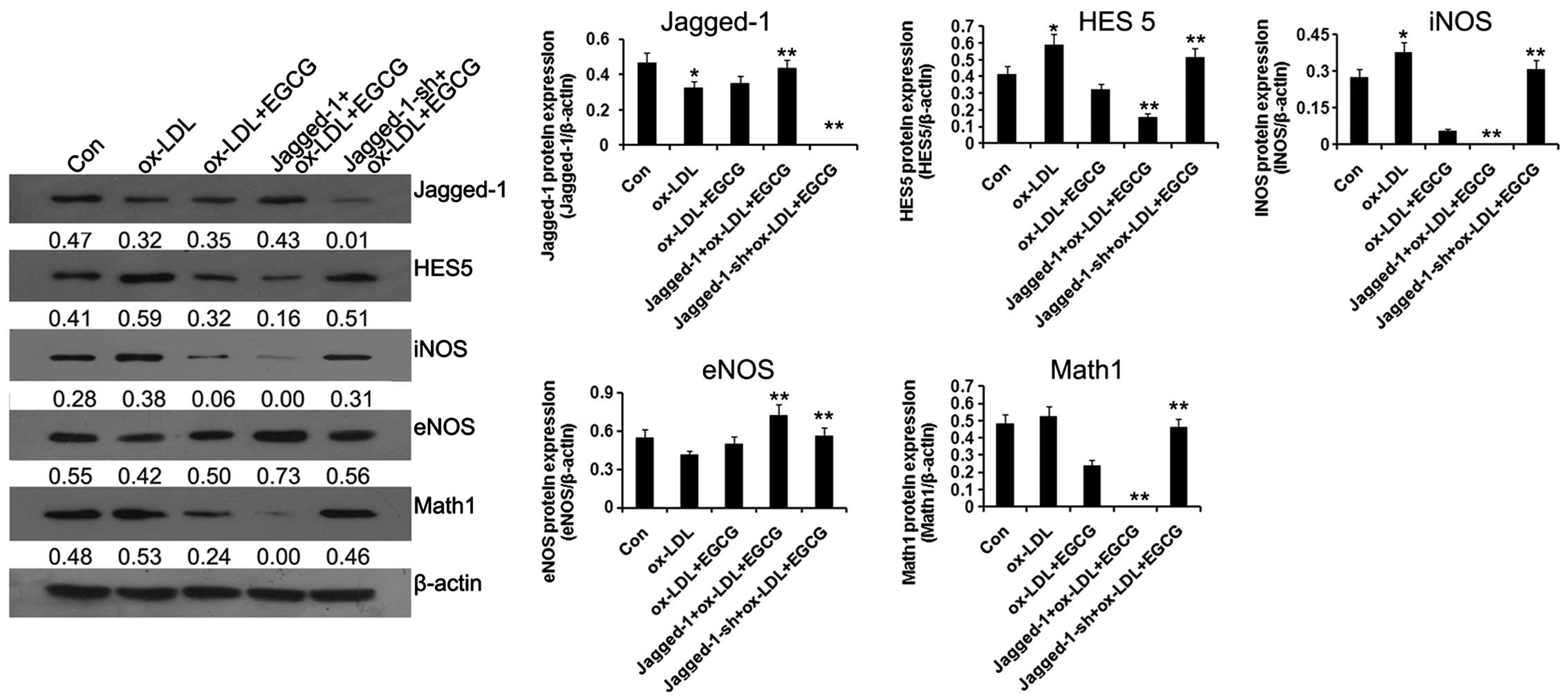
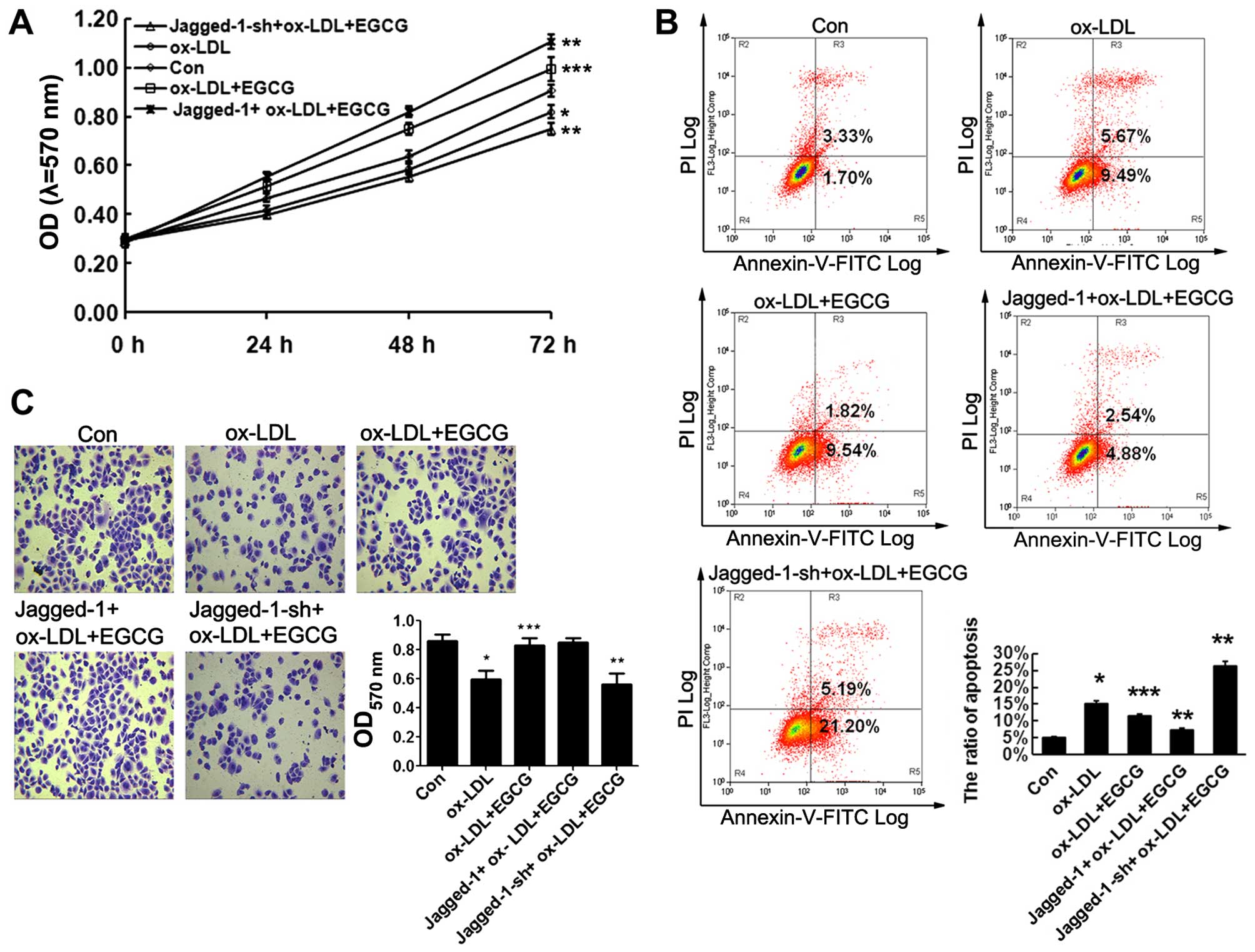
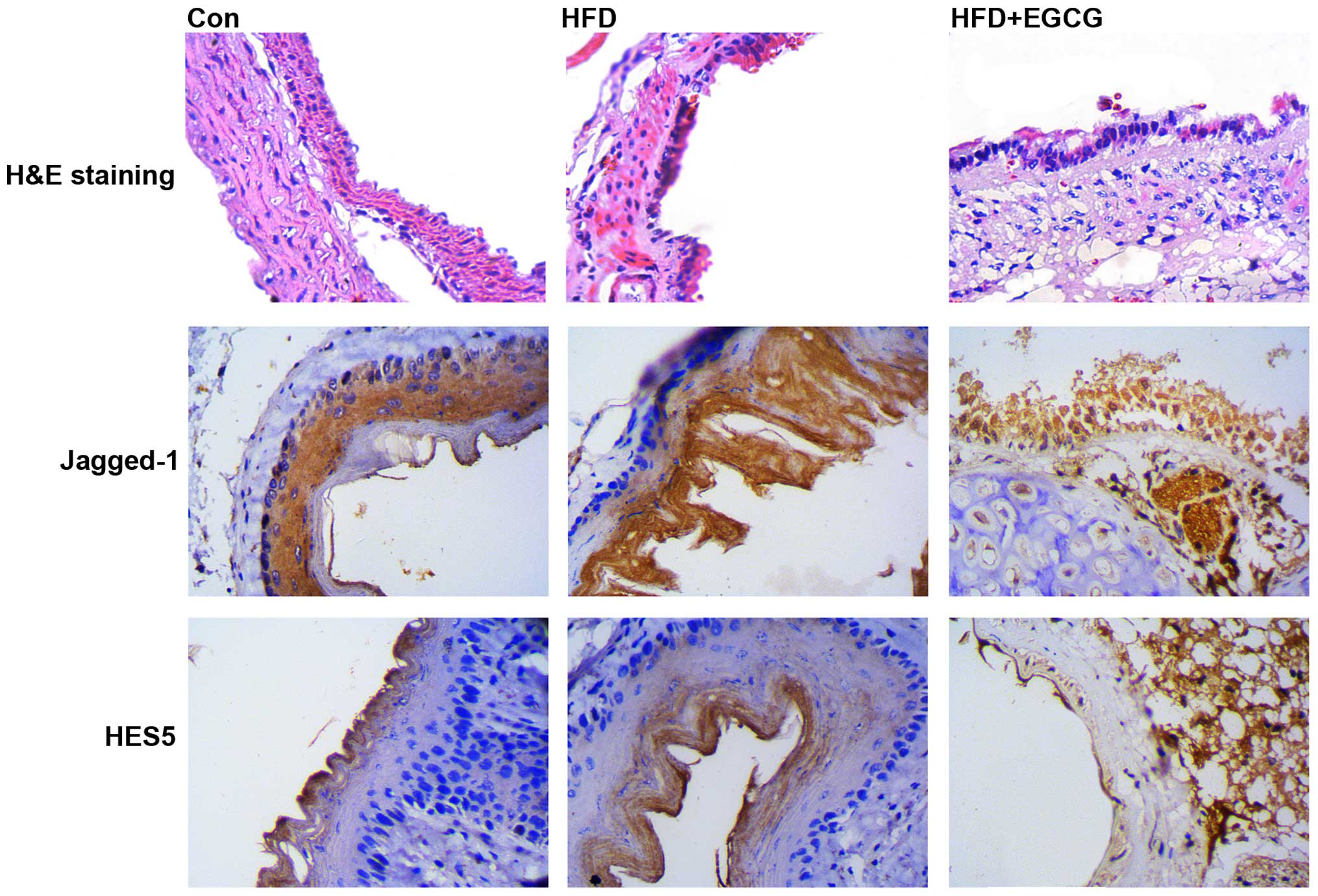
|
1
|
Stocker R and Keaney JF Jr: Role of
oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiol Rev.
84:1381–1478. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galkina E and Ley K: Immune and
inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis (*). Annu Rev Immunol.
27:165–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Parthasarathy S, Raghavamenon A, Garelnabi
MO and Santanam N: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Methods Mol
Biol. 610:403–417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chisolm GM and Steinberg D: The oxidative
modification hypothesis of atherogenesis: an overview. Free Radic
Biol Med. 28:1815–1826. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller NJ and Paganga G: Antioxidant
activity of low-density lipoprotein. Methods Mol Biol. 108:325–335.
1998.
|
|
6
|
Zhao W, Ma G and Chen X:
Lipopolysaccharide induced LOX-1 expression via TLR4/MyD88/ROS
activated p38MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 63:162–172.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carnevale R, Bartimoccia S, Nocella C, Di
Santo S, Loffredo L, Illuminati G, Lombardi E, Boz V, Del Ben M, De
Marco L, et al: LDL oxidation by platelets propagates platelet
activation via an oxidative stress-mediated mechanism.
Atherosclerosis. 237:108–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cominacini L, Rigoni A, Pasini AF, Garbin
U, Davoli A, Campagnola M, Pastorino AM, Lo Cascio V and Sawamura
T: The binding of oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) to
ox-LDL receptor-1 reduces the intracellular concentration of nitric
oxide in endothelial cells through an increased production of
superoxide. J Biol Chem. 276:13750–13755. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sakamoto N, Ishibashi T, Sugimoto K,
Sawamura T, Sakamoto T, Inoue N, Saitoh S, Kamioka M, Uekita H,
Ohkawara H, et al: Role of LOX-1 in monocyte adhesion-triggered
redox, Akt/eNOS and Ca2+ signaling pathways in
endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 220:706–715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wolfram S: Effects of green tea and EGCG
on cardiovascular and metabolic health. J Am Coll Nutr.
26:373S–388S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng Q, Kumagai T, Torii Y, Nakamura Y,
Osawa T and Uchida K: Anticarcinogenic antioxidants as inhibitors
against intracellular oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 35:779–788.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tipoe GL, Leung TM, Hung MW and Fung ML:
Green tea polyphenols as an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory
agent for cardiovascular protection. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug
Targets. 7:135–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mukhtar H and Ahmad N: Tea polyphenols:
prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Am J Clin Nutr.
71:1698S-1704S-1702Sdiscussion 1703S-1694S. 2000.
|
|
14
|
Cao Y and Cao R: Angiogenesis inhibited by
drinking tea. Nature. 398:3811999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Y, Kurita-Ochiai T, Hashizume T and
Yamamoto M: Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates
Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced atherosclerosis. Pathog Dis.
67:76–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi YJ, Kang JS, Park JH, Lee YJ, Choi JS
and Kang YH: Polyphenolic flavonoids differ in their antiapoptotic
efficacy in hydrogen peroxide-treated human vascular endothelial
cells. J Nutr. 133:985–991. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi JS, Choi YJ, Shin SY, Li J, Kang SW,
Bae JY, Kim DS, Ji GE, Kang JS and Kang YH: Dietary flavonoids
differentially reduce oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis in human
endothelial cells: Role of MAPK- and JAK/STAT-signaling. J Nutr.
138:983–990. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ahn HY and Kim CH:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate regulates inducible nitric oxide
synthase expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Lab
Anim Res. 27:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahn HY, Kim CH and Ha TS:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate regulates NADPH oxidase expression in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
14:325–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giniger E: Notch signaling and neural
connectivity. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 22:339–346. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Delidakis C and
Fehon RG: The Notch locus and the cell biology of neuroblast
segregation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 7:427–452. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koch U, Lehal R and Radtke F: Stem cells
living with a Notch. Development. 140:689–704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Sato C, Cerletti M and Wagers A:
Notch signaling in the regulation of stem cell self-renewal and
differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 92:367–409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tu J, Li Y and Hu Z: Notch1 and 4
signaling responds to an increasing vascular wall shear stress in a
rat model of arteriovenous malformations. Biomed Res Int.
2014:3680822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guichet PO, Guelfi S, Teigell M, Hoppe L,
Bakalara N, Bauchet L, Duffau H, Lamszus K, Rothhut B and Hugnot
JP: Notch1 stimulation induces a vascularization switch with
pericyte-like cell differentiation of glioblastoma stem cells. Stem
Cells. 33:21–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee SH, Lee S, Yang H, Song S, Kim K,
Saunders TL, Yoon JK, Koh GY and Kim I: Notch pathway targets
proangiogenic regulator Sox17 to restrict angiogenesis. Circ Res.
115:215–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Caolo V, Molin DG and Post MJ: Notch
regulation of hematopoiesis, endothelial precursor cells, and blood
vessel formation: orchestrating the vasculature. Stem Cells Int.
2012:8056022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalka C, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka-Moll
WM, Silver M, Kearney M, Li T, Isner JM and Asahara T:
Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells
for therapeutic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:3422–3427. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu B, Che W, Xue J, Zheng C, Tang K,
Zhang J, Wen J and Xu Y: SIRT4 prevents hypoxia-induced apoptosis
in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:655–662.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Dai M and Jia W: Paeonol attenuates
high-fat-diet-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits by
anti-inflammatory activity. Planta Med. 75:7–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu S, Shen H, Xu M, Liu O, Zhao L, Liu S,
Guo Z and Du J: FRP inhibits ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell
apoptosis through an Akt-NF-(kappa)B-Bcl-2 pathway and inhibits
endothelial cell apoptosis in an apoE-knockout mouse model. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E351–E363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bai YP, Hu CP, Yuan Q, Peng J, Shi RZ,
Yang TL, Cao ZH, Li YJ, Cheng G and Zhang GG: Role of VPO1, a newly
identified heme-containing peroxidase, in ox-LDL induced
endothelial cell apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1492–1500.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jia SJ, Jiang DJ, Hu CP, Zhang XH, Deng HW
and Li YJ: Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced elevation of asymmetric
dimethylarginine level by the NADPH oxidase pathway in endothelial
cells. Vascul Pharmacol. 44:143–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xu H, Duan J, Wang W, Dai S, Wu Y, Sun R
and Ren J: Reactive oxygen species mediate oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced endothelin-1 gene expression via extracellular
signal-regulated kinase in vascular endothelial cells. J Hypertens.
26:956–963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nagle DG, Ferreira D and Zhou YD:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Chemical and biomedical
perspectives. Phytochemistry. 67:1849–1855. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Persson IA, Josefsson M, Persson K and
Andersson RG: Tea flavanols inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme
activity and increase nitric oxide production in human endothelial
cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 58:1139–1144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hishikawa K, Nakaki T and Fujita T: Oral
flavonoid supplementation attenuates atherosclerosis development in
apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:442–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu VW and Huang PL: Cardiovascular roles
of nitric oxide: a review of insights from nitric oxide synthase
gene disrupted mice. Cardiovasc Res. 77:19–29. 2008.
|
|
39
|
Huang JJ, Shi YQ, Li RL, Hu A, Lu ZY, Weng
L, Wang SQ, Han YP, Zhang L, Li B, et al: Angiogenesis effect of
therapeutic ultrasound on HUVECs through activation of the
PI3K-Akt-eNOS signal pathway. Am J Transl Res. 7:1106–1115.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rueckschloss U, Duerrschmidt N and
Morawietz H: NADPH oxidase in endothelial cells: impact on
atherosclerosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:171–180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen T, Margariti A, Kelaini S, Cochrane
A, Guha ST, Hu Y, Stitt AW, Zhang L and Xu Q: MicroRNA-199b
modulates vascular cell fate during iPS cell differentiation by
targeting the notch ligand jagged1 and enhancing VEGF signaling.
Stem Cells. 33:1405–1418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miura Y, Chiba T, Tomita I, Koizumi H,
Miura S, Umegaki K, Hara Y, Ikeda M and Tomita T: Tea catechins
prevent the development of atherosclerosis in apoprotein
E-deficient mice. J Nutr. 131:27–32. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|