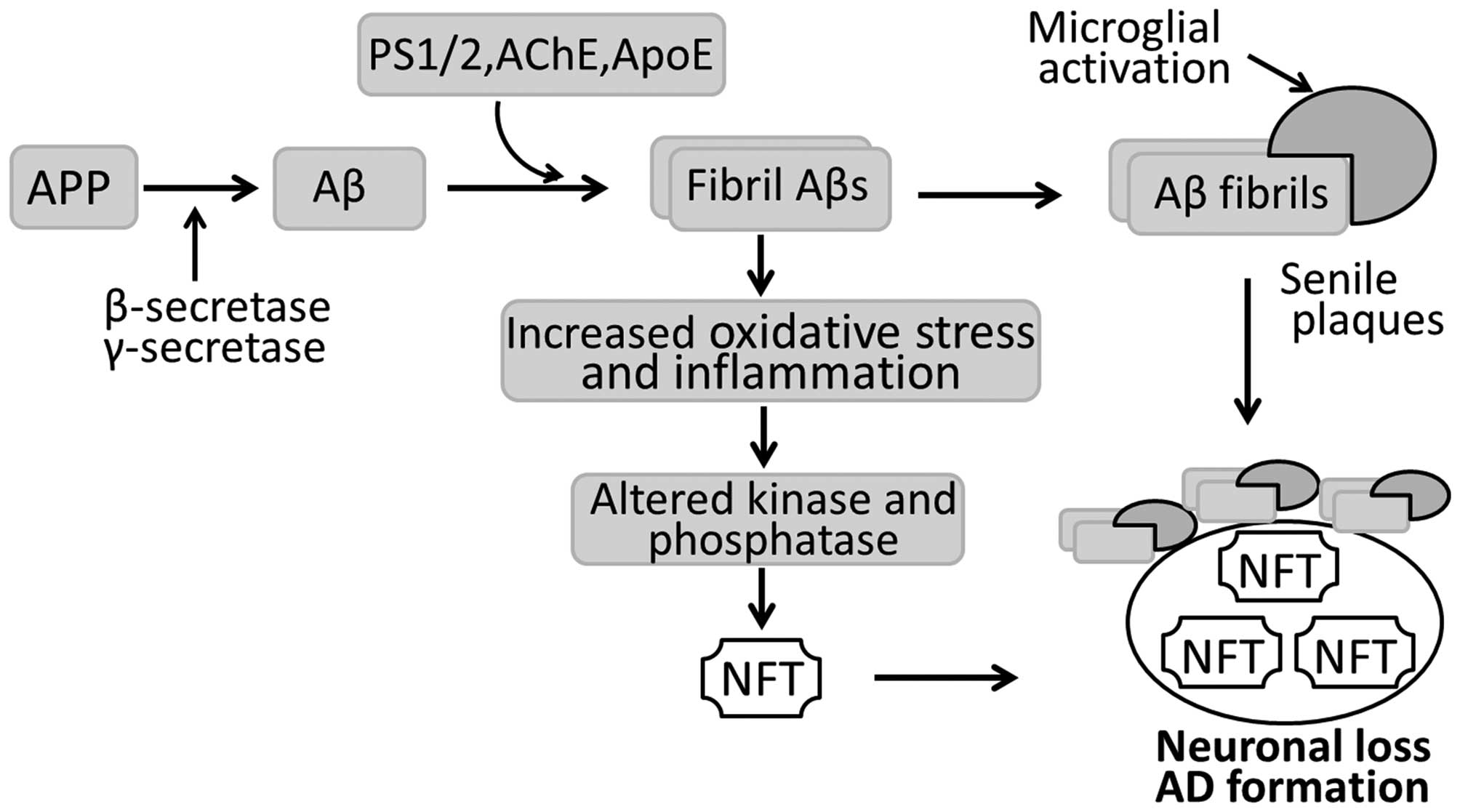
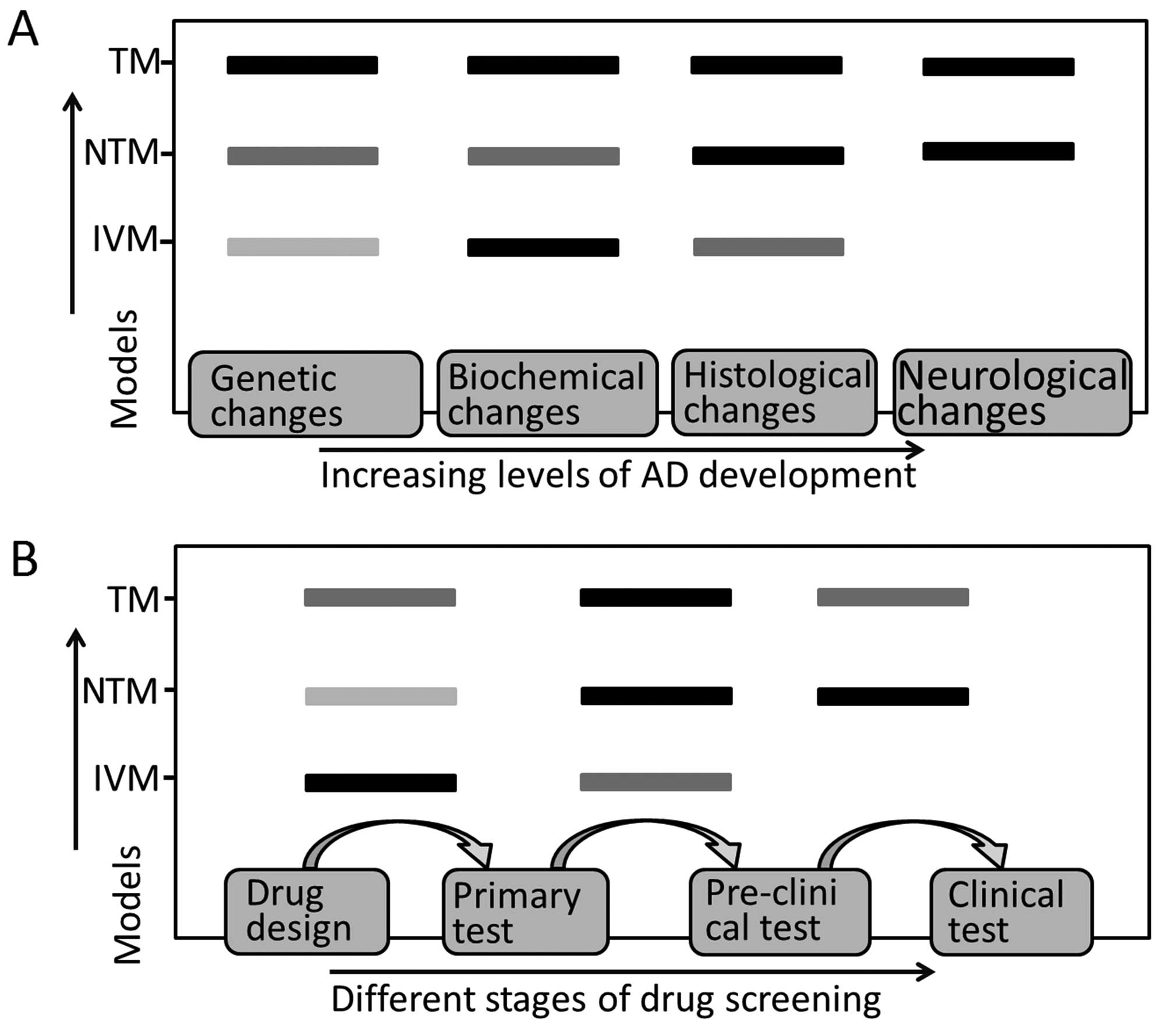
|
1
|
Li XY, Bao XJ and Wang RZ: Potential of
neural stem cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's disease. J
Neurosci Res. 93:1313–1324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bateman RJ, Xiong C, Benzinger TL, Fagan
AM, Goate A, Fox NC, Marcus DS, Cairns NJ, Xie X, Blazey TM, et al
Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network: Clinical and biomarker
changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med.
367:795–804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fleisher AS, Chen K, Quiroz YT, Jakimovich
LJ, Gomez MG, Langois CM, Langbaum JB, Ayutyanont N, Roontiva A,
Thiyyagura P, et al: Florbetapir PET analysis of amyloid-β
deposition in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer's
disease kindred: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol.
11:1057–1065. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Do Carmo S and Cuello AC: Modeling
Alzheimer's disease in transgenic rats. Mol Neurodegener. 8:372013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Elder GA, Gama Sosa MA and De Gasperi R:
Transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Mt Sinai J Med.
77:69–81. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mattsson MO and Simkó M: Is there a
relation between extremely low frequency magnetic field exposure,
inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases? A review of in vivo
and in vitro experimental evidence. Toxicology. 301:1–12. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yankner BA, Duffy LK and Kirschner DA:
Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein:
reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 250:279–282. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Itokazu Y, Kato-Negishi M, Nakatani Y,
Ariga T and Yu RK: Effects of amyloid β-peptides and gangliosides
on mouse neural stem cells. Neurochem Res. 38:2019–2027. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Blasko I, Stampfer-Kountchev M, Robatscher
P, Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P and Grubeck-Loebenstein B: How chronic
inflammation can affect the brain and support the development of
Alzheimer's disease in old age: the role of microglia and
astrocytes. Aging Cell. 3:169–176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schindowski K, Bretteville A, Leroy K,
Bégard S, Brion JP, Hamdane M and Buée L: Alzheimer's disease-like
tau neuropathology leads to memory deficits and loss of functional
synapses in a novel mutated tau transgenic mouse without any motor
deficits. Am J Pathol. 169:599–616. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N,
DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA and Katzman R: Physical basis of
cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the
major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 30:572–580.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Pérez CA, Moreno
RD, Vicente M, Linker C, Casanueva OI, Soto C and Garrido J:
Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-beta-peptides
into Alzheimer's fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of
the enzyme. Neuron. 16:881–891. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alvarez A, Opazo C, Alarcón R, Garrido J
and Inestrosa NC: Acetylcholinesterase promotes the aggregation of
amyloid-beta-peptide fragments by forming a complex with the
growing fibrils. J Mol Biol. 272:348–361. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alvarez A, Alarcón R, Opazo C, Campos EO,
Muñoz FJ, Calderón FH, Dajas F, Gentry MK, Doctor BP, De Mello FG
and Inestrosa NC: Stable complexes involving acetylcholinesterase
and amyloid-beta peptide change the biochemical properties of the
enzyme and increase the neurotoxicity of Alzheimer's fibrils. J
Neurosci. 18:3213–3223. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamada K and Nabeshima T: Animal models of
Alzheimer's disease and evaluation of anti-dementia drugs.
Pharmacol Ther. 88:93–113. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chartier-Harlin MC, Crawford F, Houlden H,
Warren A, Hughes D, Fidani L, Goate A, Rossor M, Roques P, Hardy J
and Mullan M: Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations
at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature.
353:844–846. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rogaev EI, Sherrington R, Rogaeva EA,
Levesque G, Ikeda M, Liang Y, Chi H, Lin C, Holman K, Tsuda T, et
al: Familial Alzheimer's disease in kindreds with missense
mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer's
disease type 3 gene. Nature. 376:775–778. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levy-Lahad E, Wijsman EM, Nemens E,
Anderson L, Goddard KA, Weber JL, Bird TD and Schellenberg GD: A
familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 1. Science.
269:970–973. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goedert M and Spillantini MG: Tau
mutations in frontotemporal dementia FTDP-17 and their relevance
for Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1502:110–121. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Levy-Lahad E, Lahad A, Wijsman EM, Bird TD
and Schellenberg GD: Apolipoprotein E genotypes and age of onset in
early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 38:678–680.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neha, Sodhi RK, Jaggi AS and Singh N:
Animal models of dementia and cognitive dysfunction. Life Sci.
109:73–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao A, Nitsch RM, Greenberg SM, Finckh U,
Blacker D, Albert M, Rebeck GW, Gomez-Isla T, Clatworthy A, Binetti
G, et al: Genetic association of an alpha2-macroglobulin
(Val1000lle) polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet.
7:1953–1956. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dahiyat M, Cumming A, Harrington C,
Wischik C, Xuereb J, Corrigan F, Breen G, Shaw D and St Clair D:
Association between Alzheimer's disease and the NOS3 gene. Ann
Neurol. 46:664–667. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lithner CU, Hedberg MM and Nordberg A:
Transgenic mice as a model for Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer
Res. 8:818–831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Quon D, Wang Y, Catalano R, Scardina JM,
Murakami K and Cordell B: Formation of beta-amyloid protein
deposits in brains of transgenic mice. Nature. 352:239–241. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Higgins LS, Rodems JM, Catalano R, Quon D
and Cordell B: Early Alzheimer disease-like histopathology
increases in frequency with age in mice transgenic for beta-APP751.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:4402–4406. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, Barbour
R, Berthelette P, Blackwell C, Carr T, Clemens J, Donaldson T,
Gillespie F, et al: Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic
mice overex-pressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature.
373:523–527. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C,
Harigaya Y, Younkin S, Yang F and Cole G: Correlative memory
deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice.
Science. 274:99–102. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Calhoun ME, Wiederhold KH, Abramowski D,
Phinney AL, Probst A, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Sommer B
and Jucker M: Neuron loss in APP transgenic mice. Nature.
395:755–756. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Richards JG, Higgins GA, Ouagazzal AM,
Ozmen L, Kew JN, Bohrmann B, Malherbe P, Brockhaus M, Loetscher H,
Czech C, et al: PS2APP transgenic mice, coexpressing hPS2mut and
hAPPswe, show age-related cognitive deficits associated with
discrete brain amyloid deposition and inflammation. J Neurosci.
23:8989–9003. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Braidy N, Muñoz P, Palacios AG,
Castellano-Gonzalez G, Inestrosa NC, Chung RS, Sachdev P and
Guillemin GJ: Recent rodent models for Alzheimer's disease:
clinical implications and basic research. J Neural Transm.
119:173–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lewis J, Dickson DW, Lin WL, Chisholm L,
Corral A, Jones G, Yen SH, Sahara N, Skipper L, Yager D, et al:
Enhanced neuro-fibrillary degeneration in transgenic mice
expressing mutant tau and APP. Science. 293:1487–1491. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Götz J, Probst A, Spillantini MG, Schäfer
T, Jakes R, Bürki K and Goedert M: Somatodendritic localization and
hyperphos-phorylation of tau protein in transgenic mice expressing
the longest human brain tau isoform. EMBO J. 14:1304–1313.
1995.
|
|
34
|
James ND, Davis DR, Sindon J, Hanger DP,
Brion JP, Miller CC, Rosenberg MP, Anderton BH and Propst F:
Neurodegenerative changes including altered tau phosphorylation and
neurofilament immunoreactivity in mice transgenic for the
serine/threonine kinase Mos. Neurobiol Aging. 17:235–241. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Allen B, Ingram E, Takao M, Smith MJ,
Jakes R, Virdee K, Yoshida H, Holzer M, Craxton M, Emson PC, et al:
Abundant tau filaments and nonapoptotic neurodegeneration in
transgenic mice expressing human P301S tau protein. J Neurosci.
22:9340–9351. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Forman MS, Lal D, Zhang B, Dabir DV,
Swanson E, Lee VM and Trojanowski JQ: Transgenic mouse model of tau
pathology in astrocytes leading to nervous system degeneration. J
Neurosci. 25:3539–3550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Higuchi M, Zhang B, Forman MS, Yoshiyama
Y, Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM: Axonal degeneration induced by
targeted expression of mutant human tau in oligodendrocytes of
transgenic mice that model glial tauopathies. J Neurosci.
25:9434–9443. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ribé EM, Pérez M, Puig B, Gich I, Lim F,
Cuadrado M, Sesma T, Catena S, Sánchez B, Nieto M, et al:
Accelerated amyloid deposition, neurofibrillary degeneration and
neuronal loss in double mutant APP/tau transgenic mice. Neurobiol
Dis. 20:814–822. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Götz J, Chen F, van Dorpe J and Nitsch RM:
Formation of neurofibrillary tangles in P301l tau transgenic mice
induced by Abeta 42 fibrils. Science. 293:1491–1495. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, Murphy MP,
Golde TE, Kayed R, Metherate R, Mattson MP, Akbari Y and LaFerla
FM: Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and
tangles: Intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron.
39:409–421. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Janelsins MC, Mastrangelo MA, Oddo S,
LaFerla FM, Federoff HJ and Bowers WJ: Early correlation of
microglial activation with enhanced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression specifically within
the entorhinal cortex of triple transgenic Alzheimer's disease
mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2:232005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kimura R and Ohno M: Impairments in remote
memory stabi-lization precede hippocampal synaptic and cognitive
failures in 5XFAD Alzheimer mouse model. Neurobiol Dis. 33:229–235.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Oakley H, Cole SL, Logan S, Maus E, Shao
P, Craft J, Guillozet-Bongaarts A, Ohno M, Disterhoft J, Van Eldik
L, et al: Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration,
and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer's
disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J
Neurosci. 26:10129–10140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Clarke J, Thornell A, Corbett D, Soininen
H, Hiltunen M and Jolkkonen J: Overexpression of APP provides
neuroprotection in the absence of functional benefit following
middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Eur J Neurosci.
26:1845–1852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Flood DG, Lin YG, Lang DM, Trusko SP,
Hirsch JD, Savage MJ, Scott RW and Howland DS: A transgenic rat
model of Alzheimer's disease with extracellular Abeta deposition.
Neurobiol Aging. 30:1078–1090. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ruiz-Opazo N, Kosik KS, Lopez LV,
Bagamasbad P, Ponce LR and Herrera VL: Attenuated
hippocampus-dependent learning and memory decline in transgenic
TgAPPswe Fischer-344 rats. Mol Med. 10:36–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Filipcik P, Zilka N, Bugos O, Kucerak J,
Koson P, Novak P and Novak M: First transgenic rat model developing
progressive cortical neurofibrillary tangles. Neurobiol Aging.
33:1448–1456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Van Dam D and De Deyn PP: Animal models in
the drug discovery pipeline for Alzheimer's disease. Br J
Pharmacol. 164:1285–1300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Watanabe K,
Sekiguchi M, Hosoki E, Kawashima-Morishima M, Lee HJ, Hama E,
Sekine-Aizawa Y and Saido TC: Identification of the major
Abeta1-42-degrading catabolic pathway in brain parenchyma:
suppression leads to biochemical and pathological deposition. Nat
Med. 6:143–150. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vekrellis K, Ye Z, Qiu WQ, Walsh D,
Hartley D, Chesneau V, Rosner MR and Selkoe DJ: Neurons regulate
extracellular levels of amyloid beta-protein via proteolysis by
insulin-degrading enzyme. J Neurosci. 20:1657–1665. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Solà C, García-Ladona FJ, Sarasa M, Mengod
G, Probst A, Palacios G and Palacios JM: Beta APP gene expression
is increased in the rat brain after motor neuron axotomy. Eur J
Neurosci. 5:795–808. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gonzalo-Ruiz A, González I and
Sanz-Anquela JM: Effects of beta-amyloid protein on serotoninergic,
noradrenergic, and cholinergic markers in neurons of the
pontomesencephalic tegmentum in the rat. J Chem Neuroanat.
26:153–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Du P, Wood KM, Rosner MH, Cunningham D,
Tate B and Geoghegan KF: Dominance of amyloid precursor protein
sequence over host cell secretases in determining beta-amyloid
profiles studies of interspecies variation and drug action by
internally standardized immunoprecipitation/mass spectrometry. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:1144–1152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Beck M, Bigl V and Rossner S: Guinea pigs
as a nontransgenic model for APP processing in vitro and in vivo.
Neurochem Res. 28:637–644. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen Y, Wei G, Nie H, Lin Y, Tian H, Liu
Y, Yu X, Cheng S, Yan R, Wang Q, et al: β-Asarone prevents
autophagy and synaptic loss by reducing ROCK expression in
asenescence-accelerated prone 8 mice. Brain Res. 1552:41–54. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Takeda T, Hosokawa M, Takeshita S, Irino
M, Higuchi K, Matsushita T, Tomita Y, Yasuhira K, Hamamoto H and
Shimizu K: A new murine model of accelerated senescence. Mech
Ageing Dev. 17:183–194. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Flood JF and Morley JE: Learning and
memory in the SAMP8 mouse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 22:1–20. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stefanova NA, Kozhevnikova OS, Vitovtov
AO, Maksimova KY, Logvinov SV, Rudnitskaya EA, Korbolina EE,
Muraleva NA and Kolosova NG: Senescence-accelerated OXYS rats: a
model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to
abnormalities in Alzheimer disease. Cell Cycle. 13:898–909. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stefanova NA, Muraleva NA, Skulachev VP
and Kolosova NG: Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in
senescence-accelerated OXYS rats can be partially retarded with
mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQ1. J Alzheimers Dis.
38:681–694. 2014.
|
|
60
|
Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G and
Butterfield DA: Free radicals: key to brain aging and heme
oxygenase as a cellular response to oxidative stress. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 59:478–493. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bosch MN, Pugliese M, Gimeno-Bayón J,
Rodríguez MJ and Mahy N: Dogs with cognitive dysfunction syndrome:
A natural model of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res.
9:298–314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Head E, Callahan H, Muggenburg BA, Cotman
CW and Milgram NW: Visual-discrimination learning ability and
beta-amyloid accumulation in the dog. Neurobiol Aging. 19:415–425.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Head E, McCleary R, Hahn FF, Milgram NW
and Cotman CW: Region-specific age at onset of beta-amyloid in
dogs. Neurobiol Aging. 21:89–96. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hou Y, White RG, Bobik M, Marks JS and
Russell MJ: Distribution of beta-amyloid in the canine brain.
Neuroreport. 8:1009–1012. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Satou T, Cummings BJ, Head E, Nielson KA,
Hahn FF, Milgram NW, Velazquez P, Cribbs DH, Tenner AJ and Cotman
CW: The progression of beta-amyloid deposition in the frontal
cortex of the aged canine. Brain Res. 774:35–43. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Cuyckens F, Balcaen LI, De Wolf K, De
Samber B, Van Looveren C, Hurkmans R and Vanhaecke F: Use of the
bromine isotope ratio in HPLC-ICP-MS and HPLC-ESI-MS analysis of a
new drug in development. Anal Bioanal Chem. 390:1717–1729. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Head E: Combining an antioxidant-fortified
diet with behavioral enrichment leads to cognitive improvement and
reduced brain pathology in aging canines: strategies for healthy
aging. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1114:398–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Papaioannou N, Tooten PC, van Ederen AM,
Bohl JR, Rofina J, Tsangaris T and Gruys E: Immunohistochemical
investigation of the brain of aged dogs. I. Detection of
neurofibrillary tangles and of 4-hydroxynonenal protein, an
oxidative damage product, in senile plaques. Amyloid. 8:11–21.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pugliese M, Mascort J, Mahy N and Ferrer
I: Diffuse beta-amyloid plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau are
unrelated processes in aged dogs with behavioral deficits. Acta
Neuropathol. 112:175–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Languille S, Blanc S, Blin O, Canale CI,
Dal-Pan A, Devau G, Dhenain M, Dorieux O, Epelbaum J, Gomez D, et
al: The grey mouse lemur: a non-human primate model for ageing
studies. Ageing Res Rev. 11:150–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Bons N, Rieger F, Prudhomme D, Fisher A
and Krause KH: Microcebus murinus: a useful primate model for human
cerebral aging and Alzheimer's disease? Genes Brain Behav.
5:120–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kraska A, Dorieux O, Picq JL, Petit F,
Bourrin E, Chenu E, Volk A, Perret M, Hantraye P, Mestre-Frances N,
et al: Age-associated cerebral atrophy in mouse lemur primates.
Neurobiol Aging. 32:894–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Giannakopoulos P, Silhol S, Jallageas V,
Mallet J, Bons N, Bouras C and Delaère P: Quantitative analysis of
tau protein-immunoreactive accumulations and beta amyloid protein
deposits in the cerebral cortex of the mouse lemur, Microcebus
murinus. Acta Neuropathol. 94:131–139. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Laurijssens B, Aujard F and Rahman A:
Animal models of Alzheimer's disease and drug development. Drug
Discov Today Technol. 10:e319–e327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bélanger N, Grégoire L, Bédard PJ and Di
Paolo T: DHEA improves symptomatic treatment of moderately and
severely impaired MPTP monkeys. Neurobiol Aging. 27:1684–1693.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Yue F, Lu C, Ai Y, Chan P and Zhang Z:
Age-associated changes of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β and tau in
cynomolgus monkeys. Neurobiol Aging. 35:1656–1659. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Molteni R, Barnard RJ, Ying Z, Roberts CK
and Gómez-Pinilla F: A high-fat, refined sugar diet reduces
hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neuronal plasticity,
and learning. Neuroscience. 112:803–814. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Demetrius LA and Driver J: Alzheimer's as
a metabolic disease. Biogerontology. 14:641–649. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Herculano B, Tamura M, Ohba A, Shimatani
M, Kutsuna N and Hisatsune T: β-alanyl-L-histidine rescues
cognitive deficits caused by feeding a high fat diet in a
transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
33:983–997. 2013.
|
|
80
|
Haley RW and Dietschy JM: Is there a
connection between the concentration of cholesterol circulating in
plasma and the rate of neuritic plaque formation in Alzheimer
disease? Arch Neurol. 57:1410–1412. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gibson Wood W, Eckert GP, Igbavboa U and
Müller WE: Amyloid beta-protein interactions with membranes and
cholesterol: Causes or casualties of Alzheimer's disease. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1610:281–290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu YY, Wang X, Tan L, Liu D, Liu XH, Wang
Q, Wang JZ and Zhu LQ: Lithium attenuates scopolamine-induced
memory deficits with inhibition of GSK-3β and preservation of
post-synaptic components. J Alzheimers Dis. 37:515–527. 2013.
|
|
83
|
Vandal M, White PJ, Tremblay C, St-Amour
I, Chevrier G, Emond V, Lefrançois D, Virgili J, Planel E, Giguere
Y, et al: Insulin reverses the high-fat diet-induced increase in
brain Aβ and improves memory in an animal model of Alzheimer
disease. Diabetes. 63:4291–4301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Pinton S, Brüning CA, Sartori Oliveira CE,
Prigol M and Nogueira CW: Therapeutic effect of organoselenium
dietary supplementation in a sporadic dementia of Alzheimer's type
model in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 24:311–317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Nakamura S, Murayama N, Noshita T, Annoura
H and Ohno T: Progressive brain dysfunction following
intracerebroventricular infusion of beta(1-42)-amyloid peptide.
Brain Res. 912:128–136. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Winslow JT and Camacho F: Cholinergic
modulation of a decrement in social investigation following
repeated contacts between mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
121:164–172. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Sain H, Sharma B, Jaggi AS and Singh N:
Pharmacological investigations on potential of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists in
hyperhomocysteinemia-induced vascular dementia in rats.
Neuroscience. 192:322–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kamat PK, Rai S and Nath C: Okadaic acid
induced neuro-toxicity: An emerging tool to study Alzheimer's
disease pathology. Neurotoxicology. 37:163–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhang J, Li P and Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang Z,
Cheng W and Wang Y: Ameliorative effects of a combination of
baicalin, jasminoidin and cholic acid on ibotenic acid-induced
dementia model in rats. PLoS One. 8:e566582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Bonda DJ, Lee HG, Blair JA, Zhu X, Perry G
and Smith MA: Role of metal dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer's disease.
Metallomics. 3:267–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Squire LR and Zola-Morgan S: Memory: Brain
systems and behavior. Trends Neurosci. 11:170–175. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu J, Zhang Z, Li JT, Zhu YH, Zhou HL,
Liu S and Wang TH: Effects of NT-4 gene modified fibroblasts
transplanted into AD rats. Neurosci Lett. 466:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Savage LM, Sweet AJ, Castillo R and
Langlais PJ: The effects of lesions to thalamic lateral internal
medullary lamina and posterior nuclei on learning, memory and
habituation in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 82:133–147. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Avaliani N, Sørensen AT, Ledri M, Bengzon
J, Koch P, Brüstle O, Deisseroth K, Andersson M and Kokaia M:
Optogenetics reveal delayed afferent synaptogenesis on grafted
human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors.
Stem Cells. 32:3088–3098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Green KN, Smith IF and Laferla FM: Role of
calcium in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and transgenic
models. Subcell Biochem. 45:507–521. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Nepovimova E, Uliassi E, Korabecny J,
Peña-Altamira LE, Samez S, Pesaresi A, Garcia GE, Bartolini M,
Andrisano V, Bergamini C, et al: Multitarget drug design strategy:
quinone-tacrine hybrids designed to block amyloid-β aggregation and
to exert anticholinesterase and antioxidant effects. J Med Chem.
57:8576–8589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Akhter R, Sanphui P and Biswas SC: The
essential role of p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (Puma)
and its regulation by FoxO3a transcription factor in
β-amyloid-induced neuron death. J Biol Chem. 289:10812–10822. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Matlack KE, Tardiff DF, Narayan P,
Hamamichi S, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA and Lindquist S: Clioquinol
promotes the degradation of metal-dependent amyloid-β (Aβ)
oligomers to restore endocytosis and ameliorate Aβ toxicity. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:4013–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Gong CX, Lidsky T, Wegiel J, Grundke-Iqbal
I and Iqbal K: Metabolically active rat brain slices as a model to
study the regulation of protein phosphorylation in mammalian brain.
Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 6:134–140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Roder S, Danober L, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl
K, Wiederhold KH and Olpe HR: Electrophysiological studies on the
hippocampus and prefrontal cortex assessing the effects of
amyloidosis in amyloid precursor protein 23 transgenic mice.
Neuroscience. 120:705–720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Li L, Sengupta A, Haque N, Grundke-Iqbal I
and Iqbal K: Memantine inhibits and reverses the Alzheimer type
abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau and associated
neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett. 566:261–269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jang J, Yoo JE, Lee JA, Lee DR, Kim JY,
Huh YJ, Kim DS, Park CY, Hwang DY, Kim HS, et al: Disease-specific
induced pluripotent stem cells: A platform for human disease
modeling and drug discovery. Exp Mol Med. 44:202–213. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Yagi T, Ito D, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Nihei
Y, Yoshizaki T, Yamanaka S, Okano H and Suzuki N: Modeling familial
Alzheimer's disease with induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Mol
Genet. 20:4530–4539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Israel MA, Yuan SH, Bardy C, Reyna SM, Mu
Y, Herrera C, Hefferan MP, Van Gorp S, Nazor KL, Boscolo FS, et al:
Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease using induced
pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 482:216–220. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kondo T, Asai M, Tsukita K, Kutoku Y,
Ohsawa Y, Sunada Y, Imamura K, Egawa N, Yahata N, Okita K, et al:
Modeling Alzheimer's disease with iPSCs reveals stress phenotypes
associated with intracellular Aβ and differential drug
responsiveness. Cell Stem Cell. 12:487–496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Macias MP, Gonzales AM, Siniard AL, Walker
AW, Corneveaux JJ, Huentelman MJ, Sabbagh MN and Decourt B: A
cellular model of amyloid precursor protein processing and
amyloid-β peptide production. J Neurosci Methods. 223:114–122.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
107
|
Meng P, Yoshida H, Tanji K, Matsumiya T,
Xing F, Hayakari R, Wang L, Tsuruga K, Tanaka H, Mimura J, et al:
Carnosic acid attenuates apoptosis induced by amyloid-β 1-42 or
1-43 in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Res. 94:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Giunta S, Andriolo V and Castorina A: Dual
blockade of the A1 and A2A adenosine receptor prevents amyloid beta
toxicity in neuroblastoma cells exposed to aluminum chloride. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 54:122–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Denis PA: Alzheimer's disease: A gas
model. The NADPH oxidase-Nitric Oxide system as an antibubble
biomachinery. Med Hypotheses. 81:976–987. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Minicozzi V, Chiaraluce R, Consalvi V,
Giordano C, Narcisi C, Punzi P, Rossi GC and Morante S:
Computational and experimental studies on β-sheet breakers
targeting Aβ1-40 fibrils. J Biol Chem. 289:11242–11252. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Götz J and Ittner LM: Animal models of
Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurosci.
9:532–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Viet MH, Chen CY, Hu CK, Chen YR and Li
MS: Discovery of dihydrochalcone as potential lead for Alzheimer's
disease: In silico and in vitro study. PLoS One. 8:e791512013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Lo AC, Iscru E, Blum D, Tesseur I,
Callaerts-Vegh Z, Buée L, De Strooper B, Balschun D and D'Hooge R:
Amyloid and tau neuro-pathology differentially affect prefrontal
synaptic plasticity and cognitive performance in mouse models of
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 37:109–125. 2013.
|
|
114
|
Okuma Y and Nomura Y:
Senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM) as an animal model of senile
dementia: pharmacological, neurochemical and molecular biological
approach. Jpn J Pharmacol. 78:399–404. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|