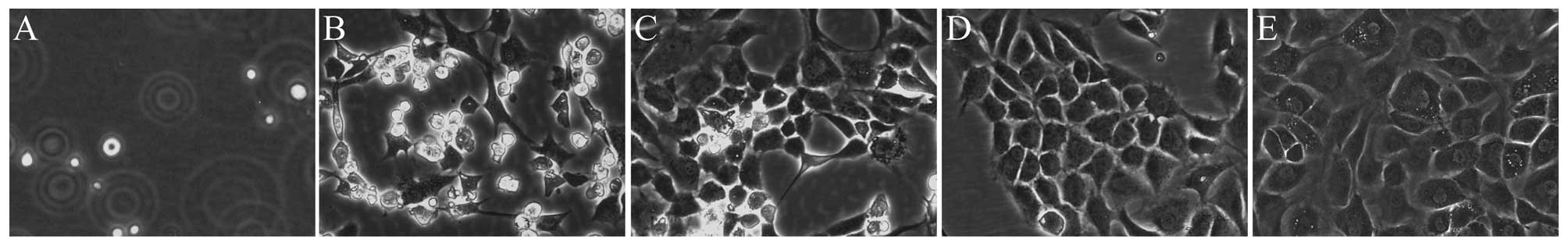
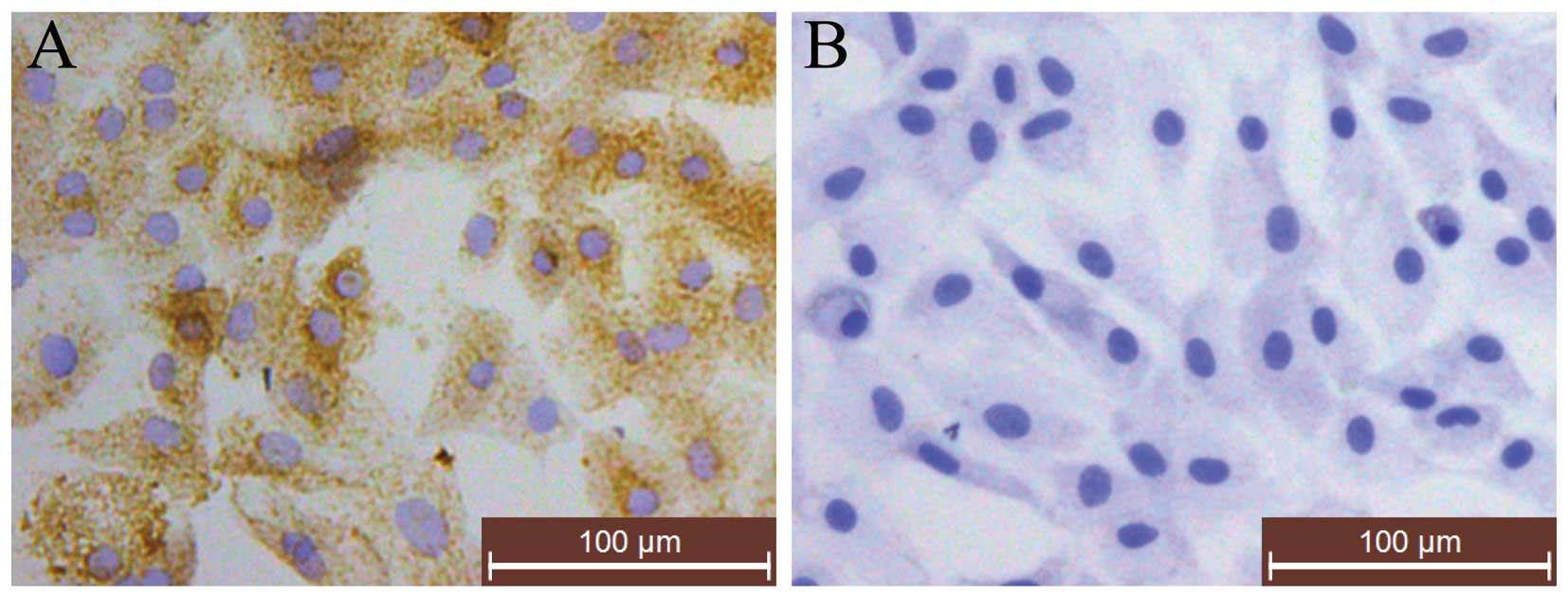
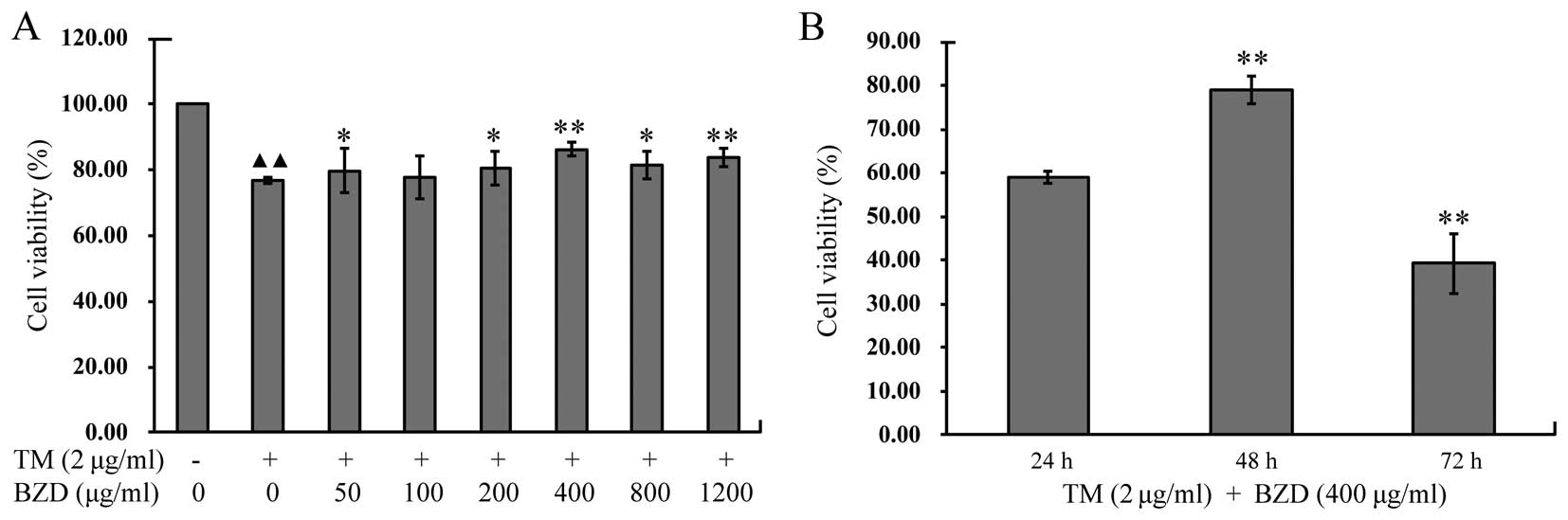
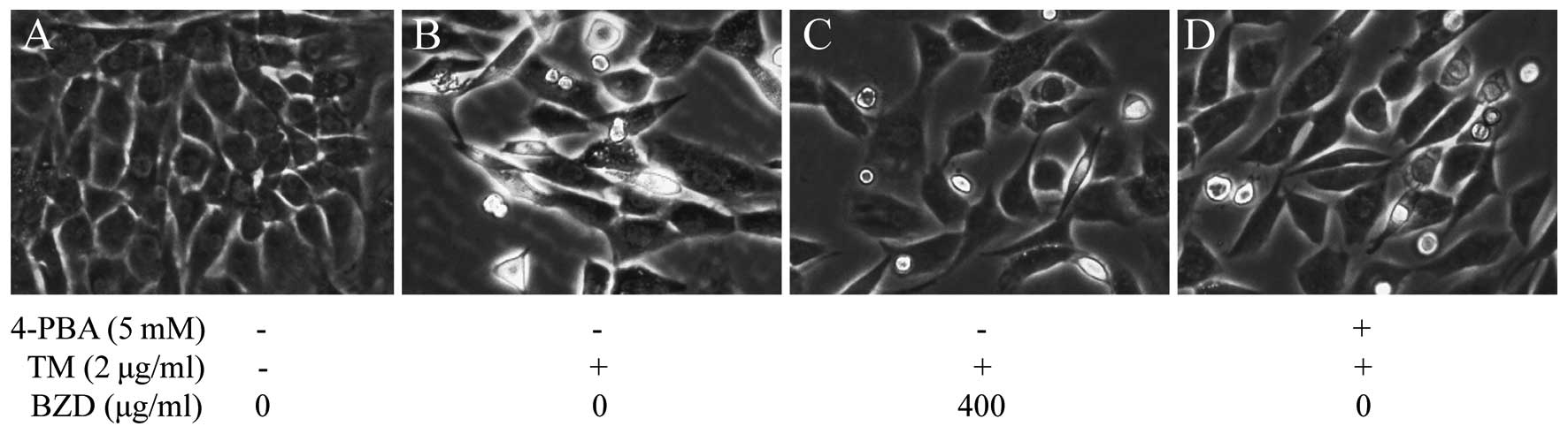
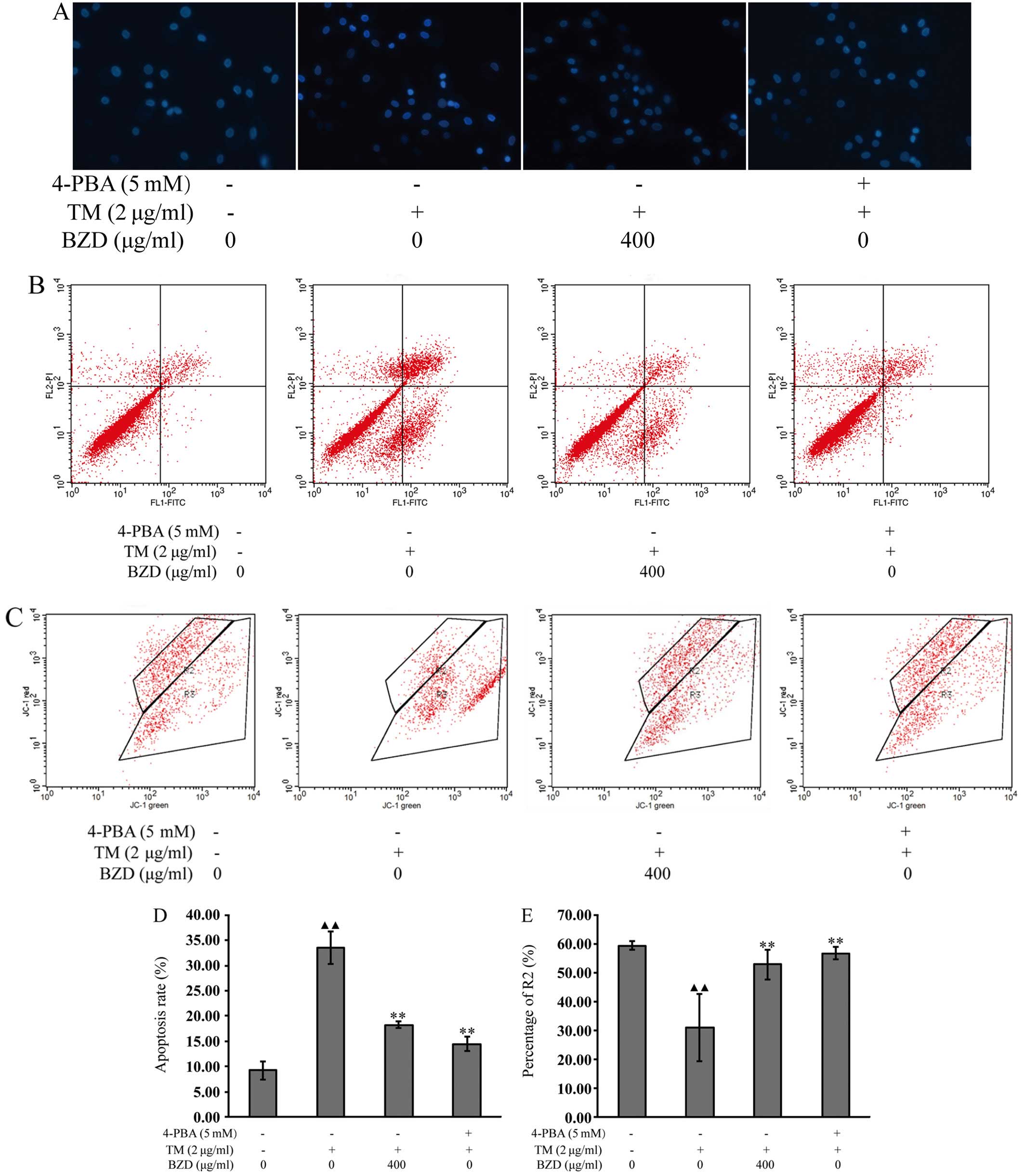
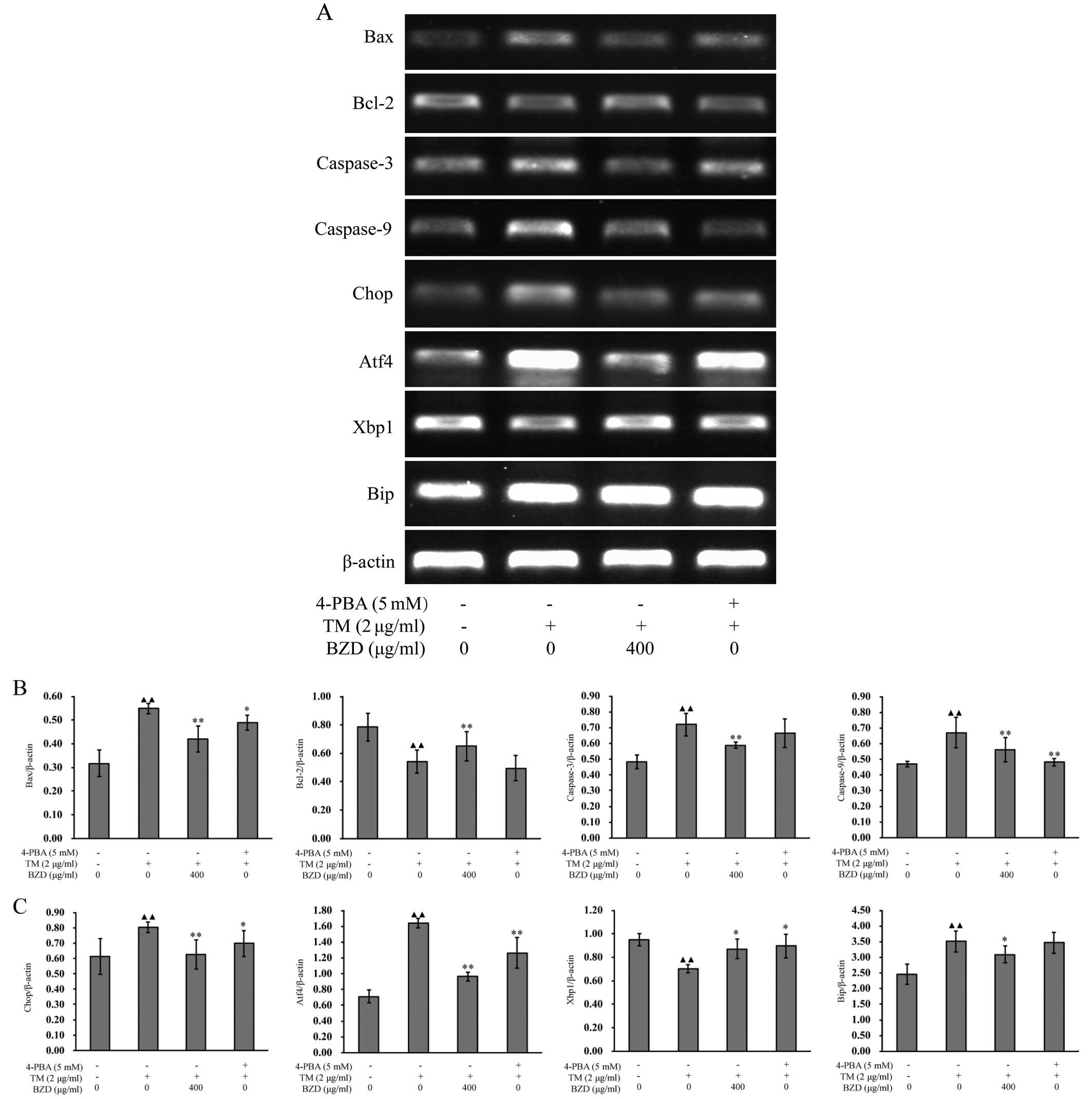
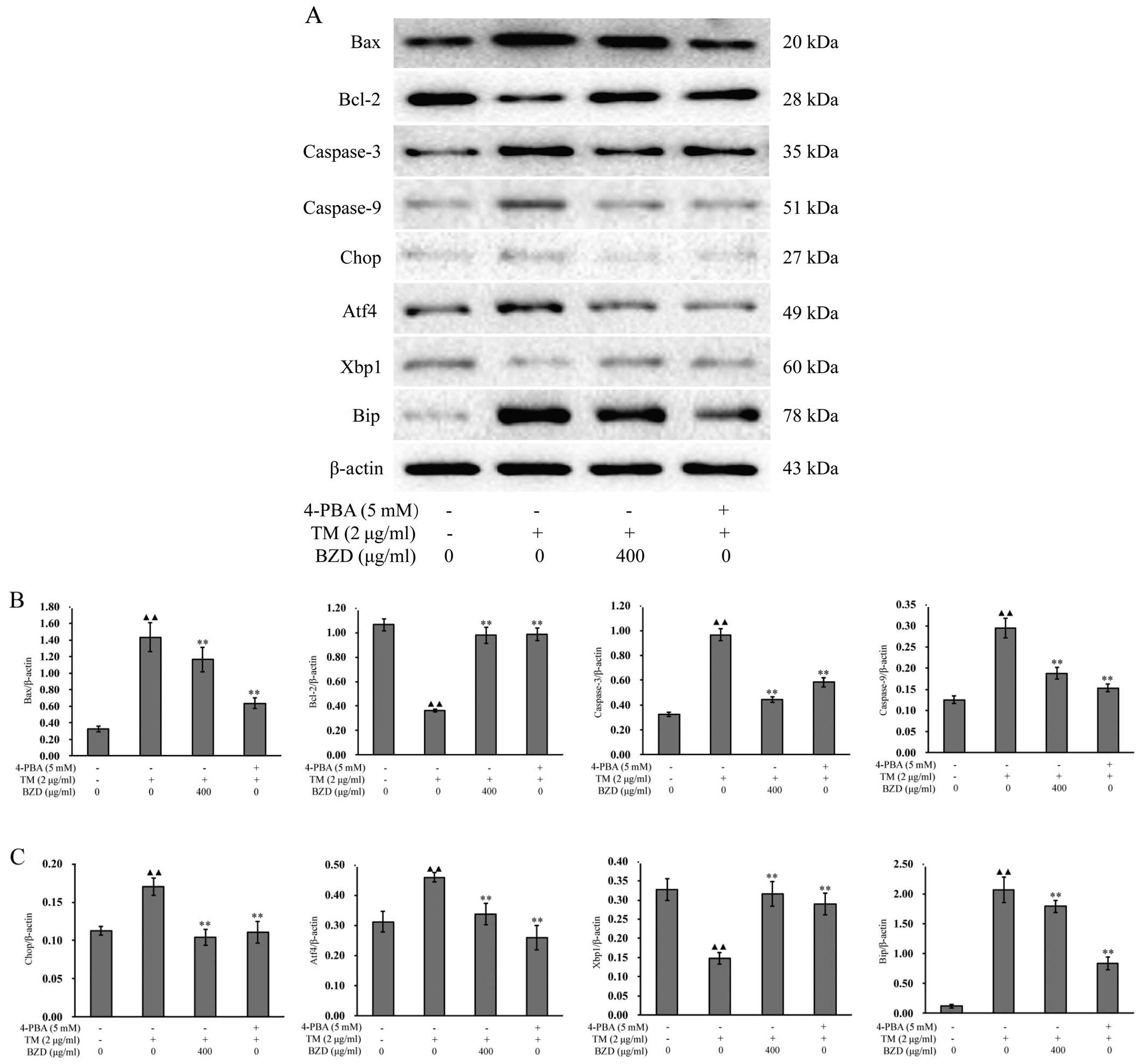
|
1
|
Chu CR, Millis MB and Olson SA:
Osteoarthritis: from palliation to prevention: AOA critical issues.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 96:e1302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loeser RF: Aging and osteoarthritis: the
role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage
matrix. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Del Carlo M Jr and Loeser RF: Cell death
in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 10:37–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim HA, Lee YJ, Seong SC, Choe KW and Song
YW: Apoptotic chondrocyte death in human osteoarthritis. J
Rheumatol. 27:455–462. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thomas CM, Fuller CJ, Whittles CE and
Sharif M: Chondrocyte death by apoptosis is associated with the
initiation and severity of articular cartilage degradation. Int J
Rheum Dis. 14:191–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hashimoto S, Ochs RL, Komiya S and Lotz M:
Linkage of chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in human
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 41:1632–1638. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Almonte-Becerril M, Navarro-Garcia F,
Gonzalez-Robles A, Vega-Lopez MA, Lavalle C and Kouri JB: Cell
death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and
autophagy during the pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis within an
experimental model. Apoptosis. 15:631–638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han X, Zhang P, Jiang R, Xia F, Li M and
Guo FJ: Explore on the effect of ATF6 on cell growth and apoptosis
in cartilage development. Histochem Cell Biol. 142:497–509. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uehara Y, Hirose J, Yamabe S, Okamoto N,
Okada T, Oyadomari S and Mizuta H: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis contributes to articular cartilage
degeneration via C/EBP homologous protein. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 22:1007–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang L, Xie H and Liu H: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress, diabetes mellitus, and tissue injury. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 15:812–818. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsuo M, Nishida K, Yoshida A, Murakami T
and Inoue H: Expression of caspase-3 and -9 relevant to cartilage
destruction and chondrocyte apoptosis in human osteoarthritic
cartilage. Acta Med Okayama. 55:333–340. 2001.
|
|
15
|
Takada K, Hirose J, Senba K, Yamabe S,
Oike Y, Gotoh T and Mizuta H: Enhanced apoptotic and reduced
protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum
stress in osteo-arthritic cartilage. Int J Exp Pathol. 92:232–242.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou GS, Li XF and Guan GH: Effects of
Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction containing serum on the apoptosis of
chondrocytes induced by mechanics stimulus. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He Za Zhi. 32:789–792. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Chen J, Liang W, Li H, Liu F, Weng
X, Lin P, Chen W, Zheng C, Xu H, et al: Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction
promotes chondrocyte proliferation by stimulating cell cycle
progression. Exp Ther Med. 9:839–844. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Liang W, Dang C, et al: Empirical
study on Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction inhibiting inflammatory
cytokine expression experiments to delay the degeneration of
articular cartilage. Feng Shi Bing Yu Guan Jie Yan. 3:20–25.
2014.In Chinese.
|
|
19
|
Li H, Li X, Liu G, Chen J, Weng X, Liu F,
Xu H, Liu X and Ye H: Bauhinia championi (Benth.) Benth.
polysaccharides upregulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes.
Int J Mol Med. 32:1329–1336. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zeng W, Guo YH, Qi W, Chen JG, Yang LL,
Luo ZF, Mu J and Feng B: 4-Phenylbutyric acid suppresses
inflammation through regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress of
endothelial cells stimulated by uremic serum. Life Sci. 103:15–24.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weng X, Lin P, Liu F, Chen J, Li H, Huang
L, Zhen C, Xu H, Liu X, Ye H and Li X: Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharides activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to
promote chon-drocyte proliferation. Int J Mol Med. 34:1045–1050.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu F, Li X, Cai L, Li H, Chen J, Wong X,
Xu H, Zheng C, Liu X and Ye H: Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharides induce chon-drocyte proliferation via the promotion
of the G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep. 7:935–940.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ishizeki K, Kagiya T, Fujiwara N, Otsu K
and Harada H: Expression of osteogenic proteins during the
intrasplenic transplantation of Meckel's chondrocytes: a
histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Arch Histol Cytol.
72:1–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Araki E, Oyadomari S and Mori M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetes mellitus. Intern Med.
42:7–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rojas C, Pan-Castillo B, Valls C, Pujadas
G, Garcia-Vallve S, Arola L and Mulero M: Resveratrol enhances
palmitate-induced ER stress and apoptosis in cancer cells. PLoS
One. 9:e1139292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw
TY and Holbrook NJ: Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic
reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the
cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1249–1259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim HT, Lo MY and Pillarisetty R:
Chondrocyte apoptosis following intraarticular fracture in humans.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 10:747–749. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
D'Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Chen PC, Colwell
CW Jr and Lotz MK: Human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to
mechanical injury. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 9:712–719. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tsai CC, Chou YY, Chen YM, Tang YJ, Ho HC
and Chen DY: Effect of the herbal drug guilu erxian jiao on muscle
strength, articular pain, and disability in elderly men with knee
osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:2974582014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gloth FM III: Pharmacological management
of persistent pain in older persons: focus on opioids and
nonopioids. J Pain. 12(3 Suppl 1): S14–S20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schnitzer TJ, Hochberg MC, Marrero CE,
Duquesroix B, Frayssinet H and Beekman M: Efficacy and safety of
naproxcinod in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a 53-week
prospective randomized multicenter study. Semin Arthritis Rheum.
40:285–297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dostrovsky NR, Towheed TE, Hudson RW and
Anastassiades TP: The effect of glucosamine on glucose metabolism
in humans: a systematic reviewof the literature. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 19:375–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lai JN, Chen HJ, Chen CC, Lin JH, Hwang JS
and Wang JD: Duhuo jisheng tang for treating osteoarthritis of the
knee: a prospective clinical observation. Chin Med. 2:42007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen FP, Chang CM, Hwang SJ, Chen YC and
Chen FJ: Chinese herbal prescriptions for osteoarthritis in Taiwan:
analysis of National Health Insurance dataset. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 14:912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moudgil KD and Berman BM: Traditional
Chinese medicine: potential for clinical treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 10:819–822. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng CS, Ye HZ, Li XH, Xu HF, Wu GW and
Liu XX: Study on the active components groups of BUSHENZHUANGJIN
decoction for osteoarthritis by molecular docking method. J Tradit
Chin Orthop Traumatol. 24:8–10. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
38
|
Guo FJ, Xiong Z, Lu X, Ye M, Han X and
Jiang R: ATF6 upregulates XBP1S and inhibits ER stress-mediated
apoptosis in osteoarthritis cartilage. Cell Signal. 26:332–342.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bull VH and Thiede B: Proteome analysis of
tunicamycin-induced ER stress. Electrophoresis. 33:1814–1823. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koyama M, Furuhashi M, Ishimura S, Mita T,
Fuseya T, Okazaki Y, Yoshida H, Tsuchihashi K and Miura T:
Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by 4-phenylbutyric acid
prevents the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 306:H1314–H1323.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang G, Gurtu V, Kain SR and Yan G: Early
detection of apoptosis using a fluorescent conjugate of Annexin V.
Biotechniques. 23:525–531. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dapat E, Jacinto S and Efferth T: A
phenolic ester from Aglaia loheri leaves reveals cytotoxicity
towards sensitive and multidrug-resistant cancer cells. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 13:2862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Acton BM, Jurisicova A, Jurisica I and
Casper RF: Alterations in mitochondrial membrane potential during
preimplantation stages of mouse and human embryo development. Mol
Hum Reprod. 10:23–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zheng C, Ye Z, Li X, Xu H, Wu G and Liu X:
Study on diversity and drug-like property of compounds in Bushen
Zhuangjin decoction based on computer simulation. Fujian Zhongyi
Xueyuan Xuebao. 22:22–25. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
46
|
Chevet E, Hetz C and Samali A: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-activated cell reprogramming in oncogenesis.
Cancer Discov. 5:586–597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Puthalakath H, O'Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L,
Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin
J, Motoyama N, et al: ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating
BH3-only protein Bim. Cell. 129:1337–1349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fu HY, Okada K, Liao Y, Tsukamoto O,
Isomura T, Asai M, Sawada T, Okuda K, Asano Y, Sanada S, et al:
Ablation of C/EBP homologous protein attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum-mediated apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction induced by
pressure overload. Circulation. 122:361–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
B'chir W, Maurin AC, Carraro V, Averous J,
Jousse C, Muranishi Y, Parry L, Stepien G, Fafournoux P and Bruhat
A: The eIF2α/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced autophagy
gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:7683–7699. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Creagh EM: Caspase crosstalk: integration
of apoptotic and innate immune signalling pathways. Trends Immunol.
35:631–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Allan LA and Clarke PR: Apoptosis and
autophagy: Regulation of caspase-9 by phosphorylation. FEBS J.
276:6063–6073. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR and
Porter AG: Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and
morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
273:9357–9360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sharif M, Whitehouse A, Sharman P, Perry M
and Adams M: Increased apoptosis in human osteoarthritic cartilage
corresponds to reduced cell density and expression of caspase-3.
Arthritis Rheum. 50:507–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu F, Liu G, Liang W, Ye H, Weng X, Lin
P, Li H, Chen J, Liu X and Li X: Duhuo Jisheng decoction treatment
inhibits the sodium nitroprussiate-induced apoptosis of
chondrocytes through the mitochondrial-dependent signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Med. 34:1573–1580. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hildeman DA, Zhu Y, Mitchell TC, Kappler J
and Marrack P: Molecular mechanisms of activated T cell death in
vivo. Curr Opin Immunol. 14:354–359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|