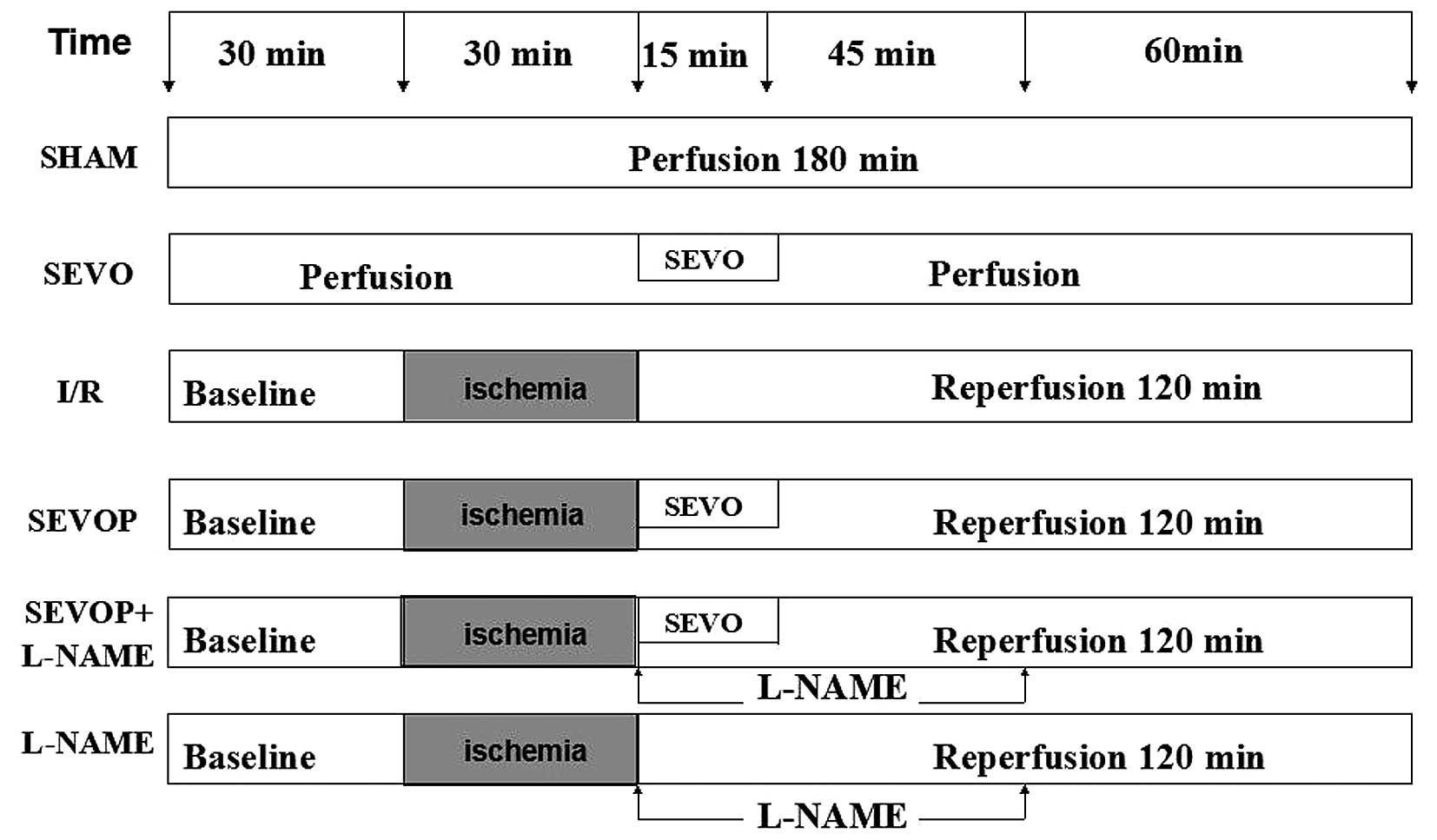
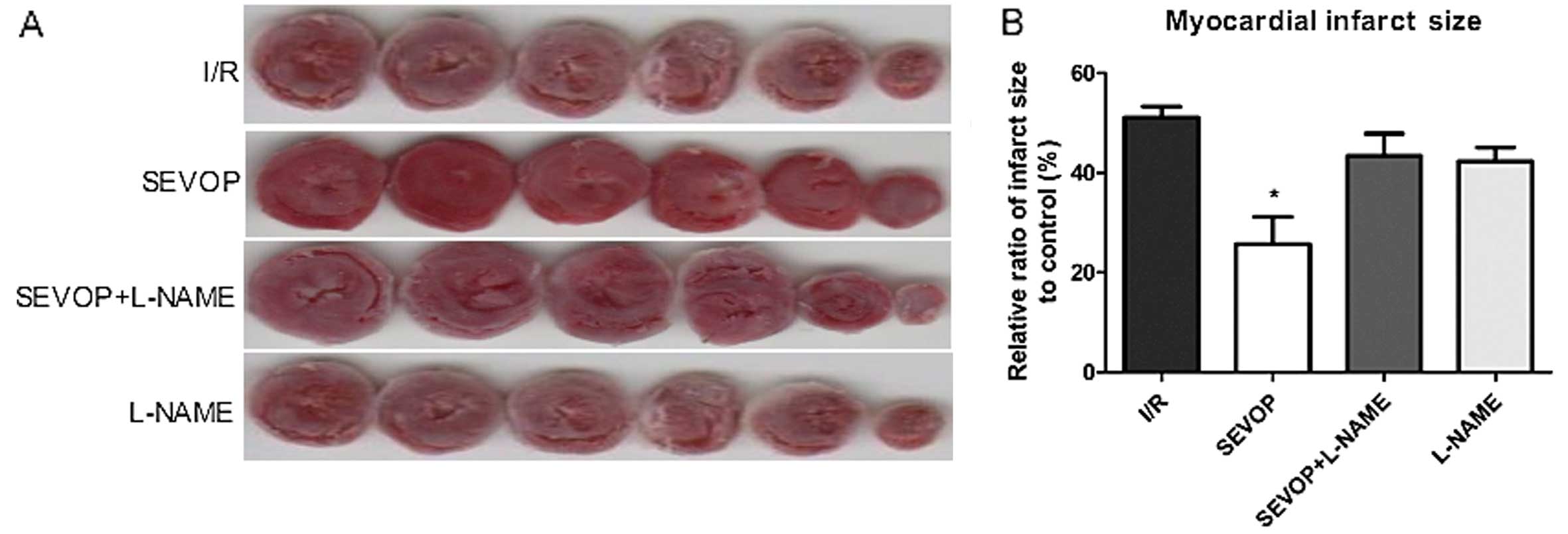
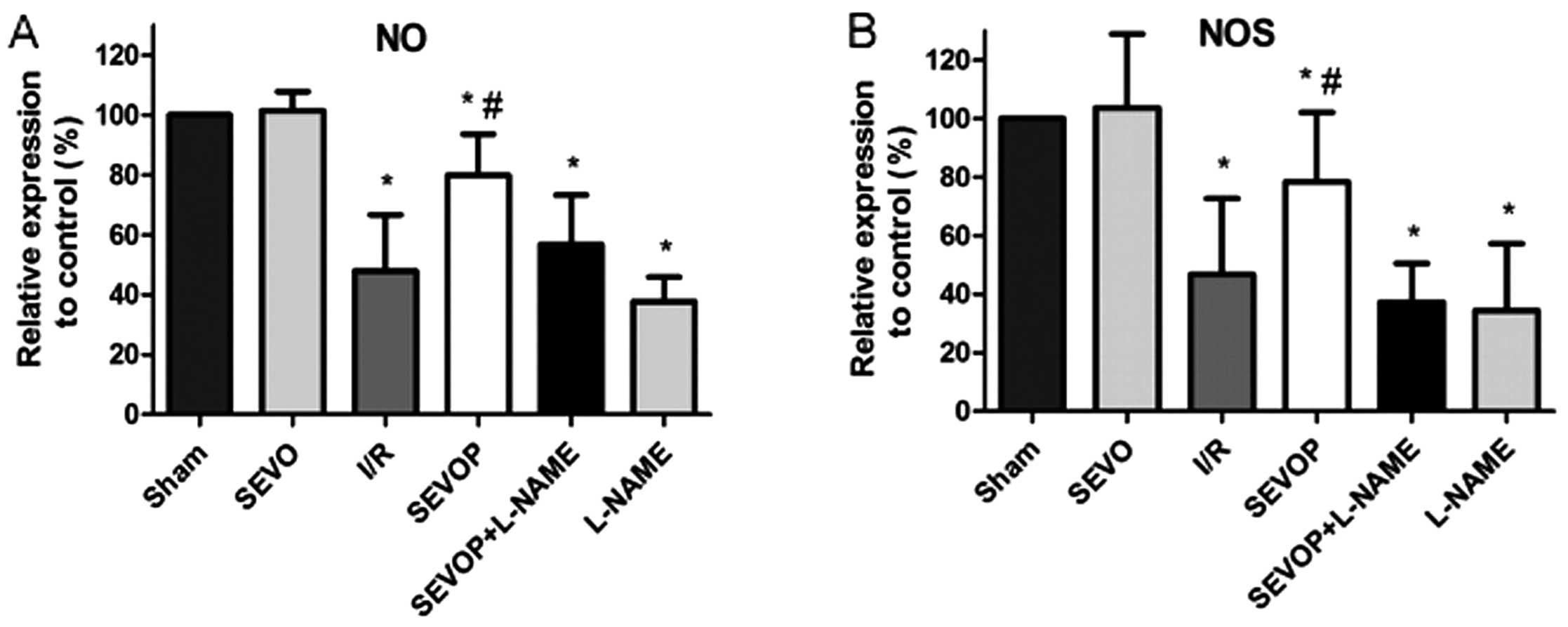
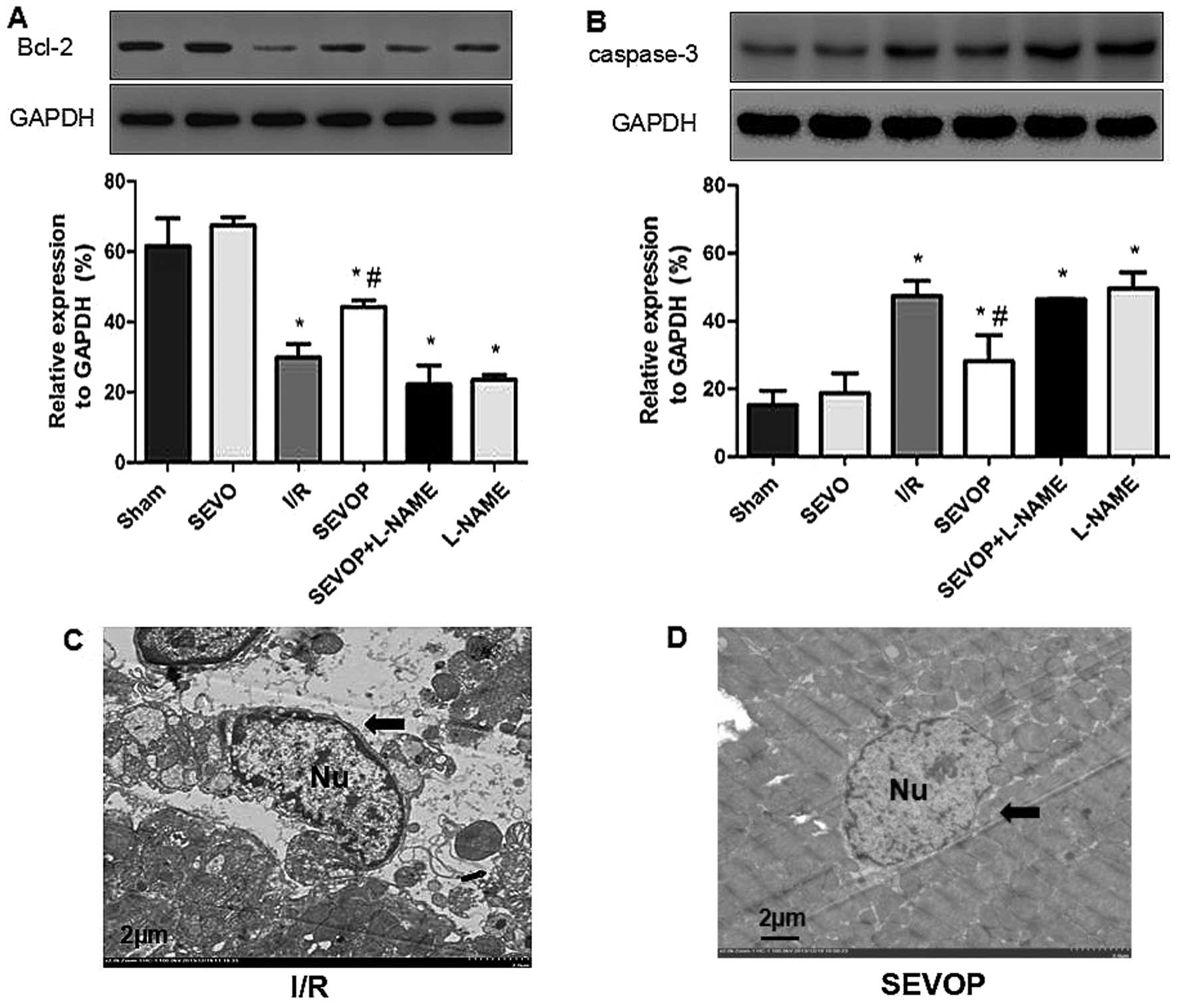
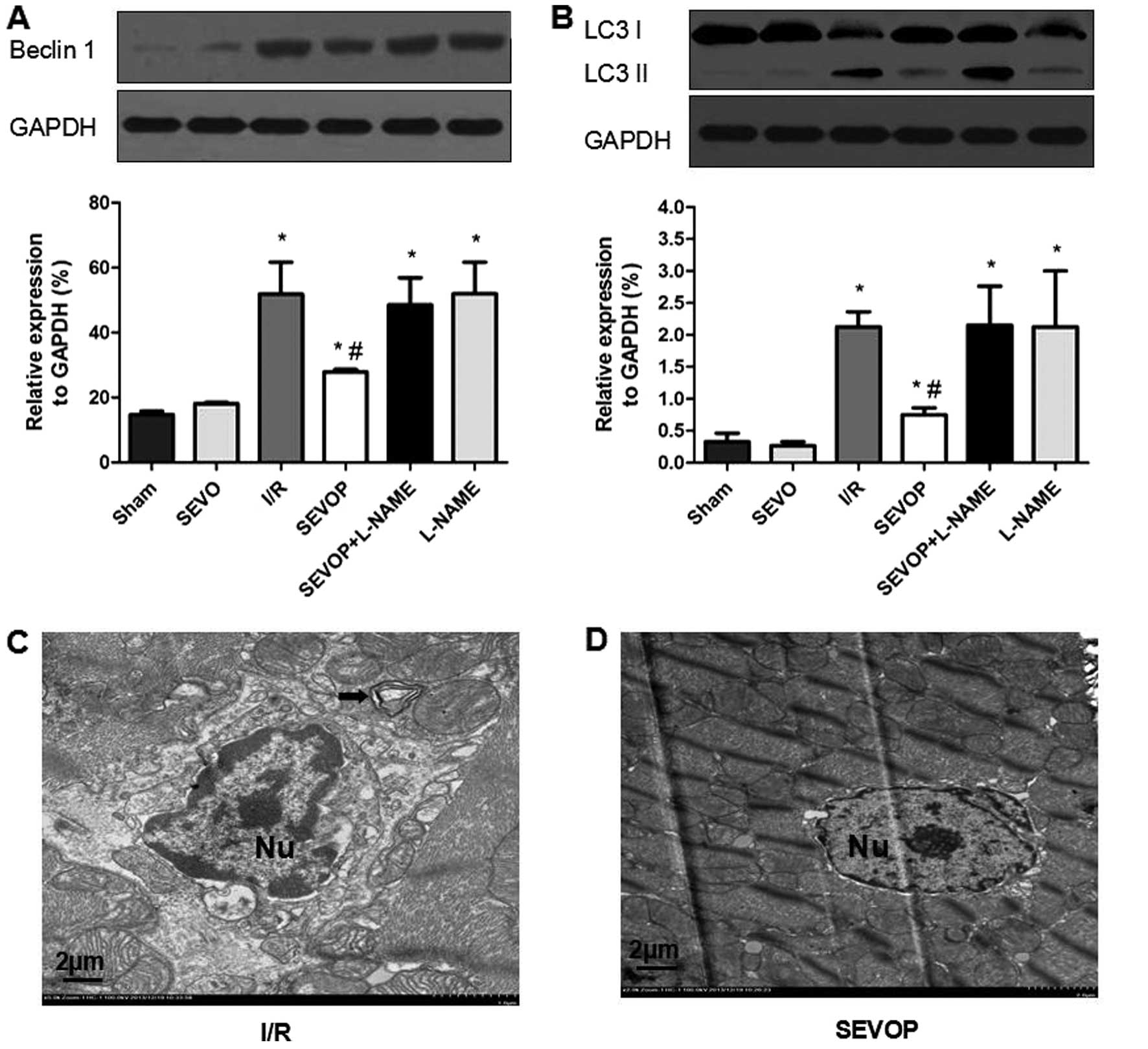
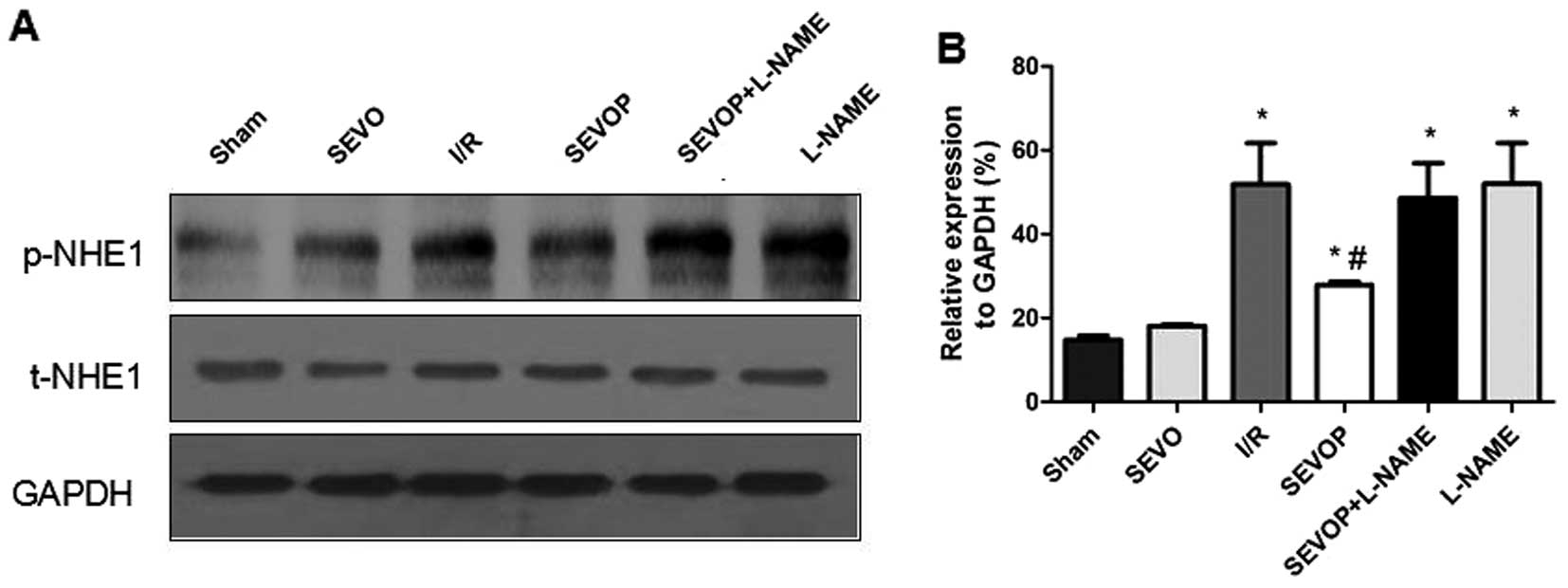
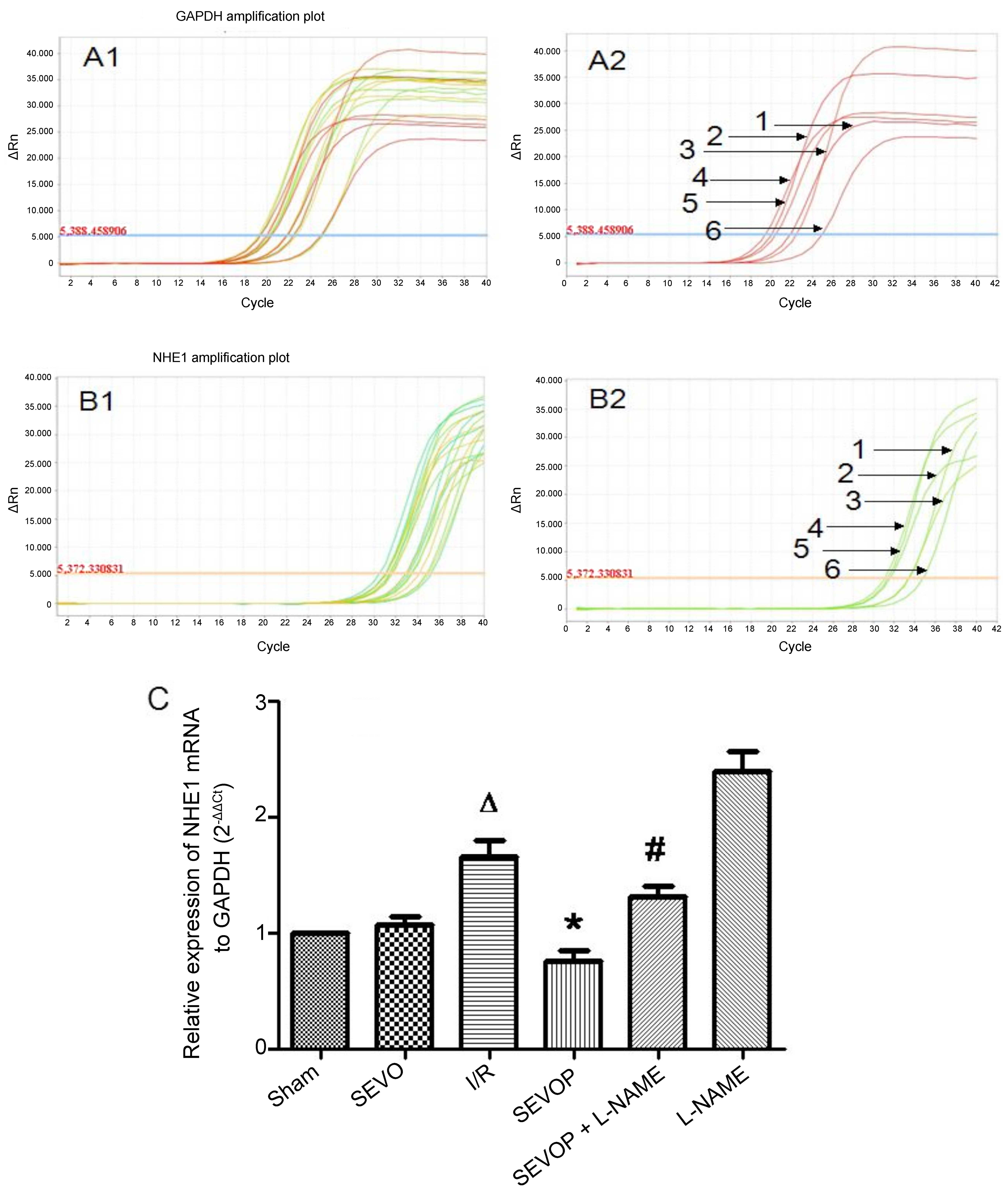
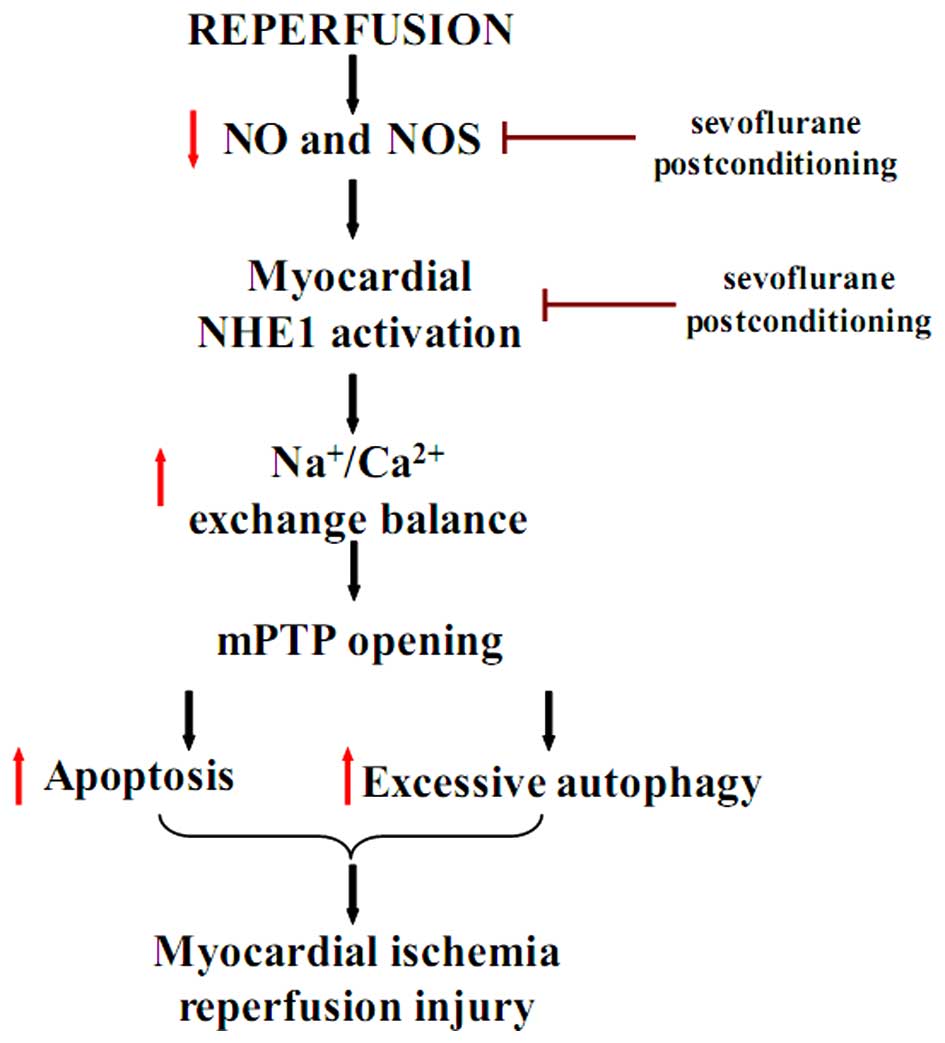
|
1
|
Hu Q, Chen J, Jiang C and Liu HF: Effect
of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist on
heart of rabbits with acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 7:271–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu M, Feng J, Lucchinetti E, Fischer G,
Xu L, Pedrazzini T, Schaub MC and Zaugg M: Ischemic
postconditioning protects remodeled myocardium via the PI3K-PKB/Akt
reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res.
72:152–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xia A, Xue Z, Wang W, Zhang T, Wei T, Sha
X, Ding Y and Zhou W: Naloxone postconditioning alleviates rat
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting JNK activity.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 18:67–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yao YY, Zhu MH, Zhang FJ, Wen CY, Ma LL,
Wang WN, Wang CC, Liu XB, Yu LN, Qian LB, et al: Activation of Akt
and cardioprotection against reperfusion injury are maximal with
only five minutes of sevoflurane postconditioning in isolated rat
hearts. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 14:511–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakai EM, Connolly LA and Klauck JA:
Inhalation anesthesiology and volatile liquid anesthetics: Focus on
isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane. Pharmacotherapy.
25:1773–1788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng Z, Yang M, Zhang F, Yu J, Wang J, Ma
L, Zhong Y, Qian L, Chen G, Yu L and Yan M: Gender-related
difference of sevoflurane postconditioning in isolated rat hearts:
Focus on phosphatidylino-sitol-3-kinase/Akt signaling. J Surg Res.
170:e3–e9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inamura Y, Miyamae M, Sugioka S, Domae N
and Kotani J: Sevoflurane postconditioning prevents activation of
caspase 3 and 9 through antiapoptotic signaling after myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion. J Anesth. 24:215–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ceyhan D, Tanrıverdi B and Bilir A:
Comparison of the effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane on
myocardial protection in coronary bypass surgery. Anadolu Kardiyol
Derg. 11:257–262. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao YT, Li LH, Chen L, Wang WP, Li LB and
Gao CQ: Sevoflurane postconditioning protects isolated rat hearts
against ischemia-reperfusion injury: The role of radical oxygen
species, extracellular signal-related kinases 1/2 and mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Mol Biol Rep. 37:2439–2446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gong JS, Yao YT, Fang NX and Li LH:
Sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates reperfusion-induced
ventricular arrhythmias in isolated rat hearts exposed to
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Biol Rep. 39:6417–6425. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao Y, Li L, Li L, Gao C and Shi C:
Sevoflurane postconditioning protects chronically-infarcted rat
hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury by activation of
pro-survival kinases and inhibition of mitochondrial permeability
transition pore opening upon reperfusion. Biol Pharm Bull.
32:1854–1861. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zweier JL, Flaherty JT and Weisfeldt ML:
Direct measurement of free radical generation following reperfusion
of ischemic myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:1404–1407. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshida A, Asanuma H, Sasaki H, Sanada S,
Yamazaki S, Asano Y, Shinozaki Y, Mori H, Shimouchi A, Sano M, et
al: H2 mediates cardioprotection via involvements of K
channels and permeability transition pores of mitochondria in dogs.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 26:217–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Petrosillo G, Di Venosa N, Moro N,
Colantuono G, Paradies V, Tiravanti E, Federici A, Ruggiero FM and
Paradies G: In vivo hyperoxic preconditioning protects against
rat-heart ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrial
permeability transition pore opening and cytochrome c release. Free
Radic Biol Med. 50:477–483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Prasad V, Lorenz JN, Miller ML, Vairamani
K, Nieman ML, Wang Y and Shull GE: Loss of NHE1 activity leads to
reduced oxidative stress in heart and mitigates high-fat
diet-induced myocardial stress. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 65:33–42. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goldman A, Shahidullah M, Goldman D,
Khailova L, Watts G, Delamere N and Dvorak K: A novel mechanism of
acid and bile acid-induced DNA damage involving
Na+/H+ exchanger: implication for Barrett's
oesophagus. Gut. 59:1606–1616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qian GQ, Peng X, Cai C and Zhao GP: Effect
on eNOS/NO Pathway in MIRI rats with preconditioning of GFPC from
Dang Gui Si Ni decoction. Pharmacognosy Res. 6:133–137. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakamura TY, Iwata Y, Arai Y, Komamura K
and Wakabayashi S: Activation of Na+/H+
exchanger 1 is sufficient to generate Ca2+ signals that
induce cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Circ Res.
103:891–899. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwamoto T, Wakabayashi S and Shigekawa M:
Growth factor-induced phosphorylation and activation of aortic
smooth muscle Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol
Chem. 270:8996–9001. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Villa-Abrille MC, Cingolani E, Cingolani
HE and Alvarez BV: Silencing of cardiac mitochondrial NHE1 prevents
mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1237–H1251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Testai L, Martelli A, Cristofaro M,
Breschi MC and Calderone V: Cardioprotective effects of different
flavonoids against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in
Langendorff-perfused rat hearts. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:750–756.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deyhimy DI, Fleming NW, Brodkin IG and Liu
H: Anesthetic preconditioning combined with postconditioning offers
no additional benefit over preconditioning or postconditioning
alone. Anesth Analg. 105:316–324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burley DS and Baxter GF: B-type
natriuretic peptide at early reperfusion limits infarct size in the
rat isolated heart. Basic Res Cardiol. 102:529–541. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lecour S, Smith RM, Woodward B, Opie LH,
Rochette L and Sack MN: Identification of a novel role for
sphingolipid signaling in TNF alpha and ischemic preconditioning
mediated cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:509–518. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng C, Sun Z, Tong G, Yi W, Ma L, Zhao B,
Cheng L, Zhang J, Cao F and Yi D: α-Lipoic acid reduces infarct
size and preserves cardiac function in rat myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e583712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kern SE, Price-Whelan A and Newman DK:
Extraction and measurement of NAD(P)+ and NAD(P)H.
Methods Mol Biol. 1149:311–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vessey DA, Li L, Kelley M and Karliner JS:
Combined sphingosine, S1P and ischemic postconditioning rescue the
heart after protracted ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
375:425–429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng XY, Yu HL, Zhang WC, Wang TH, Mai X,
Liu HT and Xu RC: ZFP580, a novel zinc-finger transcription factor,
is involved in cardioprotection of intermittent high-altitude
hypoxia against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
9:e946352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Di Lisa F and Ziegler M:
Pathophysiological relevance of mitochondria in NAD(+) metabolism.
FEBS Lett. 492:4–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek
WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ and Doevendans PA: Role of apoptosis
in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:414–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao ZQ, Morris CD, Budde JM, Wang NP,
Muraki S, Sun HY and Guyton RA: Inhibition of myocardial apoptosis
reduces infarct size and improves regional contractile dysfunction
during reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 59:132–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ling H, Wu L and Li L: Corydalis yanhusuo
rhizoma extract reduces infarct size and improves heart function
during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion by inhibiting apoptosis in
rats. Phytother Res. 20:448–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han Z, Cao J, Song D, Tian L, Chen K, Wang
Y, Gao L, Yin Z, Fan Y and Wang C: Autophagy is involved in the
cardioprotection effect of remote limb ischemic postconditioning on
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in normal mice, but not
diabetic mice. PLoS One. 9:e868382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao X, Chen A, Yang P, Song X, Liu Y, Li
Z, Wang X, Wang L and Li Y: Alpha-lipoic acid protects
cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting
autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:935–940. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balligand JL, Feron O and Dessy C: eNOS
activation by physical forces: from short-term regulation of
contraction to chronic remodeling of cardiovascular tissues.
Physiol Rev. 89:481–534. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manoury B, Montiel V and Balligand JL:
Nitric oxide synthase in post-ischaemic remodelling: new pathways
and mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res. 94:304–315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jin H, Wang Y, Wang X, Sun Y, Tang C and
Du J: Sulfur dioxide preconditioning increases antioxidative
capacity in rat with myocardial ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Nitric Oxide. 32:56–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gonzalez FM, Shiva S, Vincent PS, Ringwood
LA, Hsu LY, Hon YY, Aletras AH, Cannon RO III, Gladwin MT and Arai
AE: Nitrite anion provides potent cytoprotective and antiapoptotic
effects as adjunctive therapy to reperfusion for acute myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 117:2986–2994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Corr PB and Yamada KA: Selected metabolic
alterations in the ischemic heart and their contributions to
arrhythmogenesis. Herz. 20:156–168. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Doods H and Wu D: Sabiporide reduces
ischemia-induced arrhythmias and myocardial infarction and
attenuates ERK phosphorylation and iNOS induction in rats. Biomed
Res Int. 2013:5043202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Perez NG, Nolly MB, Roldan MC,
Villa-Abrille MC, Cingolani E, Portiansky EL, Alvarez BV, Ennis IL
and Cingolani HE: Silencing of NHE-1 blunts the slow force response
to myocardial stretch. J Appl Physiol. 111:874–880. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|