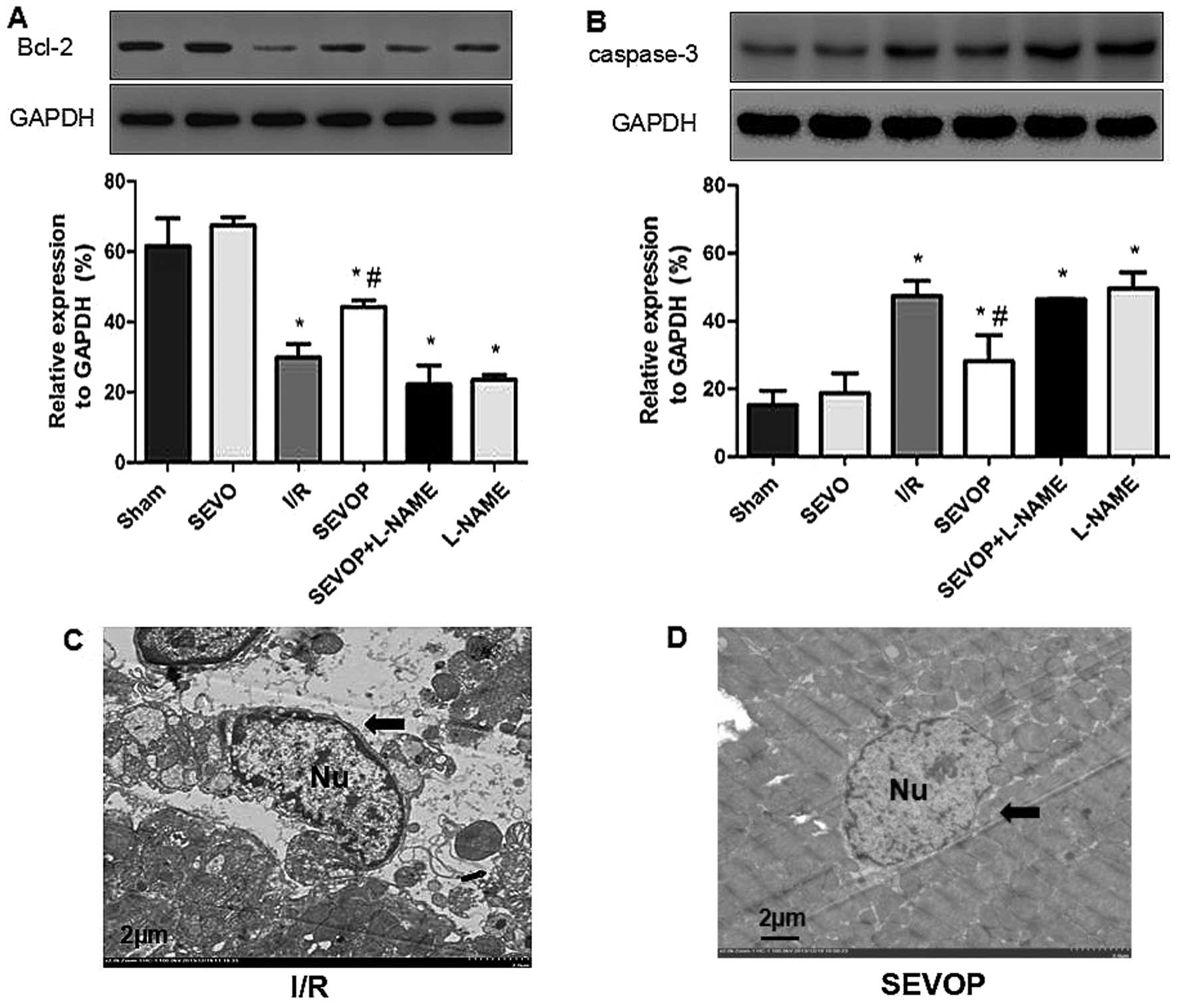 | Figure 4Alterations in Bcl-2 expression and
cleaved-caspase-3 activity following sevoflurane post-conditioning.
Shown are myocardial western blots of Bcl-2 and cleaved caspase-3
expression. (A and B) Representative western blots of Bcl-2 and
cleaved-caspase-3, respectively, in Sham, SEVO, I/R, SEVOP,
SEVOP+L-NAME and L-NAME groups. (C and D) Representative
transmission electron microscopy images from the I/R and SEVOP
groups, respectively (original magnification, ×2000; scale bar, 2
µm). Images show that apoptosomes were decreased in the
SEVOP group when compared with the I/R group. As indicated by the
arrows, panel (C) shows mild swelling of the nucleus, chromatin
edge set along the nuclear membrane, loose cytoplasm and moderate
swelling of the mitochondria These effects were attenuated in the
SEVOP group (D). The data are presented as the means ± SD (n=5
experiments). A one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test was
used to determine statistical significance. *P<0.05
vs. sham. #P<0.05 vs. I/R. SEVO, sevoflurane group
(no I/R injury); I/R, ischemia/reperfusion injury group; SEVOP,
sevoflurane post-conditioning group; L-NAME, group treated with
NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (NOS inhibitor); Nu, nucleus. |
Sevoflurane post-conditioning inhibits
autophagy following MIRI
To examine whether the protective effects if
sevoflurane post-conditioning in MIRI are mediated by the
inhibition of autophagy in vivo, we detected the expression
of the autophagic markers, LC3-I/II and Beclin-1. Western blot and
quantitative analyses indicated that the LC3-I/II and Beclin-1
levels were significantly higher in the I/R group when compared
with the sham-operated group (Fig. 5A
and B). However, sevoflurane post-conditioning decreased
Beclin-1 and LC3-I/II expression (Fig. 5A and B). However, treatment with
L-NAME largely abolished these effects, suggesting that sevoflurane
post-conditioning reduces the I/R-mediated activation of autophagy
(Fig. 5A and B). We also used TEM
to detect the formation of autophagosomes and double limiting
membranes in the I/R group. Ultrastructural image analysis revealed
that the number of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) was markedly increased
in the heart tissue subjected to I/R (Fig. 5C). Sevoflurane post-conditioning
decreased the number of AVs (Fig.
5D).
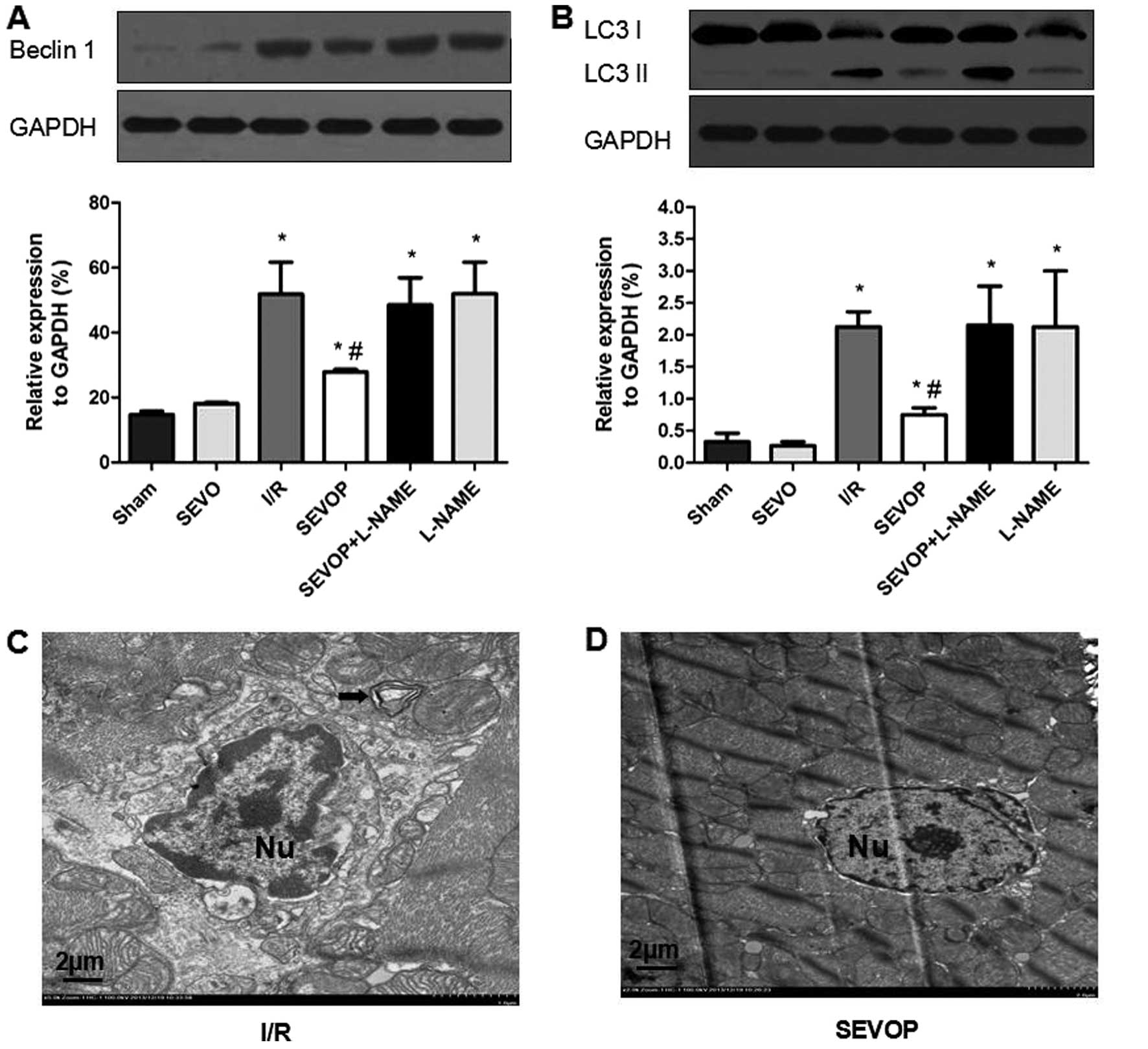 | Figure 5Alterations in LC3-II/I and Beclin-1
expression following sevoflurane post-conditioning. Shown are
myocardial western blots of LC3-II/I and Beclin-1 expression. (A
and B) Representative western blots of Beclin-1 and LC3II/I,
respectively, in the Sham, SEVO, I/R, SEVOP, SEVOP + L-NAME and
L-NAME groups. Values are expressed as the means ± SD (n=5
experiments). A one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test was
used to determine statistical significance. *P<0.05
vs Sham. #P<0.05 vs I/R. (C and D) Representative
transmission electron microscopy images from the I/R and SEVOP
groups, respectively (original magnification, ×2,000; scale bar, 2
µm), showing that the number of autophagic vacuoles (AVs)
decreased in the sevoflurane post-conditioning group when compared
with the I/R group. (C) Arrow indicates autophagic vacuole. Sham,
sham-operated group; SEVO, sevoflurane group (no I/R injury); I/R,
ischemia/reperfusion injury group; SEVOP, sevoflurane
post-conditioning group; L-NAME, group treated with
NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (NOS inhibitor); Nu, nucleus. |
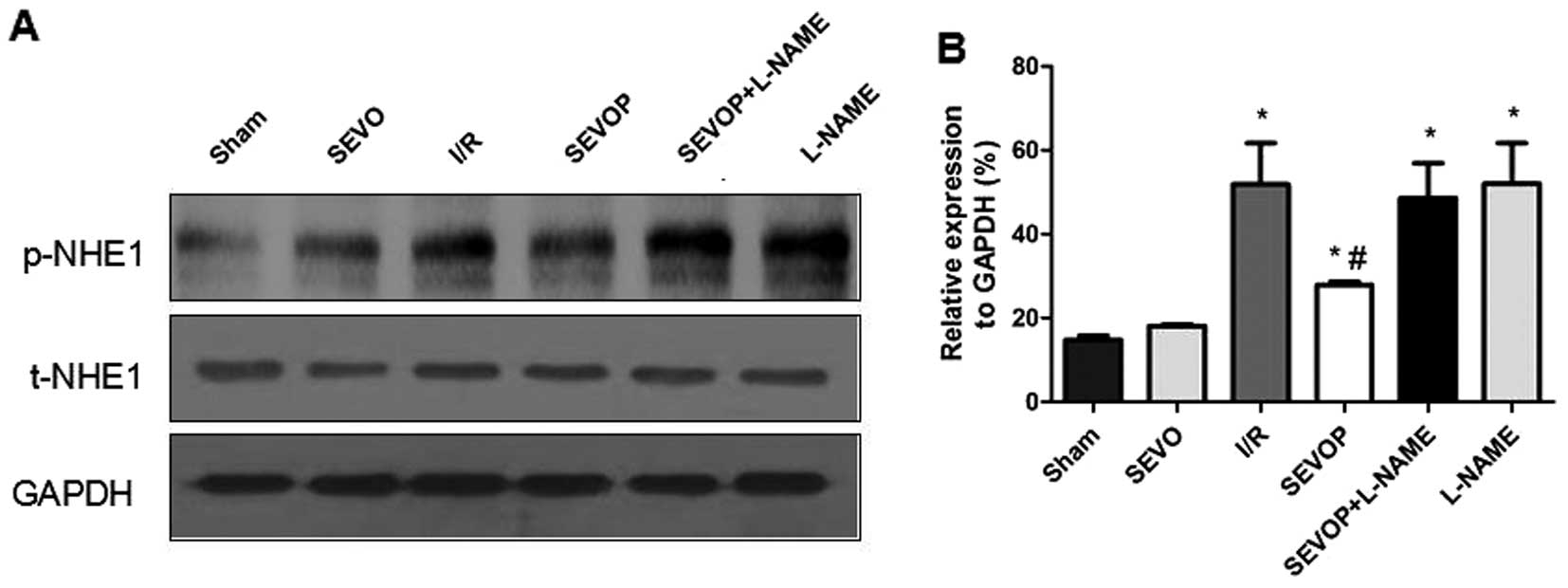
Protein expression of p-NHE1 and NHE1
mRNA expression is inhibited in myocardial tissues subjected to I/R
following sevoflurane post-conditioning
We investigated whether the NHE1 phosphorylation
levels are altered in myocardial tissues subjected to I/R. We
measured the protein expression levels of p-NHE1 and total (t-)NHE1
by western blot analysis. The ratio of p-NHE1 to NHE1 protein
increased significantly in the I/R group when compared with the
sham-operated group. p-NHE1 protein expression was significantly
decreased following sevoflurane post-conditioning. However,
treatment with L-NAME abolished the reducing effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning on p-NHE1 expression (Fig. 6). Furthermore, the results of
RT-qPCR confirmed the significant increase in NHE1 mRNA expression
in the I/R group compared with the sham-operated group (P<0.05).
Moreover, when compared with the untreated I/R group, the NHE1 mRNA
levels were decreased in the sevoflurane post-conditioning group
and were restored in the L-NAME treatment group (Fig. 7).
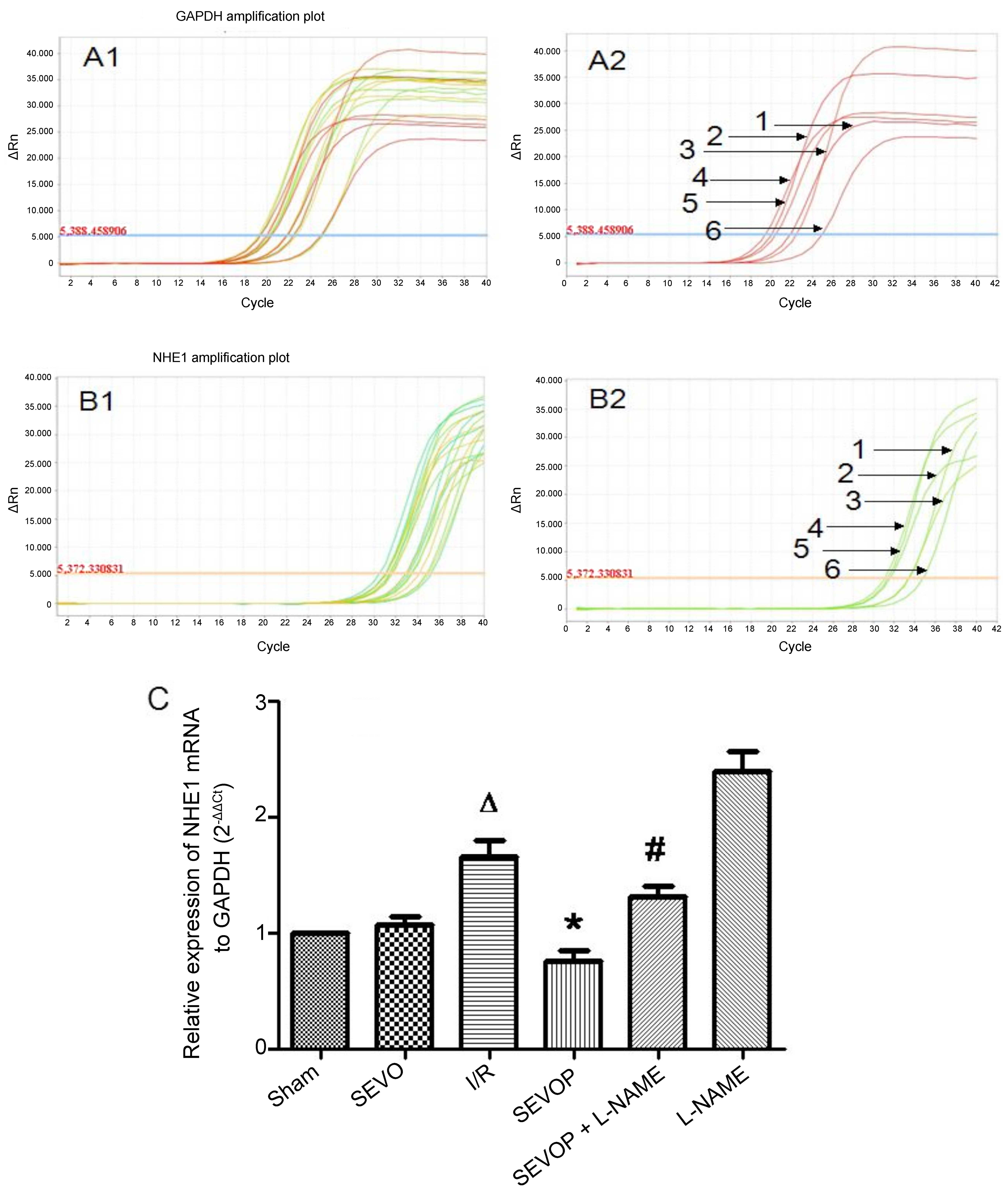 | Figure 7Sevoflurane post-conditioning
inhibits NHE1 mRNA expression. (A1) Representative amplification
plot of GAPDH; 3 microwells/group, 6 groups; 3 different colors
indicate 3 microwells. (A2) Representative amplification plot of
GAPDH for 6 groups. Numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, represent the
amplification plot of GAPDH for the Sham, SEVO, I/R, SEVOP, SEVOP +
L-NAME and L-NAME groups, respectively. (B1) Representative
amplification plot of NHE1; 3 microwells/ group, 6 groups; 3
different colors indicate 3 microwells. (B2) Representative
amplification plot of NHE1 for 6 groups. Numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and
6, represent the amplification plot of NHE1 for the Sham, SEVO,
I/R, SEVOP, SEVOP + L-NAME and L-NAME groups, respectively. (C)
mRNA expression of NHE1 relative to GAPDH, in the Sham, SEVO, I/R,
SEVOP, SEVOP + L-NAME and L-NAME groups, respectively. Values are
expressed as the means ± SD (n=3). A one-way ANOVA followed by
Tukey's post-hoc test was used to determine statistical
significance. ΔP<0.05 vs. Sham, *P<0.05
vs. I/R, #P<0.05 vs. SEVOP.. |
Discussion
In the present study, we used a rat model of MIRI
nvestigate a novel mechanism through which sevoflurane
post-conditioning protects the heart against MIRI. Our results
confirmed I/R induced apoptosis and excessive autophagy, eventually
causing myocardial infarction. Notably, sevoflurane
post-conditioning significantly attenuated MIRI and inhibited
apoptosis and excessive autophagy. Furthermore, the NHE1
phosphorylation and mRNA expression levels were markedly
downregulated by sevoflurane post-conditioning. These effects were
all abolished by treatment with L-NAME.
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is
the first to demonstrate that sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces
MIRI in vitro, and furthermore, that this protective
mechanism is mediated through an increase in NOS and a decrease in
p-NHE1 levels.
Apoptosis is one of the major mechanisms responsible
for cell death in MIRI (28,30). The inhibition of apoptosis has
been demonstrated to be a key mechanisms that reduces myocardial
infarct size (31,32). Additionally, it has been suggested
that the appropriate upregulation of autophagy exerts
cardioprotective effects during I/R injury (33). However, other studies have
demonstrated that certain drugs, such as α-lipoic acid, protect the
heart against injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy (34). In the present study, we observed
that sevoflurane post-conditioning elevated Bcl-2 expression,
decreased the Beclin-1 and LC3-I/II levels, and attenuated I/R
injury. As confirmed by by our TEM observations, our results
suggest that sevoflurane post-conditioning protects the heart
tissue following myocardial infarction and reduces MIRI through the
inhibition of apoptosis and excessive autophagy.
NO, which is generated from L-arginine by NOS1, NOS2
and NOS3, is a key factor which has been demonstrated to exert
protective effects against cardiac injury (35,36). Previous studies have also
demonstrated that NO is associated with the pathogenesis of MIRI
(37) and that it regulates
cytoprotection during I/R injury (38). In the present study, both NO and
NOS levels expression were significantly increased by sevoflurane
post-conditioning when compared with the I/R group. We also found
that treatment with L-NAME attenuated the effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning on the NO and NOS levels. This indicates that NOS
regulates the NO/ONOO− balance and mediates the
protective effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning in MIRI.
The inhibition of MPTP opening is a potential
cardioprotective mechanism. Thus, to investigate the role of MPTP
opening in MIRI following sevoflurane post-conditioning, we
measured the NAD+ levels, which indirectly represent
MPTP opening (14). Compared with
the sham-operated group, the NAD+ levels were
significantly decreased in the I/R group; however, sevoflurane
post-conditioning inhibited the loss of NAD+ (Table I). We also observed that treatment
with L-NAME inhibited the effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning
on the NAD+ levels.
MIRI has been demonstrated to be associated with a
variety of significant intracellular and extracellular metabolic
alterations, including elevated potassium, increased lactate and
acidosis (39,40). NHE is a membrane transport protein
that is activated by ischemia and that catalyzes the exchange of
Na+ for H+. Intracellular Na+ and
Ca2+ overload may lead to cardiac injury following
myocardial ischemia. Recent studies have confirmed that NHE1
inhibition prevents MPTP opening and reduces myocardial ischemia
injury (40,41). In the present study, sevoflurane
post-conditioning reduced the phosphorylation and transcription
levels of NHE1, whereas L-NAME inhibited these effects (Fig. 7). However, when compared with the
I/R group, treatment with L-NAME alone did not affect the
phosphorylated NHE1 protein or NHE1 mRNA levels.
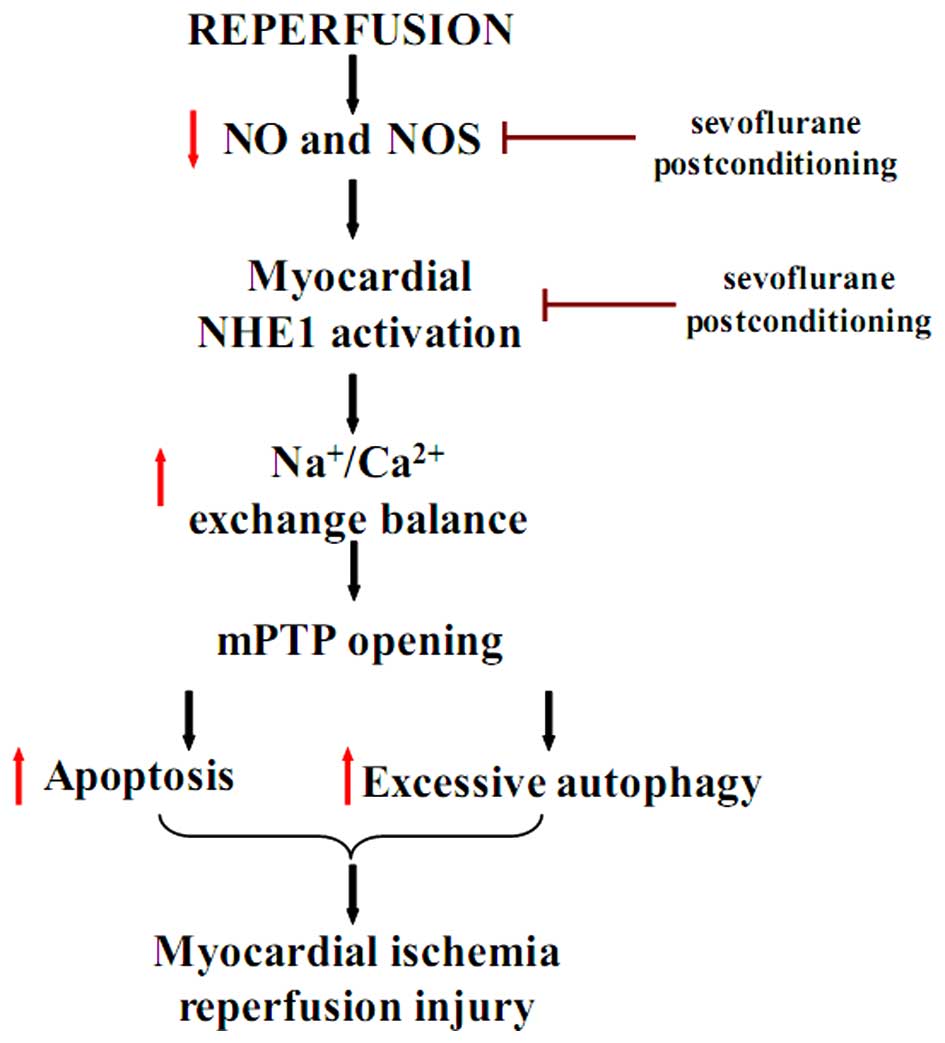
In conclusion, the findings of the present study
confirm the cardioprotective effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning against MIRI through the inhibition of apoptosis
and excessive autophagy. The protective effects of sevoflurane
post-conditioning following I/R injury in vitro may be
regulated by the increase in NOS and the decrease in p-NHE1 levels
(Fig. 8). The present study
provides evidence for a new protective mechanism of sevoflurane
post-conditioning against MIRI. The mechanisms reported in this
study may aid the future design of therapeutic strategies to
prevent MIRI in humans and therefore, further clinical studies are
warranted to explore optimal sevoflurane post-conditioning
treatment conditions.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81372024, to J.Z.),
the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (grant
no. BK20141187, to C.W), and the Science and Technology Development
Plan of Suzhou City, China (grant no. SYSD2012085, to J.C.)
References
|
1
|
Hu Q, Chen J, Jiang C and Liu HF: Effect
of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist on
heart of rabbits with acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 7:271–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu M, Feng J, Lucchinetti E, Fischer G,
Xu L, Pedrazzini T, Schaub MC and Zaugg M: Ischemic
postconditioning protects remodeled myocardium via the PI3K-PKB/Akt
reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res.
72:152–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xia A, Xue Z, Wang W, Zhang T, Wei T, Sha
X, Ding Y and Zhou W: Naloxone postconditioning alleviates rat
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting JNK activity.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 18:67–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yao YY, Zhu MH, Zhang FJ, Wen CY, Ma LL,
Wang WN, Wang CC, Liu XB, Yu LN, Qian LB, et al: Activation of Akt
and cardioprotection against reperfusion injury are maximal with
only five minutes of sevoflurane postconditioning in isolated rat
hearts. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 14:511–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakai EM, Connolly LA and Klauck JA:
Inhalation anesthesiology and volatile liquid anesthetics: Focus on
isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane. Pharmacotherapy.
25:1773–1788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng Z, Yang M, Zhang F, Yu J, Wang J, Ma
L, Zhong Y, Qian L, Chen G, Yu L and Yan M: Gender-related
difference of sevoflurane postconditioning in isolated rat hearts:
Focus on phosphatidylino-sitol-3-kinase/Akt signaling. J Surg Res.
170:e3–e9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inamura Y, Miyamae M, Sugioka S, Domae N
and Kotani J: Sevoflurane postconditioning prevents activation of
caspase 3 and 9 through antiapoptotic signaling after myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion. J Anesth. 24:215–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ceyhan D, Tanrıverdi B and Bilir A:
Comparison of the effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane on
myocardial protection in coronary bypass surgery. Anadolu Kardiyol
Derg. 11:257–262. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao YT, Li LH, Chen L, Wang WP, Li LB and
Gao CQ: Sevoflurane postconditioning protects isolated rat hearts
against ischemia-reperfusion injury: The role of radical oxygen
species, extracellular signal-related kinases 1/2 and mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Mol Biol Rep. 37:2439–2446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gong JS, Yao YT, Fang NX and Li LH:
Sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates reperfusion-induced
ventricular arrhythmias in isolated rat hearts exposed to
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Biol Rep. 39:6417–6425. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao Y, Li L, Li L, Gao C and Shi C:
Sevoflurane postconditioning protects chronically-infarcted rat
hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury by activation of
pro-survival kinases and inhibition of mitochondrial permeability
transition pore opening upon reperfusion. Biol Pharm Bull.
32:1854–1861. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zweier JL, Flaherty JT and Weisfeldt ML:
Direct measurement of free radical generation following reperfusion
of ischemic myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:1404–1407. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshida A, Asanuma H, Sasaki H, Sanada S,
Yamazaki S, Asano Y, Shinozaki Y, Mori H, Shimouchi A, Sano M, et
al: H2 mediates cardioprotection via involvements of K
channels and permeability transition pores of mitochondria in dogs.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 26:217–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Petrosillo G, Di Venosa N, Moro N,
Colantuono G, Paradies V, Tiravanti E, Federici A, Ruggiero FM and
Paradies G: In vivo hyperoxic preconditioning protects against
rat-heart ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrial
permeability transition pore opening and cytochrome c release. Free
Radic Biol Med. 50:477–483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Prasad V, Lorenz JN, Miller ML, Vairamani
K, Nieman ML, Wang Y and Shull GE: Loss of NHE1 activity leads to
reduced oxidative stress in heart and mitigates high-fat
diet-induced myocardial stress. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 65:33–42. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goldman A, Shahidullah M, Goldman D,
Khailova L, Watts G, Delamere N and Dvorak K: A novel mechanism of
acid and bile acid-induced DNA damage involving
Na+/H+ exchanger: implication for Barrett's
oesophagus. Gut. 59:1606–1616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qian GQ, Peng X, Cai C and Zhao GP: Effect
on eNOS/NO Pathway in MIRI rats with preconditioning of GFPC from
Dang Gui Si Ni decoction. Pharmacognosy Res. 6:133–137. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakamura TY, Iwata Y, Arai Y, Komamura K
and Wakabayashi S: Activation of Na+/H+
exchanger 1 is sufficient to generate Ca2+ signals that
induce cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Circ Res.
103:891–899. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwamoto T, Wakabayashi S and Shigekawa M:
Growth factor-induced phosphorylation and activation of aortic
smooth muscle Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol
Chem. 270:8996–9001. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Villa-Abrille MC, Cingolani E, Cingolani
HE and Alvarez BV: Silencing of cardiac mitochondrial NHE1 prevents
mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1237–H1251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Testai L, Martelli A, Cristofaro M,
Breschi MC and Calderone V: Cardioprotective effects of different
flavonoids against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in
Langendorff-perfused rat hearts. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:750–756.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deyhimy DI, Fleming NW, Brodkin IG and Liu
H: Anesthetic preconditioning combined with postconditioning offers
no additional benefit over preconditioning or postconditioning
alone. Anesth Analg. 105:316–324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burley DS and Baxter GF: B-type
natriuretic peptide at early reperfusion limits infarct size in the
rat isolated heart. Basic Res Cardiol. 102:529–541. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lecour S, Smith RM, Woodward B, Opie LH,
Rochette L and Sack MN: Identification of a novel role for
sphingolipid signaling in TNF alpha and ischemic preconditioning
mediated cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:509–518. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng C, Sun Z, Tong G, Yi W, Ma L, Zhao B,
Cheng L, Zhang J, Cao F and Yi D: α-Lipoic acid reduces infarct
size and preserves cardiac function in rat myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e583712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kern SE, Price-Whelan A and Newman DK:
Extraction and measurement of NAD(P)+ and NAD(P)H.
Methods Mol Biol. 1149:311–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vessey DA, Li L, Kelley M and Karliner JS:
Combined sphingosine, S1P and ischemic postconditioning rescue the
heart after protracted ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
375:425–429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng XY, Yu HL, Zhang WC, Wang TH, Mai X,
Liu HT and Xu RC: ZFP580, a novel zinc-finger transcription factor,
is involved in cardioprotection of intermittent high-altitude
hypoxia against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
9:e946352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Di Lisa F and Ziegler M:
Pathophysiological relevance of mitochondria in NAD(+) metabolism.
FEBS Lett. 492:4–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek
WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ and Doevendans PA: Role of apoptosis
in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:414–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao ZQ, Morris CD, Budde JM, Wang NP,
Muraki S, Sun HY and Guyton RA: Inhibition of myocardial apoptosis
reduces infarct size and improves regional contractile dysfunction
during reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 59:132–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ling H, Wu L and Li L: Corydalis yanhusuo
rhizoma extract reduces infarct size and improves heart function
during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion by inhibiting apoptosis in
rats. Phytother Res. 20:448–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han Z, Cao J, Song D, Tian L, Chen K, Wang
Y, Gao L, Yin Z, Fan Y and Wang C: Autophagy is involved in the
cardioprotection effect of remote limb ischemic postconditioning on
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in normal mice, but not
diabetic mice. PLoS One. 9:e868382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao X, Chen A, Yang P, Song X, Liu Y, Li
Z, Wang X, Wang L and Li Y: Alpha-lipoic acid protects
cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting
autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:935–940. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balligand JL, Feron O and Dessy C: eNOS
activation by physical forces: from short-term regulation of
contraction to chronic remodeling of cardiovascular tissues.
Physiol Rev. 89:481–534. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manoury B, Montiel V and Balligand JL:
Nitric oxide synthase in post-ischaemic remodelling: new pathways
and mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res. 94:304–315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jin H, Wang Y, Wang X, Sun Y, Tang C and
Du J: Sulfur dioxide preconditioning increases antioxidative
capacity in rat with myocardial ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Nitric Oxide. 32:56–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gonzalez FM, Shiva S, Vincent PS, Ringwood
LA, Hsu LY, Hon YY, Aletras AH, Cannon RO III, Gladwin MT and Arai
AE: Nitrite anion provides potent cytoprotective and antiapoptotic
effects as adjunctive therapy to reperfusion for acute myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 117:2986–2994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Corr PB and Yamada KA: Selected metabolic
alterations in the ischemic heart and their contributions to
arrhythmogenesis. Herz. 20:156–168. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Doods H and Wu D: Sabiporide reduces
ischemia-induced arrhythmias and myocardial infarction and
attenuates ERK phosphorylation and iNOS induction in rats. Biomed
Res Int. 2013:5043202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Perez NG, Nolly MB, Roldan MC,
Villa-Abrille MC, Cingolani E, Portiansky EL, Alvarez BV, Ennis IL
and Cingolani HE: Silencing of NHE-1 blunts the slow force response
to myocardial stretch. J Appl Physiol. 111:874–880. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|