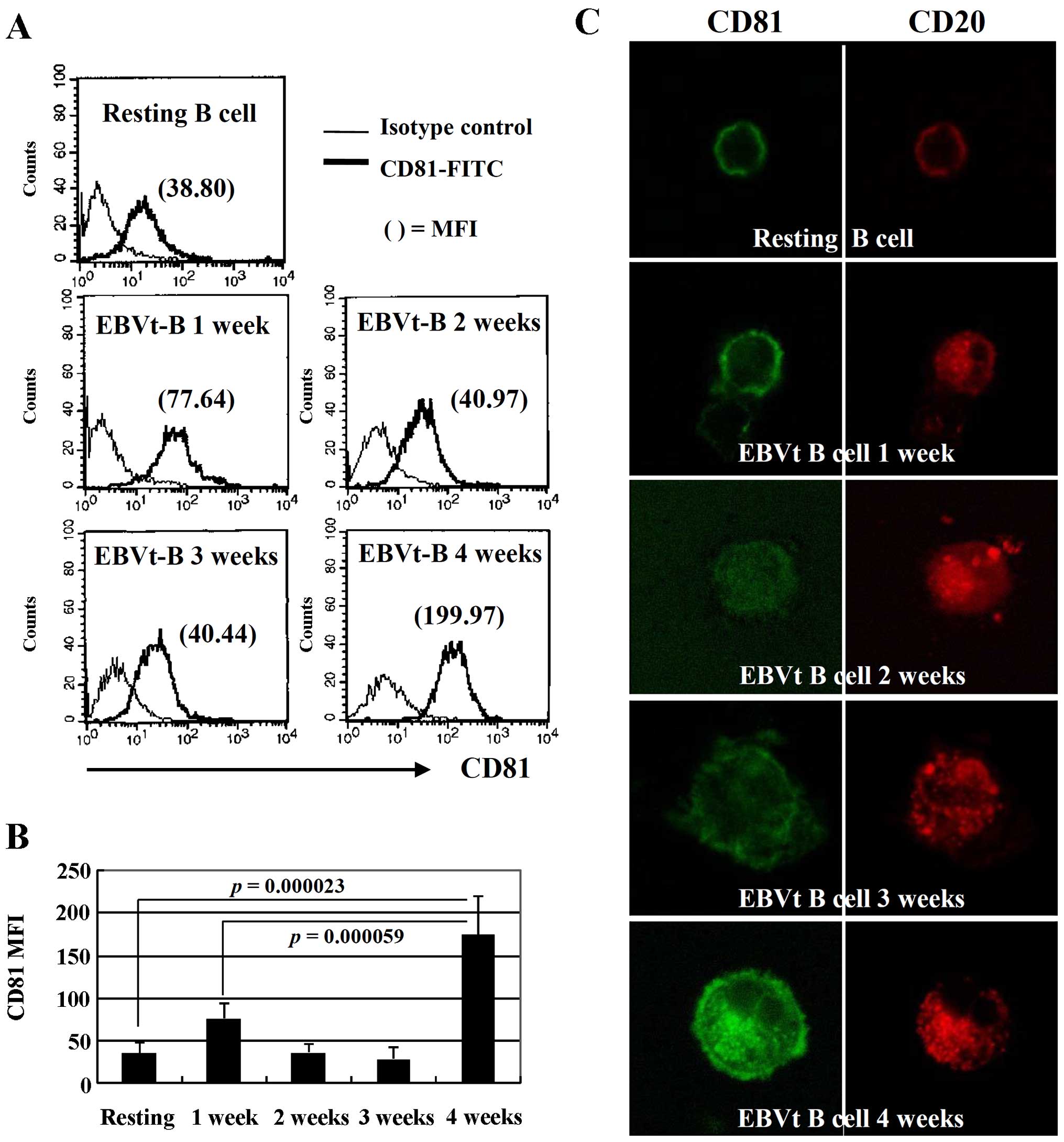
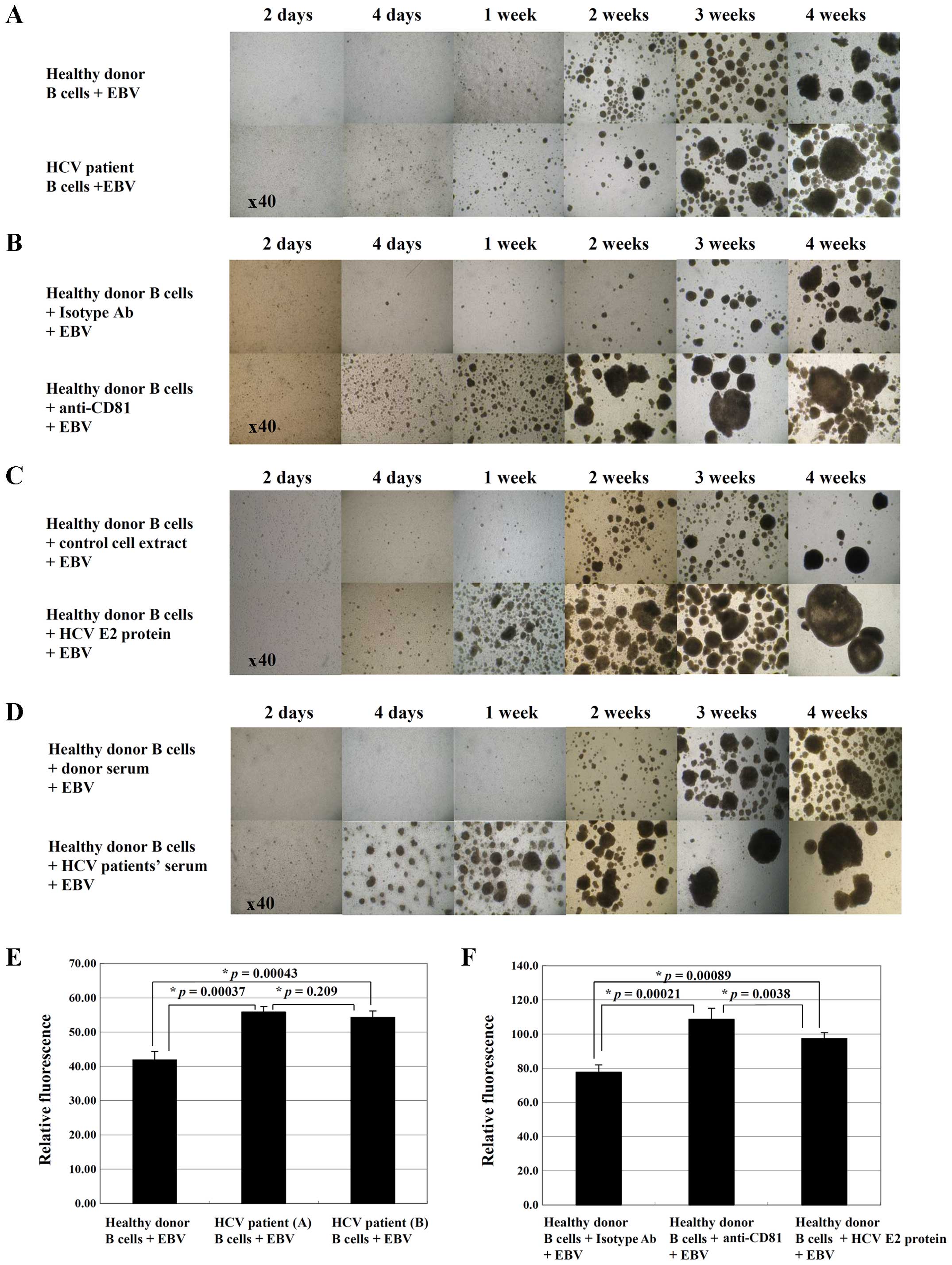
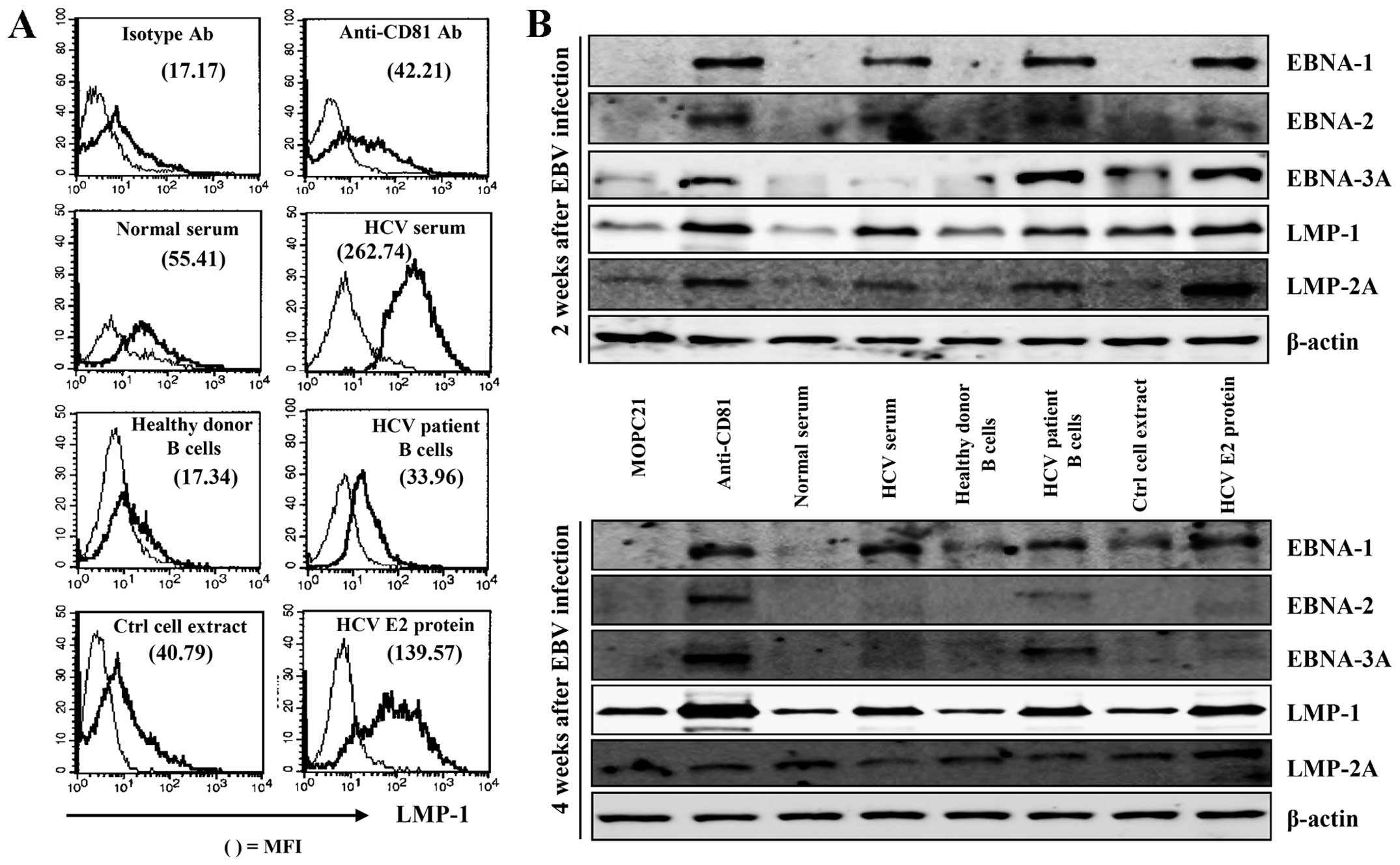
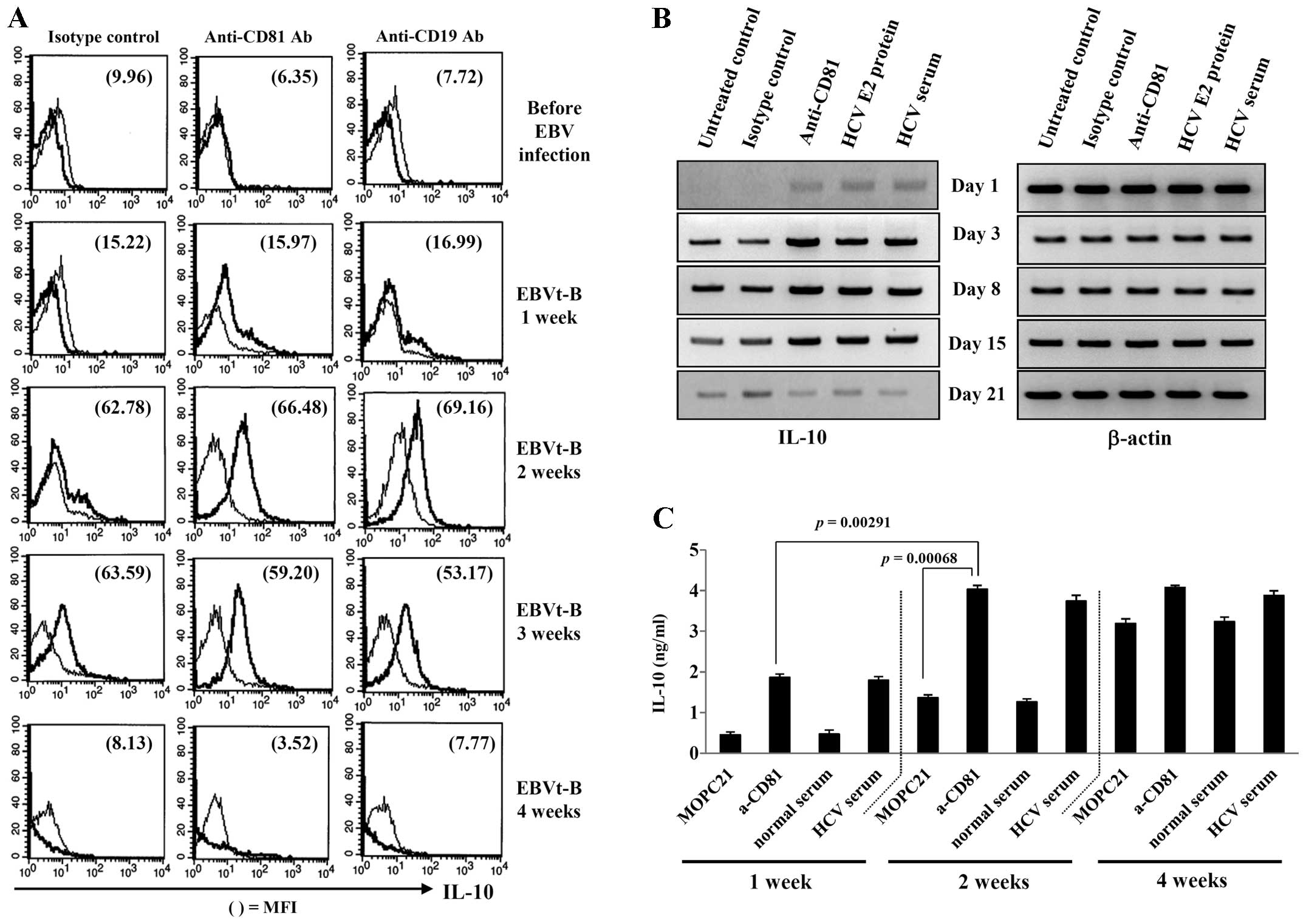
|
1
|
Bradbury LE, Kansas GS, Levy S, Evans RL
and Tedder TF: The CD19/CD21 signal transducing complex of human B
lymphocytes includes the target of antiproliferative antibody-1 and
Leu-13 molecules. J Immunol. 149:2841–2850. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsumoto AK, Martin DR, Carter RH,
Klickstein LB, Ahearn JM and Fearon DT: Functional dissection of
the CD21/CD19/TAPA-1/Leu-13 complex of B lymphocytes. J Exp Med
Oct. 178:1407–1417. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Carter RH and Fearon DT: CD19: lowering
the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes.
Science. 256:105–107. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levy S, Todd SC and Maecker HT: CD81
(TAPA-1): a molecule involved in signal transduction and cell
adhesion in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:89–109. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Zelm MC, Smet J, Adams B, Mascart F,
Schandené L, Janssen F, Ferster A, Kuo CC, Levy S, van Dongen JJ
and van der Burg M: CD81 gene defect in humans disrupts CD19
complex formation and leads to antibody deficiency. J Clin Invest.
120:1265–1274. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miyazaki T, Müller U and Campbell KS:
Normal development but differentially altered proliferative
responses of lymphocytes in mice lacking CD81. EMBO J.
16:4217–4225. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsitsikov EN, Gutierrez-Ramos JC and Geha
RS: Impaired CD19 expression and signaling, enhanced antibody
response to type II T independent antigen and reduction of B-1
cells in CD81-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:10844–10849. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR,
Bradley DW and Houghton M: Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a
blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science.
244:359–362. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferri C, La Civita L, Longombardo G,
Zignego AL and Pasero G: Mixed cryoglobulinaemia: a cross-road
between autoimmune and lymphoproliferative disorders. Lupus.
7:275–279. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dammacco F, Sansonno D, Piccoli C,
Racanelli V, D'Amore FP and Lauletta G: The lymphoid system in
hepatitis C virus infection: autoimmunity, mixed cryoglobulinemia,
and Overt B cell malignancy. Semin Liver Dis. 20:143–157. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Quinn ER, Chan CH, Hadlock KG, Foung SK,
Flint M and Levy S: The B cell receptor of a hepatitis C virus
(HCV)-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma binds the viral E2 envelope
protein, implicating HCV in lymphomagenesis. Blood. 98:3745–3749.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Machida K, Cheng KT, Pavio N, Sung VM and
Lai MM: Hepatitis C virus E2-CD81 interaction induces hypermutation
of the immunoglobulin gene in B cells. J Virol. 79:8079–8089. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pileri P, Uematsu Y, Campagnoli S, Galli
G, Falugi F, Petracca R, Weiner AJ, Houghton M, Rosa D, Grandi G
and Abrignani S: Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science.
282:938–941. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burlone ME and Budkowska A: Hepatitis C
virus cell entry: role of lipoproteins and cellular receptors. J
Gen Virol. 90:1055–1070. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roccasecca R, Ansuini H, Vitelli A, Meola
A, Scarselli E, Acali S, Pezzanera M, Ercole BB, McKeating J,
Yagnik A, et al: Binding of the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein
to CD81 is strain specific and is modulated by a complex interplay
between hyper-variable regions 1 and 2. J Virol. 77:1856–1867.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Challine D, Buisson M, Cadilhac M,
Germanidis G, Joab I, Eliaszewicz M, Caumes E, Flahault A, Fillet
AM, Pawlotsky JM and Seigneurin JM: Hepatitis C virus-Epstein-Barr
virus interaction in patients with AIDS. J Med Virol. 67:510–515.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ferri C, Lo Jacono F, Monti M, Caracciolo
F, La Civita L, Barsanti LA, Longombardo G, Lombardini F, Careccia
G and Zignego AL: Lymphotropic virus infection of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells in B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Acta Haematol.
98:89–94. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Roque-Cuéllar MC, Sánchez B, García-Lozano
JR, Garrido-Serrano A, Sayago M, Praena-Fernández JM, Núñez-Roldán
A and Aguilar-Reina J: Expression of CD81, SR-BI and LDLR in
lymphocytes and monocytes from patients with classic and occult
hepatitis C virus infection. J Med Virol. 84:1727–1736. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Molina S, Castet V, Pichard-Garcia L,
Wychowski C, Meurs E, Pascussi JM, Sureau C, Fabre JM, Sacunha A,
Larrey D, et al: Serum-derived hepatitis C virus infection of
primary human hepatocytes is tetraspanin CD81 dependent. J Virol.
82:569–574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Petracca R, Falugi F, Galli G, Norais N,
Rosa D, Campagnoli S, Burgio V, Di Stasio E, Giardina B, Houghton
M, et al: Structure-function analysis of hepatitis C virus
envelope-CD81 binding. J Virol. 74:4824–4830. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fornasieri A, Bernasconi P, Ribero ML,
Sinico RA, Fasola M, Zhou J, Portera G, Tagger A, Gibelli A and
D'amico G: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) in lymphocyte subsets and in B
lymphocytes expressing rheumatoid factor cross-reacting idiotype in
type II mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 122:400–403.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sung VM, Shimodaira S, Doughty AL, Picchio
GR, Can H, Yen TS, Lindsay KL, Levine AM and Lai MM: Establishment
of B cell lymphoma cell lines persistently infected with hepatitis
C virus in vivo and in vitro: the apoptotic effects of virus
infection. J Virol. 77:2134–2146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brazzoli M, Bianchi A, Filippini S, Weiner
A, Zhu Q, Pizza M and Crotta S: CD81 is a central regulator of
cellular events required for hepatitis C virus infection of human
hepatocytes. J Virol. 82:8316–8329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Zhu Y, Ren Y, Tong Y, Hua X, Zhu
F, Huang L, Liu Y, Luo Y, Lu W, et al: Hepatitis C virus protects
human B lymphocytes from Fas-mediated apoptosis via E2-CD81
engagement. PLoS One. 6:e189332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim YS, Park GB, Lee HK, Song H, Choi IH,
Lee WJ and Hur DY: Cross-linking of B7-H1 on EBV-transformed B
cells induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species production,
JNK signaling activation, and fasL expression. J Immunol.
181:6158–6169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song H, Park G, Kim YS, Hur I, Kim H, Ryu
JW, Lee HK, Cho DH, Choi IH, Lee WJ and Hur DY: B7-H4 reverse
signaling induces the apoptosis of EBV-transformed B cells through
Fas ligand up-regulation. Cancer Lett. 266:227–237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heo TH, Chang JH, Lee JW, Foung SK,
Dubuisson J and Kang CY: Incomplete humoral immunity against
hepatitis C virus is linked with distinct recognition of putative
multiple receptors by E2 envelope glycoprotein. J Immunol.
173:446–455. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rosa D, Saletti G, De Gregorio E, Zorat F,
Comar C, D'Oro U, Nuti S, Houghton M, Barnaba V, Pozzato G and
Abrignani S: Activation of naïve B lymphocytes via CD81, a
pathogenetic mechanism for hepatitis C virus-associated B
lymphocyte disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:18544–18549.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Poppema S: Immunobiology and
pathophysiology of Hodgkin lymphomas. Hematology Am Soc Hematol
Educ Program. 2005:231–238. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nakagomi H, Dolcetti R, Bejarano MT, Pisa
P, Kiessling R and Masucci MG: The Epstein-Barr virus latent
membrane protein-1 (LMP1) induces interleukin-10 production in
Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 57:240–244. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kis LL, Takahara M, Nagy N, Klein G and
Klein E: IL-10 can induce the expression of EBV-encoded latent
membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) in the absence of EBNA-2 in B
lymphocytes and in Burkitt lymphoma- and NK lymphoma-derived cell
lines. Blood. 107:2928–2935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Saelens X, Festjens N, Vande Walle L, van
Gurp M, van Loo G and Vandenabeele P: Toxic proteins released from
mitochondria in cell death. Oncogene. 23:2861–2874. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang M, Zhang L, Han X, Yang J, Qian J,
Hong S, Samaniego F, Romaguera J and Yi Q: Atiprimod inhibits the
growth of mantle cell lymphoma in vitro and in vivo and induces
apoptosis via activating the mitochondrial pathways. Blood.
109:5455–5462. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spencer JP, Rice-Evans C and Williams RJ:
Modulation of pro-survival Akt/protein kinase B and ERK1/2
signaling cascades by quercetin and its in vivo metabolites
underlie their action on neuronal viability. J Biol Chem.
278:34783–34793. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Allander T, Forns X, Emerson SU, Purcell
RH and Bukh J: Hepatitis C virus envelope protein E2 binds to CD81
of tamarins. Virology. 277:358–367. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Higginbottom A, Quinn ER, Kuo CC, Flint M,
Wilson LH, Bianchi E, Nicosia A, Monk PN, McKeating JA and Levy S:
Identification of amino acid residues in CD81 critical for
interaction with hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2. J
Virol. 74:3642–3649. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tedder TF, Zhou LJ and Engel P: The
CD19/CD21 signal transduction complex of B lymphocytes. Immunol
Today. 15:437–442. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hur DY, Lee MH, Kim JW, Kim JH, Shin YK,
Rho JK, Kwack KB, Lee WJ and Han BG: CD19 signalling improves the
Epstein-Barr virus-induced immortalization of human B cell. Cell
Prolif. 38:35–45. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dolcetti R and Masucci MG: Epstein-Barr
virus: induction and control of cell transformation. J Cell
Physiol. 196:207–218. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bornkamm GW and Hammerschmidt W: Molecular
virology of Epstein-Barr virus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
356:437–459. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sugawara Y, Mizugaki Y, Uchida T, Torii T,
Imai S, Makuuchi M and Takada K: Detection of Epstein-Barr virus
(EBV) in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue: a novel EBV latency
characterized by the absence of EBV-encoded small RNA expression.
Virology. 256:196–202. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Akhter S, Liu H, Prabhu R, DeLucca C,
Bastian F, Garry RF, Schwartz M, Thung SN and Dash S: Epstein-Barr
virus and human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 192:49–57.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Welker MW, Hofmann WP, Lange CM, Herrmann
E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S and Kronenberger B: CD81 expression for
discrimination between sustained virologic response and relapse in
patients with chronic hepatitis C. Scand J Gastroenterol.
46:973–980. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hermine O, Lefrère F, Bronowicki JP,
Mariette X, Jondeau K, Eclache-Saudreau V, Delmas B, Valensi F,
Cacoub P, Brechot C, et al: Regression of splenic lymphoma with
villous lymphocytes after treatment of hepatitis C virus infection.
N Engl J Med. 347:89–94. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Altomonte M, Montagner R, Pucillo C and
Maio M: Triggering of target of an antiproliferative antibody-1
(TAPA-1/CD81) up-regulates the release of tumour necrosis
factor-alpha by the EBV-B lymphoblastoid cell line JY. Scand J
Immunol. 43:367–373. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Snow AL, Chen LJ, Nepomuceno RR, Krams SM,
Esquivel CO and Martinez OM: Resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis
in EBV-infected B cell lymphomas is due to defects in the proximal
Fas signaling pathway. J Immunol. 167:5404–5411. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tepper CG and Seldin MF: Modulation of
caspase-8 and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression as a potential
mechanism of Epstein-Barr virus tumorigenesis in Burkitt's
lymphoma. Blood. 94:1727–1737. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Andreyev AY, Kushnareva YE and Starkov AA:
Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 70:200–214. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Filomeni G, Aquilano K, Rotilio G and
Ciriolo MR: Reactive oxygen species-dependent c-Jun NH2-terminal
kinase/c-Jun signaling cascade mediates neuroblastoma cell death
induced by diallyl disulfide. Cancer Res. 63:5940–5949.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zignego AL, Macchia D, Monti M, Thiers V,
Mazzetti M, Foschi M, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Gentilini P and Bréchot
C: Infection of peripheral mononuclear blood cells by hepatitis C
virus. J Hepatol. 15:382–386. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zuckerman E, Slobodin G, Kessel A, Sabo E,
Yeshurun D, Halas K and Toubi E: Peripheral B cell CD5 expansion
and CD81 overexpression and their association with disease severity
and autoimmune markers in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin
Exp Immunol. 128:353–358. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|